Key Takeaways
- DEX Aggregators vs Standalone DEXs represents a fundamental choice between multi-source liquidity access and single-protocol simplicity in decentralized trading.
- A DEX Aggregator searches across multiple exchanges simultaneously, using smart routing algorithms to find optimal prices and minimize slippage for traders.
- A Standalone DEX operates with native liquidity pools, providing direct protocol interaction and community-driven liquidity within isolated ecosystems.
- Multi-DEX liquidity through aggregators enables larger trades with reduced price impact compared to trading against single liquidity sources.
- The difference between DEX Aggregator and DEX lies primarily in liquidity access, with aggregators combining sources while standalone DEXs use internal pools only.
- DEX trading comparison shows aggregators typically deliver better rates for larger trades, while standalone DEXs offer simpler experiences for basic swaps.
- DeFi trading platforms continue evolving with aggregators addressing liquidity fragmentation and standalone DEXs improving AMM efficiency.
- Choosing between these decentralized trading platforms depends on trade size, frequency, and preference for direct protocol interaction versus automated optimization.
The decentralized exchange landscape offers traders two distinct approaches to accessing DeFi liquidity. Understanding DEX Aggregators vs Standalone DEXs helps traders select the right tools for their specific needs. Each model offers unique advantages, and the optimal choice depends on trading patterns, volume requirements, and personal preferences for direct protocol interaction versus automated optimization.
What Is a Standalone DEX?
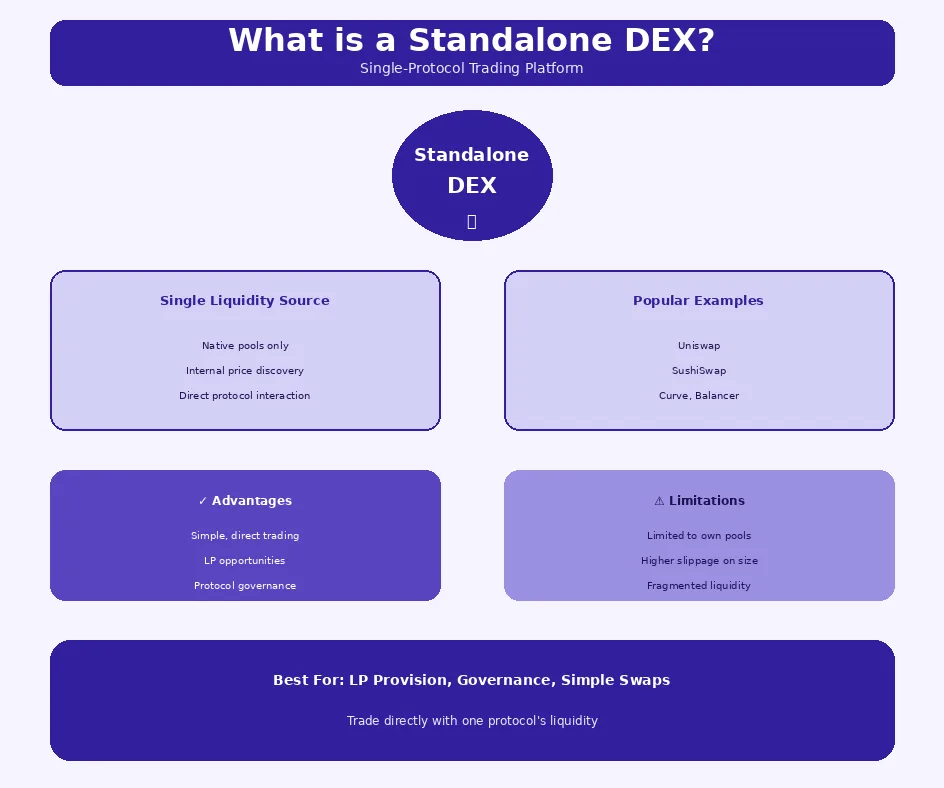
A Standalone DEX is a decentralized exchange that operates independently with its own liquidity infrastructure. Understanding what is a Standalone DEX requires recognizing that these platforms maintain native token pools where all trading activity occurs within the protocol’s ecosystem. Popular examples include Uniswap, SushiSwap, Curve, and Balancer, each offering unique features while operating as self-contained trading venues.
Core Features of Standalone DEXs
Core features of Standalone DEXs center on self-contained liquidity and protocol-native functionality. These platforms build and maintain their own liquidity pools, with all trades executing against internally held assets. This single liquidity source model creates predictable trading environments where pool dynamics directly determine user experiences.
Native liquidity pools form the foundation of Standalone DEX operations. Liquidity providers deposit token pairs into protocol-managed smart contracts, receiving pool tokens representing their share. Traders swap against these pools with prices determined by algorithmic market makers. Understanding order books and AMM mechanisms in DEX provides essential context for these dynamics.
How Standalone DEXs Handle Liquidity
Standalone DEXs handle liquidity through automated market maker pools that algorithmically determine prices based on token ratios. AMM-based liquidity pools use mathematical formulas to enable continuous trading without requiring order matching. The constant product formula (x * y = k) remains popular, though newer models offer variations optimized for specific use cases.
Trading within isolated ecosystems means all swaps execute against the specific DEX’s pools. If a token pair has limited liquidity on a particular platform, traders experience higher slippage regardless of deeper liquidity existing elsewhere. This isolation represents both a feature (simplicity, predictability) and limitation (missed optimization opportunities) of the standalone model.
Advantages of Standalone DEXs
Advantages of Standalone DEXs include simplicity and protocol-level control that appeals to many users. Direct interaction with a single protocol reduces complexity, making it easier to understand exactly how trades execute. Users can participate in governance, earn protocol-specific rewards, and engage with community-driven liquidity initiatives.
Protocol-level control enables features impossible in aggregated environments. Liquidity providers know exactly where their assets reside, governance participants can influence specific protocol parameters, and developers can build integrations with predictable behavior. This direct relationship supports the community-driven ethos central to DeFi philosophy. Building crypto exchanges with these principles requires careful attention to decentralized exchange protocol design.
Limitations of Standalone DEXs
Limitations of Standalone DEXs stem primarily from liquidity fragmentation across the DeFi ecosystem. When liquidity spreads across dozens of platforms, each individual DEX holds only a fraction of total available liquidity. Traders accessing single platforms may receive worse rates than if they could tap the combined market.
Higher slippage during large trades represents a significant limitation for substantial positions. When trade sizes exceed what a pool can absorb efficiently, prices move dramatically against the trader. This slippage problem intensifies for less liquid tokens where standalone DEX pools may be particularly shallow.
Market Reality: The proliferation of decentralized exchanges has created significant liquidity fragmentation, with trading pairs spread across dozens of platforms. This fragmentation drives demand for aggregation solutions that can unify access to dispersed liquidity.
What Is a DEX Aggregator?
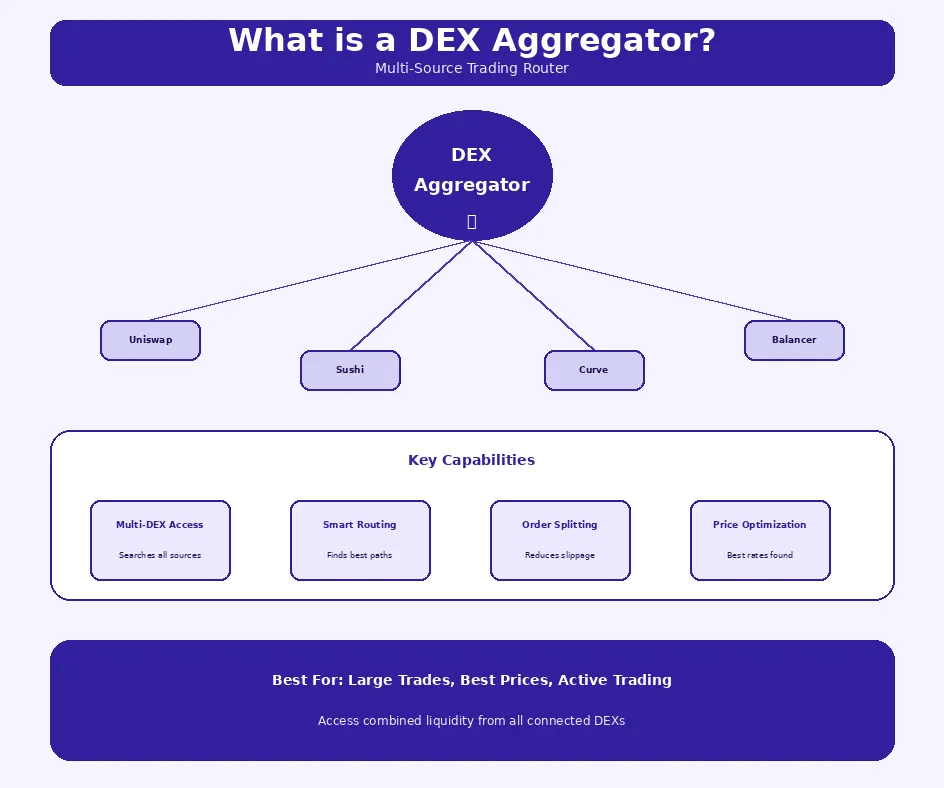
A DEX Aggregator is a platform that connects to multiple decentralized exchanges, comparing prices and routing trades through optimal paths. Understanding what is a DEX Aggregator reveals how these platforms solve liquidity fragmentation by providing unified access to the entire DeFi trading ecosystem. Rather than maintaining their own pools, aggregators leverage existing DEX infrastructure for trade execution.
How DEX Aggregators Work
Understanding how DEX Aggregators work starts with liquidity aggregation from multiple DEXs. When users request quotes, aggregators query connected platforms simultaneously, comparing available rates and liquidity depth. This real-time analysis enables identification of optimal execution paths that may span multiple sources.
Smart routing for optimal trades determines how orders actually execute. Algorithms consider not just prices but also gas costs, slippage expectations, and route complexity. For large orders, smart routing may split trades across multiple DEXs, achieving better average execution than any single source could provide.
Key Features of DEX Aggregator Platforms
Key features of DEX Aggregator platforms center on multi-DEX liquidity access that transforms fragmented markets into unified trading venues. Users see single quotes representing the best available rates across all connected sources. This consolidation simplifies decision-making while ensuring competitive execution.
Automated price discovery eliminates the need for manual comparison across platforms. Aggregators continuously monitor prices, updating quotes as market conditions change. This automation saves traders significant time while often identifying opportunities they would miss through manual searches.
Advantages of DEX Aggregators
Advantages of DEX Aggregators include reduced slippage through access to combined liquidity depth. By drawing from multiple pools, aggregators can absorb larger trades without the severe price impact that single-source execution would create. This capability is particularly valuable for substantial positions or less liquid tokens.
Better swap rates result from comprehensive price discovery across the DeFi ecosystem. Aggregators often identify routing opportunities that individual traders would miss, including multi-hop paths through intermediate tokens that provide better overall execution. These optimizations compound into meaningful value for active traders.
Challenges Faced by DEX Aggregators
Challenges faced by DEX Aggregators include smart contract complexity that increases potential attack surfaces. Aggregator contracts must interact safely with numerous external protocols, each with its own potential vulnerabilities. This complexity requires extensive auditing and ongoing security attention.
Dependency on external liquidity sources means aggregators cannot guarantee liquidity availability. If underlying DEXs experience issues, aggregators are affected by extension. This dependency creates systemic risk that standalone DEXs, controlling their own infrastructure, can mitigate more directly.
DEX Aggregator vs Standalone DEX Comparison
| Aspect | DEX Aggregator | Standalone DEX |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity Source | Multiple DEXs combined | Single internal pools |
| Price Discovery | Cross-platform comparison | Internal pricing only |
| Trade Routing | Optimized multi-hop | Direct pool swaps |
| Large Trade Slippage | Reduced (split orders) | Higher (single pool) |
| Complexity | Higher (more contracts) | Lower (single protocol) |
| LP Opportunities | Indirect (via underlying DEXs) | Direct pool participation |
DEX Aggregators vs Standalone DEXs
The comparison of DEX Aggregators vs Standalone DEXs reveals fundamental trade-offs that inform platform selection. Each model excels in different scenarios, and understanding these differences enables traders to optimize their DeFi experience based on specific needs and preferences.
Liquidity Access Comparison
Liquidity access comparison highlights the core difference between DEX Aggregator and DEX trading. Single-source vs multi-source liquidity fundamentally affects execution quality, particularly for larger trades or less common token pairs. Aggregators’ ability to combine pools creates effectively deeper markets.
Single-source liquidity through standalone DEXs provides predictability and simplicity but limits available depth. Multi-source liquidity through aggregators offers more options but introduces complexity and dependency on multiple protocols. Understanding yield mechanics in decentralized exchanges reveals additional considerations for liquidity-related decisions.
Pricing and Slippage Differences
Pricing and slippage differences emerge from the impact of liquidity depth on trade execution. When trading against shallow pools, large orders move prices significantly. Aggregators mitigate this by distributing volume across multiple sources, each absorbing only a portion of the total trade.
The practical impact varies by trade size and token liquidity. For small trades in liquid pairs, differences may be minimal. For larger positions or less common tokens, aggregator advantages become more pronounced. DEX trading comparison should account for typical trade sizes when evaluating platforms.
Gas Fee Optimization
Gas fee optimization affects total trading costs and varies between approaches. Trade routing efficiency in aggregators must balance better prices against potentially higher gas costs from complex routes. Simple standalone DEX swaps typically consume less gas but may provide worse execution.
Cost implications for traders depend on network conditions and trade economics. During high gas periods, the additional cost of aggregated routes may offset price benefits. Some aggregators optimize specifically for gas efficiency, accepting slightly worse rates for lower transaction costs.
User Experience and Trade Efficiency
User experience and trade efficiency differ between manual swaps vs automated routing approaches. Standalone DEXs offer straightforward interfaces for direct trading, while aggregators provide optimized but more complex experiences. User preferences for simplicity versus optimization influence platform choice.
Trade efficiency encompasses both execution quality and user effort. Aggregators reduce the effort required to find best rates while typically improving execution. Standalone DEXs offer more direct control and transparency about exactly where trades execute.
Trade Execution Lifecycle Comparison
| Step | DEX Aggregator Process | Standalone DEX Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Query multiple DEXs | Check internal pool |
| 2 | Compare all available routes | Calculate direct swap price |
| 3 | Determine optimal split/route | Present quote to user |
| 4 | Present optimized quote | User confirms trade |
| 5 | Execute across DEXs | Execute against pool |
| 6 | Deliver tokens to user | Deliver tokens to user |
DEX Aggregator vs DEX – Which Is Better for Traders?
Determining which platform type suits specific traders requires analyzing use cases and priorities. The DEX Aggregator vs DEX decision depends on trading patterns, volume, and preferences for direct protocol engagement versus automated optimization. Both approaches serve important roles in the DeFi ecosystem.
Use Cases for Standalone DEXs
Use cases for Standalone DEXs favor scenarios requiring direct protocol interaction. Liquidity providers must use standalone platforms to deposit assets into pools. Governance participants need direct engagement with specific protocols. Developers building integrations benefit from predictable, single-protocol behavior.
Community-driven liquidity initiatives occur on standalone platforms where participants can direct resources to specific pools. These platforms support the relationship between liquidity providers and traders that forms DeFi’s foundation. Exploring token launch mechanisms on DEX reveals additional standalone platform functions.
Use Cases for DEX Aggregators
Use cases for DEX Aggregators favor large-volume trades where slippage reduction provides significant value. When executing substantial positions, the ability to split orders across multiple sources often delivers better outcomes than any single DEX could provide.
Best-price execution across DeFi matters most for active traders executing frequent transactions. The cumulative benefit of consistently better rates compounds into meaningful value over time. Price-sensitive traders and those managing significant portfolios typically prefer aggregator efficiency.
Platform Selection Criteria
When choosing between aggregators and standalone DEXs, consider:
- Trade Size: Larger trades benefit more from aggregation
- Trading Frequency: Active traders save more with optimization
- LP Interest: Liquidity provision requires standalone platforms
- Governance: Protocol participation needs direct engagement
- Simplicity: Basic users may prefer standalone clarity
- Gas Sensitivity: Consider gas costs vs price improvement
Role of DEX Aggregators in the DeFi Ecosystem
The role of DEX Aggregators in the DeFi ecosystem extends beyond individual trading benefits to systemic improvements. By solving liquidity fragmentation, aggregators enhance overall market efficiency and create infrastructure that benefits all participants. Understanding exchange platform architecture reveals these systemic contributions.
Solving Liquidity Fragmentation
Solving liquidity fragmentation through aggregation provides unified access to DeFi liquidity that would otherwise remain dispersed across dozens of platforms. This unification creates effectively deeper markets, reducing slippage ecosystem-wide and enabling larger trades than fragmented liquidity would support.
The systemic benefit extends beyond individual users to improve overall market efficiency. Better price discovery through aggregation helps establish accurate market prices, benefiting all participants including those using standalone DEXs who benefit from arbitrage that keeps prices aligned.
Enhancing Decentralized Trading Efficiency
Enhancing decentralized trading efficiency through optimized on-chain trading flows improves the overall DeFi experience. Aggregators demonstrate that decentralized systems can provide execution quality comparable to centralized alternatives, supporting broader DeFi adoption.
Optimized trading flows also reduce wasted resources across the ecosystem. Better routing means fewer failed transactions, more efficient gas usage, and improved outcomes for all participants. These efficiency gains compound as aggregation becomes more sophisticated.
Important Notice: Both DEX aggregators and standalone DEXs involve smart contract risks, market volatility, and potential for impermanent loss. Always conduct thorough research, verify you are using legitimate platforms, and never trade more than you can afford to lose. Past performance does not guarantee future results in DeFi trading.
Future of Decentralized Exchanges
The future of decentralized exchanges involves continued evolution of both aggregators and standalone platforms. Best decentralized exchanges will increasingly combine the advantages of both models, with aggregators becoming more sophisticated and standalone DEXs addressing their liquidity limitations. Understanding DEX architecture and construction provides insight into these emerging trends.
Trends in DEX Aggregation
Trends in DEX aggregation include cross-chain swaps that extend aggregation across blockchain boundaries. As multi-chain ecosystems expand, aggregators are evolving to route trades across networks, not just within single chains. This capability will become increasingly important as DeFi continues fragmenting across numerous blockchain environments.
Advanced routing algorithms continue improving with machine learning optimization, intent-based systems, and more sophisticated modeling of slippage and gas costs. These improvements will deliver even better execution quality while reducing the complexity users experience.
Build Your Own DEX or Aggregator Today
Partner with us to create a secure, high-performance DEX or DEX aggregator. Maximize liquidity, reduce slippage, and deliver seamless trading experiences.
Launch Your Exchange Now
Evolution of Standalone DEX Models
Evolution of standalone DEX models focuses on improved AMM designs that offer better capital efficiency and reduced impermanent loss. Concentrated liquidity, dynamic fee structures, and protocol-owned liquidity mechanisms all address traditional AMM limitations. These improvements make standalone DEXs more competitive for various trading scenarios.
Deeper liquidity incentives through enhanced tokenomics and sustainability mechanisms aim to attract and retain liquidity providers. Standalone DEXs are developing innovative approaches to build loyal liquidity bases that reduce dependency on mercenary capital seeking short-term yields.
Future Evolution Comparison
| Trend | DEX Aggregators | Standalone DEXs |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Chain | Multi-chain routing | Native on specific chains |
| Liquidity | Better aggregation | Concentrated liquidity |
| User Experience | Intent-based trading | Simplified interfaces |
| Efficiency | AI-optimized routing | Capital-efficient AMMs |
Conclusion
The comparison of DEX Aggregators vs Standalone DEXs reveals complementary approaches serving different needs within the DeFi ecosystem. DEX Aggregators excel at finding optimal prices across fragmented liquidity, while Standalone DEXs provide direct protocol interaction and community-driven trading environments. Understanding these differences enables informed platform selection aligned with specific trading requirements.
The difference between DEX Aggregator and DEX trading ultimately comes down to multi-source versus single-source liquidity access. Aggregators shine for larger trades and price-sensitive execution, while standalone DEXs remain essential for liquidity provision, governance participation, and direct protocol engagement. Most active DeFi traders benefit from using both types strategically.
As decentralized trading platforms continue evolving, both aggregators and standalone DEXs will become more sophisticated. Cross-chain capabilities, improved AMM designs, and enhanced routing algorithms will further blur distinctions while improving outcomes for all DeFi participants. The best approach for most users combines the strengths of both models based on specific transaction needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
A standalone DEX operates with its own liquidity pools and executes trades only within its ecosystem, while a DEX aggregator searches across multiple DEXs to find the best trading rates. Aggregators route trades through optimal paths across platforms, whereas standalone DEXs rely solely on their internal liquidity for trade execution.
The better option depends on your trading needs. DEX aggregators typically offer better prices for larger trades by accessing multi-DEX liquidity, while standalone DEXs provide simpler experiences and direct protocol interaction. Active traders seeking best rates often prefer aggregators, while liquidity providers may prefer specific standalone platforms.
DEX aggregators do not necessarily have lower base fees but often provide better net outcomes through price optimization. While aggregated routes may involve multiple protocol fees, the improved execution prices typically offset these costs. Gas efficiency varies, with some aggregators optimizing for total transaction cost including gas.
A DEX aggregator platform is a service that connects to multiple decentralized exchanges to find optimal trading routes. These platforms use algorithms to compare prices, analyze liquidity depth, and route trades through the most efficient paths. Popular examples include 1inch, Paraswap, and Matcha, which aggregate liquidity from dozens of DEX sources.
Standalone DEXs work by maintaining their own liquidity pools where users deposit token pairs. When someone trades, the DEX executes swaps against these internal pools using automated market maker algorithms. Prices adjust based on pool ratios, and liquidity providers earn fees from trades executed through their deposited assets.
Multi-DEX liquidity refers to combined access to liquidity pools across multiple decentralized exchanges. DEX aggregators provide this access by connecting to numerous platforms simultaneously. This combined liquidity enables larger trades with less slippage than any single DEX could support independently.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







