Key Takeaways
- A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a cryptocurrency trading platform that operates on blockchain technology without central authority, enabling users to trade directly through smart contracts while maintaining custody of their assets.
- How decentralized exchanges work involves automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools that replace traditional order books, allowing instant trades without requiring a counterparty to be online.
- Benefits of DEX include non-custodial trading where users control their private keys, enhanced privacy with minimal KYC requirements, and transparency through publicly verifiable blockchain transactions.
- Peer-to-peer crypto trading on DEX platforms eliminates intermediary risks, meaning users are not exposed to exchange hacks, insolvency, or asset freezes that can affect centralized platforms.
- Risks of decentralized exchanges include lower liquidity compared to major centralized platforms, higher complexity for beginners, smart contract vulnerabilities, and irreversible transactions without customer support.
- DEX vs centralized exchange comparison reveals trade-offs between security and convenience, where DEX offers greater control while centralized platforms provide faster execution and easier fiat on-ramps.
- DEX trading platform functionality requires users to connect personal cryptocurrency wallets, manage gas fees, and understand slippage settings to execute trades successfully.
- Decentralized crypto trading has grown substantially with leading DEX platforms processing billions in daily volume, demonstrating viable alternatives to traditional centralized exchange models.
- What is a DEX fundamentally represents a shift toward financial sovereignty, allowing anyone with an internet connection to access global cryptocurrency markets without permission or identity verification.
Introduction to Decentralized Exchanges
The cryptocurrency ecosystem has evolved dramatically since Bitcoin’s inception, giving rise to sophisticated infrastructure for trading digital assets. Among the most significant innovations in this space is the decentralized exchange, a revolutionary approach to cryptocurrency trading that aligns with blockchain’s core principles of decentralization, transparency, and user sovereignty. Understanding what a DEX offers and how it functions has become essential knowledge for anyone participating in the digital asset economy.
Decentralized exchanges represent a fundamental shift in how cryptocurrency trading occurs, moving away from centralized intermediaries toward peer-to-peer systems governed by code rather than corporations. This transformation addresses many concerns that arose from high-profile centralized exchange failures, hacks, and regulatory crackdowns that left users unable to access their funds. The growth of decentralized crypto trading demonstrates both market demand for alternatives and the technical maturity of blockchain-based financial infrastructure.
What is a DEX?
A decentralized exchange is a cryptocurrency trading platform that facilitates direct peer-to-peer transactions between users without relying on a central authority to hold funds or execute trades. Instead of depositing assets to an exchange-controlled wallet, DEX users connect their personal wallets directly to the trading platform and maintain custody of their cryptocurrencies throughout the entire trading process. Smart contracts handle the mechanics of trade execution, ensuring trustless exchanges where neither party must rely on the other’s honesty.
The question of what is a DEX extends beyond simple definitions to encompass the philosophical and practical differences from traditional exchange models. DEX platforms operate as protocols running on blockchain networks rather than as companies holding customer assets. This architecture means no single entity can unilaterally freeze accounts, restrict access, or misappropriate user funds. Popular DEX examples include Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance, and dYdX, each offering different features and operating on various blockchain networks.
How Decentralized Crypto Trading Works
Understanding how decentralized exchanges work requires familiarity with the underlying mechanisms that enable trustless trading. Most modern DEX platforms utilize automated market makers (AMMs) that replace traditional order book models. Instead of matching buy and sell orders between traders, AMMs use mathematical formulas and liquidity pools to determine prices and execute trades instantly against pooled assets.
When a user initiates a trade on a DEX trading platform, their wallet broadcasts a transaction to the blockchain network. This transaction interacts with the DEX smart contract, which calculates the exchange rate based on the current pool ratios, deducts the appropriate amount from the user’s wallet, and sends the exchanged tokens back. The entire process occurs atomically, meaning either the complete trade succeeds or nothing happens, eliminating partial execution risks.
| Component | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Contracts | Execute trades automatically when conditions are met | Uniswap Router Contract |
| Liquidity Pools | Provide trading liquidity through pooled assets | ETH/USDC Pool |
| AMM Algorithm | Calculate exchange rates based on pool ratios | Constant Product Formula (x*y=k) |
| User Wallet | Store assets and sign transactions | MetaMask, Trust Wallet |
| Blockchain Network | Process and confirm transactions | Ethereum, Solana, BNB Chain |
Importance of Decentralized Exchanges in Blockchain
Decentralized exchanges fulfill a critical role in the blockchain ecosystem by providing trustless infrastructure for exchanging value. Without DEX platforms, users would remain dependent on centralized services that contradict blockchain’s fundamental premise of removing intermediaries. The growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) depends heavily on DEX infrastructure, as lending protocols, yield aggregators, and other applications require reliable on-chain trading capabilities.
The importance extends beyond ideology to practical considerations. DEX platforms provide price discovery mechanisms, liquidity for new token launches, and trading access in regions where centralized exchanges face regulatory restrictions. They serve as essential infrastructure for the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem, enabling applications that would be impossible with only centralized trading options.
Core Principle: Decentralized exchanges embody the cryptocurrency ethos of self-sovereignty. By eliminating custodial requirements, DEX platforms ensure users maintain complete control over their assets at all times, reducing systemic risks from centralized points of failure.
How Decentralized Exchanges Work
Diving deeper into how decentralized exchanges work reveals sophisticated mechanisms that enable trustless trading at scale. The technical architecture of DEX platforms has evolved significantly from early designs, with modern implementations achieving impressive efficiency while maintaining decentralization principles. Understanding these mechanisms helps traders use DEX platforms effectively and evaluate different options.
Peer-to-Peer Crypto Trading on a DEX
Peer-to-peer crypto trading on DEX platforms differs significantly from the peer-to-peer model used in traditional P2P exchanges. Rather than directly matching buyers with sellers who negotiate terms, DEX trading occurs against liquidity pools where smart contracts serve as the counterparty. This approach enables instant trade execution without requiring another user to be online and willing to take the opposite side of your trade.
The peer-to-peer nature manifests in the absence of intermediary custody. Your tokens move directly from your wallet to the smart contract and the exchanged tokens return to your wallet in a single atomic transaction. No company holds your assets at any point, and no approval is needed from any authority to execute trades. This represents true peer-to-peer crypto trading in its purest form.
Role of Smart Contracts in DEX Operations
Smart contracts form the foundation of all DEX operations, serving as immutable programs that execute predetermined actions when specific conditions are met. In the context of decentralized exchanges, smart contracts handle pool creation, liquidity management, trade execution, fee distribution, and governance functions. Once deployed on the blockchain, these contracts operate autonomously according to their programmed logic.
The security of DEX platforms depends heavily on smart contract quality. Well-audited contracts from established protocols have processed billions in trading volume without exploits, while poorly designed or unaudited contracts have suffered devastating hacks. Users should verify that DEX smart contracts have undergone professional security audits before trusting them with significant funds.
| Step | DEX Trade Lifecycle | Technical Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wallet Connection | User connects wallet to DEX interface, granting read access to balances |
| 2 | Token Approval | User approves smart contract to spend tokens (one-time per token) |
| 3 | Trade Configuration | User selects tokens, amount, and slippage tolerance settings |
| 4 | Transaction Signing | User signs transaction in wallet, authorizing the swap |
| 5 | Blockchain Processing | Transaction enters mempool, validators include in block |
| 6 | Smart Contract Execution | Contract swaps tokens atomically, deducting fees to liquidity providers |
| 7 | Confirmation | Swapped tokens appear in user wallet, trade complete |
DEX Liquidity Pools and Their Function
Liquidity pools represent the innovation that made modern DEX platforms viable. Before AMM-based pools, decentralized exchanges struggled with liquidity because they required active participants on both sides of each trade. Liquidity pools solve this by allowing users to deposit token pairs that others can trade against, creating always-available liquidity regardless of whether another trader wants the opposite position.
Liquidity providers deposit equal values of two tokens into pools and receive LP (liquidity provider) tokens representing their share. When trades occur, a small fee (typically 0.3%) is collected and distributed proportionally to LP token holders. This mechanism incentivizes liquidity provision while enabling seamless trading. However, providers face impermanent loss risk when token prices diverge significantly from deposit ratios.
Advantages of Using a DEX
The benefits of DEX usage extend across security, privacy, cost, and accessibility dimensions. Understanding these advantages helps traders evaluate whether decentralized trading aligns with their priorities and risk tolerance. While no platform type is universally superior, DEX advantages are compelling for users who value self-custody and trustless systems.
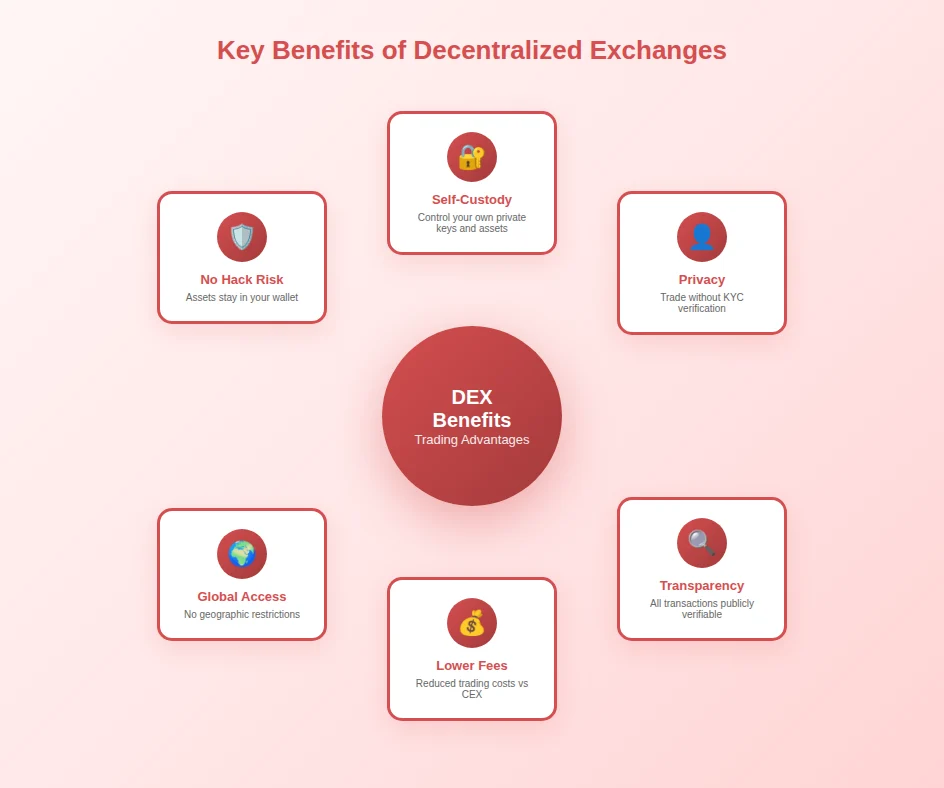
Security and Privacy Benefits
The benefits of DEX in terms of security stem from the fundamental architecture that eliminates centralized custody points. Users never surrender control of their private keys, meaning their funds remain secure in personal wallets throughout the trading process. This design removes the risk category associated with exchange hacks, insider theft, and insolvency that has resulted in billions of dollars in losses from centralized platforms.
Non-Custodial Nature of DEX
The non-custodial nature of DEX platforms means users maintain complete ownership of their assets at all times. Unlike centralized exchanges where depositing funds transfers them to exchange-controlled wallets, DEX trading occurs directly from personal wallets. This eliminates the “not your keys, not your coins” risk and ensures users cannot be locked out of their funds by platform decisions, regulatory actions, or business failures.
Reduced Risk of Hacks
While no system is completely immune to security risks, DEX architecture significantly reduces hack exposure. Centralized exchanges present attractive targets for hackers due to concentrated asset storage. DEX platforms, by contrast, distribute assets across thousands of individual wallets and typically hold only liquidity pool assets in smart contracts. Well-audited smart contracts have proven remarkably resilient, though users should still research contract security before trading.
Transparency in Trading
Every transaction on a DEX is recorded on the public blockchain, creating complete transparency in trading operations. Anyone can verify pool balances, trading volumes, fee distributions, and individual transactions. This transparency contrasts sharply with centralized exchanges where internal operations remain opaque and claims about liquidity or trading activity cannot be independently verified.
Transparency extends to the smart contract code itself. DEX protocols typically publish their contract source code, allowing technical users and security researchers to audit the logic governing their funds. This open-source approach enables community oversight and rapid identification of potential vulnerabilities.
Lower Fees Compared to Centralized Exchanges
DEX trading fees are often lower than centralized exchange fees, typically around 0.3% compared to 0.1-0.5% on centralized platforms plus withdrawal fees. However, the total cost comparison depends on blockchain network gas fees. On Ethereum mainnet, gas costs can exceed trading fees significantly during congestion, while Layer 2 solutions and alternative blockchains offer dramatically lower total costs that clearly favor DEX trading for many use cases.
Cost Consideration: When comparing DEX and centralized exchange costs, consider the total expense including trading fees, gas fees, withdrawal fees, and spread/slippage. The optimal choice varies by trade size, network conditions, and token pair liquidity.
Risks and Limitations of Decentralized Exchanges
Understanding risks of decentralized exchanges is essential for informed trading decisions. While DEX platforms offer significant advantages, they also present unique challenges and limitations that users must navigate. Acknowledging these drawbacks enables realistic expectations and appropriate risk management strategies.
Liquidity Challenges on DEX Platforms
Liquidity on DEX platforms varies dramatically between trading pairs and is generally lower than major centralized exchanges for most assets. While popular pairs like ETH/USDC have deep liquidity enabling large trades with minimal slippage, less common tokens may have shallow pools where even moderate trades cause significant price impact. This limitation makes DEX less suitable for large-volume trading in illiquid markets.
Liquidity fragmentation across multiple DEX platforms and blockchain networks further compounds this challenge. The same token might have liquidity split between Uniswap, SushiSwap, and various chains, preventing consolidated order flow that would improve execution quality. DEX aggregators partially address this by routing trades through multiple sources, but fragmentation remains an inherent limitation.
Slower Trading Speeds Compared to Centralized Exchanges
DEX trading speed is constrained by blockchain confirmation times, which range from seconds to minutes depending on the network. Centralized exchanges execute trades instantly within their internal systems, providing a significant advantage for time-sensitive strategies. Traders requiring rapid execution for arbitrage or active trading may find DEX latency unacceptable, particularly on congested networks where transactions can remain pending for extended periods.
Complexity for Beginners
The learning curve for DEX usage significantly exceeds that of centralized exchanges. Users must understand wallet management, gas fees, token approvals, slippage settings, and smart contract interactions. Mistakes like approving unlimited token spending, setting incorrect slippage, or interacting with malicious contracts can result in complete fund loss with no recourse. This complexity creates barriers for new users and increases error risk even for experienced traders unfamiliar with specific DEX interfaces.
Risk Warning: Decentralized exchanges involve risks including smart contract vulnerabilities, scam tokens, irreversible transactions, and impermanent loss for liquidity providers. Always verify token contract addresses, start with small amounts, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
DEX vs Centralized Exchange
The DEX vs centralized exchange comparison reveals fundamental trade-offs that inform platform selection based on individual priorities. Neither model is universally superior; each serves different needs and use cases effectively. Understanding these differences enables strategic decisions about when to use each platform type.
Key Differences Between DEX and Centralized Exchange
| Aspect | DEX | Centralized Exchange |
|---|---|---|
| Custody | Non-custodial, user controls keys | Custodial, exchange holds funds |
| KYC Requirements | None or minimal | Full verification required |
| Trading Speed | Blockchain confirmation dependent | Instant internal execution |
| Liquidity | Variable, often lower | Generally higher |
| Fiat Support | No direct fiat trading | Full fiat on/off ramps |
| Customer Support | Community/documentation only | Dedicated support teams |
| Token Availability | Any token on supported chain | Curated listings only |
Benefits of Choosing a DEX Over Centralized Platforms
Choosing DEX over centralized exchanges makes sense when security through self-custody is paramount, privacy is important, or access to newly launched tokens is desired. DEX platforms enable trading of any token deployed on their blockchain without waiting for exchange listings, providing early access to emerging projects. Users in regions with limited exchange access or facing account restrictions also benefit from DEX’s permissionless nature.
For traders seeking professional guidance on building customized trading solutions, working with experienced decentralized trading platform specialists can help navigate the complex technical requirements of both centralized and decentralized exchange implementations.
Situations Where Centralized Exchanges May Be Better
Centralized exchanges remain preferable for fiat currency on-ramps and off-ramps, large volume trading requiring deep liquidity, advanced order types like limit orders and stop-losses, and users who prefer customer support availability. The convenience of integrated services, faster execution speeds, and simpler interfaces make centralized platforms more suitable for many traders, particularly beginners and those trading large volumes.
How to Start Trading on a DEX
Getting started with DEX trading requires several preparation steps before executing your first trade. This section provides practical guidance for new DEX users, covering wallet setup, platform connection, and the trading process itself.
Setting Up a Crypto Wallet for DEX Trading
DEX trading requires a compatible cryptocurrency wallet that can connect to web-based applications. Popular options include MetaMask (browser extension and mobile), Trust Wallet (mobile), and Phantom (for Solana). Choose a wallet that supports the blockchain network where you plan to trade. Download only from official sources, securely backup your recovery phrase, and never share it with anyone.
Fund your wallet by transferring cryptocurrency from a centralized exchange or receiving from another wallet. Ensure you have sufficient native tokens (ETH for Ethereum, BNB for BNB Chain, SOL for Solana) to pay gas fees for transactions. Without gas tokens, you cannot execute trades regardless of other token balances.
Connecting Your Wallet to a DEX Platform
Navigate to your chosen DEX website and locate the connect wallet button, typically in the upper right corner. Select your wallet type from the available options. Your wallet will prompt you to approve the connection request. This connection allows the DEX to view your balances and request transaction signatures but does not give the platform access to move your funds without explicit approval for each transaction.
Verify you are on the correct website by checking the URL carefully. Phishing sites that mimic popular DEX interfaces are common scam vectors. Bookmark legitimate DEX URLs and access them only through your bookmarks rather than search results or links from unfamiliar sources.
Step-by-Step Guide to Trading on a DEX
DEX Selection Criteria
Blockchain Network: Choose a DEX operating on a blockchain that balances your needs for security, speed, and cost. Ethereum offers maximum liquidity but higher fees, while alternatives like Arbitrum, Polygon, or Solana provide lower costs with good liquidity for many pairs.
Liquidity Depth: Verify sufficient liquidity exists for your intended trading pairs by checking pool sizes and recent volume. Low liquidity results in high slippage that can significantly impact trade execution.
Security Track Record: Research the DEX’s history including smart contract audits, time in operation, and any past security incidents. Established protocols with clean track records present lower risk than new, unaudited alternatives.
Feature Requirements: Consider whether you need basic swaps or advanced features like limit orders, concentrated liquidity positions, or cross-chain trading. Different DEX platforms specialize in different capabilities.
User Interface Quality: A clear, intuitive interface reduces error risk. Test the platform with small amounts before committing larger trades, ensuring you understand all aspects of the trading process.
Execute your first trade by selecting the tokens you want to swap, entering the amount, reviewing the expected output and price impact, adjusting slippage tolerance if needed (typically 0.5-1% for stable pairs, higher for volatile tokens), and confirming the transaction in your wallet. Monitor the transaction status through your wallet or a blockchain explorer until confirmation.
Building robust crypto exchanges requires deep understanding of both DEX and centralized models to serve diverse trading needs effectively.
Conclusion
Decentralized exchanges represent a transformative development in cryptocurrency trading, offering an alternative to centralized platforms that aligns with blockchain’s core principles of decentralization and self-sovereignty. Understanding what is a DEX and how decentralized exchanges work enables informed decisions about when and how to utilize these platforms effectively.
The benefits of DEX including non-custodial trading, enhanced privacy, transparency, and permissionless access make them compelling options for users who prioritize security and autonomy. Peer-to-peer crypto trading through DEX protocols has matured from experimental technology to critical infrastructure processing billions in daily volume across multiple blockchain networks.
However, acknowledging risks of decentralized exchanges including liquidity limitations, complexity, and irreversible transactions is essential for realistic expectations. The DEX vs centralized exchange comparison reveals that neither model is universally superior; each serves different needs and circumstances. Many sophisticated traders maintain presence on both platform types, leveraging each for its particular strengths.
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues evolving, DEX technology advances in parallel. Innovations in Layer 2 scaling, cross-chain interoperability, and user experience design are progressively addressing current limitations while maintaining the decentralization principles that define these platforms. Whether you choose DEX trading platform options for all your activity or combine them with centralized services, understanding decentralized crypto trading has become essential knowledge for anyone serious about participating in digital asset markets.
The future of cryptocurrency trading will likely feature continued coexistence and integration between decentralized and centralized models, each serving the needs of different users and use cases. By understanding both approaches, traders can make informed decisions that optimize for their individual priorities around security, convenience, cost, and privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
A decentralized exchange is a cryptocurrency trading platform that operates without a central authority, allowing users to trade directly with each other through smart contracts on blockchain networks. Unlike centralized exchanges where a company holds your funds, DEX platforms enable peer-to-peer crypto trading where users maintain custody of their assets throughout the trading process. Trades execute automatically through smart contracts when conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
The primary benefits of DEX include enhanced security through non-custodial trading where users control their private keys, greater privacy with minimal or no KYC requirements, and resistance to censorship since no central entity can freeze accounts or restrict access. DEX platforms also offer transparency as all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be verified by anyone. Additionally, users avoid counterparty risks associated with exchange insolvency or mismanagement.
Trading on a DEX presents a steeper learning curve for beginners compared to centralized platforms due to the requirement to manage personal wallets, understand gas fees, and navigate smart contract interactions. While DEX platforms are technically secure through blockchain technology, new users face risks from errors like sending funds to wrong addresses or falling victim to fake token scams. Beginners should start with small amounts and thoroughly research before trading.
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptocurrency tokens locked in a smart contract that provides the funds necessary for trading on automated market maker (AMM) based DEX platforms. Users called liquidity providers deposit equal values of two tokens into pools and earn a share of trading fees generated when others trade against the pool. This mechanism replaces traditional order books and enables instant trades even for less popular token pairs.
Gas fees on DEX platforms are payments made to blockchain validators for processing and confirming transactions on the network. These fees vary based on network congestion and the complexity of the smart contract interaction required for the trade. On networks like Ethereum, gas fees can become expensive during high-demand periods, while alternative blockchains like Solana, Polygon, or BNB Chain offer significantly lower transaction costs for DEX trading.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







