Key Takeaways
- Blockchain technology has evolved from cryptocurrency infrastructure into a mainstream enterprise technology adopted across industries.
- Enterprises use blockchain to improve transparency, strengthen data integrity, and reduce reliance on intermediaries.
- Financial services benefit from real-time settlements, lower transaction costs, and improved cross-border payment efficiency.
- Supply chain organizations use blockchain to achieve end-to-end traceability, reduce fraud, and improve product authenticity.
- Healthcare providers apply blockchain to give patients control over their medical data while maintaining privacy and regulatory compliance.
- Governments adopt blockchain to improve public records, enable secure digital identity, and enhance voting system transparency.
- Real estate platforms use blockchain to eliminate title fraud and simplify property ownership verification.
- Smart contracts automate business processes, reduce manual effort, and minimize disputes across multiple sectors.
Blockchain technology has fundamentally evolved beyond its initial association with Bitcoin and cryptocurrency. The revolutionary distributed ledger technology that powered digital currencies has matured into a robust enterprise solution deployed across financial institutions, healthcare systems, supply chains, and government agencies worldwide. According to recent industry reports, blockchain market spending is expected to exceed 19 billion dollars by 2024, with enterprises recognizing the technology’s ability to enhance transparency, reduce costs, and eliminate intermediaries.
While cryptocurrencies remain the most visible application, the real transformation is happening behind the scenes. Major corporations are implementing blockchain to solve critical business problems that traditional databases and systems cannot address efficiently. From JPMorgan Chase reducing international settlement times from days to seconds, to Walmart tracking food products in just two seconds instead of seven days, blockchain is delivering quantifiable value across every major industry sector.
A blockchain is a decentralized, immutable, and distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers simultaneously. Each block contains transaction data, timestamps, and cryptographic hash functions that link sequentially to previous blocks, creating a tamper-proof chain of records.
Top Applications of Blockchain Technology in 2026
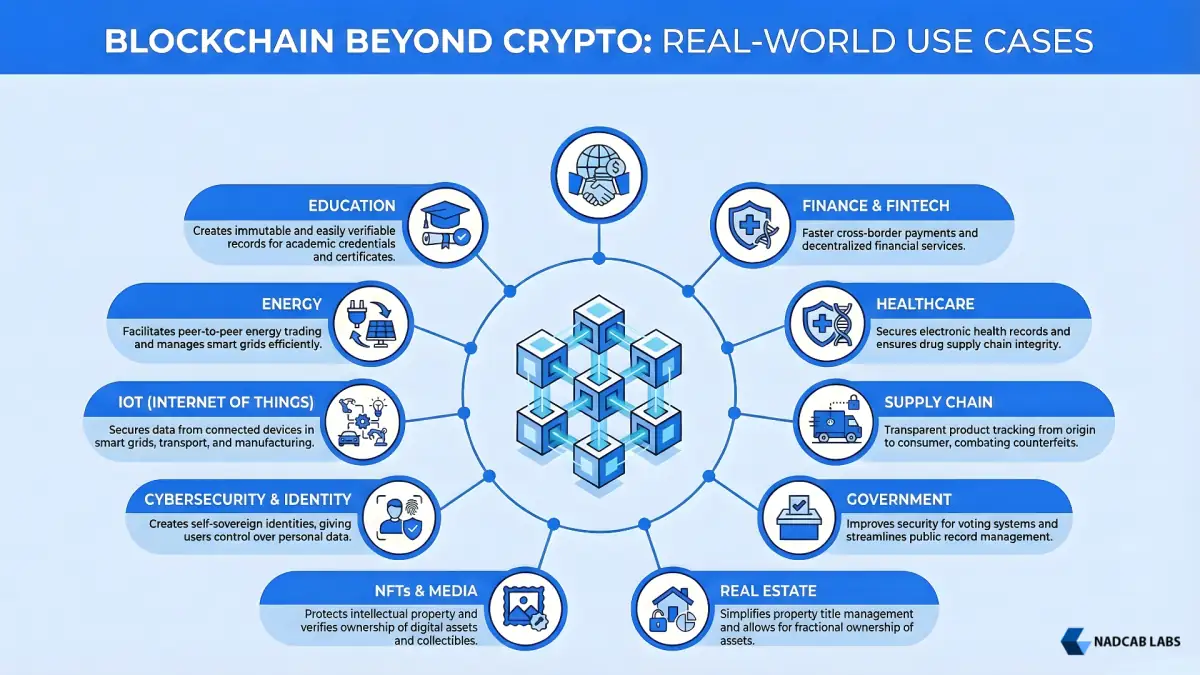
Blockchain technology is no longer limited to cryptocurrency use. Today, enterprises across multiple industries are using blockchain to solve real business challenges, improve data integrity, reduce operational costs, and build trust across digital systems. The following sections present the most impactful blockchain applications, explained with real-world examples, measurable outcomes, and practical insights that demonstrate how blockchain is transforming modern business operations.
| # | Use Case | Company | Industry | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Financial Services & Cross-Border Payments | JPMorgan Chase Onyx | Financial | 2-3 days to seconds settlement |
|
2
|
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Circle & Chainalysis | Financial | Borderless stablecoin transfers |
|
3
|
Supply Chain & Product Traceability | Walmart & IBM Food Trust | Supply Chain | 7 days to 2 seconds tracking |
|
4
|
Pharmaceutical Authentication | MediLedger | Supply Chain | Prevent 1M+ counterfeit deaths |
|
5
|
Logistics & Shipping Transparency | DHL | Supply Chain | Digital ledger for 500K+ companies |
|
6
|
Healthcare Data Management | BurstIQ LifeGraph | Healthcare | Patient-controlled with HIPAA |
|
7
|
Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Medicalchain & Pfizer | Healthcare | Immutable clinical trial data |
|
8
|
Real Estate Title Management | Propy | Real Estate | Fraud-proof property records |
|
9
|
Smart Contracts for Automation | Multiple Industries | Real Estate | Self-executing agreements |
|
10
|
Government Services & Voting | Voatz & Dubai | Government | Secure voting & tamper-proof records |
|
11
|
Self-Sovereign Digital Identity | Civic | Government | Prevent $8.8B identity theft |
|
12
|
Copyright Protection | Kodak KODAKOne & Pixsy | Creative | Tamper-proof authorship proof |
|
13
|
IoT Device Security | Xage Security & Filament | Technology | Multi-factor auth & self-healing |
|
14
|
Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading | Powerledger | Technology | Decentralized renewable market |
|
15
|
NFT & Digital Asset Ownership | OpenSea & Dapper Labs | Creative | $20B+ digital asset trading |
|
16
|
Educational Credentials | MIT | Education | Verifiable digital diplomas |
|
17
|
Insurance Claims | Multiple Insurance Companies | Insurance | Weeks to minutes payouts |
1. Financial Services and Cross-Border Payments
The financial services industry represents one of blockchain’s most significant application areas. Traditional international payment systems involve multiple intermediaries, including correspondent banks, clearinghouses, and regulatory bodies. This complexity creates several critical problems: high transaction fees averaging 5 to 15 percent for international transfers, settlement delays lasting 3 to 5 business days, and limited accessibility for smaller financial institutions.
JPMorgan Chase’s Onyx Network
JPMorgan Chase launched Onyx, a proprietary blockchain network, to revolutionize interbank settlements. The initiative leverages a permissioned blockchain infrastructure to enable direct institution-to-institution transactions. In 2023, JPMorgan partnered with six major Indian banks to pilot real-time settlement of US dollar transactions using Onyx technology. The results were transformative: settlement times reduced from 2 to 3 days to mere seconds, transaction costs decreased substantially, and participating banks gained immediate visibility into payment status and balances.[1]
This use case demonstrates blockchain’s value beyond speculation. JPMorgan’s investment in blockchain infrastructure signals institutional recognition that the technology solves genuine operational challenges that traditional banking infrastructure cannot address economically.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Alternative Banking
Beyond traditional banking improvements, blockchain enables entirely new financial models. Circle’s fintech platform facilitates seamless exchange of traditional and cryptocurrency payments, utilizing stablecoin technology to move capital between digital currencies with minimal friction. Circle’s merchant payment services support payments in Bitcoin, Ethereum, USD Coin, and Euro Coin, enabling truly borderless commerce.
Chainalysis serves the regulatory and compliance angle of blockchain finance, helping financial institutions monitor cryptocurrency exchanges and investigate blockchain activity. Their tools detect fraudulent trading patterns, money laundering schemes, and compliance violations while quantifying NFT security risks.
3. Supply Chain Management and Product Traceability
Supply chain management involves countless stakeholders across multiple geographic regions. Traditional systems struggle with data fragmentation, limited visibility, and vulnerability to fraud. Blockchain creates an immutable, transparent record of every transaction and movement throughout the supply chain, enabling stakeholders to verify product authenticity and track products from origin to consumer.
IBM Food Trust and Walmart
IBM Food Trust, developed in collaboration with Walmart, represents one of blockchain’s most successful enterprise deployments. When a foodborne illness outbreak occurred, Walmart needed to identify the contaminated product source and notify affected customers immediately. Using traditional database systems, this identification process required 7 days of manual investigation.
With IBM Food Trust blockchain, the identification process now takes just 2 seconds. The system records every product’s journey from harvest to consumer, creating an immutable audit trail. When contamination is detected, the system instantly identifies all affected batches and notifies relevant parties. This capability has transformed food safety from a reactive to a proactive process, preventing foodborne illness outbreaks and potentially saving lives.
The economic impact extends beyond food safety. Reducing investigation times from weeks to seconds significantly decreases the financial burden of product recalls, reducing waste and protecting brand reputation. Multiple major retailers now implement blockchain-based traceability systems, recognizing that transparency builds consumer trust and protects corporate assets.
4. Pharmaceutical Supply Chain and Drug Authentication
Counterfeit pharmaceutical products represent a critical global threat. The World Health Organization estimates that counterfeit drugs cause approximately 1 million deaths annually. Blockchain enables end-to-end pharmaceutical traceability from manufacturer to patient.
MediLedger and similar platforms record temperature, location, and handling conditions for every pharmaceutical shipment. IoT sensors integrated with blockchain ensure real-time monitoring of conditions critical to drug efficacy. This capability enables manufacturers and healthcare providers to instantly verify drug authenticity, preventing fake medications from reaching patients.
5. Logistics and Shipping Transparency
With over 500,000 shipping companies operating in the United States alone, according to a joint Accenture and DHL study, data siloing and transparency issues plague the industry. DHL’s blockchain solution maintains a digital ledger of all shipments, recording critical information including origin, destination, handling, temperature conditions, and final delivery status. By recording every product’s journey on an immutable blockchain, DHL enables customers to verify shipment authenticity, reducing losses from counterfeit goods and protecting brand integrity.
6. Healthcare: Secure Data Management and Drug Supply Chain
Healthcare organizations manage patient data across fragmented systems. A single patient may have medical records distributed across multiple hospitals, clinics, and specialist offices, creating coordination challenges and increasing the risk of medical errors. Blockchain enables patients to maintain control of their medical data while granting healthcare providers instant, secure access when needed.
BurstIQ’s LifeGraph Platform
BurstIQ combines blockchain with artificial intelligence to create LifeGraph, a comprehensive data management platform for healthcare and life science organizations. LifeGraph securely integrates sensitive health data while ensuring HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance. The platform enables researchers to access valuable health insights without compromising individual patient privacy. Importantly, patients retain ownership of their data and can grant or revoke access at any time.
This approach addresses a critical healthcare challenge: data fragmentation leads to inefficient care delivery and increased costs. By maintaining a comprehensive, patient-controlled health record on blockchain, BurstIQ enables coordinated care across multiple providers while maintaining regulatory compliance and respecting patient privacy preferences.
Explore Healthcare with Blockchain Technology
Blockchain in healthcare solves fragmented data management, ensures drug authenticity, and prevents counterfeit medications. Enable patient-controlled records, HIPAA-compliant data sharing, and real-time drug tracking—all on an immutable, transparent system.
Counterfeit Drug Prevention
Counterfeit pharmaceutical products represent a critical global threat. The World Health Organization estimates that counterfeit drugs cause approximately 1 million deaths annually, making drug authentication as critical as diagnosis. Blockchain enables end-to-end pharmaceutical traceability from manufacturer to patient.
Blockchain-based platforms record temperature, location, and handling conditions for every pharmaceutical shipment. IoT sensors integrated with blockchain ensure real-time monitoring of conditions critical to drug efficacy. This capability enables manufacturers and healthcare providers to instantly verify drug authenticity, preventing fake medications from reaching patients. Companies like MediLedger actively combat counterfeit drugs through blockchain transparency in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
7. Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Clinical Trials
Medicalchain enables patients to maintain ownership of their medical data while granting healthcare providers secure access when needed. This ensures data integrity, improves care coordination, and reduces the risk of medical errors.
Pfizer and other pharmaceutical giants have explored blockchain to streamline clinical trials, ensuring that data remains accurate and accessible. Blockchain provides an immutable record of trial data, including participant consent, research outcomes, and audit trails, reducing the risk of data manipulation.
8. Real Estate Title Management and Property Ownership
Property ownership records in many jurisdictions remain vulnerable to fraud and tampering. Propy pioneered blockchain-based property title management systems. By recording property ownership on a distributed ledger, Propy eliminates traditional title fraud risks while accelerating transactions. Blockchain also enables fractional property ownership, allowing investors to purchase portions of real estate assets rather than requiring complete ownership.
9. Smart Contracts for Automated Agreements
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on a blockchain that automatically enforce terms once conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and adds levels of accountability.
Real estate transactions often involve lengthy processes from contract negotiations to escrow services. Smart contracts on blockchain automate these steps, ensuring transactions are executed once predefined conditions are met. This reduces delays, eliminates the need for intermediaries, and minimizes associated costs.
Insurance companies use smart contracts to validate claims and keep records of all people buying insurance and paying premiums on time. Some applications allow customers to pay for car insurance only when driving, reducing costs and creating fairer pricing models.
10. Government Services: Democratic Voting and Public Records
Governments worldwide face challenges in ensuring election integrity while maintaining voter privacy and accessibility. Blockchain-based voting systems provide transparency that voters can independently verify while maintaining ballot secrecy. Public records stored on blockchain become tamper-proof, reducing corruption and bureaucratic inefficiency.
Voatz Mobile Voting Platform
West Virginia became one of the first US states to utilize Voatz, a blockchain-based mobile voting platform. Voatz enables eligible military personnel and citizens traveling abroad to vote securely from anywhere in the world. The encrypted biometric security system prevents unauthorized access, while the blockchain ensures no tampering occurs with recorded votes. This capability dramatically increases accessibility for citizens unable to vote in person, while maintaining election security.
Other blockchain voting initiatives include Follow My Vote, which implements end-to-end voting security using blockchain technology, and Agora, a Swiss company developing open-source blockchain voting systems. These platforms demonstrate how blockchain enables democratic participation while maintaining security that surpasses traditional voting infrastructure.
Dubai’s Public Records Integration
Dubai leads global digital transformation initiatives by integrating blockchain into public services infrastructure. Birth certificates, licenses, land registries, and government records stored on blockchain become tamper-proof and instantly accessible. This transformation reduces bureaucratic inefficiencies, accelerates service delivery, and builds citizen trust through unprecedented transparency.
11. Self-Sovereign Digital Identity
Identity theft and fraud impose enormous societal costs. AARP (American Association of Retired Persons) data indicates that Americans lost over 8.8 billion dollars to identity theft and fraud in 2022 alone. Blockchain enables self-sovereign identity, where individuals control their digital credentials without relying on vulnerable centralized authorities.
Civic and similar platforms allow users to verify their identities securely, sharing only information necessary for specific transactions. This approach minimizes data exposure compared to traditional systems, where users provide complete identity documents to numerous organizations. Financial institutions leverage blockchain for Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance, reducing onboarding times while preventing fraud.
Blockchain-based identity verification is especially valuable for underbanked populations lacking traditional documentation. Individuals can establish verifiable identity credentials on blockchain, enabling financial inclusion and access to services previously restricted to those with traditional identity documents.
12. Copyright Protection and Digital Rights Management
Digital piracy costs content creators billions annually. Kodak’s KODAKOne platform allows photographers to register their work on blockchain, establishing tamper-proof ownership that holds up in legal proceedings. Pixsy implements similar blockchain-based copyright registration for creatives, providing proof of authorship that protects against unauthorized use.
Smart contracts automate royalty distribution, ensuring artists receive fair compensation without payment delays. Streaming platforms can program contracts that automatically distribute subscription fees to artists proportionally based on plays. This eliminates intermediaries that traditionally skim substantial percentages from artist earnings.
13. IoT Device Security and Network Management
IoT devices create significant cybersecurity challenges. As billions of connected devices generate data, securing these networks and ensuring device authenticity becomes critical. Xage Security operates as the world’s first blockchain-enabled cybersecurity platform for IoT companies, managing multiple devices simultaneously using multi-factor authentication and self-healing services that automatically respond to security breaches. Companies like Microsoft, Dell, and the US Air Force utilize Xage to secure critical IoT infrastructure.
Filament, a Nevada-based company, creates IoT microchip hardware and software that lets connected devices run on blockchain technology. The encrypted and secured ledger data distributes information to other blockchain-connected devices and allows monetization of machines based on usage of time stamps.
14. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading and Smart Grids
The energy sector is undergoing a significant transformation as blockchain technology introduces new ways to decentralize energy markets. Powerledger enables peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to buy and sell surplus energy directly within their communities. This approach reduces reliance on traditional utility companies and fosters the adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Smart grids integrated with blockchain enable efficient energy distribution. Blockchain ensures the secure exchange of data between connected devices, enabling real-time tracking of energy consumption and production. This data-driven approach helps utilities optimize grid performance, reduce waste, and enhance resilience against disruptions.
15. Non-Fungible Tokens and Digital Asset Ownership
Non-fungible tokens represent blockchain’s most visible application beyond cryptocurrency. NFTs enable creators to establish unique, verifiable ownership of digital assets, including art, music, videos, gaming items, and collectibles.
Dapper Labs partnered with the NBA to create NBA Top Shot, an NFT marketplace where fans own authenticated digital moments from their favorite players. Users can own verified collectible moments from LeBron James dunks to Anthony Davis blocks, with ownership recorded immutably on blockchain.
OpenSea operates the largest NFT marketplace globally, with trading volume exceeding 20 billion dollars, enabling creators worldwide to monetize digital assets directly.
16. Educational Credentials and Academic Records
Educational institutions implement blockchain for credentialing, creating verifiable student achievement records that can be universally recognized. MIT pioneered blockchain-based digital diplomas, allowing graduates to hold cryptographic proof of their credentials that educational institutions and employers can instantly verify.
This capability eliminates diploma fraud and streamlines hiring processes. Employers can verify academic credentials directly on blockchain without contacting educational institutions, reducing hiring times and preventing fraudulent credential claims.
17. Insurance Claims Processing and Fraud Prevention
Insurance companies use blockchain to streamline claims processing and prevent fraud. Smart contracts automatically validate insurance claims and execute payouts once predefined conditions are met. This reduces claims processing times from weeks to minutes and prevents fraudulent claims by creating immutable records of incidents.
Parametric insurance leverages blockchain and IoT to automatically trigger payouts when predefined conditions are met. For example, flight delay insurance automatically triggers when a flight is delayed beyond a specified time, with blockchain recording the transaction immutably.
Additional Emerging Applications
Automotive and Odometer Fraud Prevention: Bosch’s IoT lab developed blockchain-enabled odometers preventing mileage tampering. Smart odometers connected to the internet frequently write car mileage to the blockchain, creating secure digital certificates that cannot be falsified.
Legal Document Authentication: Online platforms allow registration of documents on the Bitcoin or Ethereum blockchain. Once a document is added, creators can prove they created it at a particular point in time, similar to a notary, but with cryptographic proof.
Gaming and In-Game Asset Ownership: Gaming companies tokenize in-game assets on blockchain, enabling true ownership and cross-game asset portability. Players can buy, sell, and trade in-game assets with permanent ownership records.
Conclusion: Enterprise Blockchain is Mainstream
Blockchain has matured from speculative technology to a practical enterprise solution. Fortune 500 companies, including JPMorgan Chase, Walmart, IBM, Google, DHL, Microsoft, Dell, and the US Air Force, are deploying blockchain to solve real business problems, achieve operational efficiency, and gain competitive advantages. The 18+ use cases presented demonstrate that blockchain’s value extends far beyond cryptocurrency speculation.
Organizations evaluating blockchain implementation should focus on challenges that require transparency, eliminate intermediaries, or require immutable record-keeping. Financial institutions seeking to accelerate settlements, supply chain companies needing product traceability, healthcare organizations managing fragmented data, governments improving citizen services, and creative professionals protecting intellectual property all benefit from strategic blockchain deployment.
The technology continues evolving rapidly. Layer 2 scaling solutions are addressing throughput limitations that plagued early blockchain implementations. Integration with artificial intelligence creates unprecedented capabilities for decision-making based on immutable data. Regulatory frameworks like the EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets regulation provide clarity for institutional adoption.
Organizations that embrace blockchain solutions today position themselves as industry leaders tomorrow. The technology’s trajectory is clear: from experimental application to foundational infrastructure supporting business operations across industries. Now is the optimal time for enterprises to explore blockchain’s potential and harness its transformative capabilities to gain sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly digital and decentralized global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Blockchain applications extend far beyond digital currencies. The technology solves problems in financial services, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, government, media, IoT, and energy industries. Any sector requiring transparent, immutable record-keeping or eliminating intermediaries benefits from blockchain deployment.
Blockchain evolution progresses through four stages:
-Blockchain 1.0 introduced cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, demonstrating peer-to-peer payments without intermediaries.
-Blockchain 2.0 introduced smart contracts and Ethereum, enabling programmable agreements.
-Blockchain 3.0 focused on scalability and interoperability, addressing throughput limitations.
-Blockchain 4.0 represents enterprise integration and mainstream adoption, with institutions deploying blockchain for operational efficiency.
Bitcoin, introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, was the first blockchain application. Bitcoin demonstrated how blockchain could enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, establishing the foundational use case that inspired all subsequent blockchain applications and proving the technology’s viability.
Financial services, supply chain logistics, healthcare, real estate, government, media, and energy sectors demonstrate the highest adoption rates. Industries requiring transparency, security, decentralization, or the elimination of intermediaries benefit most from blockchain implementation.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.