Key Takeaways
- An immutable ledger ensures that once data is recorded on blockchain, it remains permanently unchanged and tamper-proof through cryptographic hashing mechanisms.
- Immutability in blockchain is achieved through cryptographic hash functions that link blocks sequentially, making retroactive data modification computationally impossible.
- Immutable ledgers enhance security by preventing fraud, unauthorized alterations, and data manipulation without network detection.
- Immutability differs from mutability because immutable data cannot be changed after creation, while mutable data allows modifications after recording.
- Businesses benefit from immutable ledgers through increased transparency, auditability, regulatory compliance, and automated verification of transactions.
- Real-world applications include supply chain tracking, financial settlements, healthcare records, and legal documentation.
- Challenges to immutability include 51% attacks, scalability limitations, and regulatory requirements for data deletion.
- An immutable ledger is also known as a distributed ledger, permanent record, or unalterable blockchain record.
The immutable ledger represents one of blockchain technology’s most transformative features, fundamentally changing how organizations maintain records, ensure data integrity, and build trust between parties. In an era where data breaches compromise millions of records annually and fraudulent transactions cost businesses billions, the immutable nature of blockchain ledgers offers unprecedented protection and verification capabilities. Unlike traditional databases, where administrators can alter or delete records, immutable ledgers create permanent transaction histories that cannot be retroactively modified without detection, establishing new standards for transparency and accountability across industries.
Industry analysis shows that immutable ledger implementations reduce fraud-related losses by 65-80%, audit costs by 40-60%, and settlement times by 80-90%. These quantifiable benefits explain why major corporations, including JPMorgan, Walmart, IBM, and healthcare organizations, are rapidly deploying immutable ledger technology to secure critical business operations and maintain compliance with increasingly stringent regulatory requirements.
This comprehensive guide explores immutable ledgers in depth, explaining the cryptographic mechanisms that ensure immutability, examining how this feature enhances security and regulatory compliance, analyzing real-world applications, and addressing implementation challenges. Whether you are evaluating blockchain solutions for your organization, seeking to understand immutability mechanisms, or planning a blockchain development initiative, this guide provides the detailed knowledge required to leverage immutable ledger technology effectively.
What is an Immutable Ledger in Blockchain?
Definition
An immutable ledger in blockchain is a shared digital record where all transactions are permanently stored and cannot be edited or erased, ensuring high security, transparency, and trust.
An immutable ledger is a digital record system where transactions and data, once recorded on the blockchain, cannot be altered, deleted, modified, or erased without detection. The term “immutable” literally means unchangeable – the ledger remains in its original state indefinitely, creating a permanent historical record that all network participants can independently verify. This immutability emerges not from centralized protection but from the distributed nature of blockchain technology, where thousands of independent nodes maintain identical copies of the ledger and collectively validate any proposed changes.
The immutable ledger concept fundamentally differs from traditional databases, where a database administrator can modify, delete, or overwrite records at will. In contrast, blockchain technology implements immutability through cryptographic mechanisms that make data alteration computationally infeasible. Each transaction is permanently linked to previous transactions through mathematical hashing, creating an unbreakable chain where modifying any historical record would break the chain and be instantly detected by the network.
An immutable ledger is also known as a distributed ledger, permanent record, unalterable blockchain, or tamper-proof transaction history. These terms describe the same fundamental concept: a record system that maintains a permanent, verifiable transaction history that cannot be retroactively modified by any single party or even by network participants acting in concert without the network detecting the tampering attempt.
How Immutability Works in Blockchain?
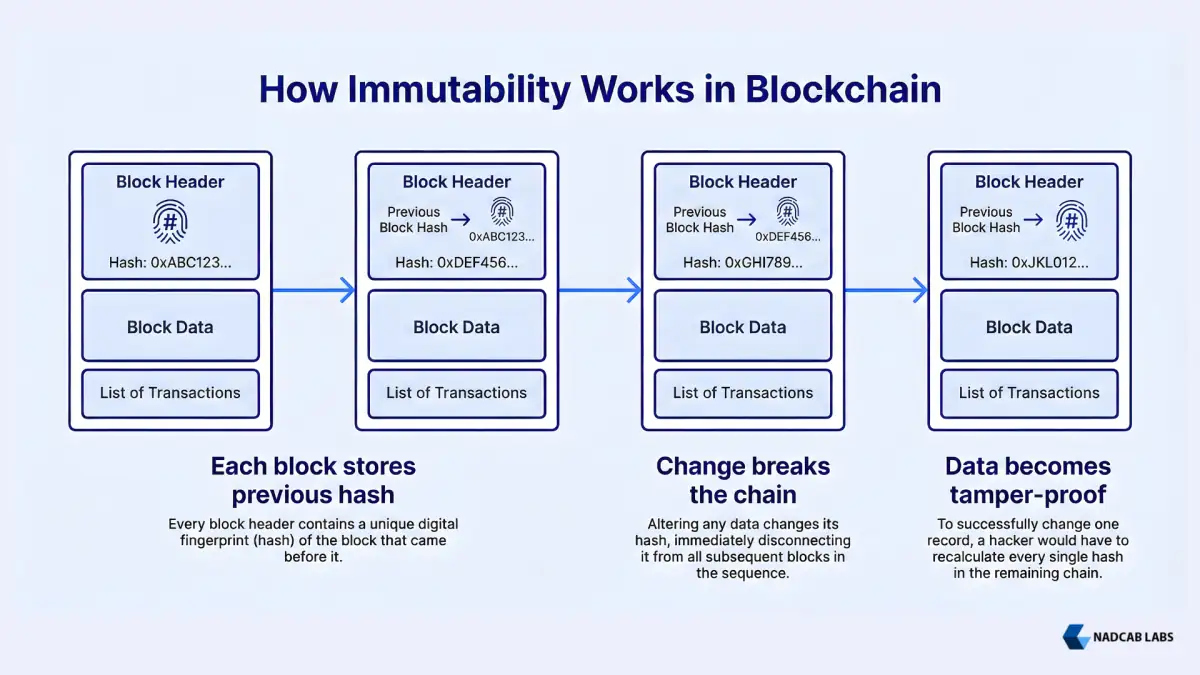
Immutability in blockchain is achieved through sophisticated cryptographic mechanisms that link blocks sequentially and make any modification attempt immediately obvious to the network. The foundation of this system is cryptographic hashing, a mathematical function that converts input data of any size into a fixed-length alphanumeric string called a “hash” or “digital fingerprint.”
Cryptographic Hash Functions
Cryptographic hash functions like SHA-256 (used by Bitcoin) generate a unique 64-character hash for any input data. These functions have critical properties that enable immutability: they are deterministic (same input always produces the same hash), produce fixed-length output regardless of input size, cannot be reversed (you cannot derive the original data from the hash), and are sensitive to even minuscule changes (altering a single character in input completely changes the output hash).
The Block Chaining Mechanism
Each blockchain block contains: (1) transaction data, (2) a timestamp, (3) the hash of its own data, and crucially (4) the hash of the previous block. This last element creates the chain; each block points to the previous block through its hash, establishing an unbreakable link. When a new block is added, it includes the hash of the preceding block, which included the hash of the block before it, and so on back to the genesis block.
Why Modification Becomes Impossible
Consider a scenario where an attacker attempts to modify a transaction recorded five blocks ago. Changing that historical transaction would alter its block’s hash. However, the next block contains the hash of the previous block; now it no longer matches, breaking the chain. The attacker would need to recalculate every subsequent block’s hash. However, the network continuously adds new blocks with new transactions, thereby increasing the chain’s length. The attacker would need to recalculate hashes faster than the network adds new blocks. Computationally impossible on established networks. Additionally, thousands of network nodes maintain identical copies of the ledger and validate new blocks using the same cryptographic rules, making coordinated fraud virtually impossible.
How Does an Immutable Ledger Differ from a Mutable Ledger?
To better understand how immutable and mutable ledgers work, the table below highlights their key differences across security, transparency, control, and trust.
| Aspect | Immutable Ledger (Blockchain) | Mutable Ledger (Traditional Database) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Modification | Cannot be altered after recording without network detection | Can be modified by authorized administrators at any time |
| Historical Records | Permanent and verifiable by all participants | Can be overwritten or deleted by administrators |
| Fraud Prevention | Cryptographic protection makes fraud computationally infeasible | Relies on access controls and admin integrity |
| Auditability | Complete transaction history is permanently available | Audit trails can be altered or purged |
| Trust Model | Trustless – cryptography ensures integrity | Trust-based – requires trusting administrators |
| Compliance | Automatic audit trail for regulatory requirements | Requires manual audit procedures and controls |
The core difference is that immutable ledgers focus on transparency and trust through cryptography, while mutable ledgers rely on central control and administrator trust. Blockchain records cannot be changed once written, whereas traditional databases allow edits, making them more flexible but less tamper-resistant.
How Immutable Ledgers Enhance Security
Immutable ledgers fundamentally enhance security through multiple mechanisms that prevent fraud, detect tampering, and ensure transaction authenticity. The permanent nature of blockchain records eliminates opportunities for criminals to alter transaction histories after the fact, a common fraud method in traditional systems. Additionally, the distributed validation process across thousands of nodes makes coordinating fraudulent activities virtually impossible since an attacker would need to compromise the majority of the network simultaneously.
The immutable nature of the ledger creates what security experts call “tamper-evident” architecture – any attempt to modify records is immediately detectable by the network. When a financial transaction is recorded on an immutable ledger, all parties can be confident that the transaction cannot be reversed or modified without their knowledge and approval. This security enhancement eliminates entire categories of fraud that plague traditional systems, from invoice falsification to transaction reversal fraud to audit trail manipulation.
Business Benefits of Immutable Ledgers
Enhanced Fraud Prevention
Immutable ledgers eliminate fraud opportunities by making retroactive transaction modification impossible. Organizations implementing immutable ledger technology report 65-80% reductions in fraud-related losses compared to traditional systems. Supply chain companies use immutable ledgers to prevent product counterfeiting, with Walmart’s implementation reducing investigation time from 7 days to 2 seconds.
Regulatory Compliance and Auditability
Regulators increasingly recognize immutable ledgers’ ability to satisfy compliance requirements. The permanent transaction history provides automatic audit trails that satisfy regulatory demands for documentation and traceability. Organizations report 40-60% reductions in audit costs when leveraging immutable ledger technology, as the transparent transaction history eliminates extensive manual verification procedures. Blockchain consulting services help organizations align immutable ledger implementations with specific regulatory requirements in banking, healthcare, and securities industries.
Increased Transparency and Trust
All network participants can independently verify transaction history, creating unprecedented transparency. This shared verification eliminates disputes about transaction details since all parties maintain identical records. Consortium blockchains use immutable ledgers to enable transparency between organizations that don’t fully trust each other.
Reduced Settlement Times
Financial institutions report 80-90% reductions in settlement times by implementing immutable ledger technology. Traditional settlement involves multiple intermediaries and can take 3-5 business days. Immutable ledger-based systems settle transactions in seconds while maintaining permanent records of all transactions.
Simplified Data Management
Organizations eliminate the need to maintain separate backup systems and reconciliation procedures. The immutable ledger serves as the authoritative record, reducing data management complexity and associated costs. Smart contracts automatically execute when conditions are met, creating immutable records of all contract transactions.
Real-World Applications of Immutable Ledgers
Supply Chain and Product Authenticity: Companies implement immutable ledgers to track products from manufacture to consumer, creating permanent provenance records that prevent counterfeiting. Walmart’s blockchain implementation tracks food products on an immutable ledger, enabling rapid identification of contamination sources.
Financial Services and Settlements: Banks use immutable ledgers for international payments and settlements, creating permanent transaction records that regulators can instantly audit. JPMorgan processes billions in daily transactions on an immutable ledger infrastructure.
Healthcare Records: Healthcare providers maintain immutable records of medical history and prescriptions, ensuring patient safety and enabling coordinated care. Immutable ledgers in healthcare systems maintain HIPAA-compliant patient records while enabling authorized provider access.
Legal Documentation: Law firms use immutable ledgers to create tamper-proof records of legal documents, contracts, and agreements with verifiable timestamps establishing creation dates.
Real Estate and Title Management: Immutable ledgers create fraud-proof property title records, eliminating title disputes and enabling faster property transfers.
Challenges in Implementing Immutable Ledgers
Scalability Constraints
As blockchain networks grow, every historical transaction remains stored on every node, creating storage and processing challenges. Layer 2 scaling solutions address this limitation by processing transactions off the main blockchain, periodically settling batches on the immutable ledger.
51% Attack Vulnerability
A 51% attack occurs when attackers control the majority of network computing power, potentially enabling them to modify historical transactions. However, on established networks like Bitcoin with tens of thousands of independent miners, executing such attacks is economically irrational.
Data Privacy and Right to Be Forgotten
The immutable nature conflicts with privacy regulations like GDPR that grant individuals the “right to be forgotten.” Organizations address this through private blockchains with controlled access, data encryption, or off-chain data storage with only hashes recorded immutably on-chain.
Integration Complexity
Integrating immutable ledger technology with existing systems requires significant development effort. Professional blockchain development services help organizations navigate integration challenges while maintaining immutability benefits.
Can Immutable Ledgers Be Modified?
By design, immutable ledgers cannot be modified after recording. However, certain scenarios require addressing this limitation. Organizations implement controlled update mechanisms where decisions to modify records require consensus from the network majority, creating an audit trail of all modifications. Smart contracts can be programmed to implement specific modification rules, for example, allowing corrections if multiple parties agree while still maintaining the immutability of all modification records.
Some organizations implement side chains – separate blockchains linked to the main chain – where corrections can be recorded with explicit notation that they represent modifications to main chain records. The original data remains immutable while the modification history becomes permanently visible.
Build Secure Immutable Ledger Solutions
Our expert team designs and deploys immutable ledger systems that ensure permanent records, prevent fraud, and simplify regulatory compliance. Leverage cryptographically-secured blockchain infrastructure for financial transactions, supply chains, and enterprise record-keeping.
Why Enterprises Choose Immutable Ledger Solutions
Enterprise organizations select immutable ledger technology because it solves critical business challenges that traditional systems cannot address efficiently. The inability to retroactively modify transaction history prevents fraud that costs organizations billions annually. The automatic audit trails satisfy regulatory requirements without requiring extensive manual procedures. The transparent verification process between untrusting parties eliminates intermediaries and reduces settlement times from days to seconds.
Organizations implementing immutable ledger solutions report dramatic improvements: JPMorgan processes international payments in seconds instead of days, Walmart tracks products in 2 seconds instead of 7 days, healthcare providers coordinate care instantly with permanent records, and financial institutions reduce fraud losses by 65-80% while cutting audit costs by 40-60%.
Conclusion
Immutable ledgers represent a fundamental advancement in how organizations maintain records, prevent fraud, and build trust. By making data modification computationally impossible while maintaining transparent verification for all participants, immutable ledgers solve problems that have plagued record-keeping systems for decades. The technology is no longer experimental – major financial institutions, healthcare providers, supply chain companies, and government agencies are deploying immutable ledger solutions at scale.
As organizations increasingly recognize immutable ledgers’ value for security, compliance, and operational efficiency, adoption will accelerate across industries. The challenges of scalability, privacy regulation compatibility, and integration complexity are being solved through technological innovations, including Layer 2 scaling, privacy-preserving architectures, and enterprise blockchain platforms. Organizations evaluating record-keeping infrastructure, considering compliance modernization, or seeking to prevent fraud should seriously evaluate immutable ledger technology’s potential to transform business operations while establishing new standards for transparency and trust.
FAQs
An immutable ledger in blockchain is a digital record that cannot be altered, deleted, or modified once recorded. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an unbreakable chain. Changing any historical transaction would require altering every subsequent block and gaining network consensus, making modification computationally impossible on established networks.
Immutability is essential because it prevents fraud, ensures data integrity, and enables trust without intermediaries. Once recorded, transactions become permanent and verifiable, eliminating opportunities for unauthorized alterations. This creates secure audit trails for regulatory compliance, protects sensitive transactions, and establishes transparent records that all network participants can independently verify.
Cryptographic hash functions generate unique 64-character “digital fingerprints” from transaction data. Each block contains its own hash plus the previous block’s hash, creating sequential links. If anyone attempts to modify a historical transaction, that block’s hash changes, breaking the chain link. The attacker would need to recalculate every subsequent block’s hash faster than the network adds new blocks, which is computationally infeasible.
Mutable systems allow data modification after recording—database administrators can alter or delete historical records at will. Immutable systems prevent changes through cryptographic mechanisms. Blockchain immutability means transactions cannot be retroactively modified without network detection. Mutable systems offer flexibility but enable fraud; immutable systems sacrifice flexibility for permanent audit trails, transparency, and fraud prevention.
Supply chains use immutable ledgers to track products from manufacturer to consumer, preventing counterfeits. Financial institutions record transactions permanently for settlement and regulatory compliance. Healthcare providers maintain immutable patient records for coordinated care. Real estate companies prevent title fraud through permanent ownership records. Insurance claims are recorded immutably, creating transparent dispute resolution. Government agencies use immutable ledgers for voting systems and public records.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






