Key Takeaways
- Eco-friendly NFTs use energy-efficient blockchains like Proof-of-Stake to cut carbon emissions by up to 99% compared to traditional Proof-of-Work systems.
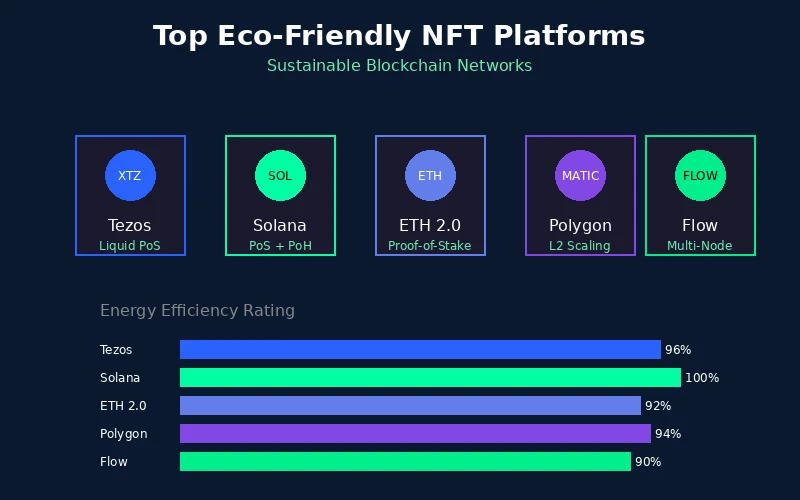
- Popular green NFT platforms include Tezos, Solana, Flow, Polygon, and Ethereum 2.0, each offering different benefits for sustainable digital asset creation.
- Carbon offsetting programs allow creators to neutralize their environmental impact through investments in renewable energy and reforestation projects.
- The shift toward sustainable NFTs is driven by consumer demand, with eco-conscious buyers actively seeking green alternatives in the digital collectibles market.
- Creating eco-friendly NFTs involves choosing the right blockchain, minting responsibly, offsetting emissions, and promoting sustainability within your community.
The world of digital collectibles has grown at a remarkable pace over the past few years. Artists, musicians, and creators of all kinds have embraced non-fungible tokens as a way to sell their work directly to collectors without middlemen. However, this growth has come with a significant environmental cost that many people find troubling.
Traditional NFTs rely on blockchain networks that consume enormous amounts of electricity. A single transaction on some networks can use as much power as an average household does in several days. This has led to a growing conversation about how the NFT space can become more responsible and sustainable.
Eco-friendly NFTs represent a solution to this problem. These digital assets are created using technologies that dramatically reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. For anyone interested in participating in the NFT market while caring for the planet, understanding these green alternatives is essential.
At Nadcab Labs, we have spent over eight years working with blockchain technology and digital asset development. Our team has witnessed the evolution of the NFT space from its early days to the current push for sustainability. This guide draws on that experience to help you understand what eco-friendly NFTs are, why they matter, and how you can participate in building a greener digital future.
What Are Eco-Friendly NFTs and How Do They Work?
Eco-friendly NFTs are digital tokens that are created, bought, and sold using blockchain networks designed to minimize environmental harm. Unlike traditional NFTs that often run on energy-hungry systems, these green alternatives use technologies that require far less electricity to operate.
The key difference lies in how these blockchains verify transactions. Traditional networks like the original Ethereum used a process called Proof-of-Work, where computers compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. This competition requires massive amounts of computing power and electricity.
Green NFT platforms use alternative methods such as Proof-of-Stake, where validators are chosen based on how many tokens they hold and are willing to lock up as collateral. This approach eliminates the need for energy-intensive competition and reduces power consumption by roughly 99 percent.
According to Wikipedia’s explanation of Proof-of-Stake, this consensus mechanism selects validators in proportion to their quantity of holdings in the associated cryptocurrency. This fundamental shift in how blockchains operate makes sustainable NFTs possible.
When you create or purchase an eco-friendly NFT, you participate in a system that prioritizes environmental responsibility without sacrificing the benefits that make NFTs attractive in the first place. You still get verifiable ownership, scarcity, and the ability to trade your digital assets freely.
The Environmental Impact of Traditional NFTs
Understanding why eco-friendly alternatives matter requires looking honestly at the environmental footprint of traditional NFTs. The numbers can be startling for those unfamiliar with blockchain energy consumption.
Networks that use Proof-of-Work consensus require specialized computers called miners to run continuously. These machines perform trillions of calculations every second, all competing to validate the next block of transactions. The winner receives a reward, but all that computational effort from the losing miners is essentially wasted energy.
Studies have estimated that a single NFT transaction on a Proof-of-Work blockchain can generate hundreds of kilograms of carbon dioxide equivalent. When you consider that millions of NFT transactions happen annually, the cumulative impact becomes significant.
This environmental cost has sparked criticism from artists, collectors, and environmental advocates alike. Some creators have refused to participate in the NFT space until greener options became available. Others have faced backlash from their communities for minting NFTs on energy-intensive platforms.
The good news is that the blockchain industry has responded to these concerns. The development of energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and the migration of major platforms to greener technologies shows that sustainability and innovation can work together. If you want to understand how NFTs are evolving beyond just environmental considerations, our guide on the future of NFT metaverse with blockchain and VR explores the broader technological landscape.
Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work vs Proof-of-Stake
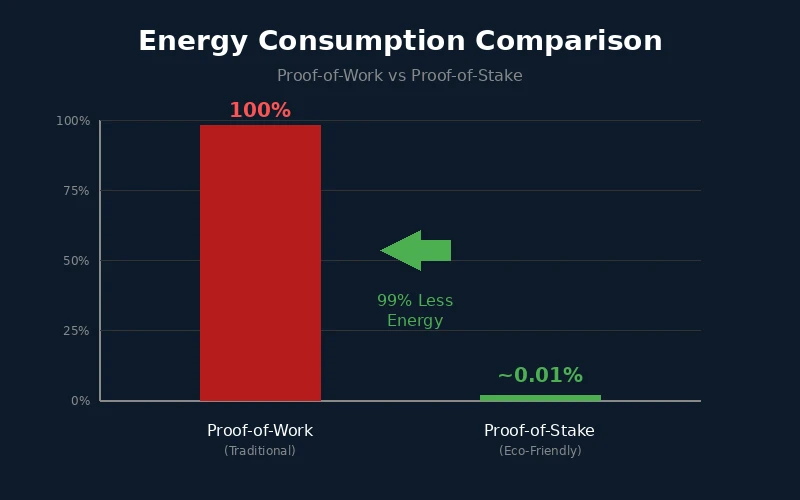
| Factor | Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy per Transaction | High (equivalent to days of household use) | Minimal (fraction of a kilowatt-hour) |
| Hardware Requirements | Specialized mining equipment | Standard computer hardware |
| Carbon Footprint | Substantial emissions | Near-zero emissions |
| Electricity Cost | Major operational expense | Negligible |
| Environmental Sustainability | Low | High |
Why Eco-Friendly NFTs Matter for Creators and Collectors
The shift toward sustainable NFTs is not just about feeling good or avoiding criticism. There are practical reasons why choosing green alternatives makes sense for anyone participating in the digital asset economy.
Meeting Consumer Expectations
Buyers today are more environmentally conscious than ever before. Many collectors specifically seek out NFTs created on sustainable platforms. By choosing eco-friendly options, creators can tap into this growing market segment and build stronger connections with their audience.
Lower Transaction Costs
Energy-efficient blockchains often have lower transaction fees because they do not require the massive computational resources of Proof-of-Work systems. This means more of the sale price goes to creators rather than network fees.
Future-Proofing Your Work
Regulations around carbon emissions are tightening worldwide. Businesses and individuals that adopt sustainable practices now will be better positioned as environmental standards become stricter. Creating on green platforms protects your work and reputation for the long term.
Supporting Technological Progress
Every eco-friendly NFT created and purchased sends a signal to the market. It demonstrates that sustainability matters to participants and encourages further investment in green blockchain technologies.
For collectors looking to store and manage their sustainable digital assets, choosing the right wallet is crucial. Our comprehensive overview of the 8 best NFT wallets can help you find secure storage solutions that work with eco-friendly platforms.
Build Sustainable NFT Solutions
Partner with Nadcab Labs to create eco-friendly NFT platforms that align with your environmental values. Our team brings 8+ years of blockchain expertise to every project.
Key Features That Define Eco-Friendly NFTs
Not all green NFTs are created equal. Understanding the specific features that make an NFT environmentally responsible helps you make informed decisions about which platforms and projects to support.
Energy-Efficient Consensus Mechanisms
The foundation of any eco-friendly NFT is the blockchain it runs on. Look for platforms that use Proof-of-Stake, Delegated Proof-of-Stake, or other low-energy consensus methods. These technologies validate transactions without the computational arms race that makes traditional blockchains so power-hungry.
Carbon Neutral or Carbon Negative Operations
Some platforms go beyond simply reducing emissions. They actively offset their carbon footprint by investing in environmental projects like reforestation, renewable energy development, or carbon capture technologies. These initiatives ensure that the net environmental impact of the platform is zero or even positive.
Transparent Environmental Reporting
Trustworthy eco-friendly platforms publish data about their energy consumption and environmental impact. This transparency allows users to verify claims and make informed choices. Be cautious of platforms that claim to be green without providing supporting evidence.
Sustainable Infrastructure
Beyond the blockchain itself, truly green NFT platforms consider the environmental impact of their entire operation. This includes using servers powered by renewable energy, implementing efficient code to minimize processing requirements, and designing systems that scale without proportionally increasing energy use.
Popular Platforms for Creating Eco-Friendly NFTs
Several blockchain networks have established themselves as leaders in sustainable NFT creation. Each offers unique advantages depending on your needs as a creator or collector.
Tezos
Tezos pioneered eco-friendly NFT creation and remains one of the most popular choices for environmentally conscious creators. The network uses a Proof-of-Stake mechanism called Liquid Proof-of-Stake that consumes approximately two million times less energy than Proof-of-Work alternatives. Tezos has attracted major artists and institutions looking to participate in NFTs without environmental guilt.
Solana
Solana combines its Proof-of-Stake system with a unique technology called Proof-of-History that creates a verifiable record of events over time. This combination allows for extremely fast transactions with minimal energy consumption. A single Solana transaction uses about as much energy as two Google searches, making it one of the most efficient options available.
Flow Blockchain
Developed by the team behind CryptoKitties, Flow was built from the ground up with sustainability in mind. The network has partnered with major brands and sports leagues for NFT projects, including NBA Top Shot. Flow uses a multi-node architecture that distributes work efficiently and reduces overall energy requirements.
Polygon
Polygon operates as a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, meaning it handles transactions off the main Ethereum chain while still benefiting from Ethereum’s security. This approach dramatically reduces energy consumption per transaction while maintaining compatibility with the broader Ethereum ecosystem. Many NFT marketplaces now offer Polygon as a minting option.
Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake, completed in September 2022, transformed the largest NFT ecosystem into a far greener option. The upgrade reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by approximately 99.95 percent. For creators who value Ethereum’s established infrastructure and wide marketplace support, this change was significant.
Eco-Friendly NFT Platform Comparison
| Platform | Consensus Mechanism | Transaction Speed | Gas Fees | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tezos | Liquid Proof-of-Stake | 30 seconds | Very Low | Digital art, collectibles |
| Solana | PoS + Proof-of-History | 400 milliseconds | Extremely Low | High-volume projects |
| Flow | Proof-of-Stake | 2.5 seconds | Low | Sports, entertainment |
| Polygon | Proof-of-Stake (L2) | 2 seconds | Very Low | Ethereum compatibility |
| Ethereum 2.0 | Proof-of-Stake | 12 seconds | Variable | Established marketplace |
The Lifecycle of an Eco-Friendly NFT
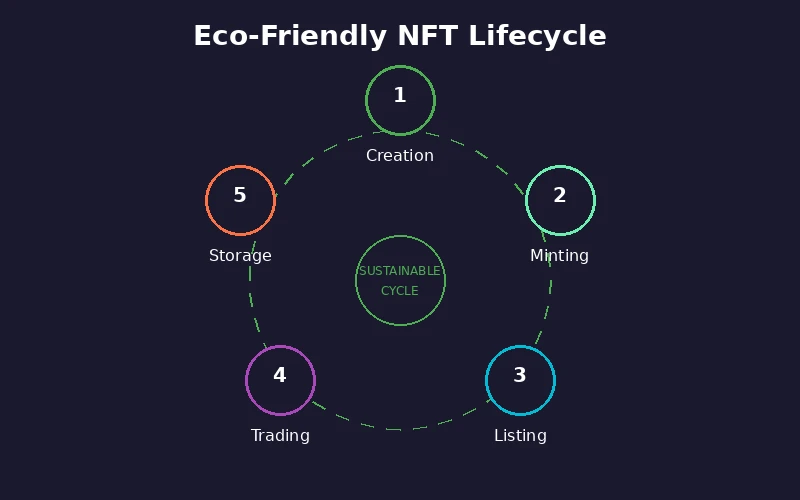
Understanding how sustainable NFTs move through their existence helps creators and collectors appreciate where environmental savings occur. Each stage of the lifecycle presents opportunities to reduce environmental impact.
Stage 1: Creation and Design
The journey begins when an artist or creator develops the digital content that will become an NFT. This stage is largely platform-independent, as the environmental impact comes primarily from the creator’s own equipment and electricity use. Artists can reduce their footprint here by using energy-efficient devices and renewable energy sources.
Stage 2: Minting
Minting transforms digital content into a verified NFT on the blockchain. This is where the choice of platform matters most. On a Proof-of-Work blockchain, minting triggers energy-intensive computational processes. On a Proof-of-Stake chain, the same action requires minimal energy because validators are selected based on their stake rather than computational competition.
Stage 3: Listing and Discovery
Once minted, NFTs are listed on marketplaces where potential buyers can discover them. The environmental impact at this stage depends on the infrastructure of the marketplace servers. Platforms committed to sustainability often use data centers powered by renewable energy.
Stage 4: Trading and Transfers
Each time an NFT changes hands, the transaction must be recorded on the blockchain. Green platforms ensure these transfers happen with minimal energy expenditure. Smart contract execution on Proof-of-Stake networks is far more efficient than on traditional systems.
Stage 5: Long-term Storage
NFTs persist on the blockchain indefinitely, but the energy required to maintain them is distributed across normal network operations. Sustainable blockchains continue to process and validate the existence of all NFTs without the ongoing power drain of mining operations.
The concept of fractional ownership has made NFTs more accessible to a wider audience. Our detailed explanation of fractional NFTs shows how this innovation works within both traditional and eco-friendly ecosystems.
How to Create Eco-Friendly NFTs: A Step-by-Step Process
Creating sustainable NFTs is straightforward once you understand the basics. Follow these steps to mint your first green digital asset.
Step 1: Choose Your Platform Carefully
Research the blockchain networks discussed earlier and select one that aligns with your goals. Consider factors like transaction fees, marketplace availability, community size, and the specific environmental credentials of each option. For most beginners, Tezos or Polygon offer a good balance of accessibility and sustainability.
Step 2: Set Up a Compatible Wallet
Each blockchain requires a specific type of wallet to store your tokens and NFTs. Download and configure a wallet that works with your chosen platform. Ensure you follow security best practices, including backing up your seed phrase and enabling any available security features. Our guide on how to create an NFT wallet walks you through this process in detail.
Step 3: Acquire Some Platform Tokens
You will need a small amount of the native cryptocurrency for your chosen blockchain to pay for minting fees. These fees are typically very low on eco-friendly platforms. Purchase tokens from a reputable exchange and transfer them to your wallet.
Step 4: Prepare Your Digital Content
Create or gather the digital files you want to transform into NFTs. This could be artwork, music, video, or any other digital content. Consider the format requirements of your chosen marketplace and optimize your files accordingly.
Step 5: Connect to a Marketplace
Visit an NFT marketplace that supports your chosen blockchain. Connect your wallet to the platform by following the authentication prompts. This connection allows the marketplace to interact with your wallet for minting and trading.
Step 6: Mint Your NFT
Use the marketplace’s minting interface to upload your content and fill in the required details like title, description, and any attributes. Review the gas fee estimate and confirm the transaction. Within moments, your eco-friendly NFT will exist on the blockchain.
Step 7: Consider Carbon Offsetting
Even though you chose a green platform, you might want to go further. Some services allow you to purchase carbon offsets that fund environmental projects to compensate for any remaining emissions. This step is optional but demonstrates extra commitment to sustainability.
Carbon Offsetting and Neutrality in the NFT Space
Carbon offsetting has become a popular way for NFT platforms and creators to address environmental concerns. Understanding how these programs work helps you evaluate their effectiveness and decide whether to participate.
Carbon offset programs work by calculating the emissions associated with an activity and then funding projects that remove or prevent an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Common offset projects include planting trees, investing in renewable energy installations, protecting existing forests, and supporting clean cooking initiatives in developing countries.
In the NFT context, some platforms automatically calculate and offset the carbon footprint of every transaction. Others allow creators to voluntarily purchase offsets when minting. Still others claim carbon neutrality based on company-wide offset purchases.
The effectiveness of carbon offsetting depends heavily on the quality of the projects funded. Look for platforms that work with verified offset providers and publish transparent reports about their environmental initiatives. Third-party certifications from organizations like Gold Standard or Verra indicate higher-quality offsets.
Critics argue that offsetting can become a way to avoid necessary changes while continuing harmful practices. The most responsible approach combines offsetting with genuine efforts to reduce emissions at the source. This means choosing efficient platforms first and using offsets as a supplementary measure rather than a primary solution.
Real-World Applications of Eco-Friendly NFTs
Sustainable NFTs are finding applications across various industries, demonstrating that environmental responsibility and commercial success can coexist.
Digital Art and Collectibles
Artists worldwide have embraced green NFT platforms to sell their work. Major artists and galleries have specifically chosen platforms like Tezos to avoid the environmental criticism that accompanies Proof-of-Work minting. This has created a thriving market for sustainably created digital art.
Music and Entertainment
Musicians are using eco-friendly NFTs to sell exclusive content, concert tickets, and fan experiences. The low transaction costs on green platforms make it economically viable to sell lower-priced items that would be impractical on networks with higher fees.
Event Ticketing
NFT-based tickets offer advantages over traditional ticketing systems, including easier transfer, built-in royalties for secondary sales, and verifiable authenticity. When implemented on sustainable blockchains, these systems provide benefits without environmental drawbacks. Our article on NFT ticketing explores how this technology is transforming the events industry.
Gaming and Virtual Worlds
Video game developers are integrating eco-friendly NFTs as in-game items, characters, and assets. Players can truly own their digital possessions and trade them across platforms. Games built on sustainable blockchains can offer these features without the environmental concerns that have plagued blockchain gaming.
Real Estate and Physical Assets
The tokenization of real-world assets is a growing use case for NFTs. Properties, luxury goods, and other physical items can be represented as NFTs for easier trading and ownership verification. Our analysis of how real-world assets are transforming NFT lending shows the practical implications of this trend.
Case Study: Building Sustainable NFT Infrastructure
Practical examples illustrate how organizations are successfully implementing eco-friendly NFT solutions. At Nadcab Labs, we have worked with clients across multiple sectors to develop sustainable digital asset platforms.
One notable project involved creating a decentralized NFT lending protocol that prioritized energy efficiency from the ground up. The BendDAO NFT decentralized solutions case study demonstrates how thoughtful technical decisions can create platforms that serve users well while minimizing environmental impact.
The project required balancing multiple considerations: user experience, security, scalability, and sustainability. Our team’s eight years of blockchain experience proved essential in navigating these tradeoffs and delivering a solution that met all requirements.
Key lessons from this and similar projects include the importance of choosing the right blockchain foundation from the start, designing smart contracts for efficiency, and building infrastructure that can scale without proportionally increasing environmental costs.
“The future of NFTs lies in sustainable technology. At Nadcab Labs, we have witnessed the industry’s evolution over eight years, and the shift toward eco-friendly solutions is not just a trend but a fundamental transformation. Organizations that embrace green blockchain technologies now will lead the market as environmental standards continue to tighten.”
— Nadcab Labs Development Team
Launch Your NFT Marketplace
Ready to build a sustainable NFT platform? Our NFT marketplace development services combine technical excellence with environmental responsibility.
Economic Opportunities in Sustainable NFTs
The eco-friendly NFT market offers substantial economic opportunities for creators, collectors, and developers. Understanding how to participate effectively can lead to meaningful income while supporting sustainable practices.
For creators, green platforms often mean lower barriers to entry. Reduced transaction fees make it economically viable to sell work at various price points. Artists can experiment more freely without worrying about high minting costs eating into their profits.
Collectors benefit from the growing demand for sustainably created digital assets. As environmental awareness increases, eco-friendly NFTs may appreciate in value as buyers specifically seek green alternatives. The documented sustainability of an NFT becomes part of its provenance and potential value proposition.
Developers and entrepreneurs can build businesses around sustainable NFT infrastructure. Marketplaces, tools, and services that cater to environmentally conscious creators and collectors represent a growing market segment. Our beginner guide to making money with NFTs provides detailed strategies for entering this space.
Challenges Facing Eco-Friendly NFTs
Despite the progress made, sustainable NFTs still face several challenges that the industry continues to address.
Market Fragmentation
The existence of multiple green platforms creates fragmentation. Collectors might need wallets and accounts on several different networks to access the full range of eco-friendly NFTs. This complexity can discourage participation, particularly among newcomers.
Liquidity Concerns
Some sustainable platforms have smaller user bases than established networks, which can affect liquidity. NFTs on less popular platforms may be harder to sell quickly because there are fewer active buyers.
Greenwashing Risks
As sustainability becomes marketable, some platforms may overstate their environmental credentials. Users must be vigilant about verifying claims and seeking transparent reporting from the platforms they use.
Technical Tradeoffs
Different consensus mechanisms involve different security assumptions. While Proof-of-Stake has proven secure over years of operation, some technical debates continue about the long-term security properties of various approaches.
Educational Gaps
Many potential users still do not understand the environmental differences between blockchain platforms. Increased education and awareness are needed to help people make informed choices.
The Future of Sustainable Digital Assets
The trajectory of eco-friendly NFTs points toward continued growth and mainstream adoption. Several trends indicate where the market is heading.
Major institutions and brands are increasingly choosing sustainable platforms for their NFT initiatives. This corporate adoption brings legitimacy and resources that accelerate the development of green blockchain technologies.
Regulatory attention to carbon emissions is increasing globally. Blockchain projects that can demonstrate low environmental impact will have advantages as reporting requirements become more stringent.
Technical innovation continues to improve the efficiency of blockchain networks. Layer 2 solutions, more efficient consensus mechanisms, and improved smart contract design all contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of digital asset creation and trading.
Consumer awareness is rising. As more people understand the environmental implications of their digital purchases, demand for sustainable options will continue to grow. This demand creates market incentives for further green innovation.
For more insights into emerging trends, our exploration of smart and sustainable eco-friendly NFTs examines the latest developments in this rapidly evolving space.
Conclusion: Participating in the Green NFT Movement
Eco-friendly NFTs represent a significant evolution in how we create, collect, and trade digital assets. By choosing sustainable platforms and practices, participants in the NFT space can enjoy all the benefits of blockchain technology without contributing to environmental harm.
The tools and platforms for creating green NFTs are accessible to anyone willing to learn. From established artists to complete beginners, the opportunity to participate responsibly exists today.
At Nadcab Labs, our team has spent over eight years building expertise in blockchain technology and sustainable digital asset solutions. We have seen the industry transform from energy-intensive beginnings to the increasingly green landscape of today. This evolution gives us confidence that the future of NFTs will be both innovative and environmentally responsible.
Whether you are an artist looking to mint your first sustainable collection, a collector seeking green alternatives, or a business exploring NFT integration, the path forward is clear. Choose platforms that prioritize energy efficiency. Verify environmental claims with transparent data. Support initiatives that advance sustainable blockchain technology.
The NFT market will continue to grow. By making conscious choices today, you help shape that growth in a direction that benefits both the digital economy and our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Eco-friendly NFTs are created on blockchains that use energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake instead of the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work system. Traditional NFTs on Proof-of-Work networks require miners to compete using massive amounts of computational power, consuming electricity equivalent to small countries. Green NFTs use validator systems that select transaction approvers based on their staked tokens rather than computing power, reducing energy consumption by approximately 99 percent while maintaining the same security and ownership benefits that make NFTs valuable.
The leading eco-friendly blockchain platforms for NFT creation include Tezos, Solana, Flow, Polygon, and Ethereum 2.0 after its transition to Proof-of-Stake. Tezos is particularly popular among digital artists for its extremely low energy consumption and established art community. Solana offers the fastest transaction speeds with minimal environmental impact. Polygon provides Ethereum compatibility with dramatically reduced energy costs. Each platform has unique strengths, so the best choice depends on your specific needs regarding transaction fees, marketplace availability, and community size.
Creating an NFT on eco-friendly platforms is significantly cheaper than on traditional Proof-of-Work networks. Minting fees on platforms like Tezos and Polygon typically range from a few cents to a couple of dollars, compared to fees that could reach hundreds of dollars during peak times on old Ethereum. The exact cost varies based on network congestion and the complexity of your NFT smart contract. Many green platforms also offer lazy minting options where the NFT is only fully created when purchased, eliminating upfront minting costs for creators entirely.
Moving NFTs between blockchains is technically complex because each blockchain maintains its own separate record of ownership. You cannot simply transfer an existing NFT from one chain to another. However, you can burn your original NFT and re-mint it on an eco-friendly platform, though this creates a new token rather than moving the original. Some bridge services exist that create wrapped versions of NFTs on different chains, but these come with technical risks and complexity. For new projects, starting on a green platform from the beginning is the most straightforward approach.
Yes, eco-friendly NFTs built on established Proof-of-Stake blockchains offer comparable security to traditional Proof-of-Work NFTs. The security model differs in that instead of requiring attackers to control massive computing resources, they would need to acquire a significant portion of the staked tokens to manipulate the network. Major Proof-of-Stake networks like Ethereum 2.0, Solana, and Tezos have operated for years without successful attacks on their consensus mechanisms. The underlying cryptographic principles ensuring NFT ownership and authenticity remain the same regardless of which consensus mechanism the blockchain uses.
Carbon offset programs for NFT platforms calculate the estimated emissions from blockchain operations and then fund projects that remove or prevent equivalent amounts of carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere. Common offset projects include reforestation initiatives, renewable energy development, and methane capture from landfills. Some platforms automatically purchase offsets for every transaction, while others offer voluntary offset options to users. The quality of offsets varies significantly, so look for platforms that work with verified providers certified by standards like Gold Standard or Verra to ensure your offsets represent genuine environmental benefits.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.