Key Takeaways
- The global NFT market reached 48.7 billion in 2025, showing a strong recovery from previous volatility, with projections suggesting growth toward 247 billion by 2029, driven by broader adoption and real-world utility use cases.
[1] - OpenSea maintains market dominance with 90 percent of Ethereum NFT trading volume as of October 2024, hosting over 80 million NFTs and generating approximately 14.68 billion in 2024 trading volume.[2]
- NFT marketplace development costs range from 30,000 to 150,000 dollars, depending on features, with basic platforms costing 30,000 to 50,000 and advanced platforms with custom smart contracts and multi-chain support reaching 150,000 or more.[3]
- Gaming NFTs represent a massive market valued at approximately 471.90 billion in 2024, with forecasts projecting growth to 942.58 billion by 2029, with trading volume concentrated heavily in PFP assets at 37 percent and gaming at 25 percent.[4]
- Smart contracts automate NFT transactions by handling cryptocurrency transfers, NFT delivery to buyers, royalty distributions to creators, and permanent blockchain recording without intermediaries.[5]
- Virtual real estate NFTs are predicted to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 27.4 percent, with platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox enabling users to buy, develop, and monetize digital property.[6]
- Security challenges remain significant, with over 100 million worth of NFTs stolen from July 2021 to July 2022, with scammers averaging around 300,000 per incident, making robust security measures essential.[7]
Understanding NFT marketplaces has become increasingly important as the digital economy continues to evolve in ways we couldn’t have imagined just a few years ago. These platforms are transforming how we think about ownership, creativity, and value in the digital world.
Understanding NFT Marketplaces
An NFT marketplace works as a digital platform where people can create, buy, sell, and trade non-fungible tokens. Think of it like eBay or Amazon, but instead of physical products, you’re dealing with unique digital assets that live on the blockchain. The difference is huge because each NFT has its own identity, history, and proof of ownership that nobody can fake or duplicate.
NFT marketplaces connect creators with collectors through blockchain technology. When someone uploads a digital file like artwork, music, or even a video game item, the marketplace converts it into an NFT through a process called minting. This creates a unique token on the blockchain that represents ownership of that specific digital asset.
The global NFT market has shown remarkable growth patterns. In 2025, the market stands at approximately 48.7 billion dollars, up from 36.2 billion in 2024. What makes this even more interesting is that analysts project the market could reach nearly 247 billion by 2029. These numbers aren’t just hype; they represent real transactions happening across various industries from digital art to gaming assets.
Recommended Reading:
How NFT Marketplaces Actually Work
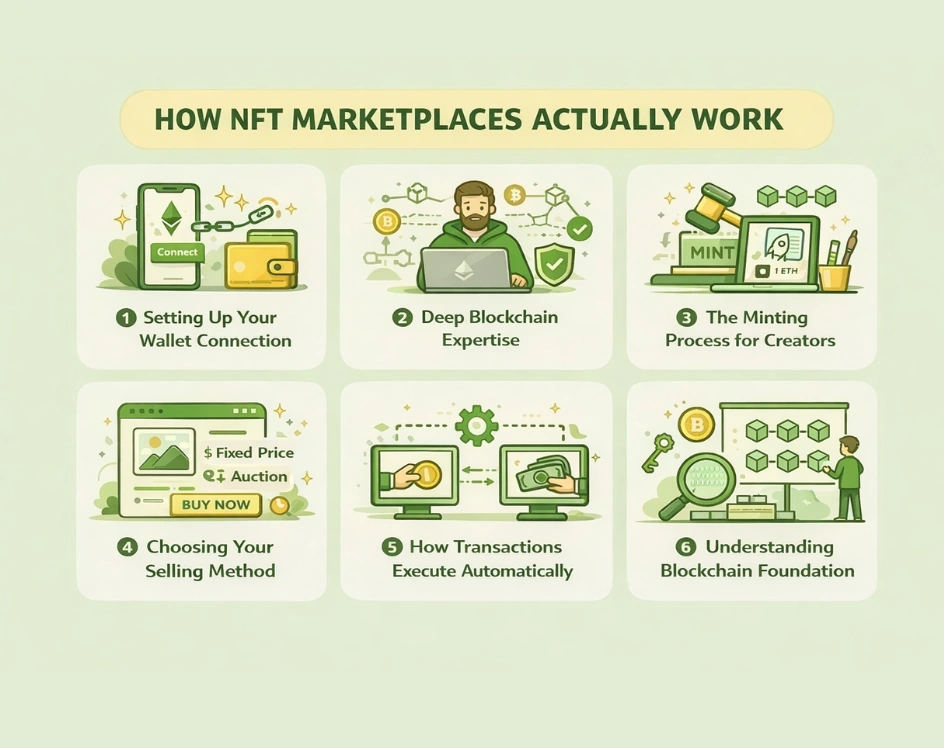
The mechanics behind NFT marketplaces involve several interconnected systems working together. Let me break down the entire process into digestible steps.
- Setting Up Your Wallet Connection
The first thing you need to do is connect a crypto wallet to the marketplace. Popular options include MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, or WalletConnect. These wallets don’t actually store your NFTs like files on your computer. Instead, they hold the keys that prove you own those assets on the blockchain. Think of it like having a key to a safe deposit box rather than carrying the valuables in your pocket. - The Minting Process for Creators
For creators, the journey starts with uploading their digital work to the platform. The marketplace reads this file and creates metadata that includes details about the creator, the creation date, and any specific attributes of the piece. Then comes minting, where the platform generates a unique token on the blockchain and assigns it to the creator’s wallet address. This is where your digital file transforms into a verifiable, ownable asset. - Choosing Your Selling Method
Sellers get to choose how they want to sell their NFTs. Some prefer setting a fixed price where buyers can purchase immediately, like buying something from a regular online store. Others opt for auctions where people bid against each other, often creating more excitement and potentially higher sale prices. The marketplace handles all these transactions through smart contracts, which are basically automated agreements written in code. - How Transactions Execute Automatically
When someone buys an NFT, the magic of smart contracts takes over. The contract executes automatically without any human intervention. It transfers the cryptocurrency from the buyer’s wallet, sends the NFT to the buyer’s address, distributes any royalties to the creator if applicable, and records everything on the blockchain. This entire process happens without any intermediary holding the funds or assets, which is what makes it decentralized and trustless. - Understanding Blockchain Foundation
Blockchain technology underpins everything in the NFT world. Most NFT marketplaces use Ethereum because it was the first blockchain to really support NFTs through standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155. However, other blockchains like Solana, Binance Smart Chain, and Cardano have also gained traction because they offer lower transaction fees and faster processing times. Each blockchain has its own advantages depending on what you’re trying to accomplish.
The Major Players in NFT Marketplaces
OpenSea remains the largest NFT marketplace with a commanding presence in the industry. In March 2024, OpenSea accounted for 87 percent of NFT trading volume, and by October 2024, this share had risen to 90 percent. The platform hosts over 80 million NFTs across multiple blockchains and has generated approximately 14.68 billion in trading volume throughout 2024.
What makes OpenSea particularly appealing is its user-friendly interface and broad support for different types of digital assets. Whether you’re looking for digital art, virtual real estate, gaming items, or collectibles, OpenSea probably has it. The platform launched its OS2 upgrade in May 2025, which brought multi-chain support across 19 blockchains, faster transactions, lower gas fees, and a rewards system called Voyages, where users earn points for trading activity.
Blur entered the scene as a challenger focused on professional traders. While OpenSea appeals to everyone from beginners to experienced collectors, Blur built its reputation by offering tools that serious traders need. The platform allows bulk trades, real-time floor price tracking, and advanced analytics. In 2023 and early 2024, many traders moved from OpenSea to Blur because they could execute trades faster and more cheaply.
The competition between these two has been fascinating to watch. Blur briefly overtook OpenSea in Ethereum trading volume before slipping back. What’s interesting is that despite Blur’s trading volume dominance at certain points, OpenSea consistently maintains more individual traders, with over 377,000 traders compared to Blur’s 36,000. This suggests much of Blur’s volume comes from high-frequency traders rather than casual collectors.
Rarible takes a different approach by focusing on community governance and creator empowerment. The platform introduced its RARI governance token, which allows users to vote on important decisions like feature updates, fee changes, and marketing strategies. Artists appreciate Rarible because it offers lazy minting, where creators can list NFTs without paying upfront gas costs. The platform also allows custom-branded storefronts where creators can build their own marketplace presence.
Magic Eden started on Solana but has expanded to support Ethereum, Polygon, and even Bitcoin Ordinals. This multi-chain strategy has helped it position itself as an agile challenger in the marketplace landscape. The platform has actually overtaken Blur in recent months, showing how quickly the competitive dynamics can shift in this space.
NFT Marketplace Development Process
Building an NFT marketplace involves multiple stages that each require careful planning and execution. The first step is always defining your niche and target audience. Instead of trying to compete with giants like OpenSea as a general marketplace, successful platforms focus on specific domains where they can excel, whether that’s gaming NFTs, real estate tokenization, fine art, or branded collections.
Platform Architecture Decisions:
When you’re building an NFT marketplace, architecture decisions directly impact how well your platform can scale and handle growing user numbers. The choice of blockchain integration affects both security protocols and transaction efficiency. Ethereum remains the most popular choice, powering about 62 percent of NFT transactions. However, developers also consider alternatives like Solana for lower fees or Binance Smart Chain for compatibility with Ethereum tools.
Token standards matter significantly. ERC-721 is the standard for creating unique NFT’s where each token is completely different from others. ERC-1155 allows for both fungible and non-fungible tokens in the same contract, which is useful for games where you might have both unique items and stackable resources. Choosing the right standard depends on what kind of assets your marketplace will support.
Storage solutions require careful consideration. While the NFT itself lives on the blockchain, the actual media files, such as images or videos, are often too large to store there. Many platforms use IPFS, a decentralized storage solution that ensures digital content remains accessible and resistant to censorship. This approach balances blockchain security with practical file storage needs.
Essential Features to Include:
A proper storefront is your marketplace’s face to the world. Buyers need to see clear item previews, current prices, active bids, and ownership history. Transparency builds trust, especially in a market built on the concept of digital scarcity. When thousands of NFTs get listed daily, effective filters become essential. Users should be able to sort by category, price range, popularity, blockchain, and creator.
The minting and listing process should feel simple for creators. Upload the file, add metadata like description and attributes, set royalty percentages, and list it for sale. If this process takes too long or feels complicated, talented creators will go to competitor platforms instead.
Flexible auction mechanics keep trading active and engaging. Some NFTs sell best at fixed prices for immediate purchase, while others thrive in competitive bidding situations. Your marketplace should support both, along with features like auction timers, automatic bid extensions, and watchlists where users can track items they’re interested in.
Wallet integration is absolutely non-negotiable. Without connecting crypto wallets, the marketplace simply cannot function. Supporting multiple wallet options like MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, and WalletConnect gives users flexibility in how they manage their assets.
Smart contracts automate the entire transaction process. When someone buys an NFT, the smart contract handles transferring the payment, moving the NFT to the new owner, calculating and distributing any royalty fees to the original creator, and recording all of this permanently on the blockchain.
Development Timeline and Costs:
The cost to develop an NFT marketplace in 2025 varies significantly based on complexity and features. A basic marketplace with essential functionality like user authentication, bidding, asset uploading, and purchasing typically ranges from 30,000 to 50,000 dollars. However, platforms with advanced features, including integrated wallets, custom smart contracts, decentralized storage, secondary market support, and robust security measures, can cost 150,000 dollars or more.
Several factors influence these costs. The development method matters tremendously. Building from scratch gives you complete control over every aspect, but takes longer and costs more. White-label solutions are pre-built platforms with essential features that you can customize for your specific needs, offering a faster and more budget-friendly option.
Your choice of blockchain affects development expenses. Ethereum integration typically costs between 10,000 and 20,000 dollars. Binance Smart Chain uses a Proof of Staked Authority mechanism that provides lower transaction fees and compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine, meaning smart contracts can operate on both platforms without extra development work. Cardano uses an energy-efficient proof-of-stake protocol but only started enabling smart contracts in 2021, so the ecosystem is still maturing.
The expertise and size of your development team play a significant role in overall costs. Hiring experienced blockchain developers, UI/UX designers, and security specialists ensures a high-quality product but requires substantial investment. Security implementation is particularly important, with regular audits and security checks essential to prevent vulnerabilities and hacks.
NFT Marketplace Development Costs
| Development Component | Cost Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Platform Features | $30,000 – $50,000 | User authentication, NFT minting, buying/selling functionality, basic wallet integration |
| Advanced Platform Features | $100,000 – $150,000+ | Custom smart contracts, multi-chain support, advanced analytics, decentralized storage, royalty management |
| UI/UX Design | $5,000 – $20,000 | Simple interface vs. custom-branded design with intricate elements |
| Blockchain Integration | $10,000 – $20,000 | Ethereum most common, alternatives like Solana or BSC may vary |
| Smart Contract Development | Included in platform costs | Token standards (ERC-721, ERC-1155), security audits, testing |
| Security Implementation | $5,000 – $15,000 | Encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits |
| Ongoing Maintenance | $1,000 – $5,000/month | Server hosting, updates, customer support, security monitoring |
Real-World Use Cases for NFT Marketplaces
NFT marketplaces have expanded far beyond just digital art. Let me show you how different industries are using this technology in practical ways.
Digital Art Revolution
Digital art was one of the first major breakthroughs for NFTs. Artists can now tokenize their work on the blockchain and sell it as unique digital pieces. The famous sale of Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days” for 69.3 million through Christie’s auction house brought NFTs into mainstream consciousness. Since 2021, OpenSea alone reported 38 billion in trading volume, showcasing the massive financial scale of NFT artwork. Artists who previously struggled to monetize digital work now have a viable marketplace.
Gaming and Virtual Items
Gaming represents another major sector embracing NFTs with enthusiasm. In many online games, players spend real money on virtual items like character skins, weapons, and other digital goods. NFTs allow these virtual items to have provable ownership, meaning players can buy, sell, and trade them like physical collectibles. Games like Axie Infinity, Decentraland, and The Sandbox have built entire economies around NFT-based assets. The gaming NFT market shows impressive growth, with values around 471.90 billion in 2024 and forecasts projecting growth to 942.58 billion by 2029.
Virtual Real Estate Investment
Virtual real estate NFTs extend beyond gaming into the broader metaverse concept. In these virtual worlds, land ownership is tracked through NFTs, creating true digital property rights. Major celebrities like Snoop Dogg and Paris Hilton, along with corporations like Gucci and iHeartMedia, have purchased virtual real estate to establish their presence in the metaverse. The virtual real estate market is predicted to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 27.4 percent in the coming years. Virtual land owners can develop properties, host events, run businesses, or rent to others.
Physical Real Estate Tokenization
Real-world real estate is also beginning to leverage NFT technology. By converting property deeds and land titles into NFTs, blockchain-based platforms simplify ownership verification and trading. This approach proves particularly beneficial in regions with underdeveloped land registration systems, providing an immutable and decentralized way to track ownership. Platforms like Landano on Cardano are pioneering blockchain-integrated property registration in Africa.
Fractional Property Ownership
NFTs enable fractional ownership of real estate, allowing investors to purchase shares of a property instead of buying an entire building. This increases liquidity in real estate markets and makes property investment more accessible to regular people who couldn’t afford whole properties. Platforms like Omni-PSI launched as the world’s first fractional real estate NFT marketplace, allowing users to purchase interests in properties and receive distributions from rental income according to their ownership shares.
Sports Collectibles and Memorabilia
Sports NFTs have created new ways for fans to engage with their favorite teams and athletes. NBA Top Shot, built on the Flow blockchain, sells official basketball highlight clips as NFTs. These “moments” capture specific plays from games, and collectors trade them based on the player’s performance, rarity of the moment, and historical significance. The platform has generated substantial trading volume by connecting sports fandom with digital collectibles. It’s like trading cards for the digital age.
Event Ticketing Solutions
Event ticketing represents a practical application of NFT technology. NFTs can serve as digital tickets that prove attendance while preventing fraud and scalping. The blockchain provides a transparent record of ticket ownership and transfers, making it easier to verify authenticity. As of 2025, event ticketing NFTs make up 5.3 percent of ticket sales across major venues in the United States. Beyond entry, these NFT tickets can become collectible memorabilia that appreciate in value over time.
Music Distribution and Royalties
Music artists are using NFTs to distribute their work directly to fans and earn royalties on secondary sales. When someone resells an NFT containing a music track, the original artist can automatically receive a percentage of that sale through smart contracts. This creates ongoing revenue streams that traditional music distribution doesn’t provide. Artists also use NFTs to offer exclusive experiences, limited edition content, or special access to concerts and meet-and-greets.
Types of NFT Marketplaces
Open marketplaces like OpenSea welcome anyone to create, buy, and sell NFTs across various categories. These platforms offer the broadest selection of digital assets, from art and music to virtual real estate and domain names. The advantage is a massive variety and high liquidity, but the downside is less curation, which means quality can vary significantly. Development costs for open marketplaces typically range from 50,000 to 150,000 dollars, depending on features and scale.
Curated marketplaces take a selective approach, requiring artists to apply and receive approval before they can sell on the platform. SuperRare exemplifies this model, focusing on high-end digital art from established or carefully vetted emerging artists. These platforms maintain quality standards that appeal to serious collectors willing to pay premium prices. Foundation and KnownOrigin also follow this model. The curated approach builds trust and prestige but limits the number of creators who can participate. Development costs for curated platforms range from 80,000 to 200,000 dollars due to the additional verification systems and quality control mechanisms.
Niche marketplaces focus on specific categories or communities. NBA Top Shot concentrates solely on basketball highlights, while Axie Marketplace serves the Axie Infinity gaming community. Sorare specializes in fantasy football collectibles. These focused platforms develop deep expertise in their chosen domain and build tight-knit communities of enthusiasts. They offer specialized features that general marketplaces can’t match, like integration with specific games or sports leagues.
Gaming-focused marketplaces like Axie Marketplace and The Sandbox Marketplace cater specifically to gamers who want to trade in-game assets. These platforms understand the unique needs of gaming communities, offering features like character stats, item attributes, and integration with the actual games. The gaming NFT market is particularly robust, with transaction volumes concentrated heavily in this sector.
Types of NFT Marketplaces
| Marketplace Type | Examples | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open/General Purpose | OpenSea, Rarible, Magic Eden | Wide variety of creators and collectors | Multi-category support, largest selection, highest liquidity, minimal entry barriers |
| Curated/High-End | SuperRare, Foundation, KnownOrigin | Serious art collectors, established artists | Selective artist approval, premium quality focus, higher average prices, prestige factor |
| Gaming-Specific | Axie Marketplace, The Sandbox Marketplace, Gods Unchained | Gamers and game developers | In-game asset integration, character stats, item attributes, community tools |
| Sports NFTs | NBA Top Shot, Sorare, UFC Strike | Sports fans and collectors | Official league partnerships, moment-based collectibles, and player statistics |
| Music NFTs | Royal, Sound.xyz, Catalog | Musicians and music collectors | Audio streaming, royalty sharing, fan engagement tools, exclusive content |
| Real Estate/Metaverse | Decentraland, The Sandbox, Somnium Space | Virtual property investors | Land ownership, development tools, virtual world integration, location-based pricing |
| Domain Names | Ethereum Name Service (ENS), Unstoppable Domains | Web3 developers and investors | Blockchain-based domains, wallet addressing, and decentralized websites |
Revenue Models for NFT Marketplaces
Transaction fees represent the primary revenue source for most NFT marketplaces. Platforms typically charge between 1 and 5 percent of each sale. OpenSea charges 2.5 percent on standard transactions, while OpenSea Pro offers reduced fees ranging from 0 to 0.5 percent to attract high-volume traders. Rarible takes 1 percent from both buyers and sellers, totaling 2 percent per transaction. These fees may seem small, but when applied to billions in trading volume, they generate substantial revenue.
Gas fees or listing fees provide another income stream. When creators mint NFTs or list them for sale, they often pay fees to cover the computational costs of recording transactions on the blockchain. Some marketplaces charge these fees directly, while others have implemented “lazy minting,” where the gas fees are only paid when someone actually purchases the NFT, making it more accessible for creators to list their work.
Governance tokens offer both a revenue model and a way to build community engagement. Rareible issues RARI tokens to reward users who buy or sell collectibles on the platform. These tokens give holders voting rights on platform decisions and can appreciate in value as the marketplace grows. OpenSea announced its SEA token in February 2025 with a multi-phase airdrop rewarding users based on historical trading volume and participation in the OS2 Voyages program.
Premium features and subscriptions provide opportunities for additional revenue. Some marketplaces charge for enhanced visibility in search results, featured listings on the homepage, or access to advanced analytics tools. Professional traders often pay for these premium services to gain competitive advantages in the market.
Advertising and partnerships generate income through promotional placements. New artists or NFT projects pay to reach the marketplace’s audience through banner ads, featured collections, or newsletter mentions. Major brands partner with marketplaces to launch exclusive NFT collections, often involving revenue-sharing arrangements.
Challenges and Considerations
Running an NFT marketplace isn’t all smooth sailing. There are real challenges that platforms need to address to maintain trust and sustainability.
Security Threats and Fraud Prevention
Security concerns remain at the forefront of NFT marketplace operations. Between 2017 and 2024, more than 8 million in illegal funds were laundered through NFT platforms. Over 100 million worth of NFTs were reported stolen due to scams from July 2021 to July 2022, with scammers averaging around 300,000 per incident. July 2022 saw the highest number of NFT theft,s with more than 4,600 NFTs stolen. These numbers show why security can’t be an afterthought.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Platforms must implement robust security measures, including SSL encryption for all data transmission, two-factor authentication for user accounts, KYC and AML compliance procedures to prevent fraud, smart contract audits to identify vulnerabilities before deployment, and regular security monitoring to detect suspicious activity. Users also need education about phishing attacks, fake NFTs, and scam projects to protect themselves from common threats.
Environmental Impact Concerns
Environmental concerns about blockchain energy consumption have sparked ongoing debates. The substantial energy required for proof-of-work blockchains like Ethereum raised serious questions about the environmental impact of NFTs. Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake has helped reduce energy consumption by approximately 99.95 percent, significantly improving its environmental profile. However, concerns persist about other blockchain networks that still use energy-intensive consensus mechanisms.
Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations
Market volatility affects both creators and collectors in significant ways. NFT prices can fluctuate dramatically based on broader crypto market trends, celebrity endorsements, social media hype, and changing consumer interests. The market experienced extreme highs in 2021 and 2022, followed by significant corrections. By 2024 and 2025, trading volumes stabilized around 600 to 700 million in revenue, suggesting a shift from speculative hype toward more sustainable growth.
Navigating Regulatory Uncertainty
Regulatory uncertainty presents challenges for marketplace operators worldwide. Different countries have varying approaches to regulating NFTs, with questions about securities classification, taxation rules, intellectual property rights, and consumer protection standards. India’s Digital Asset Bill 2025 includes a 15 percent capital gains tax on NFT trades, affecting marketplace liquidity. The legal status of fractional NFTs remains unclear in many regions, with regulatory sandboxes in place in the UK and Singapore to test new approaches.
Copyright and Intellectual Property Issues
Copyright and intellectual property issues complicate the NFT landscape significantly. Just because someone mints an NFT doesn’t mean they own the copyright to the underlying work. The NFT represents ownership of the token itself, not necessarily the intellectual property rights. Some collections like Bored Ape Yacht Club explicitly transfer IP rights to NFT owners, while others like CryptoPunks initially didn’t allow commercial use but later changed their policy. Marketplaces must implement verification processes to prevent unauthorized minting of copyrighted material.
Launch Your NFT Marketplace Platform Today:
We bring 8+ years of blockchain expertise to NFT marketplace development. Our specialized team handles everything from smart contract creation to multi-chain integration, ensuring your platform is built for growth, security, and user experience. Whether you need a curated art marketplace or a gaming NFT platform, we deliver solutions that work.
The Future of NFT Marketplaces
Integration with other technologies promises to enhance NFT marketplace functionality. Virtual reality and augmented reality integration can provide immersive experiences for collectors to view and interact with their NFTs. Imagine walking through a virtual gallery displaying your NFT art collection or trying on virtual fashion NFTs in an AR mirror before purchasing.
Artificial intelligence is already reshaping NFTs, with around 30 percent of new projects in 2025 incorporating AI elements. AI-generated content fuels new NFT projects, while intelligent NFTs combine blockchain provenance with AI adaptability. These iNFTs can evolve, upgrade, and respond to user interaction, creating dynamic digital assets rather than static ones.
Cross-chain functionality is becoming increasingly important. Currently, most NFTs exist on specific blockchains and can’t easily move between them. Layer-2 solutions and cross-chain bridges are emerging to address this limitation, allowing NFTs to be traded and used across multiple blockchain networks. This interoperability will expand the potential market for each NFT and reduce friction in trading.
Utility-focused NFTs are gaining traction over purely speculative collectibles. Identity NFTs used in decentralized IDs and memberships have grown significantly, with over 12 million issued in 2025. Event ticketing NFTs now represent 5.3 percent of ticket sales across major US venues. Phygital NFTs that link digital tokens to physical goods saw a 60 percent rise in transaction volume, led by luxury brands connecting real-world products to blockchain certificates of authenticity.
Real-world asset tokenization represents one of the most promising future applications. Beyond real estate, NFTs could represent ownership of fine art, collectible cars, luxury watches, investment-grade wine, and other physical assets. This tokenization could turn into a 16 trillion market by 2030, according to some analysts. The ability to fractionalize expensive assets makes investing accessible to more people while maintaining secure, transparent ownership records.
Mainstream adoption by major brands continues to accelerate. Companies like Nike, Adidas, Gucci, and Tiffany have launched NFT collections or NFT-related products. Starbucks introduced its Odyssey program using NFTs for loyalty rewards. These corporate implementations help normalize NFTs for people who might be intimidated by crypto culture, potentially bringing millions of new users into the ecosystem.
Choosing the Right NFT Marketplace Development Partner
When businesses decide to build their own NFT marketplace, selecting the right development company becomes critical to success. Here’s what you should look for.
Evaluating Blockchain Expertise and Track Record
Look for development partners with proven track records in blockchain projects. Review their portfolio to see if they’ve successfully launched NFT marketplaces or similar blockchain applications. Ask about the challenges they faced in previous projects and how they solved them. Technical expertise in smart contract development, blockchain integration, and decentralized systems is essential but shouldn’t come at the expense of usability.
Comprehensive Service Offerings
NFT marketplace services should be comprehensive, covering everything from initial strategy and planning through design, development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance. The best companies take a consultative approach, helping you define your niche, understand your target users, and make informed decisions about features and blockchain platforms. You don’t want a developer who just codes what you ask for without providing strategic input.
Security Knowledge and Practices
Security expertise deserves special emphasis when evaluating potential development partners. Ask about their approach to smart contract auditing, penetration testing, and ongoing security monitoring. Request information about security incidents in their previous projects and how those were handled. A development company that dismisses security concerns or treats them as an afterthought is one to avoid completely.
Scalability Planning and Architecture
NFT marketplace development solutions should be scalable from the start. Your marketplace might start small, but you need architecture that can handle growth in users, transactions, and features. Ask potential partners how they approach scalability, what technologies they recommend, and how they’ve handled scaling challenges in past projects. Building something that works for 100 users but breaks at 10,000 users is a costly mistake.
Communication and Project Management
Communication and project management capabilities matter just as much as technical skills. You want a development partner who keeps you informed, explains technical concepts clearly, involves you in key decisions, and delivers on schedule. Ask about their development methodology, how often they provide updates, and how they handle change requests or unexpected challenges. Good communication prevents misunderstandings and keeps projects on track.
Frequently Asked Questions
An NFT marketplace is a digital platform where you can create, buy, sell, and trade non-fungible tokens. It works similarly to eBay or Amazon, but for unique digital assets on the blockchain. The marketplace connects creators with collectors, handling everything from minting (creating NFTs) to executing transactions through automated smart contracts.
Treasure NFT generally refers to rare or high-value digital collectibles that hold unique significance within an NFT marketplace. These NFTs may represent limited edition assets, gaming items, or themed digital collectibles that attract collectors due to their scarcity and utility.
Development costs vary significantly based on complexity. A basic marketplace with essential features typically costs $30,000 to $50,000, while advanced platforms with custom smart contracts, multi-chain support, and robust protection measures can cost $150,000 or more. Ongoing maintenance runs about $1,000 to $5,000 per month.
Ethereum powers about 62% of NFT transactions and remains the most popular choice due to its established ecosystem and token standards (ERC-721 and ERC-1155). However, alternatives like Solana offer lower transaction fees and faster processing, while Binance Smart Chain provides compatibility with Ethereum tools at reduced costs.
OpenSea is the largest general-purpose marketplace, accounting for 90% of NFT trading volume as of October 2024, with over 80 million NFTs across multiple blockchains. Other platforms differentiate themselves through specialization—Blur focuses on professional traders with advanced tools, Rarible emphasizes community governance, and platforms like NBA Top Shot concentrate on specific niches like sports collectibles.
Marketplaces primarily earn revenue through transaction fees (typically 1-5% per sale), gas or listing fees for minting NFTs, premium features and subscriptions for enhanced visibility, governance tokens that can appreciate in value, and advertising partnerships with brands and creators.
While marketplaces implement protection measures, risks exist. Between July 2021 and July 2022, over $100 million worth of NFTs were stolen through scams. Reputable platforms use SSL encryption, two-factor authentication, smart contract audits, and KYC/AML compliance. Users should also educate themselves about phishing attacks and verify NFT authenticity before purchasing.
Absolutely. NFTs are used for gaming items and virtual goods, virtual and physical real estate tokenization, sports collectibles and highlight moments, event ticketing (5.3% of major US venue ticket sales), music distribution with royalty sharing, and even fractional ownership of real-world assets like property and luxury goods.
Open marketplaces like OpenSea allow anyone to create and sell NFTs across various categories, offering maximum variety but varying quality. Curated marketplaces like SuperRare require artists to apply and receive approval, maintaining higher quality standards and premium pricing, but limiting creator access. Development costs for curated platforms ($80,000-$200,000) exceed open marketplaces ($50,000-$150,000) due to verification systems.
The global NFT market stands at approximately $48.7 billion in 2025, up from $36.2 billion in 2024. Analysts project it could reach nearly $247 billion by 2029. The gaming NFT sector alone was valued at $471.90 billion in 2024, with forecasts of $942.58 billion by 2029.
Look for proven blockchain expertise with a strong portfolio of successful projects, comprehensive services covering strategy through maintenance, thorough knowledge of protection protocols and audit practices, architecture planning that accommodates growth, and clear communication with effective project management capabilities. The partner should provide strategic input, not just coding services.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







