Crypto has changed how people think about money, ownership, and digital value. Before crypto, most digital payments depended on banks and central systems. Today, crypto works without a central authority. People can send value directly to each other using blockchain networks. This shift has opened new ways to build apps, manage assets, and create digital economies.
Since the introduction of crypto, many changes have happened. Digital payments have become faster and more global. New digital assets have appeared, such as crypto coins and crypto tokens. Entire markets have grown around them. The crypto market[1] now includes payments, finance, gaming, art, and even artificial intelligence. This change did not happen in one day. It followed a clear evolution, step by step.
Key Takeaways: Crypto Tokens & Coins
- Crypto enables peer-to-peer value transfer without banks
- Blockchain ensures transparency, security, and decentralization
- Coins power blockchains; tokens power apps and services
- Tokens are faster and cheaper to launch than new coins
- Smart contracts automate trust and token functionality
- Token standards ensure wallet and app compatibility
- Utility tokens drive access, rewards, and platform usage
- Governance tokens enable community-based decisions
- NFTs represent unique digital ownership on blockchain
- Tokenization brings real-world assets on-chain efficiently
- Security audits are critical to protect digital value
- DeFi, gaming, and AI fuel rapid token ecosystem growth
What Is Crypto?
Crypto, or cryptocurrency, is a type of money that exists only on the internet. You do not need a bank to use it, and no single company or government controls it. Crypto works on a technology called blockchain. Crypto does not exist in physical form. You cannot hold it like cash. It exists as data on the blockchain. This data is protected by cryptography. That is why it is called “crypto.”
Crypto enables users to:
- Transfer value without intermediaries
- Store digital assets securely
- Build decentralized applications
- Create verifiable digital ownership
From a practical perspective, crypto assets are divided into two categories:
- Crypto coins, which power blockchains
- Crypto tokens, which enable applications, services, and digital economies
While coins maintain the network, crypto tokens deliver functionality, making them the most widely used assets in Web3 today.
How Crypto Tokens Differ from Coins
The major difference between coin and token is that a crypto coin runs on its own blockchain, while a crypto token runs on an existing blockchain. A crypto coin operates on its own blockchain, while a crypto token runs on an existing blockchain.
For example:
- Ethereum (ETH) is a crypto coin because it powers its own blockchain.
- USDT (Tether) is a crypto token created on blockchains like Ethereum using the ERC-20 standard.
Because crypto tokens do not require building a new blockchain, they are faster to launch, easier to upgrade, and more cost-effective. This is why most modern Web3 projects prefer crypto token development over coin creation.
How Did Crypto Start?
The idea of digital money started a long time ago. In the 1980s, a computer scientist named David Chaum created a system called eCash[2]. It allowed people to send money privately using computers. However, at that time, the technology was not ready, and eCash did not become popular.
Many years later, in 2008, a person or group using the name Satoshi Nakamoto shared a paper about Bitcoin. In 2009, the Bitcoin network went live. Bitcoin was special because it worked without banks or governments. It used a new system called blockchain, which records all transactions safely and publicly.
One famous moment in crypto history happened in 2010, when a programmer bought two pizzas for 10,000 Bitcoins. At that time, Bitcoin was very cheap. Today, those Bitcoins would be worth a huge amount of money, making this purchase very famous.
In less than 15 years, cryptocurrency grew from a small idea into a massive global market worth trillions of dollars[3]. Today, people use crypto to:
- Send money quickly across countries
- Invest and trade
- Earn money using DeFi (decentralized finance) apps
- Buy and sell digital art called NFTs
- Play blockchain-based games
- Use stablecoins for daily payments
Now, even real-world things like houses, stocks, and other assets can be turned into digital tokens on a blockchain.
Crypto Token Market Trends and Industry Growth
The crypto token market has evolved from a small experimental space into a global digital economy. Tokens now represent financial instruments, access rights, digital identities, governance power, and real-world assets.
The global crypto market value has crossed over $3 trillion, with tokens representing a major share of that value across DeFi, NFTs, stablecoins, and utility ecosystems. Despite volatility, long-term growth continues as institutions, developers, and governments explore blockchain use cases.
Key market highlights:
- Global crypto market capitalization exceeding trillions of dollars
- Stablecoins and utility tokens driving daily transaction volume
- Rapid growth of DeFi, NFT, and gaming tokens
- Increasing enterprise adoption of tokenization
- Emergence of AI crypto tokens and autonomous systems
This growth shows that crypto tokens are no longer optional, they are becoming a core layer of the digital economy, supported by strong blockchain coin networks.
Tokenomics Design: Supply, Distribution & Incentives
Tokenomics defines how a token functions economically within an ecosystem. It shapes user behavior, demand, scarcity, and long-term value. A well-structured token model aligns incentives between users, builders, and the platform itself.
Poor token economics often lead to short-lived hype, inflation, or loss of trust. A balanced structure encourages participation while maintaining scarcity and fairness.
Core elements of token economics
- Total supply: Fixed or variable based on platform needs
- Circulating supply: Tokens available in the market at launch
- Distribution model: Allocation for users, team, treasury, and partners
- Vesting schedules: Prevents sudden sell-offs and market shocks
- Incentive mechanisms: Rewards for staking, usage, or governance
Common incentive structures
- Usage-based rewards for active participants
- Staking benefits for long-term holders
- Governance power for ecosystem contributors
- Fee discounts or premium access for token holders
Strong token economics turns tokens into functional assets rather than speculative instruments.
Crypto Token vs Coin Development Lifecycle
Although coins and tokens coexist, their development processes are very different. Understanding this difference explains why most modern projects focus on crypto token development.
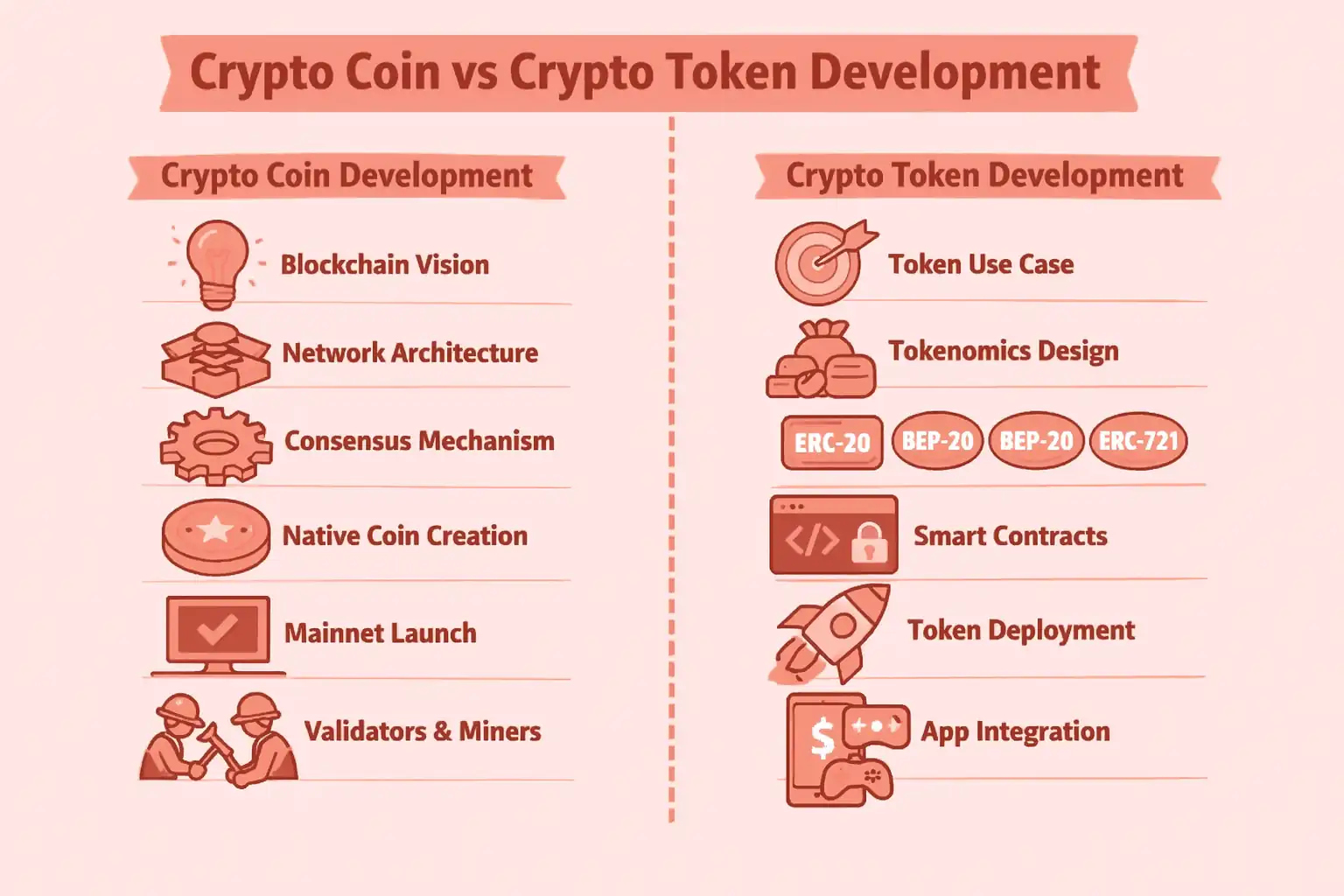
How to Develop Crypto Coin (Supporting Layer)
Crypto coin development focuses on building the core blockchain infrastructure. A coin is the native asset of its own blockchain, which means developers must design and maintain an entire network from scratch or heavily modify an existing one. This makes coin development complex, time-consuming, and capital-intensive.
Typical crypto coin development stages include:
- Vision and problem definition: Identifying a large-scale infrastructure problem such as scalability, privacy, or transaction speed
- Blockchain architecture design: Designing blocks, nodes, and network structure
- Consensus mechanism development: Implementing systems like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake
- Native coin creation: Launching the coin that powers transactions and network security
- Network testing and mainnet launch: Ensuring stability and resistance to attacks
- Validator or miner onboarding: Building a secure and decentralized ecosystem
Crypto coins primarily focus on security, decentralization, and long-term scalability, making them suitable for foundational blockchain networks rather than fast product launches.
Crypto Token Development Lifecycle: From Idea to Launch
Crypto token development follows a much faster and more flexible lifecycle because tokens are created on existing blockchains such as Ethereum or BNB Chain. This eliminates the need to build a new network, allowing teams to focus directly on application logic and business value.
Typical crypto token development stages include:
- Defining the token use case: Utility, governance, payments, rewards, or ownership
- Tokenomics design: Deciding total supply, distribution, and incentives
- Token standard selection: Choosing ERC-20, BEP-20, ERC-721, or others
- Smart contract development: Writing secure and transparent token logic
- Deployment on blockchain: Launching the token on the mainnet
- Application integration: Using tokens in DeFi, gaming, NFTs, or enterprise platforms
This streamlined lifecycle allows businesses to launch faster, reduce costs, test ideas quickly, and scale efficiently, which is why crypto token platform dominates modern Web3 innovation.
Crypto Token Architecture and Smart Contracts
Crypto token architecture defines how a token functions at a technical level. At its core, token architecture is governed by smart contracts, which are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain.
Smart contracts enforce rules automatically and transparently. Once deployed, they operate without human intervention, ensuring trust and consistency.
Internal Structure of a Crypto Token
A typical token smart contract:
- Stores the total token supply
- Tracks wallet balances
- Manages token transfers
- Controls minting and burning
- Enforces permissions and access control
Because smart contracts are immutable by default, careful planning and testing are essential. A well-designed architecture ensures scalability, security, and long-term usability.
Role of smart contracts in token systems
- Eliminate intermediaries
- Prevent unauthorized actions
- Enable DeFi, staking, and governance
- Support automation and composability
Strong crypto token architecture is the backbone of successful Web3 platforms.
Upgradeable Smart Contracts and On-Chain Governance
Smart contracts are typically immutable, which ensures trust but limits flexibility. Upgradeable structures allow improvements while preserving transparency. On-chain governance adds decentralization by allowing token holders to participate in decision-making.
Together, these systems support adaptability without sacrificing security.
Benefits of upgradeable contract structures
- Fix bugs without replacing entire systems
- Add new features over time
- Improve performance as usage grows
- Reduce long-term technical risk
On-chain governance capabilities
- Voting on protocol upgrades
- Treasury fund allocation decisions
- Parameter changes such as fees or limits
- Community-led ecosystem direction
When governance is transparent and inclusive, users become long-term stakeholders rather than passive participants.
Crypto Token Standards Explained Simply
Crypto token standards are common rules that help tokens work smoothly on a blockchain. These rules tell the blockchain how tokens should behave. Without standards, every token would work differently, and using them would be confusing and risky.
Token standards make sure that wallets, exchanges, and apps can easily support new crypto tokens. They save time and reduce errors during development. This is why standards are a key part of token development and crypto token development.
What are token standards in simple words
- A set of rules for creating and using tokens
- They define how tokens are transferred and tracked
- They help different platforms work together
Common token standards include:
| Standard | Blockchain | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| ERC-20 | Ethereum | Utility, payments, governance |
| BEP-20 | BSC | DeFi and low-cost transactions |
| ERC-721 | Ethereum | NFTs and digital collectibles |
| ERC-1155 | Ethereum | Hybrid assets |
Each standard is designed for a specific purpose. For example, ERC-20 is ideal for payments and rewards, while ERC-721 is perfect for digital art and collectibles.
Why token standards matter
- Make tokens easy to use and integrate
- Reduce development mistakes
- Improve security and trust
- Support faster launch of new crypto tokens
Standards help the crypto ecosystem grow in a stable way. They allow developers to focus on real use cases instead of rebuilding basic functions. This is why standards are essential in the modern coin and token ecosystem.
How to Choose the Right Blockchain for a Token
Selecting the right blockchain is one of the most important decisions in any token-based project. The blockchain determines transaction speed, fees, security level, ecosystem support, and long-term scalability. A poor choice can limit growth, while the right network can accelerate adoption and usability.
Different blockchains are designed for different purposes. Some prioritize decentralization and security, while others focus on speed and low transaction costs. The choice should align with the token’s purpose, user base, and expected transaction volume.
Key factors to evaluate before selecting a blockchain
- Transaction fees: Lower fees improve user experience and encourage adoption
- Network speed: High throughput is critical for gaming, DeFi, and payments
- Security model: Mature networks offer stronger resistance to attacks
- Ecosystem support: Availability of wallets, exchanges, and tools
- Community and adoption: Larger ecosystems bring trust and liquidity
Popular blockchain choices by use case
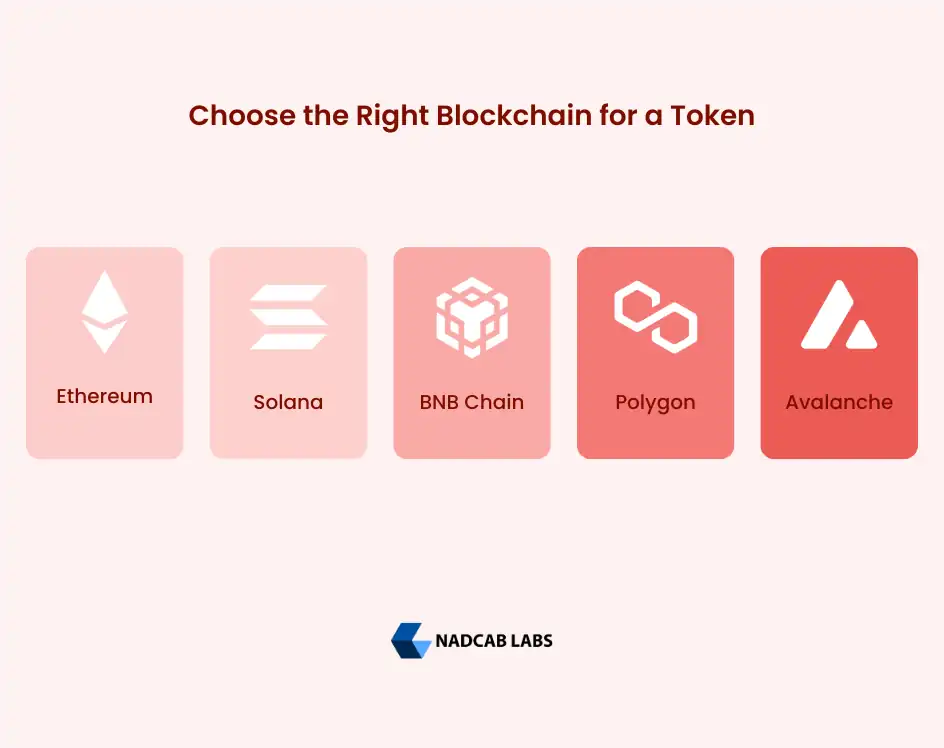
- Ethereum: Ideal for DeFi, NFTs, and governance-focused tokens
- Solana: Designed for high-speed, high-volume applications
- BNB Chain: Suitable for cost-efficient transactions and fast launches
- Polygon: Best for scalable applications with lower gas fees
- Avalanche: Great for fast DeFi, NFTs, and scalable apps
Choosing the right blockchain ensures smoother integration, lower operational friction, and better long-term sustainability.
Crypto Token Types with Real Examples
Crypto tokens come in different types based on how they are used. Each type solves a different problem and serves a specific purpose in the blockchain ecosystem. Understanding crypto token types helps learners see how tokens connect with real-world applications.
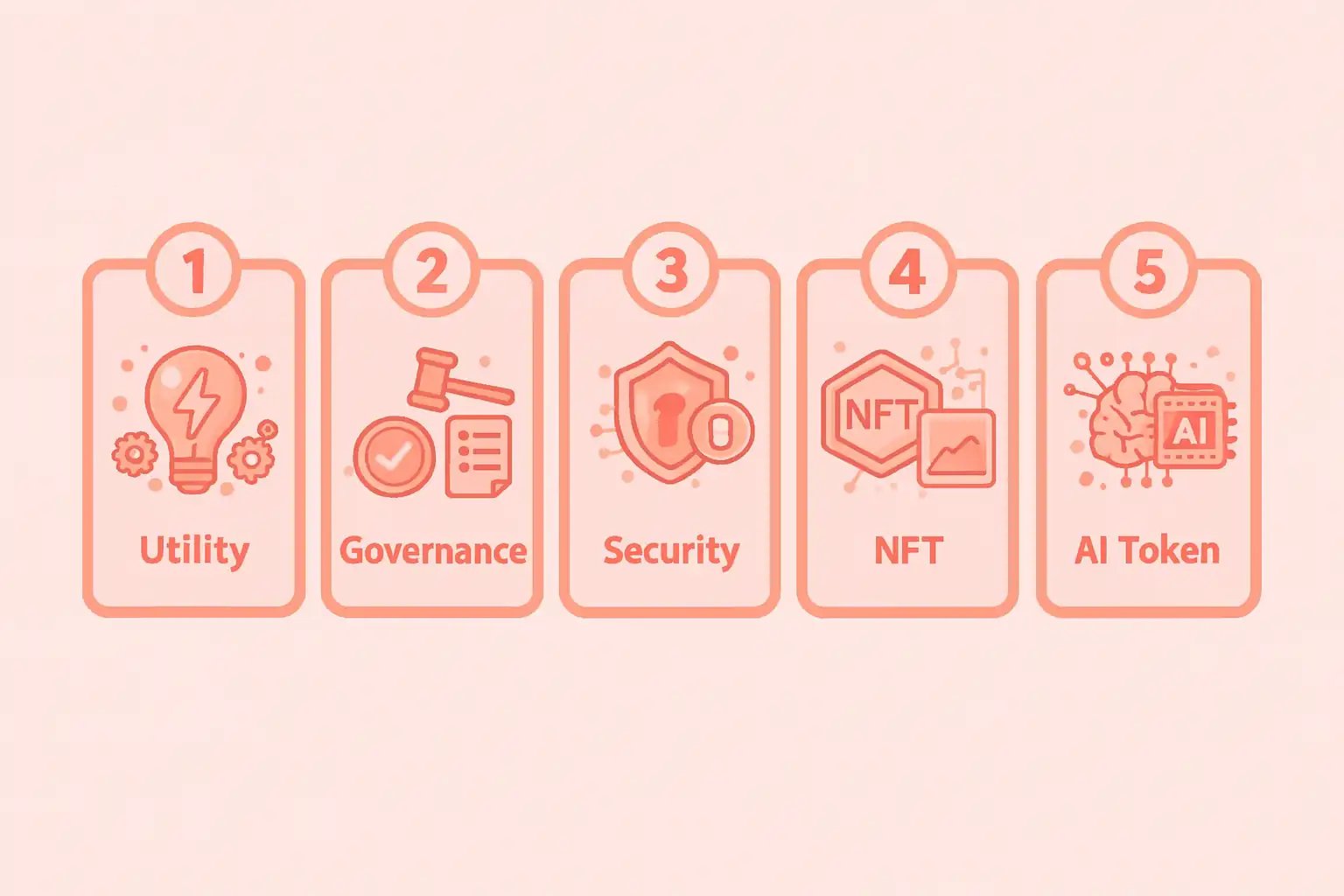
Utility tokens are the most common type. These tokens give users access to a product or service within a platform. For example, a utility token can be used to pay fees, unlock features, or receive rewards. Many DeFi platforms and apps use utility tokens to run their systems.
Main crypto token types explained
| Token Type | Purpose | Real Example |
|---|---|---|
| Utility | Platform access | BNB |
| Governance | Voting | UNI |
| Security | Investment | Tokenized stocks |
| NFT | Digital ownership | CryptoPunks |
| AI Token | AI services | Fetch.ai |
Security tokens are linked to real assets or profits and follow legal rules. Governance tokens give users voting power, allowing communities to manage platforms together. NFT tokens are used for digital art, collectibles, and gaming items. AI crypto tokens are a newer category and are used in AI-powered networks and tools.
- A DeFi app using a utility token for transaction fees
- A DAO using governance tokens for voting
- Digital artwork sold as NFT tokens
- AI platforms using tokens to access computing power
Each crypto token type plays a role in building real use cases. This variety is why the crypto tokens list continues to grow and why token-based systems dominate modern Web3 applications.
How to Launch a Crypto Successfully
Launching crypto is the execution phase, not the planning phase. At this stage, the coin or token is already designed and developed. The goal here is to make it live, usable, and accessible to users in a safe way.
Crypto launch focuses on readiness, validation, and controlled release. This applies to both crypto coins and crypto tokens, though tokens are more common due to lower cost and faster launch.
Practical launch-focused steps
- Final contract review: Recheck smart contract logic and permissions
- Security audit: Test for bugs, loopholes, and misuse risks
- Testnet validation: Run real transactions in a test environment
- Mainnet deployment: Make the crypto token or coin live on the blockchain
- Liquidity setup: Enable basic trading or usage access
- Monitoring after launch: Track performance, errors, and user activity
Launching is the most sensitive phase of coin and token development. A mistake here can damage trust permanently. This is why launch execution is treated separately from token lifecycle and token development stages.
Token Listing, Liquidity, and Market Readiness
Market readiness determines whether a token gains real traction or fades after launch. Visibility, liquidity, and accessibility are critical for user participation and price stability. Without sufficient liquidity, even strong projects struggle to grow.
Listing strategies should focus on credibility, usability, and gradual exposure.
Key components of market readiness
- Liquidity pools: Enable smooth trading and price discovery
- Exchange compatibility: Support from wallets and platforms
- Clear token utility: Real usage beyond speculation
- Transparent documentation: Whitepaper and token details
- Community awareness: Organic interest and engagement
Liquidity best practices
- Gradual liquidity introduction
- Avoid overexposure at early stages
- Balance supply release with demand
- Monitor trading behavior post-launch
Market readiness transforms tokens from technical assets into usable digital instruments.
Development Cost & Pricing Overview
Developing crypto coins and tokens involves different levels of complexity, which directly impact cost. Generally, creating a coin is more expensive because it requires building a new blockchain, while tokens are cheaper as they are deployed on existing blockchain networks using smart contracts.
| Development Type | Cost Range | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Crypto Coin | $50,000 – $150,000+ | New blockchain, high security, long development |
| Basic Crypto Token | $3,000 – $8,000 | Simple smart contract, standard features |
| Advanced Crypto Token | $10,000 – $25,000 | Custom logic, staking, governance |
| Security Audit | Additional $1,000 – $5,000+ | Highly recommended for safety |
These cost ranges are based on global market trends. Actual pricing depends on blockchain choice, token features, security audits, and platform integration. Long-term value comes from adoption and utility, not just development cost.
Legal, Compliance, and Regulatory Considerations
Legal clarity is essential for long-term credibility and global adoption. Regulatory frameworks vary by region, and token classification can differ depending on its purpose and structure. Ignoring compliance can lead to penalties, delisting, or shutdowns.
A legally aligned approach builds trust with users, exchanges, and institutional partners while reducing operational risk.
Key compliance areas to address
- Token classification: Utility, governance, or asset-backed
- KYC & AML processes: Required for platforms handling user funds
- Jurisdictional rules: Laws vary across countries and regions
- Disclosure requirements: Transparency around token supply and usage
- Consumer protection standards: Safeguards against misuse
Why compliance matters
- Enables smoother exchange listings
- Reduces legal and operational risks
- Builds long-term investor confidence
- Supports sustainable ecosystem growth
Regulation is not a barrier when approached early—it is a foundation for scale.
Security, Audits, and Risk Management
Security is one of the most important parts of crypto systems. Once a crypto coin or crypto token is live, its code controls real value. If there is a mistake, it can lead to loss of funds and user trust. This is why security must be taken seriously at every stage.
Smart contracts run automatically and cannot be easily changed. This makes them powerful but also risky if they are poorly written. A small error in logic can be exploited by attackers.
Why security is critical
- Crypto transactions cannot be reversed
- Smart contracts control real assets
- Public blockchains are always visible to attackers
Smart contract audits help reduce risks. An audit is a review of the code by experts who look for bugs, loopholes, and unsafe logic. Audits do not guarantee perfection, but they greatly improve safety.
Common risks and mistakes
- Reusing untested code
- Missing access control rules
- Poor testing before launch
- Ignoring upgrade and pause options
Security is not a one-time task. It requires continuous monitoring and regular updates. Strong security practices protect users and help maintain long-term trust in crypto token and coin projects.
Crypto Tokenization Explained
Crypto tokenization is the process of turning real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. This allows physical or financial assets to be represented, traded, and managed digitally. Tokenization brings transparency, security, and accessibility to markets that were previously difficult to enter.
Use cases of crypto tokenization
- Real estate: Property can be divided into tokens for smaller investments
- Art & collectibles: Digital certificates for physical items
- Finance: Stocks, bonds, and funds represented as tokens for faster trading
- DeFi & lending: Tokenized assets can be used as collateral
Tokenization also reduces costs and paperwork, as blockchain handles record-keeping automatically. It is becoming a key feature in Web3 applications and supports the growth of AI crypto tokens, NFTs, and other innovative platforms.
Overall, crypto tokenization is transforming how we manage and use value, making markets more efficient, transparent, and accessible to everyone.
Practical Uses of Coins and Tokens
Crypto coins and crypto tokens are not just digital money. They have many real-world applications that are changing how we pay, invest, and interact online. Understanding practical uses helps learners see why crypto is more than just speculation.
Main practical uses
- Payments: Coins like Bitcoin or stable tokens are used for fast, borderless payments without banks. Tokens can also be used for in-app purchases, subscription fees, or platform services.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): Tokens power lending, borrowing, and earning interest without traditional banks. Utility and governance tokens are often used here.
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital items, like art, music, or collectibles, are created as NFT tokens. They allow ownership, trading, and verification of digital assets.
- Gaming: Tokens are used for in-game currency, rewards, and digital assets that players can trade or sell.
- AI and automation: AI crypto tokens enable data sharing, automated decision-making, and payments between AI agents or platforms.
Coins mainly act as a base currency, while tokens provide functionality and access within ecosystems. Stable tokens reduce price risk, making them ideal for payments and savings. Governance tokens allow communities to vote and manage projects. NFT tokens make digital ownership transparent and tradable.
By using coins and tokens in practical ways, projects increase adoption and real value. This is why crypto tokenization and coin usage are essential parts of modern Web3 platforms, DeFi systems, AI networks, and digital marketplaces.
Ready to Launch Your Crypto Token or Coin?
Get expert guidance on tokenomics, smart contracts, and launch strategies to make your crypto project a success.
Future of Crypto Coins and Tokens
The future of crypto coins and tokens is full of opportunities. Coins will continue to focus on secure, fast, and scalable blockchains, supporting payments, DeFi, and infrastructure for new applications. Strong and reliable networks will remain central to the ecosystem.
Crypto tokens will grow even faster due to their flexibility. New crypto tokens will appear in gaming, NFTs, AI platforms, and DeFi projects. AI crypto tokens will connect artificial intelligence with blockchain, enabling automation, smarter decision-making, and decentralized services.
Future prospects
- Adoption: More businesses, platforms, and users will accept coins and tokens
- Innovation: AI, Web3, and DeFi will create new token-based opportunities
- Integration: Tokens and coins will work together for layered ecosystems
- Regulations: Clear rules will protect users and encourage sustainable growth
Overall, the crypto ecosystem will become more practical, secure, and widely used. Coins will provide the backbone, while tokens will unlock innovative applications. This growth will shape the next decade of digital finance, gaming, AI, and ownership models.
Conclusion
Crypto coins and crypto tokens are more than digital money. Coins provide the foundation with secure and scalable blockchains, while tokens add flexibility and real-world use through smart contracts. Together, they power payments, DeFi, NFTs, gaming, AI platforms, and tokenized assets.
Understanding their lifecycle, architecture, standards, costs, and security is essential for anyone learning about Web3. By exploring practical uses and future prospects, it becomes clear that coins and tokens will continue to transform finance, technology, and digital ownership, making crypto an important part of the digital economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Crypto, or cryptocurrency, is digital money secured by cryptography. It operates online using decentralized blockchains, enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions without banks. Popular examples include Bitcoin and Ether, used for payments, investment, or digital assets.
Crypto compliance ensures businesses follow legal and regulatory rules. This includes implementing KYC, monitoring transactions, and reporting to authorities. Requirements vary by jurisdiction, helping prevent fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes.
Regulations influence token classification, distribution, and reporting. Projects must comply with KYC/AML requirements and securities laws, ensuring legal operation and investor protection before public launch.
Crypto works on blockchain technology, which is a decentralized ledger maintained by a network of computers (nodes). Transactions are verified using cryptography, allowing users to transfer value directly without intermediaries.
Tokens leverage existing blockchains, avoiding the need to build a new network. This reduces development time, complexity, and cost compared to creating a coin with a separate blockchain.
Coins require high security for the entire blockchain network. Tokens rely on the security of the host blockchain, but smart contracts must be carefully audited to avoid exploits, as they manage real value automatically.
Efficient token contracts reduce transaction fees on blockchains like Ethereum. Lower gas costs encourage more transactions, higher user engagement, and wider adoption, especially for applications like DeFi and gaming.
Security is critical because smart contracts control real value. Audits, testing, and proper access control reduce risks, prevent hacks, and maintain trust in coins and tokens.
Smart contracts are self-executing programs on a blockchain that enforce token rules automatically, managing transfers, minting, burning, and permissions without human intervention.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures verify user identity, prevent illegal activities, and are mandatory in many regions for crypto projects involving trading, payments, or investments.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







