Blockchain has come a long way since Bitcoin first introduced the concept of a trustless, peer-to-peer digital ledger. Over the past decade, the industry has gone through several upgrades, with new layers being added to the original architecture to solve different problems. Layer 1 networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum gave us the foundation. Layer 2 solutions helped speed things up and cut costs. And now, Layer 3 blockchains are stepping in to bring the whole thing closer to everyday usability. If you have been following blockchain development but feel confused about what Layer 3 actually does and why it matters, this guide breaks it all down in plain terms.
Key Takeaways
- Layer 3 blockchains sit on top of Layer 1 and Layer 2, focusing on application-level functionality like privacy, cross-chain communication, and better user interfaces.
- They do not replace Layer 1 or Layer 2 but rely on them for security and scalability while adding specialized features for decentralized applications.
- Real-world use cases include decentralized finance, gaming, supply chain tracking, and identity verification through advanced cryptographic tools like zero-knowledge proofs.
- Adoption challenges remain, including integration complexity, security risks from cross-chain features, and the need for broader developer education.
- Companies like Nadcab Labs with 8+ years of blockchain development experience are building Layer 3 solutions that push the boundaries of what decentralized apps can do.
- Layer 3 is expected to become a critical part of the decentralized web as blockchain technology matures over the next few years.
What Exactly Are Layer 3 Blockchains?
Think of blockchain architecture like a building. The ground floor is Layer 1, where the core structure and security sit. Layer 2 is like an elevator system that helps people move faster through the building. Layer 3, then, is the individual rooms, offices, and shops inside, where the actual work and interaction happen.
In more technical terms, Layer 3 is the application layer of the blockchain stack. It is built on top of existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks and focuses on things that end users actually care about: smoother app interfaces, privacy controls, the ability to move data and assets between different blockchains, and support for complex decentralized applications (often called DApps).
Layer 3 does not replace the layers below it. Instead, it depends on them. Layer 1 provides the security backbone, Layer 2 handles the heavy lifting of transaction processing, and Layer 3 makes the whole ecosystem usable for real people and real businesses. This is why some developers and analysts refer to Layer 3 as the “user-facing” layer of blockchain.
At Nadcab Labs, a blockchain based company with over eight years of hands-on experience, we have seen this evolution firsthand. From building early smart contracts on Ethereum to designing multi-layered blockchain solutions for enterprise clients, the shift toward Layer 3 represents a natural progression in how we build decentralized systems. It is the layer where technical capability meets practical utility.
Also Read: Enterprise Blockchain Applications Guide
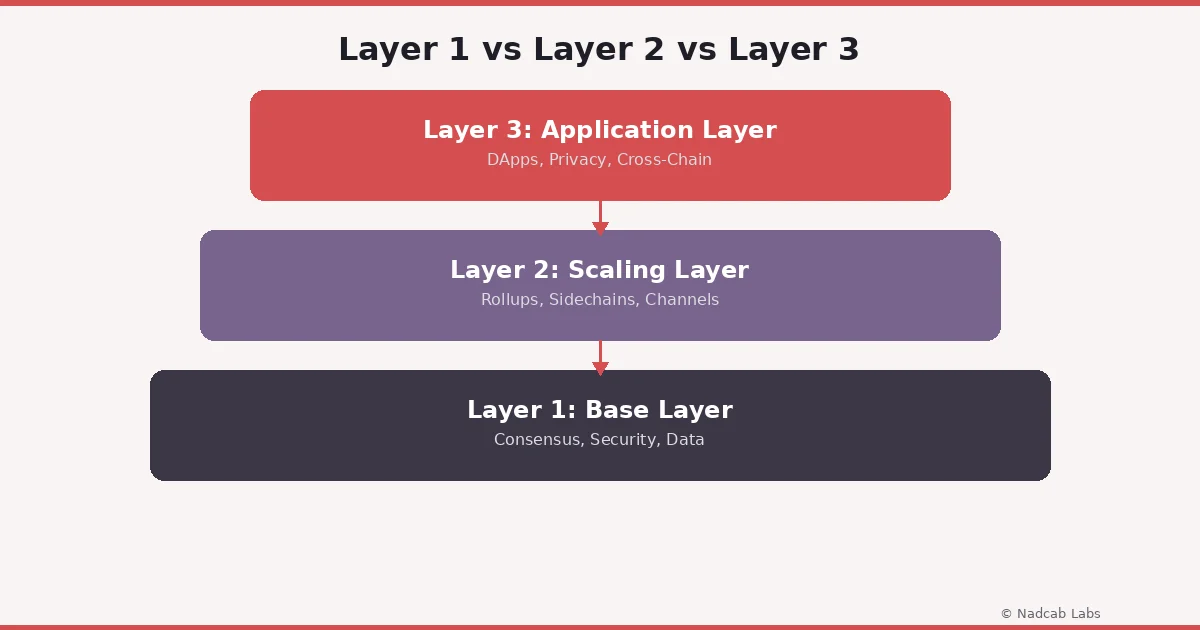
Understanding the Blockchain Layer Model: A Side-by-Side Look
Before we go deeper into Layer 3, it helps to see how all three layers compare. Each serves a distinct purpose, and understanding the differences makes it easier to see where Layer 3 fits in. The table below highlights what each layer handles, examples you might already know, and the kind of problems each one solves.
| Feature | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Consensus and security | Scalability and speed | Applications and user experience |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana | Optimistic Rollups, ZK-Rollups, Lightning Network | DApp protocols, cross-chain bridges, privacy layers |
| Transaction Speed | Moderate to slow | Fast | Fast (inherits from Layer 2) |
| Focus Area | Data integrity and decentralization | Reducing congestion and costs | Interoperability, privacy, and DApp support |
| User Interaction | Indirect (through wallets, nodes) | Moderate | Direct (apps, interfaces, tools) |
| Depends On | None (base layer) | Layer 1 | Layer 1 and Layer 2 |
As you can see, each layer builds on the one below it. Layer 3 is not trying to compete with Layer 1 or Layer 2. It is taking what they offer and turning it into something people and businesses can actually use day-to-day. This layered approach is sometimes compared to how the internet works, where lower layers handle data routing and upper layers handle web pages and apps. The concept of protocol stacking is well established in networking and applies naturally to blockchain as well (you can read more about this layered model on Wikipedia’s blockchain entry).
How Layer 1 Blockchains Set the Stage
You cannot talk about Layer 3 without first understanding what Layer 1 does and why it is not enough on its own. Layer 1 blockchains are the foundation of the entire ecosystem. Bitcoin, launched in 2009, was the first and remains the most well-known. Ethereum followed in 2015 and brought smart contracts into the picture, allowing developers to build programmable applications directly on the blockchain.
These networks are responsible for the most critical functions: validating transactions, reaching consensus across distributed nodes, and maintaining an immutable record of all activity. The security of the entire blockchain ecosystem depends on how well Layer 1 does its job.
But there is a problem. Layer 1 blockchains are often slow and expensive when demand spikes. Ethereum, for example, has historically struggled with high gas fees during periods of heavy use. Bitcoin can only process about seven transactions per second, compared to traditional payment networks that handle thousands. These limitations are what drive the need for additional layers. The way node synchronization works in blockchain also plays a role here, as keeping all nodes in agreement is computationally intensive and creates inherent throughput limits.
Our team at Nadcab Labs has worked extensively on Layer 1 infrastructure projects, including custom consensus mechanisms and node optimization. From this experience, we know that Layer 1 was never designed to do everything. It was designed to be secure and decentralized. Speed and user experience were always going to require additional layers on top.
The Role of Layer 2 in Blockchain Scaling
Layer 2 solutions were created to solve the bottleneck problem. Instead of processing every transaction on the main blockchain, Layer 2 takes a portion of the work off-chain, processes it separately, and then posts the results back to Layer 1 for final settlement. This reduces the load on the main network and makes transactions faster and cheaper.
There are several well-known approaches to Layer 2 scaling. Optimistic Rollups bundle many transactions into one and assume they are valid unless challenged. ZK-Rollups use a cryptographic technique called zero-knowledge proofs to verify transactions without revealing all the details. State channels allow two parties to transact privately off-chain and only settle the final result on-chain. And then there are sidechains, which are separate blockchains connected to the main chain through a two-way peg.
Layer 2 has been a game-changer for Ethereum in particular. Networks like Arbitrum and Optimism have made it possible to use Ethereum-based DApps without paying exorbitant gas fees. The Lightning Network has done something similar for Bitcoin, enabling near-instant micropayments.
However, Layer 2 is still primarily focused on speed and cost. It does not directly address things like cross-chain communication, privacy at the application level, or building user-friendly interfaces. That is where Layer 3 comes in. If you are interested in other Layer 2 concepts, take a look at how Plasma works in blockchain for another approach to off-chain scaling.
How Layer 3 Blockchains Actually Work
Now let us get into the specifics. Layer 3 operates on top of Layer 2 (or in some cases directly on Layer 1, depending on the architecture). Its primary job is to provide the tools and protocols that allow complex applications to run smoothly in a decentralized environment.
Here is a practical way to think about it. Suppose you want to build a decentralized trading platform that lets users swap tokens between Ethereum, Polygon, and Avalanche, with built-in privacy features and a clean, app-like interface. Layer 1 gives you the security backbone. Layer 2 gives you the speed and low costs. Layer 3 gives you the cross-chain bridge, the privacy toolkit, and the front-end application framework that ties everything together.
Some of the key technical features that Layer 3 brings to the table include zero-knowledge proofs for transaction privacy, advanced smart contract logic for complex DApps, cross-chain messaging protocols, and decentralized identity solutions. These are not simple bolt-ons. They require their own layer of protocol design and optimization, which is why Layer 3 exists as a distinct part of the stack.
The relationship between these layers is important to understand. Layer 3 does not bypass or override Layer 1 or Layer 2. It communicates with them through standardized interfaces. When a Layer 3 application needs to finalize a transaction, that transaction still gets settled on Layer 1 through Layer 2. The layers work together, not in isolation. This concept is also linked to Layer 0 blockchain basics, which defines the foundational communication protocols that allow all these layers to interact.
Real-World Applications Where Layer 3 Makes a Difference
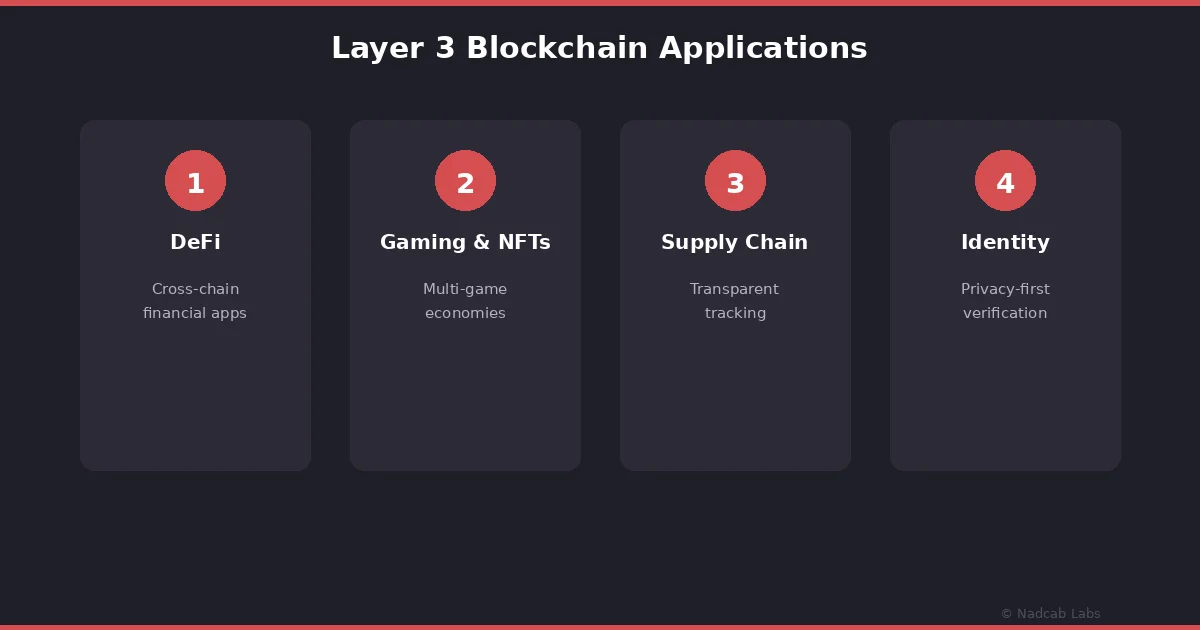
The practical applications of Layer 3 span several industries, and some of them are already being built and tested. Let us walk through the most significant ones.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is probably the sector where Layer 3 will have the most immediate impact. Current DeFi platforms often operate on a single blockchain, which limits what users can do. If your assets are on Ethereum but the best lending rates are on a Solana-based protocol, moving those assets requires multiple steps, each with its own fees and risks.
Layer 3 can solve this by enabling seamless cross-chain transactions. Imagine swapping tokens between different blockchains in a single action, without needing to manually bridge assets or worry about compatibility issues. Layer 3 protocols can also add privacy to financial transactions, letting users trade or lend without exposing their full transaction history to the public.
At Nadcab Labs, we have worked with DeFi projects that needed exactly this kind of cross-chain functionality. Building these solutions from scratch taught us that the application layer is where users either embrace blockchain or walk away frustrated. A well-designed Layer 3 solution can make DeFi feel as smooth as using a regular banking app. For related work in this space, our experience with algorithmic stablecoin contracts has given us deep insight into how financial logic works at the protocol level.
Gaming and NFTs
Blockchain gaming is growing, but it still has major limitations. Most games operate on their own blockchain or platform, meaning assets earned in one game cannot be used in another. Players are stuck within walled gardens, which is the opposite of what blockchain promises.
Layer 3 can change this by creating a shared application layer where game assets, characters, and currencies can move freely between different platforms. A sword earned in one game could be sold in another game’s marketplace or used as collateral in a DeFi protocol. This kind of interoperability requires exactly the type of cross-chain communication that Layer 3 is designed to handle.
NFTs also benefit. Layer 3 can enable richer metadata, dynamic ownership rules, and privacy features that make digital collectibles more versatile. If you want to learn how related technologies support this, check out how custom metaverse projects are developed with blockchain integration.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chains are complex, involving multiple parties, geographies, and regulatory requirements. Blockchain has already shown its value in improving supply chain transparency, but most existing solutions are limited to a single network. When different participants use different blockchains, data silos form, and the supposed transparency breaks down.
Layer 3 addresses this by integrating data from multiple blockchain networks into a unified tracking system. A pharmaceutical company could track a drug’s journey from manufacturer to pharmacy across several different blockchain networks, all through a single Layer 3 application. This kind of cross-chain data aggregation is one of the most practical use cases for Layer 3 today.
Identity and Privacy
Digital identity is one of the most personal and sensitive areas of technology. Layer 3 can enable self-sovereign identity systems where users control their own data and share only what is needed for a given transaction. Using zero-knowledge proofs, a user could prove they are over 18 without revealing their date of birth, or verify their credit score without showing their full financial history.
This has significant implications for industries like healthcare, finance, and government services, where privacy is not just preferred but legally required. Layer 3 privacy solutions can help organizations comply with data protection regulations while still benefiting from blockchain’s transparency and auditability.
Build Your Layer 3 Blockchain Solution
Ready to take your decentralized application to the next level? Nadcab Labs brings 8+ years of blockchain expertise to help you design, develop, and deploy Layer 3 solutions that deliver real results.
The Layer 3 Blockchain Development Lifecycle
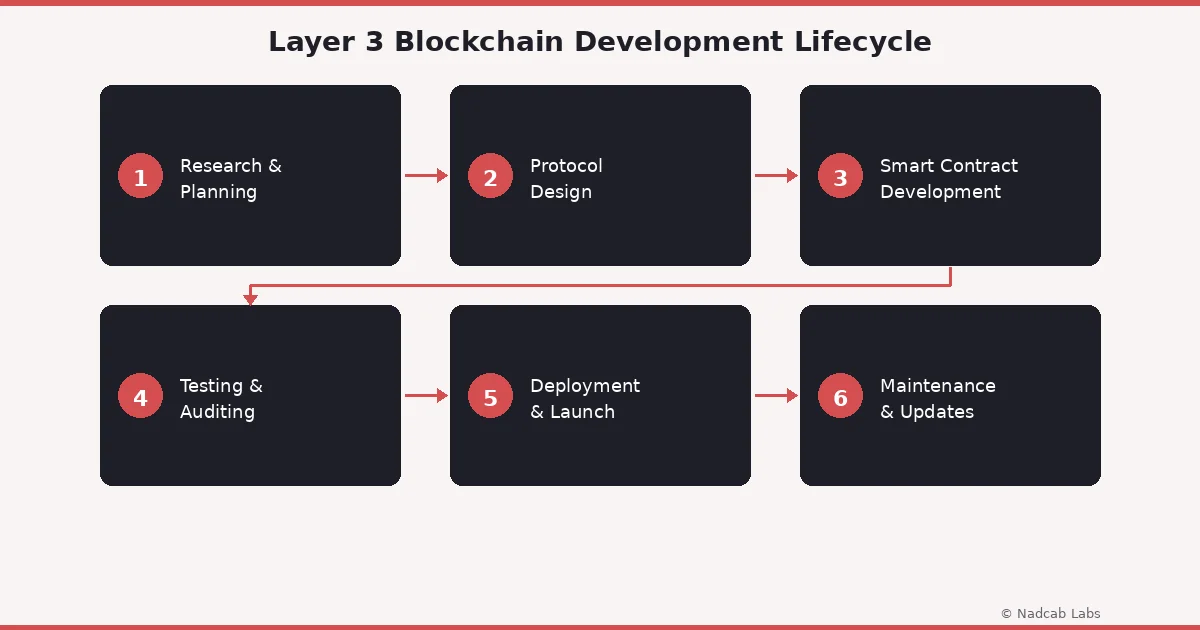
Building a Layer 3 solution is not a weekend project. It follows a structured development lifecycle that, based on our experience at Nadcab Labs, typically includes six phases.
The process starts with research and planning. Before writing a single line of code, the team needs to understand what the application requires, which blockchains it needs to interact with, what privacy or compliance standards apply, and what the end user expects. This phase often involves stakeholder interviews, competitive analysis, and technical feasibility studies.
Next comes protocol design. This is where the architecture of the Layer 3 solution is mapped out: how it communicates with Layer 1 and Layer 2, what APIs it exposes, and how cross-chain messaging will work. Decisions made here affect everything downstream, so getting it right is critical.
Smart contract development follows. The core logic of the Layer 3 application is encoded in smart contracts that handle everything from token transfers to identity verification. These contracts need to be efficient, gas-optimized, and secure. Our team often builds with modularity in mind so that contracts can be upgraded without disrupting the broader system.
Testing and auditing is the fourth phase, and arguably the most important. Every smart contract goes through multiple rounds of testing, including unit tests, integration tests, and formal verification where applicable. Independent security audits are non-negotiable, especially for applications handling financial assets or personal data.
Deployment and launch is where the solution goes live. This involves deploying contracts to the appropriate networks, setting up infrastructure like nodes and indexers, and releasing the user-facing application. Phased rollouts are common, starting with a testnet deployment before moving to mainnet.
Finally, maintenance and updates ensure the solution stays current. Blockchain networks evolve, new vulnerabilities are discovered, and user needs change. Ongoing monitoring, bug fixes, and feature updates are essential for long-term success. Understanding how orphan blocks form in blockchain is one of many technical details that developers need to stay on top of during this phase.
Technical Foundations That Power Layer 3
Layer 3 relies on several core technologies to deliver its functionality. Each of these has been developed and refined over years, and they work together within the Layer 3 framework to enable the applications we discussed earlier.
| Technology | What It Does | Layer 3 Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) | Allows one party to prove something is true without revealing the underlying data | Privacy-preserving transactions, identity verification |
| Cross-Chain Bridges | Connects separate blockchain networks to allow asset and data transfers | Multi-chain DeFi, gaming asset portability |
| Advanced Smart Contracts | Programmable logic that executes automatically based on predefined conditions | Complex DApp logic, automated compliance checks |
| Decentralized Identity (DID) | Gives users control over their digital identity without relying on centralized authorities | KYC without data exposure, self-sovereign identity |
| Interoperability Protocols | Standard communication methods that let different blockchains exchange information | Unified supply chain tracking, multi-network DApps |
Zero-knowledge proofs deserve special attention here because they are central to many Layer 3 applications. A ZKP allows someone to prove a statement is true without revealing any information beyond the fact that the statement is true. For a more detailed explanation, the Wikipedia article on zero-knowledge proofs is a good starting point. In blockchain terms, ZKPs enable private transactions where the network can verify that a transaction is valid without seeing the sender, receiver, or amount.
Consensus mechanisms also play a role in how Layer 3 solutions validate certain actions. For networks that use delegation-based consensus, understanding DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) in blockchain provides useful context. Similarly, alternative consensus approaches like Proof of Elapsed Time for permissioned blockchains show how different validation methods suit different use cases.
Why Layer 3 Matters for the Future of Decentralization
Decentralization is not just a technical concept; it is a philosophical commitment to removing single points of control and giving individuals more autonomy over their digital lives. Layer 3 is important because it is the layer that brings this commitment to everyday users.
Without Layer 3, blockchain remains largely a tool for developers and early adopters. The average person does not interact with consensus algorithms or rollup batches. They interact with apps. And if those apps are clunky, confusing, or limited to a single network, most people will stick with the centralized alternatives they already know.
Layer 3 changes this equation by making decentralized applications competitive with their centralized counterparts in terms of usability, speed, and features. It is the bridge between the technical world of blockchain protocols and the practical world of people who just want things to work.
This is a message we have been communicating to clients at Nadcab Labs for years. The technology needs to disappear into the background. Users should not need to understand gas fees, block times, or chain IDs. They should just use the app and get the benefits of decentralization, including data ownership, censorship resistance, and reduced dependence on intermediaries, without having to think about the machinery underneath.
Challenges Facing Layer 3 Blockchain Adoption
No technology is without its hurdles, and Layer 3 is no exception. There are several significant challenges that the industry needs to address before Layer 3 can reach its full potential.
The biggest challenge is adoption and integration. Most existing blockchain applications were built for Layer 1 or Layer 2. Migrating them to a Layer 3 framework or building bridges between the layers requires significant development effort. Many teams lack the expertise or resources to make this transition, which slows down the overall adoption curve.
Scalability, somewhat ironically, is still a concern. While Layer 3 inherits the scalability improvements of Layer 2, the added complexity of cross-chain operations and privacy computations can introduce new bottlenecks. Zero-knowledge proof generation, for example, is computationally intensive and can slow things down if not optimized properly. Approaches like SegWit upgrades on Bitcoin have shown how targeted protocol changes can improve performance, but similar innovation is needed at the Layer 3 level.
Security is another major concern. Cross-chain bridges, which are central to Layer 3 functionality, have been some of the most exploited components in blockchain history. Billions of dollars have been lost through bridge hacks. Building secure cross-chain communication is one of the hardest problems in blockchain engineering, and Layer 3 solutions need to solve it convincingly before they can earn trust. The TON blockchain outage and recovery is a reminder of how even established networks can face unexpected disruptions.
Regulatory uncertainty adds another layer of complexity. Privacy features, while valuable for users, can raise concerns with regulators who are focused on anti-money laundering and compliance. Layer 3 solutions need to find a balance between offering meaningful privacy and maintaining enough transparency to satisfy regulatory requirements.
How Nadcab Labs Approaches Layer 3 Development
With more than eight years of blockchain development experience, Nadcab Labs has built solutions across every layer of the blockchain stack. We have designed custom Layer 1 protocols, built Layer 2 scaling solutions, and developed application-layer tools that serve clients in finance, gaming, healthcare, and logistics.
What sets our approach apart is that we do not treat Layer 3 as a standalone product. We see it as part of an integrated system. Every Layer 3 project we work on starts with a thorough analysis of the underlying Layer 1 and Layer 2 infrastructure. We identify where the gaps are, what the application needs from each layer, and how to design the interfaces between them for maximum reliability and performance.
Our team includes specialists in smart contract development, zero-knowledge cryptography, cross-chain bridge design, and front-end application development. This breadth of expertise allows us to handle the full lifecycle of a Layer 3 project, from initial research to post-launch maintenance. We have also invested in understanding adjacent technologies like cloud consulting services that support scalable blockchain infrastructure deployment.
We believe that the blockchain industry is at a turning point. The infrastructure layers are mature enough to support real applications, and the demand from enterprises and consumers is growing. Layer 3 is where the rubber meets the road, and we are committed to building solutions that deliver on the promise of decentralization.
What the Future Holds for Layer 3 Blockchains
Looking ahead, Layer 3 is likely to become the primary interface between blockchain technology and the broader world. Several trends support this prediction.
First, interoperability is becoming non-negotiable. The blockchain space has hundreds of active networks, and users increasingly expect their assets and data to move freely between them. Layer 3 is the natural home for the protocols that make this possible.
Second, privacy is becoming a mainstream concern, not just a niche feature. As more personal and financial data moves to blockchain, users and regulators alike are demanding stronger privacy tools. Layer 3 is where these tools live.
Third, enterprise adoption is accelerating. Companies that were once skeptical of blockchain are now actively exploring it for supply chain management, identity verification, and financial operations. These enterprise use cases require the kind of application-level sophistication that Layer 3 provides.
| Trend | Impact on Layer 3 | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-chain interoperability | Drives demand for cross-chain protocols at the application layer | Already underway |
| Privacy regulation (GDPR, etc.) | Increases need for privacy-preserving DApp features | Ongoing, accelerating |
| Enterprise blockchain adoption | Creates market for enterprise-grade Layer 3 solutions | 2-5 years for significant scale |
| Mainstream DApp usage | Requires user-friendly Layer 3 interfaces | 3-7 years for mass adoption |
| ZKP technology maturation | Makes Layer 3 privacy features faster and more practical | Active R&D, steady progress |
The blockchain industry has often been criticized for being too focused on infrastructure and not enough on applications. Layer 3 is the industry’s answer to that criticism. It is where blockchain stops being a technology and starts being a tool that solves real problems for real people.
Frequently Asked Questions
A Layer 3 blockchain is the application layer built on top of Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks. While Layer 1 handles core security and consensus and Layer 2 focuses on scaling transactions, Layer 3 enables decentralized applications with advanced features like privacy, cross-chain communication, and better user interfaces. It does not replace the lower layers but adds usability and functionality for real-world applications and end users.
Layer 2 primarily solves speed and cost issues by processing transactions off-chain. However, it does not address application-level needs like cross-chain interoperability, transaction privacy, or user-friendly interfaces. Layer 3 fills these gaps by providing the protocols and tools needed to build sophisticated decentralized applications that can work across multiple blockchains and offer a smooth experience for everyday users.
Zero-knowledge proofs are a cryptographic method that lets one party prove a statement is true to another party without revealing any underlying data. In Layer 3 blockchains, ZKPs enable private transactions and identity verification. For example, a user can prove they have sufficient funds for a trade without disclosing their total balance. This technology is critical for building privacy-focused DApps on Layer 3 networks.
Several industries stand to gain from Layer 3 adoption. Decentralized finance benefits from cross-chain transactions and privacy features. Gaming and NFTs gain asset portability across platforms. Supply chain management gets unified tracking across multiple blockchain networks. Healthcare and government services can use Layer 3 identity solutions for secure, privacy-compliant verification processes that protect user data.
The primary challenges include integration difficulty with existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 systems, security risks from cross-chain bridges that have historically been targeted by hackers, computational overhead from privacy features like zero-knowledge proofs, and regulatory uncertainty around privacy-preserving technologies. Overcoming these challenges requires continued development, independent audits, and collaboration between blockchain teams and regulators.
Nadcab Labs brings over eight years of blockchain development experience across every layer of the stack. Our team handles the complete Layer 3 development lifecycle, including protocol design, smart contract development, cross-chain bridge implementation, ZKP integration, security auditing, and post-launch maintenance. We work with clients in DeFi, gaming, supply chain, and enterprise sectors to build production-ready Layer 3 solutions.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.