Key Takeaways
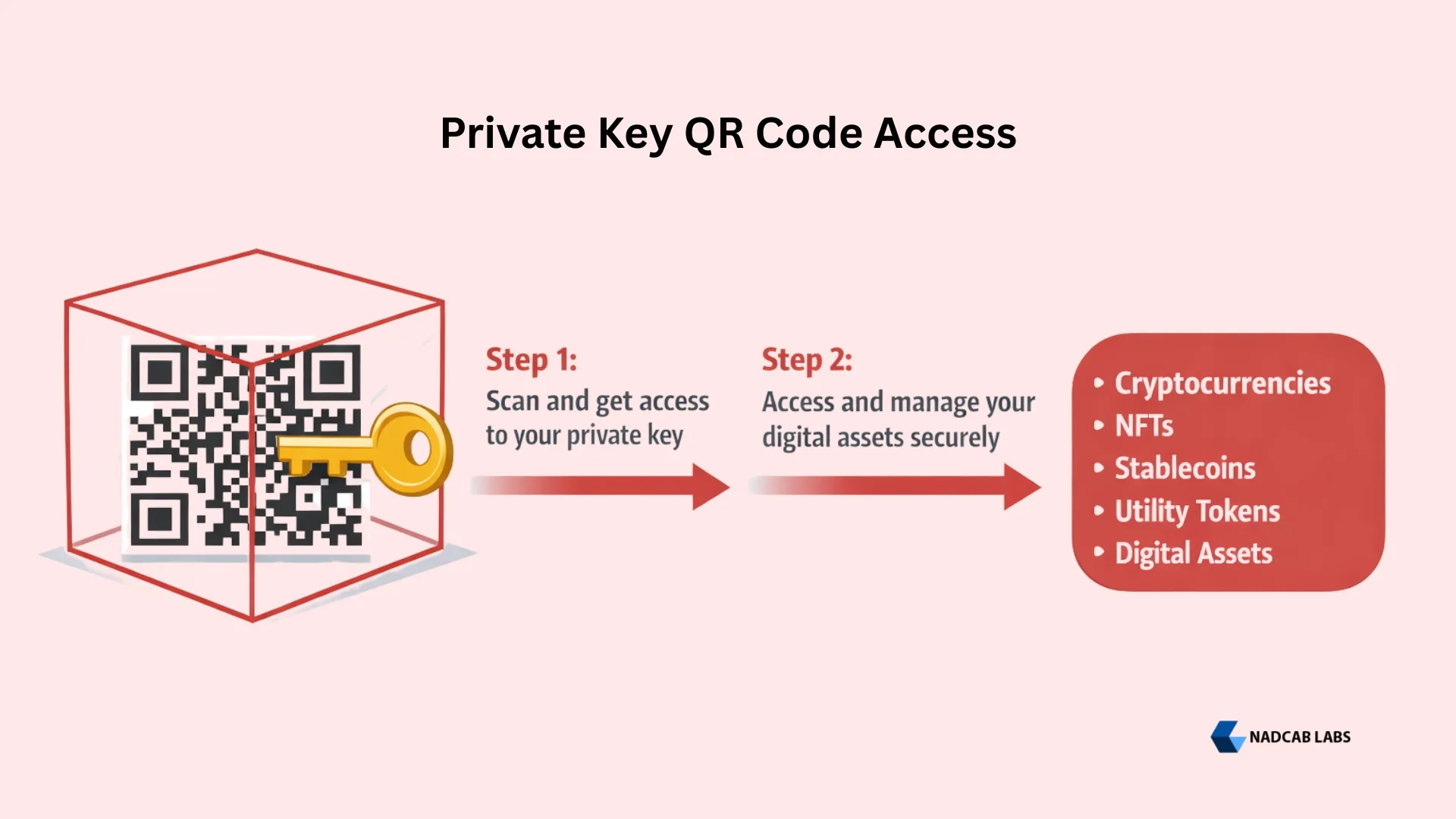
- A blockchain private key QR code is a scannable 2D barcode that encodes your private key, making it easier to import wallets, sign transactions, and manage crypto assets without manual entry.
- Private keys are typically 64-character hexadecimal strings in Ethereum or 256-bit codes in Bitcoin, and encoding them as QR codes eliminates the risk of transcription errors.
- Unlike public key (wallet address) QR codes which are safe to share, a private key QR code must never be shared with anyone — it grants full control over your funds.
- Always generate private key QR codes using trusted, offline tools to prevent exposure to malware, phishing, or malicious third-party services.
- Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor provide the most secure storage for private key QR codes by keeping keys completely offline.
- Blockchain transactions are irreversible, if someone scans your private key QR code, stolen funds cannot be recovered.
- Best practices include storing QR codes in fireproof safes, enabling two-factor authentication, creating multiple encrypted backups, and never saving QR codes on cloud-connected devices.
Managing private keys is one of the most critical aspects of cryptocurrency ownership. A single mistyped character can lock you out of your wallet forever, and exposing your key to the wrong party can drain your funds in seconds. This is where the blockchain private key QR code enters the picture — a scannable image that stores your private key in a machine-readable format, making wallet imports faster, transactions smoother, and human error virtually eliminated.
But convenience always comes with trade-offs. While a QR code simplifies the way you interact with your blockchain wallet, it also concentrates your entire digital wealth into a single scannable image. If someone photographs, copies, or scans that code without your knowledge, your assets are gone — and blockchain transactions cannot be reversed. Understanding how to generate, use, and securely store a blockchain private key QR code is therefore essential for anyone serious about crypto security.
In this complete guide, we break down everything you need to know — from how private keys work and why QR codes are used, to step-by-step generation instructions, real-world use cases, security risks, and battle-tested best practices for keeping your assets safe.
What is a Blockchain Private Key QR Code?
A visual representation of your secret cryptographic key in scannable format
Private Key
9913b1f8…ca738572
64-character hex string
QR Generator
Offline, trusted tool encodes the key into a 2D barcode
QR Code
Scannable image storing your entire private key
Wallet Import
Scan with MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Phantom, etc.
256-bit
Encryption Strength
< 2 sec
Scan-to-Import Time
0%
Transcription Error Rate
100%
Irreversible if Stolen
What is a Blockchain Private Key?
Definition
A blockchain private key is a unique, randomly generated alphanumeric string that serves as the master password for accessing and controlling your cryptocurrency assets. It is generated using elliptic curve cryptography and is mathematically paired with a public key, which is used to receive funds. Only the private key holder can authorize transactions from the associated wallet.
In Ethereum, a private key is typically a 64-character hexadecimal string. In Bitcoin, it is a 256-bit code that can be represented in several formats including Wallet Import Format (WIF). Regardless of the blockchain network, the private key performs the same fundamental functions: it signs transactions, proves ownership, and grants complete control over the associated wallet and all assets within it.
Example of a blockchain private key (64 characters, hexadecimal):
This key must never be shared with anyone. It is the only credential needed to move funds from your wallet, and unlike bank passwords, there is no recovery mechanism if it is lost or stolen. Every aspect of blockchain security begins with keeping your private key safe.
Read Also: Public Key in Blockchain: How It Works →
How Does a Blockchain Private Key Work?
Private keys are built on the principle of asymmetric cryptography, where a pair of keys — one public and one private — work together to enable secure, verifiable transactions. Here is how the process works when you send cryptocurrency:
How a Private Key Signs a Transaction
Initiate
Enter the amount and recipient’s public wallet address in your crypto wallet
The private key never leaves your device during this process — only the digital signature is broadcast to the network. This is why cryptographic hash functions and elliptic curve mathematics are so fundamental to blockchain security. The public key can verify a signature was made by the corresponding private key, but it cannot reverse-engineer the private key itself.
What is a Blockchain Private Key QR Code?
Definition
A blockchain private key QR code is a 2D barcode (Quick Response code) that encodes your private key into a scannable image format. When scanned by a compatible crypto wallet app, it allows you to instantly import your wallet, authorize transactions, and access your digital assets without manually typing the long alphanumeric key string.
The concept emerged around 2011–2012 as Bitcoin adoption grew and users needed a more practical way to handle unwieldy private key strings. Rather than writing down 64 characters on paper and risking transcription errors, a QR code captures the key perfectly every time it is scanned. Today, major wallet applications like MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet, and Phantom all support QR code scanning for key import.
Anatomy of a Private Key QR Code

The QR Image
A matrix of black & white modules encoding your 256-bit private key into a scannable visual format
📌 Finder Patterns
Three corner squares that help scanners detect and orient the QR code correctly
📌 Data Region
The encoded private key string (64 hex characters) stored as binary data modules
📌 Error Correction
Reed-Solomon codes that allow the QR to be read even if up to 30% is damaged
📌 Quiet Zone
White border margin that separates the QR from surrounding content for reliable scanning
Private Key QR vs. Public Key (Wallet Address) QR
This is a critical distinction that every blockchain user must understand:
| Feature | Public Key (Address) QR Code | Private Key QR Code |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Receive cryptocurrency from others | Access and control the wallet & funds |
| Safe to Share? | ✅ Yes — publicly shareable | ❌ NEVER — must remain secret |
| Risk if Exposed | None — others can only send you funds | Total loss — full wallet access to attacker |
| Common Use | Payment requests, invoices, websites | Offline backup, wallet import/migration |
| Analogy | Like sharing your email address | Like sharing your email password |
Always double-check which QR code you are sharing or scanning. Accidentally sharing a private key QR instead of a wallet address QR is one of the most common and devastating mistakes in crypto.
How to Generate a Blockchain Private Key QR Code
Creating a QR code from your private key requires careful attention to security. The process itself is straightforward, but the environment in which you do it matters enormously. Here is a secure, step-by-step approach:
Secure QR Code Generation Process
Choose Trusted Tool
Open-source, verified QR generator (e.g., bitaddress.org)
Go Offline
Disconnect from internet before entering your key
Generate QR
Paste private key and create the QR code
Verify
Scan with separate device to confirm accuracy
Secure Storage
Print & store in fireproof safe; clear all temp data
Step 1: Choose a Trusted QR Code Generator
Select a reputable and ideally open-source QR code generator. Tools like bitaddress.org (for Bitcoin) allow offline QR generation. Verify the security certificates and authenticity of any service before inputting sensitive data. For maximum security, download the tool and run it on an air-gapped (offline) computer.
Step 2: Go Offline Before Entering Your Key
Disconnect your device from the internet before pasting or entering your private key. This prevents any background processes, browser extensions, or malware from transmitting your key to a remote server. An air-gapped computer that has never been connected to the internet is the ideal environment.
Step 3: Paste Your Private Key and Generate
Enter or paste your private key into the plain-text field. The tool will automatically generate a QR code. Before saving, verify the generated QR by scanning it with a separate device to confirm it correctly decodes back to your original private key.
Step 4: Save and Secure the QR Code
Download or print the QR code. Store it in a physically secure location such as a fireproof safe, bank safe deposit box, or alongside your cold storage hardware wallet. Do not save the image on cloud-connected devices, shared drives, or email.
⚠️ Security Warning
A malicious QR code generator can log your private key before encoding it. Only use tools you have verified, and always generate QR codes in an offline environment. If you are unsure about a tool’s trustworthiness, do not use it. The risk of losing all your funds is not worth the convenience.
How to Use a Blockchain Private Key QR Code
Once you have a private key QR code, it can be used in several practical scenarios within the blockchain ecosystem:
1. Importing a Wallet
Most crypto wallet apps (MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Phantom, Coinbase Wallet) include an “Import Wallet” option with a QR scanner. Open your wallet app, select import, choose the scan option, and point your camera at the private key QR code. The wallet will automatically decode the key and prompt you to import the associated account with all its funds and tokens.
2. Authorizing Transactions
In some setups, particularly with decentralized applications (dApps), scanning a private key QR can be used to sign and authorize transactions quickly. This eliminates the tedious process of manually entering the key string and reduces the chance of errors that could cause a transaction to fail or funds to be sent to the wrong address.
3. Offline Backup and Recovery
One of the most common uses is as a physical backup. Printing the QR code and storing it in a secure location provides a reliable way to recover your wallet if your device is lost, damaged, or stolen. Unlike seed phrases that can be misread or misordered, a QR code captures the key precisely with zero room for human interpretation error.
4. Wallet Migration Between Devices
When switching to a new phone or computer, scanning a private key QR code is the fastest way to migrate your wallet. Instead of finding your backed-up seed phrase and typing 12–24 words, you simply scan and import in seconds.
Benefits of Using a Private Key QR Code
Speed & Convenience
Scan and import in seconds instead of manually typing 64+ character strings. Ideal for quick wallet recovery and device migration.
Zero Transcription Errors
Eliminates the risk of mistyping a single character, which could permanently lock you out of your funds or send crypto to the wrong address.
Offline Physical Backup
A printed QR code stored in a safe provides an air-gapped backup that is immune to hacking, malware, and server outages.
Universal Compatibility
QR codes can be read by any smartphone camera, making them compatible across wallet apps, platforms, and operating systems.
Risks and Dangers of Private Key QR Codes
While QR codes offer clear convenience, they also introduce specific security vulnerabilities that every crypto user must understand. Many security experts advise against encoding private keys as QR codes unless absolutely necessary.
| Risk | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Theft & Unauthorized Scanning | Anyone who scans or photographs your QR code gains full wallet access. Stolen funds are unrecoverable. | Store in locked safes, never display publicly |
| Malicious QR Generators | Untrusted tools may log your private key before generating the QR code, then drain your wallet. | Use open-source, offline-only tools |
| QR Code Tampering | A printed QR could be swapped or modified to redirect funds to an attacker’s wallet. | Verify QR contents before every use |
| Phishing Scams | Scammers may impersonate wallet providers and ask you to scan a QR code that steals your key. | Only scan codes you generated yourself |
| Accidental Sharing | Confusing your private key QR with your public address QR and posting it publicly or on social media. | Label QR codes clearly, separate storage |
| Cloud/Digital Exposure | Saving QR images on cloud storage, email, or photo libraries exposes them to breaches. | Keep QR codes strictly offline |
Best Practices for Storing and Using Private Key QR Codes
Following these security best practices can dramatically reduce the risk of loss or theft when working with blockchain private key QR codes:
1. Use Offline, Air-Gapped Generation
Always generate your QR code on a device that is disconnected from the internet. Ideally, use a dedicated computer that has never connected to the internet. After generation, clear the browser cache and any temporary files that might contain your key.
2. Store in Physically Secure Locations
Treat your private key QR code like cash or valuable jewelry. Store printed copies in fireproof safes, bank safe deposit boxes, or other tamper-evident enclosures. Restrict access to only yourself and trusted family members.
3. Use Hardware Wallets for Maximum Security
Cold storage wallets like Ledger and Trezor generate and store private keys internally, completely isolated from the internet. You can optionally create a QR code backup from the hardware wallet’s private key, but the hardware wallet itself provides the strongest day-to-day protection for your assets.
4. Create Multiple Encrypted Backups
Do not rely on a single copy. Create multiple backups of your private key in different formats — printed QR codes, metal-engraved seed phrases, and hardware wallet storage — and keep them in geographically separate secure locations.
5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Add an additional security layer to your wallet and exchange accounts with two-factor authentication. Even if a QR code is compromised, 2FA ensures the attacker cannot complete transactions without the second authentication factor.
6. Never Save QR Codes Digitally on Connected Devices
Avoid saving private key QR images in your phone’s photo gallery, email drafts, cloud storage (Google Drive, iCloud, Dropbox), or screenshots. Any online or cloud-connected location is a potential attack surface. If you must store digitally, use an encrypted USB drive kept in a physical safe.
7. Verify Before Every Scan
Before scanning any QR code into your wallet, verify its source. Only scan QR codes that you personally generated. If a QR code was printed long ago, use a general QR scanner app first to confirm the encoded text matches your known private key before importing it into a wallet app.
Private Key QR Code vs. Other Storage Methods
Understanding how QR code storage compares to other private key management methods helps you choose the right approach for your security needs:
| Method | Security Level | Convenience | Main Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Private Key QR Code (Printed) | High (if stored offline) | High — scan to import | Physical theft, fire/water damage |
| Hardware Wallet (Ledger/Trezor) | Very High | Moderate — requires device | Device loss, firmware vulnerabilities |
| Paper Wallet (Handwritten) | Moderate | Low — manual entry required | Transcription errors, physical damage |
| Software Wallet (Hot Storage) | Low–Moderate | Very High — always accessible | Malware, hacking, device compromise |
| Metal Seed Backup | Very High | Low — manual entry required | Physical theft only |
The most secure strategy combines multiple methods: a hardware wallet for daily use, a printed QR code stored in a fireproof safe for backup, and a metal seed phrase stored in a separate location for disaster recovery. This layered approach ensures no single point of failure can compromise your decentralized assets.
Need a Secure Blockchain Wallet or dApp Built?
From crypto wallet development with multi-signature security to smart contract auditing and enterprise blockchain integration, our team builds solutions that keep your digital assets protected at every layer.
Conclusion
A blockchain private key QR code is a powerful tool that bridges convenience and security in cryptocurrency management. By encoding your private key into a scannable format, it eliminates transcription errors, speeds up wallet imports, and provides a clean offline backup option. However, this same convenience means that a single exposed QR code can lead to complete and irreversible loss of funds.
The key to safe usage is treating your private key QR code with the same level of protection you would give to a physical key to a bank vault. Generate it offline using trusted tools, store it in physically secure and geographically separate locations, never save it on internet-connected devices, and combine it with hardware wallets and two-factor authentication for a layered security approach. With proper handling, a private key QR code is a valuable addition to your crypto security toolkit — without it, you are relying on methods that are slower, more error-prone, and less practical for the fast-moving world of blockchain applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A blockchain private key QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that encodes your cryptocurrency wallet’s private key into a scannable image. When scanned by a compatible wallet application, it allows you to import your wallet, sign transactions, and access your funds without manually entering the long alphanumeric key string.
It can be safe if handled correctly. The QR code must be generated offline using a trusted tool, printed on paper or stored on an encrypted offline device, and kept in a physically secure location like a fireproof safe. It should never be saved on cloud storage, emailed, or stored on internet-connected devices. Many security experts recommend using hardware wallets as the primary storage and a QR code only as a physical backup.
Yes. Anyone who scans or photographs your private key QR code gains full control over your wallet and all the funds within it. Since blockchain transactions are immutable and irreversible, stolen funds cannot be recovered. This is why the QR code must be treated with the same secrecy as the private key itself.
Use a reputable, ideally open-source QR code generator (such as bitaddress.org for Bitcoin). Download the tool for offline use, disconnect your device from the internet, enter your private key, generate the QR code, verify it with a separate scanner, then print or save it to an encrypted offline storage device. Clear all temporary data afterward.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







