Key Takeaways
- Blockchain penetration testing is a controlled security assessment that simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities in smart contracts, dApps, protocols, and infrastructure before malicious actors can exploit them.
- In 2025, blockchain security incidents resulted in $2.935 billion in losses across 200 reported events, representing a 46 percent increase from 2024 despite fewer total incidents.
- Smart contract vulnerabilities accounted for 56 security incidents in 2025, while account compromises totaled 50 cases, making these the two dominant attack vectors.
- Blockchain security audits typically cost between $5,000 and $50,000 depending on scope, complexity, compliance requirements, and team composition.
- A comprehensive blockchain audit covers architecture review, network layer analysis, ledger layer verification, code review, and compliance assessment against standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, and MiCA.
- DeFi protocols accounted for 63 percent of all reported blockchain security incidents in 2025, with combined losses reaching $649 million from 126 separate events.
- Regular pentesting and security audits are essential for regulatory compliance under frameworks including DORA, VARA, MiCA, and SOC 2, particularly for centralized exchanges and institutional crypto services.
- The five stage blockchain audit process includes planning and scoping, preparation, audit execution, reporting, and remediation with optional retesting for verification.
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain, security is not optional but foundational. Blockchain penetration testing and security audits have emerged as critical safeguards that protect billions of dollars in digital assets from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. With losses exceeding $2.9 billion in 2025 alone, the importance of proactive security measures cannot be overstated.
Whether you are building smart contracts, launching a decentralized application, or operating a cryptocurrency exchange, understanding blockchain security audits and pentesting methodologies is essential for protecting your users, assets, and reputation. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about securing your Web3 project through professional security assessments.
This article draws on authoritative data from SlowMist’s 2025 Blockchain Security Report, Chainalysis research, and established industry frameworks including OWASP, NIST, and PTES. Our blockchain development team brings extensive experience in implementing secure solutions across multiple ecosystems including Ethereum, Solana, and enterprise platforms.
What is Blockchain Penetration Testing?
Definition
Blockchain penetration testing, commonly called blockchain pentesting, is a controlled cybersecurity assessment that simulates real world attacks against blockchain-based systems. Security experts ethically attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in smart contracts, decentralized applications, consensus mechanisms, APIs, and supporting infrastructure to identify weaknesses before malicious actors can discover them. Unlike passive vulnerability scanning, pentesting involves active exploitation attempts that demonstrate the actual impact of security flaws.
Blockchain pentesting goes beyond traditional network penetration testing by addressing the unique security challenges of distributed ledger technology. This includes testing consensus algorithms, cryptographic implementations, cross chain bridges, oracle integrations, and the complex business logic embedded in smart contracts.
Professional blockchain pentesters combine automated vulnerability scanning tools with manual testing techniques to uncover security issues that automated tools might miss. They evaluate authentication mechanisms, access controls, session management, input validation, and business logic flaws across the entire Web3 technology stack, from frontend applications to on chain contracts and backend infrastructure.
Blockchain Penetration Testing Scope
Smart Contracts
Reentrancy, overflow, access control, logic flaws
Web and Mobile Apps
XSS, CSRF, IDOR, broken authentication
APIs and RPC
Input validation, rate limiting, auth bypass
Cloud Infrastructure
Misconfigurations, privilege escalation, secrets
What is a Blockchain Security Audit?
A blockchain security audit is a comprehensive examination of an organization’s security controls, policies, and technical implementations against blockchain specific standards and industry best practices. While penetration testing focuses on actively exploiting vulnerabilities, a security audit takes a broader view by evaluating the overall security posture, compliance readiness, and risk management practices of blockchain based systems.
The blockchain audit process verifies that proper measures are in place to ensure network protection, data integrity, smart contract reliability, and regulatory compliance. Auditors examine documentation, review source code, assess architecture decisions, and validate that security controls function as intended. The goal is to identify gaps between current practices and security requirements before they can be exploited.
| Aspect | Penetration Testing | Security Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Active exploitation of vulnerabilities | Comprehensive security assessment |
| Methodology | Simulated real world attacks | Documentation and code review |
| Scope | Technical vulnerabilities | Technical, policy, and compliance |
| Output | Exploitable vulnerabilities list | Comprehensive risk assessment |
| Timing | Point in time assessment | Often ongoing or periodic |
| Best For | Pre launch security validation | Compliance and governance |
Why Blockchain Security Audits Matter: 2025-26 Statistics
The importance of blockchain pentesting and security audits is underscored by alarming statistics from recent years. According to SlowMist’s 2025 Blockchain Security Report, 200 security incidents resulted in approximately $2.935 billion in losses. Despite the number of incidents declining from 410 in 2024, financial losses increased by 46 percent year over year, indicating that attacks are becoming more efficient and targeted.
The single largest event was the Bybit breach, which alone accounted for $1.46 billion of the year’s total losses. This concentration of damage in one high profile incident illustrates how a single successful attack on a major platform can dominate annual loss statistics and reshape perceptions of risk across the entire industry.
2025-26 Blockchain Security Statistics
- $2.935 billion total losses across 200 security incidents
- 46 percent increase in financial losses compared to 2024
- 63 percent of incidents targeted DeFi protocols (126 events)
- $649 million lost from DeFi protocol exploits alone
- 56 incidents caused by smart contract vulnerabilities
- 50 incidents resulted from account compromises
- $254 million in losses on Ethereum, the most affected ecosystem
Top Attack Vectors in 2025
Understanding the most common attack vectors helps organizations prioritize their security efforts. Access control vulnerabilities emerged as the dominant attack vector in 2025, responsible for 59 percent of total losses exceeding $1.6 billion in stolen funds. Smart contract vulnerabilities contributed $263 million, representing 8 percent of stolen assets in the first half of the year alone.
| Attack Vector | Incidents | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access Control Flaws | 59% of losses | $1.6B+ stolen | Multi sig, RBAC, key management |
| Smart Contract Exploits | 56 incidents | $263M+ in H1 | Code audits, formal verification |
| Account Compromises | 50 incidents | Significant | MFA, cold storage, key rotation |
| Phishing Attacks | 48% of CEX breaches | $83.85M | User education, transaction signing |
| Rug Pulls | 58 incidents (2024) | $106M | Due diligence, contract reviews |
Blockchain Components Covered by Security Audits
A comprehensive blockchain security audit examines multiple layers of the technology stack. Understanding which components of a blockchain require security assessment helps organizations scope their audit requirements appropriately.
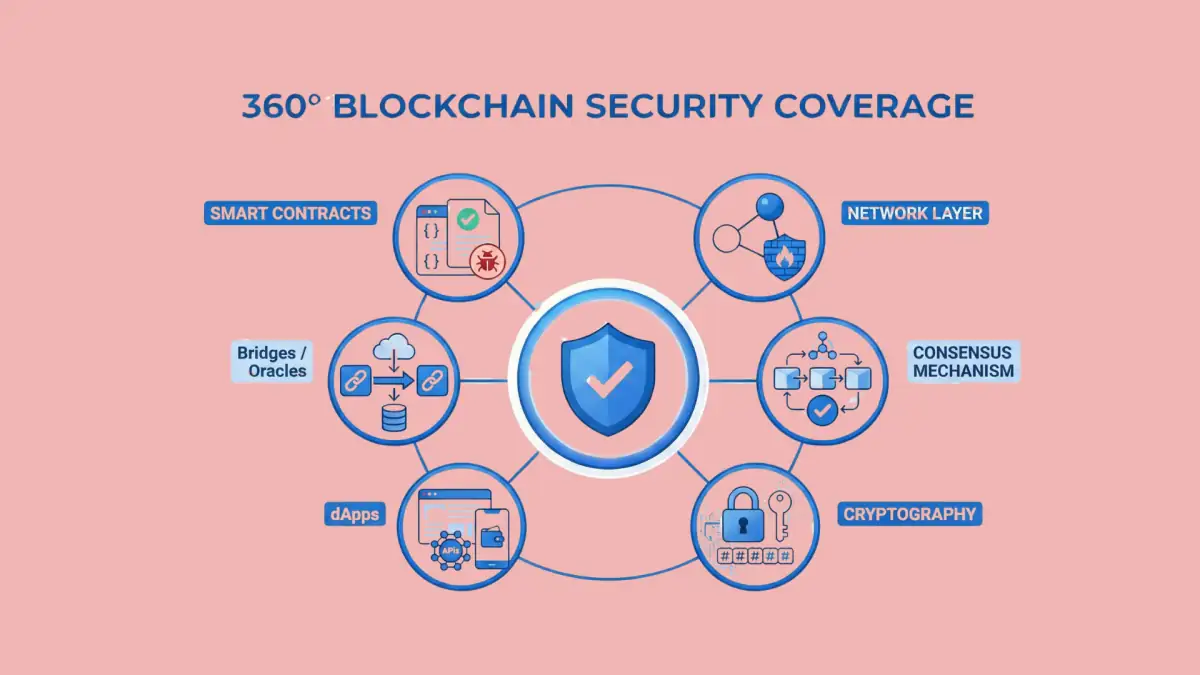
1. Smart Contracts
Smart contract audits are perhaps the most critical component of blockchain security. Auditors examine source code for vulnerabilities including reentrancy attacks, integer overflow and underflow, improper access controls, gas griefing, frontrunning vulnerabilities, and business logic flaws. Since smart contracts are often immutable once deployed, identifying vulnerabilities before launch is essential.
2. Blockchain Network Layer
Network layer audits review the P2P communication protocols, node configurations, and network topology for security weaknesses. This includes examining connection limits to protect against DDoS attacks, IP based node restrictions to prevent Sybil attacks, network identification mechanisms like ChainID, and the security of RPC endpoints.
3. Consensus Mechanisms
Auditors verify that the consensus algorithm implementation correctly ensures transaction finality and prevents double spending. This includes examining Proof of Work, Delegated Proof of Stake, and Byzantine Fault Tolerance implementations for potential attack vectors.
4. Cryptographic Implementations
Security audits examine cryptographic signatures, encryption libraries, hashing methods, and random number generators. Auditors verify that implementations are resistant to hash collision attacks, length extension attacks, and that cryptographic security meets current standards using algorithms like elliptic curve cryptography.
5. Decentralized Applications
dApp audits cover both on chain smart contracts and off chain components including web frontends, mobile applications, APIs, and backend services. Auditors examine role based access controls, cross chain operation security, sensitive data handling, and wallet integration security.
6. Cross Chain Bridges and Oracles
Cross chain bridges and blockchain oracles represent high value targets that require specialized security review. These components handle asset transfers between chains and bring external data on chain, making them critical infrastructure that demands thorough security assessment.
🔐 Wallets
Private key management, signing mechanisms, recovery processes
⛓️ Protocols
Custom blockchain protocol implementations and modifications
🪙 Tokens
Token contracts, minting logic, NFT implementations
💱 Exchanges
DEX smart contracts, order matching, liquidity pools
Types of Blockchain Security Audits
Different blockchain audit types address specific security aspects. Organizations typically combine multiple audit types based on their blockchain architecture and compliance requirements.
Architecture Audit
Auditors inspect the overall blockchain architecture against requirements for resilience, scalability, and interoperability. This ensures high availability of applications and networks, protection against DDoS attacks, and secure protocols for communication between different blockchain systems.
Network Layer Audit
This audit type reviews the blockchain network for appropriate security measures including adequate limits on P2P connections, restrictions on nodes sharing IP addresses, network identification mechanisms, and node synchronization security.
Ledger Layer Audit
Auditors verify consensus and transaction security by examining the consensus algorithm implementation, use of nonce values to prevent transaction replay, and cryptography library resistance to malleability attacks.
Code Audit
Code audits involve thorough review of smart contracts, dApp source code, encryption libraries, and hashing methods. Auditors verify security best practices that help prevent arithmetic overflow, gas griefing, reentrancy attacks, frontrunning, and other common vulnerabilities.
Compliance Audit
Compliance audits assess blockchain solutions against regulatory frameworks including PCI DSS for payment security, HIPAA for healthcare data, GDPR for data privacy, SOC 2 for service organizations, and emerging crypto specific regulations like MiCA, DORA, and VARA.
| Audit Type | Focus Areas | Key Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Audit | Resilience, scalability, interoperability | Design recommendations, risk assessment |
| Network Layer Audit | P2P security, node protection, DDoS prevention | Configuration hardening guide |
| Ledger Layer Audit | Consensus, transactions, cryptography | Protocol security validation |
| Code Audit | Smart contracts, dApps, libraries | Vulnerability report with fixes |
| Compliance Audit | PCI DSS, GDPR, MiCA, DORA, VARA | Compliance certification, gap analysis |
The Blockchain Security Audit Process
A structured approach to blockchain security audits ensures comprehensive coverage and actionable results. The following five stage process represents industry best practices for evaluating blockchain security.
Planning and Scoping
Define audit goals, scope, targets, methodology, timeline, and costs. Gather security and compliance requirements to determine which blockchain components will be examined and establish rules of engagement for testing activities.
Preparation and Documentation
Collect relevant documentation including smart contract specifications, architecture diagrams, security policies, and procedures. Review existing documentation to understand system design and identify potential areas of concern.
Audit Execution
Conduct automated testing using SAST and DAST tools followed by manual review. Security experts analyze the blockchain architecture, environment, and code while validating detected issues through controlled exploitation attempts.
Reporting
Prepare a comprehensive report including project summary, findings classified by severity and risk level, and recommended remediation actions. Include an executive summary for non technical stakeholders alongside detailed technical findings.
Remediation and Retesting
Implement fixes for identified vulnerabilities including policy improvements, configuration changes, security control implementations, and code refactoring. Conduct retesting to verify successful remediation and issue a clean audit report.
Need Professional Blockchain Security Audits?
Our certified security experts identify vulnerabilities in your smart contracts, dApps, and blockchain infrastructure before attackers do.
Common Vulnerabilities Discovered in Blockchain Audits
Understanding the most frequently discovered vulnerabilities helps developers write more secure code and helps organizations prioritize their security investments. The following issues are commonly identified during blockchain pentesting and security audits.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Reentrancy Attacks: Occur when a contract calls an external contract before updating its own state, allowing the external contract to recursively call back and drain funds. The infamous DAO hack exploited this vulnerability for $60 million.
Integer Overflow and Underflow: Mathematical operations that exceed variable limits can wrap around to unexpected values, enabling attackers to manipulate balances or bypass checks.
Access Control Flaws: Improper implementation of ownership and permission checks allows unauthorized users to execute privileged functions like minting tokens or withdrawing funds.
Frontrunning Vulnerabilities: Attackers can observe pending transactions in the mempool and submit their own transactions with higher gas fees to exploit predictable outcomes in DeFi protocols.
Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Private Key Exposure: Inadequate key management including storing keys in code repositories, insufficient encryption, or lack of hardware security modules exposes critical signing capabilities.
API Security Gaps: Missing rate limiting, authentication bypass vulnerabilities, and insufficient input validation on blockchain APIs enable various attack vectors.
Cloud Misconfigurations: Exposed storage buckets, overly permissive IAM policies, and unencrypted data stores create opportunities for data theft and system compromise.
| Vulnerability | Severity | Impact | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reentrancy | Critical | Complete fund drainage | Checks effects interactions pattern |
| Access Control | Critical | Unauthorized actions | OpenZeppelin AccessControl |
| Integer Overflow | High | Balance manipulation | SafeMath or Solidity 0.8+ |
| Frontrunning | High | MEV extraction | Commit reveal schemes |
| Gas Griefing | Medium | DoS, wasted gas | Gas limits and checks |
Blockchain Security Audit Tools and Technologies
Professional blockchain security audits leverage a combination of automated tools and manual expertise. These tools help auditors systematically identify vulnerabilities across different blockchain components.
Smart Contract Analysis Tools
Static analysis tools like Slither, Mythril, and MythX automatically scan smart contract source code for common vulnerability patterns. These tools identify issues like reentrancy, unchecked calls, and access control problems. OpenZeppelin provides secure contract templates and libraries, while Contract Library offers additional verification capabilities.
Penetration Testing Tools
Web application testing tools including Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and Acunetix assess dApp frontends and APIs. Network security tools like Nmap, Nessus, and Metasploit evaluate infrastructure components. Specialized tools like Whiteblock Genesis enable blockchain specific testing scenarios.
Code Review Tools
Static Application Security Testing tools like IBM AppScan and the Static Analyzer Security Scanner examine code for security flaws. Immunity Debugger assists with dynamic analysis and reverse engineering of compiled code.
🔍 Smart Contract Tools
- Mythril – EVM bytecode analysis
- Slither – Static analysis framework
- MythX – Security analysis API
- OpenZeppelin – Secure libraries
- Echidna – Fuzzing tool
🌐 Web and API Testing
- Burp Suite – Web security testing
- OWASP ZAP – Web app scanner
- Postman – API testing
- SQLMap – SQL injection detection
- Nikto – Web server scanner
🖧 Network Security
- Nmap – Network discovery
- Nessus – Vulnerability scanner
- Metasploit – Exploitation framework
- Wireshark – Protocol analysis
- OpenVAS – Open source scanning
Regulatory Compliance and Blockchain Security Audits
As blockchain adoption increases, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the unique security and compliance requirements of Web3 systems. Security audits play a crucial role in demonstrating compliance with these standards.
Crypto Specific Regulations
MiCA (Markets in Crypto Assets): The European Union’s comprehensive crypto regulation requires robust security measures, penetration testing, and ongoing security monitoring for licensed crypto service providers.
DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act): Mandates ICT risk management frameworks, incident reporting, and regular security testing for financial entities handling digital assets in the EU.
VARA (Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority): Dubai’s regulatory framework establishes security requirements for virtual asset service providers operating in the UAE.
Traditional Compliance Standards
PCI DSS: Required for any blockchain system processing payment card data, mandating regular security assessments and penetration testing.
SOC 2: Demonstrates security, availability, and confidentiality controls for blockchain service organizations.
ISO 27001: Information security management certification applicable to blockchain infrastructure and operations.
GDPR: Data protection requirements that intersect with blockchain’s immutable nature, requiring careful design considerations for personal data handling.
| Regulation | Region | Security Requirements | Applicable To |
|---|---|---|---|
| MiCA | European Union | Pentesting, risk management, incident response | CASPs, exchanges, stablecoin issuers |
| DORA | European Union | ICT risk framework, TLPT, third party oversight | Financial institutions with crypto |
| VARA | UAE (Dubai) | Security audits, custody requirements | VASPs in Dubai |
| PCI DSS | Global | Annual pentests, vulnerability scans | Payment processors |
| SOC 2 | Global | Security controls, monitoring, access management | Service organizations |
Blockchain Security Audit Costs
The cost of a blockchain security audit varies significantly based on several factors. Understanding these cost drivers helps organizations budget appropriately and maximize the value of their security investment.
Typical Cost Range
$5,000 – $50,000+
Depending on scope, complexity, compliance requirements, and team composition
Cost Factors
Scope of Components: The number of smart contracts, applications, APIs, and infrastructure elements included in the audit directly impacts cost. A single smart contract audit may cost $5,000 to $15,000, while a comprehensive platform assessment can exceed $50,000.
Code Complexity: Complex DeFi protocols with multiple contract interactions, cross-chain bridges, or novel mechanisms require more time and specialized expertise than straightforward token contracts.
Compliance Requirements: Regulated industries with stringent requirements like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or emerging crypto regulations require additional compliance expertise and documentation.
Team Composition: A targeted code review can be performed by one experienced auditor, while comprehensive audits with remediation services require larger teams with diverse competencies.
Timeline: Expedited audits command premium pricing. Planning audits well in advance allows for standard timelines and costs.
Cost Optimization Tips
- Prepare clear documentation including source code, specifications, and architecture diagrams to prevent misunderstandings and reduce audit time
- Prioritize auditing targets based on risk, business value, and development stage to focus resources effectively
- Freeze code before audits to avoid additional testing costs from ongoing changes during the review period
- Conduct internal security reviews first to identify and fix obvious issues before engaging external auditors
- Use automated tools to catch common vulnerabilities before manual review begins
Blockchain Security Audit Best Practices
Following established best practices ensures that blockchain security audits deliver maximum value and meaningful security improvements.
Before the Audit
- Compile comprehensive documentation including architecture diagrams, specifications, and threat models
- Ensure all code is well commented and follows consistent coding standards
- Run automated analysis tools internally to identify and fix obvious issues
- Define clear audit objectives and success criteria
- Establish communication channels and points of contact
During the Audit
- Maintain code freeze to prevent scope changes during review
- Respond promptly to auditor questions and clarification requests
- Provide access to test environments and supporting infrastructure
- Track findings and remediation progress in real time
After the Audit
- Address all critical and high severity findings before deployment
- Implement recommended security controls and policy improvements
- Request retesting to verify successful remediation
- Publish audit reports transparently to build community trust
- Establish ongoing security monitoring and periodic reassessment schedules
When to Conduct Blockchain Security Audits
Timing is critical for blockchain security audits. Conducting assessments at the right moments maximizes security benefits while minimizing costs and delays.
Pre Deployment
Security audits are most effective when conducted before smart contracts and applications are deployed to production. Since blockchain records are immutable, fixing vulnerabilities after deployment often requires complex migration procedures or contract upgrades.
After Major Changes
Conduct security reassessments whenever you introduce significant changes including new smart contracts, protocol upgrades, cross chain integrations, or major feature additions. Even small modifications can introduce unexpected vulnerabilities.
Periodic Assessment
Establish regular security assessment schedules, typically annually or quarterly for critical systems. The threat landscape evolves continuously, and periodic reviews help identify new vulnerability classes and ensure security controls remain effective.
Before Token Sales or Launches
Projects planning token sales, mainnet launches, or significant funding rounds should complete comprehensive security audits beforehand. Audit reports provide credibility to investors and users while protecting against costly post launch incidents.
Proven Blockchain Security Implementations
Our team has delivered comprehensive blockchain security solutions across multiple platforms and use cases. The following projects demonstrate our commitment to building secure Web3 infrastructure.
🎮 Ronin Chain Gaming Platform
Developed secure gaming blockchain infrastructure with robust security protocols and audit ready architecture.
🏦 Hubble Protocol DeFi
Built secure DeFi protocol with comprehensive smart contract security and penetration tested infrastructure.
🔐 Panther Protocol Privacy
Implemented privacy preserving blockchain solution with zero knowledge proof integration and security audited contracts.
💱 DEX Hunter Aggregator
Developed secure DEX aggregator on Cardano with audited smart contracts and secure API integration.
Secure Your Blockchain Project with Professional Audits
From smart contract security to comprehensive penetration testing, our experts help you identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Protect your users, assets, and reputation with industry-leading security assessments.
Conclusion
Blockchain penetration testing and security audits are essential safeguards in an industry that lost nearly $3 billion to security incidents in 2025 alone. As attacks become more sophisticated and regulatory requirements more stringent, proactive security assessments are no longer optional for serious blockchain projects.
The combination of smart contract audits, infrastructure pentesting, and compliance assessments provides comprehensive protection across the entire Web3 technology stack. Whether you are developing decentralized applications, operating cryptocurrency exchanges, or building enterprise blockchain solutions, security audits demonstrate due diligence to users, investors, and regulators.
By conducting security assessments before deployment, after major changes, and on regular schedules, organizations can identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they lead to costly incidents. The investment in professional blockchain security audits and pentesting is minimal compared to the potential losses from a successful attack or the reputational damage from a preventable breach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Blockchain penetration testing focuses on actively exploiting vulnerabilities through simulated attacks to demonstrate real impact. A security audit takes a broader view, examining documentation, policies, code quality, and compliance alongside technical security. Most organizations benefit from both approaches: pentesting validates technical defenses while audits ensure comprehensive security governance.
Blockchain security audit costs typically range from $5,000 to $50,000 or more depending on scope, complexity, compliance requirements, and team size. A simple smart contract audit may cost $5,000 to $15,000, while comprehensive platform assessments with multiple contracts, infrastructure review, and compliance evaluation can exceed $50,000. Factors like code complexity, timeline urgency, and regulatory requirements significantly impact pricing.
Blockchain security audits should be conducted before initial deployment, after any major code changes or upgrades, and periodically based on risk level, typically annually for most systems or quarterly for high value platforms. Additionally, audits are recommended before token sales, mainnet launches, or significant funding rounds to demonstrate security diligence to stakeholders.
The most common vulnerabilities discovered in blockchain audits include reentrancy attacks, access control flaws, integer overflow and underflow, frontrunning vulnerabilities, improper input validation, and business logic errors. Infrastructure issues like exposed private keys, API security gaps, and cloud misconfigurations are also frequently identified. In 2025, access control vulnerabilities were responsible for 59 percent of total blockchain security losses.
Blockchain security audit duration varies based on scope and complexity. A single smart contract audit typically takes one to two weeks. Comprehensive platform assessments including multiple contracts, dApps, APIs, and infrastructure may require four to eight weeks. Expedited timelines are possible but often command premium pricing. The audit process includes scoping, execution, reporting, and optional retesting phases.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.