Key Takeaways
- Order book based decentralized exchanges match buy and sell orders at specific prices, supporting limit orders and market orders similar to traditional exchanges.
- Automated market maker DEX platforms use mathematical formulas and liquidity pools to enable instant trades without requiring counterparty matching.
- How liquidity pools work involves paired token deposits that traders swap against, with prices determined by pool ratios and the constant product formula.
- Liquidity providers in AMM earn trading fees but face impermanent loss when token prices diverge from deposit ratios.
- Price discovery in DEX occurs through order interaction in order books or through arbitrage activities that align AMM prices with external markets.
- On-chain order book DEX offers maximum decentralization while off-chain order book DEX provides faster execution with on-chain settlement.
- Slippage in AMM DEX increases with trade size relative to pool liquidity, requiring traders to manage expectations and set appropriate tolerances.
- Hybrid DEX models combine order book and AMM approaches to offer flexible trading options and optimized execution across different scenarios.
Decentralized exchanges have revolutionized cryptocurrency trading by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without centralized intermediaries. At the heart of this revolution are two distinct trading mechanisms: traditional order books adapted for blockchain environments and innovative automated market makers that reimagined how liquidity works. Understanding how these systems function empowers traders to make informed decisions about where and how to trade. This comprehensive guide explores both mechanisms in detail, comparing their strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases.
Understanding Order Book Based Decentralized Exchanges
What Is an Order Book in a Decentralized Exchange
A decentralized exchange order book is a digital ledger that records all pending buy and sell orders for a trading pair, organized by price level. Unlike centralized exchanges where order books reside on company servers, order book based decentralized exchanges maintain this data through smart contracts or distributed systems. This blockchain based trading system ensures transparency and eliminates the need to trust any single entity with order management.
The decentralized exchange trading mechanism in order book models closely resembles traditional finance, making it familiar to experienced traders. Orders are displayed showing available liquidity at each price point, enabling traders to assess market depth and make informed decisions about order placement. This transparency in the trustless trading mechanism creates a fair environment where all participants access the same information.
Buy Orders and Sell Orders in DEX Order Books
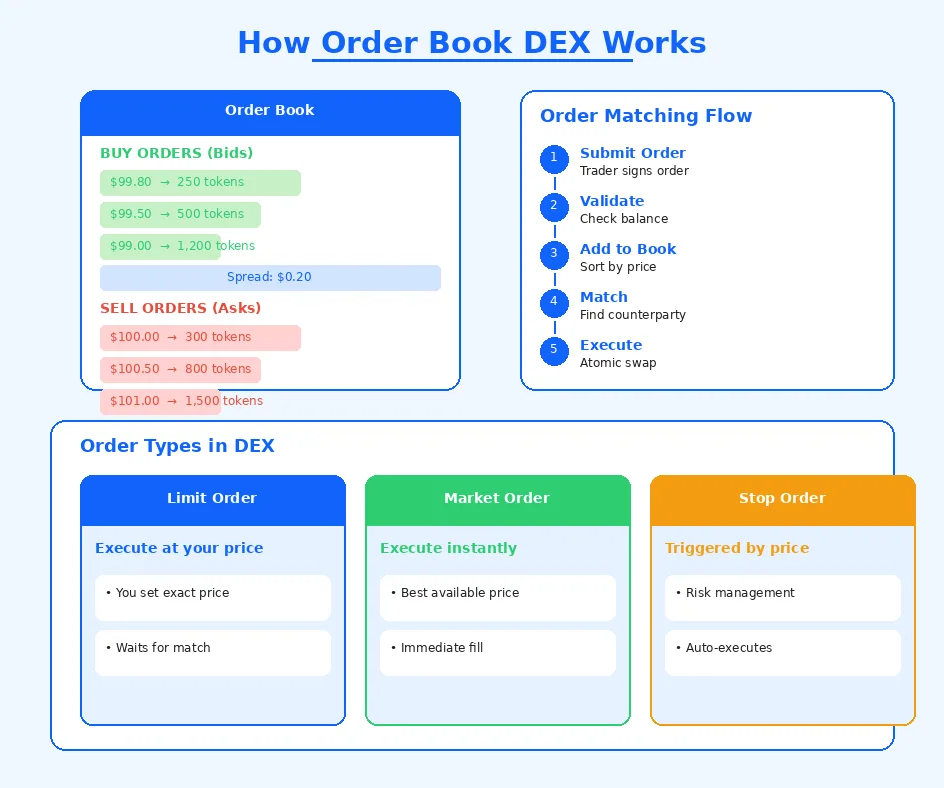
Buy orders (bids) represent traders willing to purchase assets at specified prices, while sell orders (asks) represent those willing to sell. The order book displays these orders sorted by price, with the highest bids and lowest asks closest to the market price. DEX order matching occurs when a new order’s price overlaps with existing orders on the opposite side, triggering automatic execution through smart contracts in DEX.
Limit Orders and Market Orders in Order Book DEX
Limit orders in decentralized exchange allow traders to specify exact prices for execution, providing control over entry and exit points. These orders remain in the order book until filled or canceled, enabling patient traders to wait for favorable prices. Market orders in DEX execute immediately at the best available prices, suitable for traders prioritizing speed over price precision. The availability of both order types makes order book DEX appealing to diverse trading strategies.
How Order Matching Works in Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized order matching follows price-time priority, where orders at better prices execute first, and among equal prices, earlier orders take precedence. This fair ordering principle ensures predictable execution that traders can rely on when formulating strategies. The matching algorithm runs through smart contracts, providing transparency and eliminating human discretion in trade execution.
On-Chain Order Book Execution
On-chain order book DEX processes all order management and matching directly on the blockchain. Every order placement, cancellation, and execution becomes a blockchain transaction, creating a complete and immutable audit trail. This approach maximizes decentralization and transparency but faces inherent limitations from blockchain throughput and gas fees in order book DEX operations.
Off-Chain Order Book with On-Chain Settlement
Off-chain order book DEX handles order management and matching on external servers while relying on blockchain only for final settlement. This hybrid approach dramatically reduces gas costs and enables faster order updates, making it practical for active trading. While introducing some centralization in the matching layer, on-chain settlement ensures trustless final execution and fund security.
Order Book Trade Lifecycle
| Stage | Process | Location | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Order Creation | Trader submits order details | User Interface | Order signed |
| 2. Order Validation | Verify balance and signature | On/Off-Chain | Order accepted |
| 3. Order Book Entry | Add to sorted order list | Order Book | Order visible |
| 4. Order Matching | Find compatible counterparty | Matching Engine | Match found |
| 5. Settlement | Execute atomic swap | Blockchain | Tokens exchanged |
| 6. Confirmation | Record on blockchain | Blockchain | Trade finalized |
Advantages of Order Book DEX Model
Order book based decentralized exchanges offer several compelling advantages for sophisticated traders. The ability to place limit orders provides precise control over execution prices, essential for trading strategies that depend on specific entry and exit points. Capital efficiency in AMM versus order books often favors order books for larger trades, as liquidity concentrates at specific price levels rather than spreading across a curve.
Price discovery in DEX order books mirrors traditional markets, with prices emerging from genuine supply and demand interaction. This familiar trading experience attracts professional traders and market makers who bring additional liquidity. The transparent order flow enables sophisticated analysis of market depth and potential price movements.
Limitations of Order Book Based Decentralized Exchanges
Despite their advantages, order book models face significant challenges in decentralized environments. Gas fees in order book DEX can make frequent order updates prohibitively expensive, especially during network congestion. The requirement for counterparty orders means low-volume trading pairs may lack sufficient liquidity, resulting in wide spreads or failed executions.
Trading Principle: Order book DEX models excel when sufficient trading activity exists to maintain tight spreads and quick execution. For thinly traded pairs, the lack of counterparties can result in orders remaining unfilled indefinitely or executing at unfavorable prices far from expected levels.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs) in Decentralized Exchanges
What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)
An automated market maker DEX replaces traditional order books with mathematical algorithms that determine prices based on token ratios in liquidity pools. This decentralized exchange AMM model revolutionized DeFi by enabling instant trades without requiring counterparty orders. The permissionless exchange model allows anyone to trade any available pair at any time, dramatically improving accessibility compared to order book systems.
Understanding how AMM DEX works is fundamental for DeFi participation. Rather than matching individual orders, traders swap against pooled liquidity maintained by other users. Smart contracts in DEX handle all calculations and execution automatically, creating a trustless trading mechanism that operates continuously without human intervention.
AMM Pricing Formula in Decentralized Exchanges
The AMM pricing mechanism most commonly uses the constant product formula: x * y = k, where x and y represent token quantities and k remains constant. When traders buy token A, they add token B, changing the ratio and automatically adjusting the price. This elegant mathematical approach ensures continuous liquidity availability while naturally adjusting prices based on supply and demand.
Role of Smart Contracts in AMM DEX
Smart contracts in DEX serve as the backbone of AMM functionality, handling pool management, price calculations, and trade execution. These immutable programs ensure that trades execute exactly according to defined rules without possibility of manipulation. The transparent nature of blockchain allows anyone to verify the contract logic, building trust in the trustless trading mechanism.
How Liquidity Pools Work in AMM Based DEX
Liquidity pools in AMM contain paired tokens deposited by users who want to earn trading fees. How liquidity pools work involves maintaining constant product relationships while allowing trades that shift token ratios. Each swap changes the pool composition, with the mathematical formula ensuring prices adjust appropriately. This creates a self-regulating system that provides continuous liquidity.
Liquidity Providers in Automated Market Makers
Liquidity providers in AMM deposit equal values of two tokens into pools and receive LP tokens representing their share. These providers earn proportional fees from every trade executed against their liquidity. The democratized nature of AMM liquidity provision allows anyone to become a market maker, contrasting with traditional finance where this role requires substantial capital and expertise. For deeper insights into earning potential, understanding how decentralized exchanges function provides valuable foundation.
Token Pairing in AMM Liquidity Pools
Token pairing in AMM liquidity pools requires depositing two assets in equal value ratios at current market prices. Common pairs include stablecoin pairs (low volatility, lower impermanent loss) and volatile asset pairs (higher fees but greater impermanent loss risk). The choice of pairs significantly impacts provider returns and risk exposure.
Benefits of AMM Based Decentralized Exchanges
AMM based decentralized exchanges offer transformative advantages that drove DeFi adoption. Continuous liquidity availability ensures trades execute instantly regardless of counterparty presence. The permissionless exchange model allows any token to be listed without gatekeepers, enabling trading access for long-tail assets that would never achieve order book liquidity. Passive income opportunities through liquidity provision democratize market making.
Challenges of Automated Market Makers
Despite their innovation, AMMs present significant challenges. Impermanent loss in AMM affects liquidity providers when token prices diverge, potentially exceeding earned fees. Slippage in AMM DEX increases with trade size, making large orders expensive. Capital efficiency in AMM spreads liquidity across all prices rather than concentrating at likely trading ranges, though concentrated liquidity solutions address this limitation.
Risk Warning: Impermanent loss can significantly reduce liquidity provider returns, especially in volatile markets. Before providing liquidity, calculate potential impermanent loss scenarios and ensure expected fee income justifies the risk. Stable pairs generally offer lower risk but also lower returns.
Difference Between Order Book DEX and AMM DEX
| Feature | Order Book DEX | AMM DEX |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity Source | Individual trader orders | Pooled liquidity |
| Price Mechanism | Supply/demand matching | Mathematical formula |
| Order Types | Limit, Market, Stop | Instant swaps |
| Execution | When orders match | Instant against pool |
| Best For | Active traders, large orders | Simple swaps, passive LP |
| Main Challenge | Requires counterparties | Impermanent loss |
Liquidity Management in Order Book vs AMM
AMM liquidity vs order book liquidity differs fundamentally in how capital is deployed. Order books concentrate liquidity at specific price levels where market makers expect trading activity, enabling capital efficient positioning. AMM spreads liquidity across all possible prices, ensuring availability but reducing efficiency. Concentrated liquidity AMMs address this by allowing providers to focus capital within chosen price ranges.
Price Discovery in Order Book and AMM Models
Price discovery in DEX varies significantly between models. Order books discover prices through direct interaction between buyer and seller orders, reflecting genuine supply and demand at each level. AMMs rely on arbitrageurs who profit by correcting price discrepancies between the pool and external markets, indirectly importing external price discovery rather than creating it organically.
Trading Experience on Order Book DEX vs AMM DEX
The trading experience differs substantially between models. Order book DEX offers familiar interfaces with order depth visualization, enabling sophisticated analysis and strategy execution. AMM DEX provides simpler swap interfaces optimized for quick trades, ideal for users wanting straightforward token exchanges without managing orders. Your trading style and needs should guide model selection.
Ready to build a high-performance crypto exchange with optimized trading mechanisms
Our expert team delivers secure, scalable solutions tailored to your requirements
Launch Your Exchange Now
Hybrid Decentralized Exchange Models
Combining Order Books and Automated Market Makers
The hybrid DEX model represents an evolution that combines strengths of both approaches. These platforms may route trades to whichever mechanism offers better execution, use AMM liquidity as fallback for unfilled order book orders, or enable limit orders on top of AMM pools. This flexibility serves diverse trader needs within a single platform.
Use Cases of Hybrid DEX Architecture
Hybrid DEX architecture serves multiple use cases effectively. Professional traders can place limit orders while casual users execute instant swaps. Market makers can provide liquidity through order books or pools depending on their preference. For projects looking to launch tokens with flexible trading options, exploring decentralized exchange launchpad solutions offers comprehensive pathways.
Efficiency Improvements in Hybrid DEX Systems
Hybrid systems improve efficiency by aggregating liquidity from multiple sources. Smart order routing finds the best execution path across order books and pools. This aggregation reduces slippage and improves fill rates compared to either mechanism operating independently. The combined approach represents the future direction of decentralized trading protocols.
DEX Model Selection Criteria
Trading Style
Active trading: Order Book. Simple swaps: AMM
Order Size
Large orders: Order Book. Small swaps: AMM
Price Control
Precise limits: Order Book. Market rates: AMM
Earning Income
Market making: Order Book. Passive LP: AMM
Role of Smart Contracts in Order Book and AMM DEX
Smart Contract Execution in Order Book Trading
Smart contracts in DEX order book systems handle order validation, matching confirmation, and atomic settlement. When compatible orders are identified, the contract executes simultaneous token transfers ensuring both parties receive their expected assets. This eliminates counterparty risk by making trades all-or-nothing transactions that complete fully or not at all.
Smart Contract Automation in AMM Liquidity Pools
AMM smart contracts automate pool management, price calculation, and swap execution. When users trade, contracts calculate outputs based on the constant product formula, verify slippage tolerance, and execute atomic swaps. For liquidity actions, contracts mint or burn LP tokens proportionally to deposits or withdrawals. This automation enables the trustless trading mechanism that defines DeFi.
Security and Transparency in Decentralized Exchanges
Security Risks in Order Book Based DEX
Order book DEX faces specific security challenges including front-running where observers exploit pending orders. Off-chain components introduce centralization risks if relayers act maliciously. Smart contract vulnerabilities can enable unauthorized fund access. Careful protocol design, audits, and decentralized relayer networks mitigate these risks while maintaining performance benefits.
Smart Contract Risks in AMM Based DEX
AMM based decentralized exchanges face smart contract vulnerabilities including flash loan attacks, oracle manipulation, and reentrancy exploits. Pool design flaws can enable draining attacks. Thorough auditing, formal verification, and time-tested protocols reduce these risks. For building secure trading infrastructure, professional decentralized exchange solutions provide comprehensive security frameworks.
Future of Decentralized Exchanges with Order Books and AMMs
Scalability Improvements in Order Book DEX
Future order book DEX will benefit from layer 2 scaling that dramatically reduces gas costs and latency. Rollup-based solutions enable near-instant order updates at fraction of mainnet costs. Application-specific chains optimize specifically for order book operations. These improvements will make on-chain order book DEX competitive with centralized exchange performance.
Innovation Trends in Automated Market Makers
AMM innovation continues with concentrated liquidity that improves capital efficiency, dynamic fees that adjust to market conditions, and multi-asset pools that expand trading possibilities. MEV protection mechanisms ensure fair execution. Cross-chain AMMs will unify liquidity across blockchain networks. These advances will enhance capital efficiency in AMM while reducing impermanent loss and slippage.
Quick DEXs FAQ Guide
AMMs work better in low-liquidity markets as trades can still occur if pools exist. Order Books may face wide spreads and fewer matches without active traders, limiting execution opportunities for smaller or emerging markets.
AMMs expose liquidity providers to impermanent loss, while Order Books risk slippage and low trade execution during thin markets. Each model requires understanding market conditions before choosing a trading strategy.
It keeps buy and sell orders on-chain or off-chain, matching them through smart contracts. This system provides transparent, secure transactions without intermediaries, giving traders control over price and order execution in a decentralized environment.
AMMs use formulas like x × y = k to adjust prices based on token supply and demand. This automated process allows trades without relying on traditional order matching or centralized market makers.
Yes, hybrid DEXs combine Order Books for precise pricing and AMMs for constant liquidity. This approach improves flexibility, user choice, and trading efficiency across different cryptocurrency markets.
Order Book DEXs match buyers and sellers directly, while AMMs use liquidity pools with algorithms to set prices. AMMs ensure trades continue if liquidity exists, whereas Order Books depend heavily on active traders for execution.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







