Key Takeaways
- Synthetic Asset Fundamentals: Creating synthetic assets on a DEX enables tokenized exposure to real-world assets like stocks, commodities, and currencies through smart contracts without requiring ownership of underlying assets, democratizing access to global markets through blockchain technology.
- Collateralization Requirements: Minting synthetic assets on a DEX requires posting cryptocurrency collateral typically ranging from 150% to 750% of synthetic asset value, with ratios varying based on protocol design, asset volatility, and risk management parameters.
- Platform Selection: Major protocols for synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges include Synthetix, Mirror Protocol, and UMA, each offering distinct collateralization models, supported assets, fee structures, and technical requirements suited to different user needs and expertise levels.
- Technical Process: The steps to create synthetic assets involve wallet connection, collateral deposit, parameter configuration, smart contract interaction for minting, and position management including monitoring collateralization ratios and potential liquidation risks throughout the asset lifecycle.
- Smart Contract Architecture: Synthetic assets smart contract on DEX platforms utilize oracle price feeds, collateral management systems, liquidation mechanisms, and token minting/burning functions to maintain asset pegs and system solvency through algorithmic enforcement of collateralization requirements.
- Risk Management: Creating synthetic derivatives on DEX involves managing liquidation risk through adequate collateral buffers, monitoring positions regularly, understanding protocol-specific mechanics, and implementing protective measures against market volatility and smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Deployment Considerations: Successfully deploying synthetic tokens on DEX requires understanding gas optimization strategies, liquidity provision options, trading pair creation, and integration with decentralized exchange infrastructure to ensure asset utility and trading accessibility.
- Profit Mechanisms: Revenue opportunities from synthetic asset creation include trading fee earnings from liquidity provision, collateral yield generation, arbitrage trading between synthetic and spot markets, and protocol incentive rewards distributed to platform participants.
- Regulatory Awareness: Guide to building synthetic assets on decentralized platforms must consider jurisdictional variations in regulatory treatment, with synthetic stocks facing potential securities regulation while commodity and currency synthetics existing in evolving legal frameworks requiring ongoing compliance monitoring.
- Ecosystem Integration: Effective synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges extends beyond minting to include liquidity pool integration, cross-protocol composability, oracle reliability assessment, and community engagement supporting long-term asset viability and adoption.
The decentralized finance ecosystem has revolutionized access to financial instruments, with synthetic assets representing one of the most innovative breakthroughs in blockchain technology. These digital tokens unlock exposure to virtually any real-world asset, from traditional stocks and commodities to exotic derivatives and indices, without requiring direct ownership or traditional financial intermediaries. For traders, investors, and institutions seeking global market access with blockchain’s inherent advantages, understanding how to create synthetic assets on a DEX has become an essential skill in the modern financial landscape.
This comprehensive guide explores the complete process of synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges, from fundamental concepts through technical implementation and best practices. Whether you’re an experienced DeFi participant looking to expand your capabilities or a newcomer seeking to understand this powerful financial primitive, this tutorial provides the practical knowledge necessary to navigate the synthetic asset landscape confidently. We’ll examine the underlying mechanisms, walk through step-by-step creation processes, evaluate leading platforms, and discuss critical considerations for successful synthetic asset deployment and management.
How to Create Synthetic Assets on a DEX: Introduction to Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets represent a paradigm shift in how we conceptualize and access financial markets. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized oracle networks, these innovative instruments enable anyone with an internet connection to gain exposure to assets that were previously accessible only through traditional financial systems with their associated barriers, costs, and restrictions. The ability to create and trade synthetic assets on decentralized platforms democratizes finance in ways previously unimaginable.
What are Synthetic Assets?
Synthetic assets are tokenized derivatives that mirror the price movements of underlying assets without requiring direct ownership of those assets. Think of them as digital representations or “synthetic” versions of real-world assets, created and maintained through smart contracts on blockchain networks. A synthetic gold token, for example, tracks the price of physical gold, allowing holders to gain economic exposure to gold price movements while maintaining the token on a blockchain with all the associated benefits of digital assets including 24/7 trading, instant settlement, and composability with other DeFi protocols.
The mechanism behind synthetic assets involves collateralized debt positions where users lock cryptocurrency as collateral to mint synthetic tokens representing various assets. Oracle networks continuously update price information from external markets, ensuring synthetic assets maintain accurate pricing relative to their real-world counterparts. This architecture enables creation of synthetic versions of virtually any asset with a reliable price feed, from traditional stocks and commodities to more exotic instruments like indices, volatility products, or even other cryptocurrencies. Understanding DEX architectures provides crucial context for synthetic asset mechanics.
Why Create Synthetic Assets on a DEX?
Creating synthetic assets on decentralized exchanges offers compelling advantages over traditional financial instruments. First, they provide permissionless access to global markets without geographic restrictions, account minimums, or institutional gatekeepers. A user in any corner of the world can gain exposure to assets that might be completely inaccessible through conventional channels due to regulatory barriers, capital requirements, or market hour limitations. Second, synthetic assets enable 24/7 trading without market closures, weekends, or holidays, allowing participants to respond to global events and manage positions continuously.
Beyond accessibility, synthetic assets integrate seamlessly with broader DeFi ecosystems, enabling composability that traditional assets cannot match. Synthetic tokens can be used as collateral in lending protocols, provided as liquidity in automated market makers, combined in complex yield strategies, or integrated into portfolio management tools. This composability creates innovative financial products and strategies impossible in traditional finance. Additionally, blockchain transparency provides complete auditability of synthetic asset creation, collateralization, and redemption, eliminating counterparty opacity that plagues traditional derivatives markets. The combination of global accessibility, continuous operation, DeFi integration, and transparency makes synthetic asset creation on DEX platforms increasingly attractive to sophisticated market participants.
Core Principle: Synthetic assets democratize access to global financial markets by removing intermediaries while maintaining economic exposure to virtually any asset through blockchain-based collateralization and oracle price feeds.
Understanding Synthetic Asset Creation on Decentralized Exchanges
The process of synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges relies on sophisticated smart contract systems that manage collateral, track prices, enforce liquidations, and maintain system solvency. Understanding these underlying mechanisms provides the foundation necessary for confident participation in synthetic asset markets, whether as a creator, trader, or liquidity provider. The technical architecture combines multiple DeFi primitives into cohesive systems enabling trustless creation and trading of synthetic derivatives.
Key Concepts Behind Synthetic Assets
Several fundamental concepts underpin all synthetic asset systems on DEX platforms. Collateralization forms the bedrock, where users must lock cryptocurrency exceeding the value of synthetic assets they wish to create, providing a safety buffer against price volatility. Oracle networks deliver external price data to smart contracts, enabling accurate tracking of target asset prices. Minting and burning mechanisms allow creation of new synthetic tokens when collateral is deposited and destruction of tokens when positions are closed. Liquidation systems protect protocol solvency by automatically closing undercollateralized positions, selling collateral to cover outstanding synthetic asset debt.
These concepts interact through carefully designed smart contracts that enforce rules algorithmically without human intervention. When you mint synthetic assets, the protocol calculates your collateralization ratio, ensures it exceeds minimum requirements, creates the requested tokens, and continuously monitors your position. If collateral value drops or synthetic asset value rises sufficiently to breach liquidation thresholds, the system triggers automated processes to close positions and protect overall system health. Understanding these mechanics proves essential before attempting synthetic asset creation, as improper management can result in liquidation and loss of collateral.
Collateralization of Synthetic Assets
Collateralization ratios represent the relationship between collateral value and synthetic asset debt, expressed as a percentage. A 200% collateralization ratio means you’ve deposited collateral worth twice the value of minted synthetic assets. Higher ratios provide greater safety margins against liquidation during market volatility but require more capital to create equivalent synthetic positions. Different protocols implement varying collateralization requirements based on their risk tolerance, with some using fixed ratios while others employ dynamic systems adjusting to market conditions.
When minting synthetic assets on a DEX, choosing appropriate collateralization levels involves balancing capital efficiency against liquidation risk. Maintaining ratios well above minimum requirements provides cushion for market movements, while ratios near minimums maximize capital leverage but increase liquidation probability. Some protocols offer different collateral options with varying ratios, allowing users to select risk-return profiles matching their strategies. Understanding your specific protocol’s collateralization mechanics, liquidation thresholds, and penalty structures proves critical for successful position management throughout the synthetic asset lifecycle.
Pegged vs. Non-Pegged Synthetic Tokens
Synthetic assets can be categorized as pegged or non-pegged based on their price relationship to target assets. Pegged synthetic tokens aim to maintain 1:1 value with their underlying assets through mechanisms like algorithmic supply adjustment, arbitrage incentives, or redemption guarantees. Synthetic USD stablecoins, for example, target $1 value through various stabilization mechanisms. Non-pegged synthetic derivatives track price movements proportionally but may trade at premiums or discounts to spot prices based on market conditions, similar to traditional futures contracts.
The distinction affects trading strategies and risk profiles significantly. Pegged synthetics should maintain tight correlation with spot prices, making them suitable for holding exposure long-term or using as stable value stores within DeFi ecosystems. Non-pegged synthetics may experience basis trading opportunities where price differences between synthetic and spot markets create arbitrage possibilities. When creating synthetic derivatives on DEX platforms, understanding whether your target synthetic maintains strict pegs or allows market-driven pricing informs position management and exit strategies. Most equity and commodity synthetics aim for pegged behavior, while some protocol-specific synthetic assets embrace non-pegged designs enabling unique tokenomics.
Popular DEX Protocols Supporting Synthetic Assets
Several leading protocols have emerged as go-to platforms for synthetic asset creation, each offering distinct approaches, supported assets, and user experiences. Synthetix pioneered the space with its comprehensive synthetic asset ecosystem on Ethereum and Optimism, enabling creation of synths tracking cryptocurrencies, forex, commodities, and indices. Mirror Protocol brought synthetic stocks to blockchain, allowing users to mint mAssets representing equity shares of major companies. UMA Protocol provides a flexible framework for creating custom synthetic tokens with varied parameters and use cases.
These platforms differ in collateral requirements, supported assets, fee structures, and technical complexity. Synthetix uses its native SNX token as collateral with high ratios around 400-500%, distributing trading fees to stakers. Mirror accepts multiple collateral types with lower ratios around 150%, focusing specifically on equity synthetics. UMA enables permissionless creation of synthetic assets with customizable parameters, supporting diverse use cases from KPI options to range tokens. Choosing among platforms for your DEX synthetic tokens tutorial needs involves evaluating which assets you want to create, your collateral preferences, fee tolerance, and desired level of control over parameters.
Examples of DEXs Offering Synthetic Asset Creation
Beyond the major protocols, various DEX platforms have integrated synthetic asset capabilities into their offerings. Kwenta provides a user-friendly interface for trading Synthetix synths with perpetual futures functionality. dYdX offers synthetic exposure through perpetual contracts with up to 20x leverage. Injective Protocol enables creation of synthetic perpetuals for diverse assets including equities, commodities, and forex. Each platform targets different user segments, from retail traders seeking simple interfaces to professional market makers requiring advanced order types and API access.
When evaluating platforms for deploying synthetic tokens on DEX infrastructure, consider factors beyond just technical capabilities. User base and liquidity depth affect slippage and trading costs. Protocol security track records and audit histories provide confidence in smart contract robustness. Community support and documentation quality influence learning curves and troubleshooting speed. Integration with other DeFi protocols expands use cases for created synthetic assets. Comprehensive platform evaluation ensures you select environments aligned with your expertise level, asset preferences, and strategic objectives for synthetic asset creation.
Differences Between Platforms
Platform differences in synthetic asset creation extend across multiple dimensions creating distinct user experiences and requirements. Collateral types vary from protocol-specific tokens to stablecoins to ETH and other major cryptocurrencies, affecting liquidity and value stability. Collateralization ratios range from conservative 750% requirements to aggressive 150% minimums, influencing capital efficiency and liquidation risk. Oracle implementations differ in update frequency, price sources, and manipulation resistance, critical for maintaining accurate synthetic asset prices.
Fee structures create varying economics for synthetic asset creation and trading, with some platforms charging minting fees, trading fees, redemption fees, or combinations thereof. Governance models range from centralized protocol control to fully decentralized DAO governance, affecting upgrade processes and parameter adjustments. Some platforms focus on permissionless synthetic creation allowing anyone to list new assets, while others curate asset listings ensuring quality and oracle reliability. Understanding these platform differences helps match your specific needs to optimal protocols, whether prioritizing capital efficiency, asset variety, governance participation, or integration with existing DeFi positions. Resources on DEX infrastructure illuminate these architectural choices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Synthetic Assets on a DEX
Creating your first synthetic asset on a decentralized exchange involves several distinct phases, each requiring careful attention to ensure successful minting and ongoing position management. This practical guide walks through the complete process from initial preparation through final deployment, providing actionable steps you can follow regardless of your chosen platform. While specific interfaces vary across protocols, the fundamental workflow remains consistent, enabling you to transfer knowledge across different synthetic asset platforms.
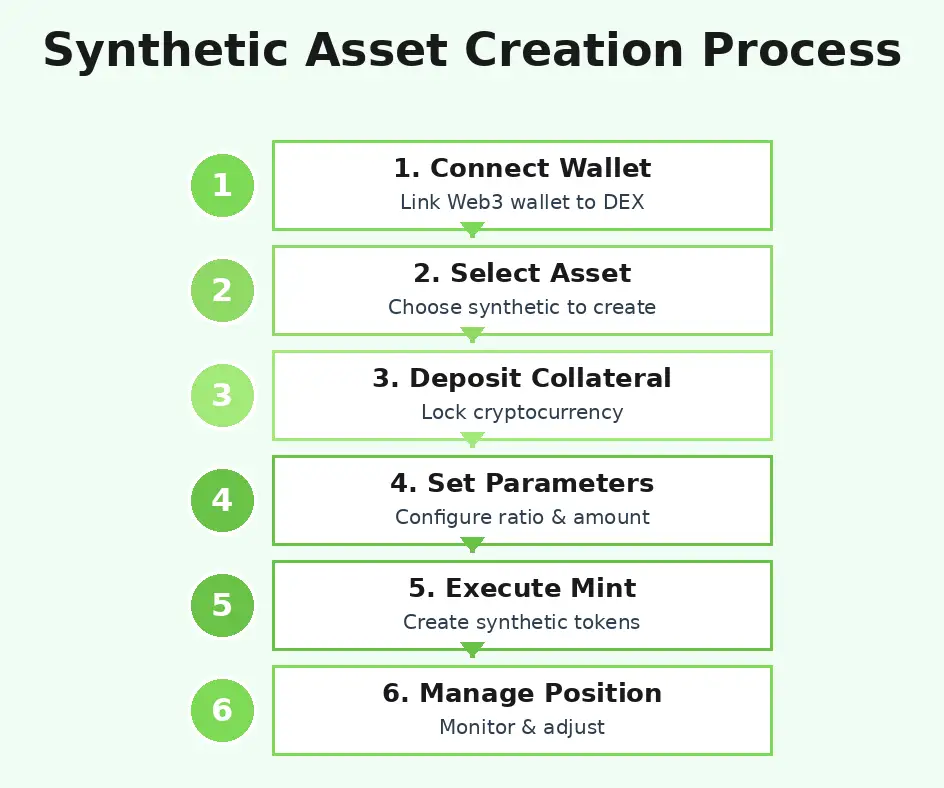
Prerequisites for Synthetic Asset Creation
Before beginning the steps to create synthetic assets, ensure you have the necessary technical setup and understanding. First, you need a Web3 wallet compatible with your chosen protocol’s blockchain, such as MetaMask for Ethereum-based platforms or Terra Station for Mirror Protocol. The wallet must contain sufficient native tokens for gas fees plus collateral for your synthetic asset position. Second, research your target synthetic asset thoroughly, understanding its price oracle sources, historical volatility, and any specific quirks in its implementation.
Third, familiarize yourself with the protocol’s documentation, particularly sections covering collateralization ratios, liquidation mechanisms, and fee structures. Many protocols offer testnet environments where you can practice synthetic asset creation with worthless tokens before risking real capital. Fourth, consider setting up position monitoring tools or alerts notifying you of collateralization ratio changes approaching liquidation thresholds. Finally, ensure you understand the tax implications of synthetic asset creation in your jurisdiction, as minting and burning may constitute taxable events depending on local regulations. Proper preparation prevents costly mistakes during the actual creation process.
Required Wallets and Tokens
Wallet selection depends on your target protocol’s blockchain and your security requirements. Hardware wallets like Ledger or Trezor provide maximum security for significant positions but may have less convenient user experiences. Software wallets like MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet, or Trust Wallet offer better usability with moderate security suitable for most users. Some protocols provide native wallets optimized for their ecosystems with enhanced features like built-in position monitoring or collateral management tools.
Token requirements include the protocol’s accepted collateral types plus native blockchain tokens for gas fees. If using Synthetix, you need SNX tokens for collateral plus ETH for gas on Ethereum mainnet or ETH on Optimism. For Mirror Protocol, acceptable collateral includes UST stablecoin, mAssets, or other approved tokens. Always maintain surplus gas tokens beyond estimated requirements, as network congestion can increase costs unexpectedly. Some platforms allow collateral swapping within their interfaces, while others require pre-acquiring specific tokens through external exchanges. Understanding exact token requirements before beginning prevents frustrating delays during the creation process when time-sensitive opportunities might be present.
Understanding Smart Contract Requirements
While you don’t need to write smart contracts for using established synthetic asset platforms, understanding the smart contract requirements they impose helps you navigate the creation process smoothly. Most protocols require token approvals allowing their smart contracts to access your collateral tokens. This approval is a separate transaction from the actual minting, requiring its own gas fee. Some protocols batch approvals and minting into single transactions for improved user experience, while others separate them.
Synthetic assets smart contract on DEX platforms enforce specific parameter constraints you must satisfy. Minimum collateralization ratios define how much collateral relative to synthetic asset value you must maintain. Minimum position sizes prevent dust positions that would be uneconomical to liquidate. Maximum position limits may exist preventing excessive concentration. Some protocols implement time locks preventing immediate withdrawal of collateral after minting. Understanding these smart contract enforced rules beforehand ensures you structure positions appropriately and avoid rejection transactions wasting gas fees. Reading protocol documentation and examining successful transactions on block explorers provides insight into exact smart contract interactions required for your chosen platform.
| Platform | Supported Assets | Collateral Type | Min. Collateral Ratio | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetix | Crypto, forex, commodities, indices | SNX token | 400-500% | Diverse synthetic exposure |
| Mirror Protocol | US equities (stocks) | UST, mAssets | 150% | Stock market exposure |
| UMA Protocol | Custom (user-defined) | Various (configurable) | Variable | Custom derivatives |
| Kwenta | Perpetual futures (various) | sUSD (Synthetix) | Varies by leverage | Leveraged trading |
Minting Synthetic Assets on a DEX
The actual minting process translates theoretical knowledge into practical action, where you execute transactions creating synthetic assets backed by your collateral. This phase involves multiple steps that must be completed correctly to successfully mint your desired synthetic position. While interfaces differ across platforms, the underlying workflow remains consistent: connect wallet, approve collateral, configure position parameters, execute minting transaction, and verify successful creation. Each step requires attention to detail ensuring proper execution.
Connecting Your Wallet to the DEX
Wallet connection initiates your interaction with the synthetic asset protocol. Navigate to the platform’s web interface and locate the wallet connection button, typically in the top right corner. Click to initiate connection, which triggers your wallet to request permission for the website to view your public address and request transaction signatures. Grant these permissions, ensuring you’re on the authentic protocol website by verifying the URL carefully to avoid phishing sites that could steal your assets.
Once connected, the interface should display your wallet address and relevant token balances. Verify that you’re on the correct blockchain network matching the protocol’s requirements. MetaMask and similar wallets support multiple networks, and connecting to the wrong network prevents transactions from executing. If balances don’t display correctly, try refreshing the page or disconnecting and reconnecting your wallet. Some protocols require you to switch between different sections like minting, trading, or staking, so locate the specific minting or asset creation interface before proceeding with collateral approval and position creation.
Selecting the Asset to Create
Asset selection determines which synthetic token you’ll mint, directly affecting your economic exposure, collateral requirements, and potential risks. Browse the protocol’s available synthetic assets, which may be organized by category like cryptocurrencies, equities, commodities, or indices. Each asset listing typically displays current price, 24-hour change, trading volume, and sometimes specific parameters like collateralization requirements or oracle sources. Research your target asset thoroughly before minting, understanding its price behavior, liquidity depth, and any unique characteristics.
Consider starting with more liquid, established synthetic assets for your first creation rather than exotic or low-volume options. Higher liquidity provides tighter spreads and easier position exits if needed. Some platforms offer different versions of similar assets with varying parameters, such as inverse synthetics that profit from price decreases or leveraged versions amplifying exposure. Ensure you understand exactly which version you’re minting, as confusion between standard and inverse synthetics can result in positions contrary to your intended exposure. Once you’ve selected your target asset, note its current price and your planned position size to calculate required collateral amounts.
Providing Collateral and Setting Parameters
Collateral provision and parameter configuration represent the critical decision-making phase of synthetic asset creation. Enter the amount of synthetic assets you wish to mint, and the protocol calculates required collateral based on current prices and minimum collateralization ratios. Most interfaces display real-time calculations showing your collateral requirement, resulting collateralization ratio, and liquidation price at which your position would become undercollateralized and subject to liquidation.
Carefully consider your target collateralization ratio, balancing capital efficiency against liquidation risk. Setting ratios well above minimum requirements provides safety buffers for market volatility but requires more locked capital. Many experienced users maintain 50-100% excess collateralization beyond protocol minimums as a safety margin. Some platforms allow you to set specific collateralization targets with automatic warnings if you approach liquidation thresholds. Review all parameters before proceeding, including any fees that will be charged, time locks on collateral withdrawal, and specific liquidation mechanics. Double-checking these details prevents costly mistakes from misunderstanding protocol mechanics or entering incorrect amounts.
Executing the Minting Transaction
Transaction execution finalizes your synthetic asset creation, moving from planning to actual blockchain state changes. Click the mint, create, or similar button to initiate the transaction. Your wallet prompts you to review and confirm the transaction, displaying estimated gas fees and requesting your approval. During high network congestion, gas fees may be substantial, so verify they’re acceptable before confirming. Some wallets allow adjusting gas prices to speed up or reduce cost of transactions based on urgency.
After confirming, the transaction broadcasts to the blockchain network where miners or validators process it. Most interfaces display transaction status with links to block explorers for tracking. Confirmation times vary by blockchain and gas fees paid, from seconds on Layer 2 solutions to minutes on Ethereum mainnet during congestion. Once confirmed, the interface should update showing your new synthetic asset position including collateral locked, synthetic tokens minted, current collateralization ratio, and liquidation price. Verify all details match your expectations, and consider noting the transaction hash for record keeping and potential tax reporting.
Risk Warning: Maintain collateralization ratios well above protocol minimums to prevent liquidation during market volatility. Set up monitoring alerts and check positions regularly, especially during periods of high market volatility or significant price movements in your collateral or synthetic assets.
Deploying Synthetic Tokens on a DEX
After successfully minting synthetic assets, deployment extends their utility beyond simple holding by integrating them into broader DeFi ecosystems. Deploying synthetic tokens on DEX infrastructure enables trading, liquidity provision, and use as collateral in other protocols. This phase transforms your synthetic assets from static positions into active participants in decentralized finance, potentially generating additional yields or enabling complex strategies not possible with traditional assets.
Verifying Token Creation
Token verification ensures your minted synthetic assets appear correctly in your wallet and on blockchain explorers. First, check your wallet’s token list for the new synthetic asset. Some wallets automatically detect new tokens, while others require manually adding the token contract address found in protocol documentation or transaction receipts. The displayed balance should match the amount you minted. Second, verify the position on the protocol’s interface, confirming collateral amount, collateralization ratio, and liquidation price align with your expectations.
Third, examine the transaction on a block explorer like Etherscan to confirm all events executed correctly. Look for token minting events, collateral transfer events, and position creation records. Any discrepancies between expected and actual results warrant investigation before deploying tokens further or adding more collateral. Some platforms provide position management interfaces showing historical changes, allowing you to track your synthetic asset’s lifecycle from creation through eventual burning. Thorough verification before proceeding prevents discovering problems later when addressing them might be more difficult or costly.
Adding Synthetic Assets to Liquidity Pools
Liquidity provision transforms synthetic assets from personal holdings into market-making positions generating trading fees. Most synthetic asset protocols integrate with or operate their own automated market makers where you can provide liquidity. To add synthetic assets to liquidity pools, navigate to the liquidity provision interface, select the pool pairing your synthetic asset with another token (often stablecoins or native protocol tokens), and enter amounts of both tokens to deposit. The interface calculates your pool share and potential fee earnings.
Understand impermanent loss risks before providing liquidity, as price divergence between paired assets can result in lower value than simply holding. Synthetic assets paired with uncorrelated tokens experience greater impermanent loss than those paired with correlated assets. Fee generation must exceed impermanent loss for profitable liquidity provision. Some protocols offer liquidity mining incentives distributing governance tokens to liquidity providers, enhancing yields beyond trading fees. Calculate expected returns including fees and incentives against impermanent loss risk before committing synthetic assets to pools. Successful case studies like innovative DEX implementations demonstrate effective liquidity strategies.
Tools and Protocols for Creating Synthetic Assets
The synthetic asset ecosystem offers diverse tools and protocols catering to varying needs, from user-friendly interfaces for beginners to powerful frameworks for advanced users creating custom synthetic derivatives. Selecting appropriate tools depends on your technical expertise, desired asset types, customization requirements, and integration needs with other DeFi protocols. This section explores the landscape of available options, helping you identify tools matching your synthetic asset creation objectives.
Smart Contract Templates for Synthetic Assets
For advanced users seeking to create custom synthetic assets beyond what established protocols offer, smart contract templates provide starting points for building synthetic asset systems. UMA Protocol offers templates for various synthetic asset types including KPI options, range tokens, and success tokens. These templates handle complex aspects like oracle integration, collateral management, and liquidation logic while allowing customization of parameters like strike prices, expiration dates, and settlement conditions.
OpenZeppelin provides audited contract libraries including components useful for synthetic asset creation such as ERC20 token standards, access control mechanisms, and upgradeable contract patterns. Synthetix publishes its smart contract code openly, enabling developers to study and adapt its proven synthetic asset architecture. When using templates, thorough testing on testnets and professional security audits prove essential before deploying with real value, as smart contract vulnerabilities can result in total loss of locked collateral. Templates accelerate creation compared to building from scratch but still require significant technical expertise to implement safely. Resources on synthetic asset mechanics provide deeper technical insights.
DEX Platforms and Protocols to Consider
Choosing the right platform for your guide to building synthetic assets on decentralized platforms involves evaluating multiple factors. Synthetix suits users seeking diverse synthetic asset exposure from a single protocol with proven track record and deep liquidity. Its high collateralization requirements and SNX token dependency may not fit all strategies. Mirror Protocol appeals to those specifically interested in equity exposure, offering lower collateralization ratios and multiple collateral options. Its focus on stocks creates regulatory considerations requiring careful navigation.
UMA Protocol serves builders and advanced users wanting to create custom synthetic assets with flexible parameters. Its permissionless nature enables innovation but requires more technical sophistication than turnkey platforms. Perpetual protocol and dYdX cater to traders seeking leveraged exposure through perpetual contracts rather than spot synthetic assets. Injective Protocol bridges centralized and decentralized finance with its cross-chain synthetic perpetuals. Evaluate each platform’s documentation quality, community activity, TVL (total value locked), security audit history, and governance structure when selecting where to deploy your synthetic asset strategies.
Step-by-Step Automation Tools
Automation tools simplify synthetic asset creation and management through streamlined interfaces and automated processes. Zapper and Zerion provide portfolio management interfaces supporting multiple synthetic asset protocols with unified views of positions across platforms. They enable one-click interactions with complex DeFi protocols, abstracting technical complexity for less experienced users. DeFi Saver specializes in position management, offering automated collateral additions or debt repayments maintaining target collateralization ratios without manual intervention.
Gelato Network enables transaction automation executing specific actions when predefined conditions are met, useful for liquidation protection or profit-taking. Instadapp provides “recipes” combining multiple DeFi interactions into single transactions, potentially including synthetic asset creation, liquidity provision, and yield farming in one step. While automation tools increase convenience, they introduce additional smart contract layers creating extra risk and often charging fees. Understanding what automations do behind the scenes and maintaining ability to manually manage positions proves important if automation fails or behaves unexpectedly during extreme market conditions.
Best Practices for Synthetic Asset Creation on DEX
Success in synthetic asset creation extends beyond technical execution to encompass risk management, security awareness, and strategic positioning. These best practices distill lessons from experienced synthetic asset creators, helping you avoid common pitfalls while maximizing the benefits of this powerful DeFi primitive. Implementing these practices from your first synthetic asset creation establishes habits supporting long-term success as you scale and diversify your positions.
Ensuring Security and Accuracy
Security begins with wallet protection through hardware wallets for significant positions, strong passwords, and careful management of seed phrases stored offline in secure locations. Enable all available security features including transaction signing confirmations and address whitelisting where supported. When interacting with synthetic asset protocols, always verify you’re on authentic websites by bookmarking official URLs and checking SSL certificates. Phishing sites mimicking legitimate protocols represent constant threats, so exercising extreme caution with any links prevents compromise.
Accuracy in transaction execution prevents costly mistakes. Double-check all parameters before confirming including synthetic asset amounts, collateral values, and collateralization ratios. Simple typos adding extra zeros or using wrong decimal places can lock excessive collateral or create unintended positions. Use protocol testnet environments to familiarize yourself with interfaces before executing real transactions. Start with small positions when first using new protocols, gradually increasing size as you gain confidence and understanding. Review transaction details carefully in your wallet before signing, and examine confirmed transactions on block explorers to verify execution matched intentions.
Managing Collateral and Liquidation Risks
Collateral management represents ongoing responsibility throughout your synthetic asset position’s lifecycle. Monitor collateralization ratios regularly, especially during volatile markets when rapid price movements can push positions toward liquidation thresholds. Set up alerts through protocol interfaces, portfolio trackers, or custom monitoring tools notifying you when ratios approach dangerous levels. Maintain meaningful buffers above minimum collateralization requirements, with many experienced users targeting ratios 50-100% above protocol minimums to weather typical volatility.
Understand your protocol’s specific liquidation mechanics including penalty amounts, liquidation speed, and whether partial or full liquidations occur. Some protocols liquidate positions gradually, while others close entire positions once thresholds are breached. Keep additional collateral readily available for quick position adjustments if needed, and know how to add collateral through protocol interfaces before emergency situations arise. Consider diversifying collateral types across multiple synthetic positions rather than concentrating risk in single collateral assets. If your collateral and synthetic asset exhibit correlation, understand how synchronized movements affect your liquidation risk differently than uncorrelated pairs.
| Risk Type | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidation Risk | Collateral value drops below minimum ratio | Maintain high collateral ratios, set alerts, monitor positions |
| Smart Contract Risk | Vulnerabilities in protocol code | Use audited protocols, diversify across platforms, limit position size |
| Oracle Risk | Price feed manipulation or failure | Choose protocols with decentralized oracles, understand price sources |
| Depegging Risk | Synthetic price diverges from target asset | Monitor price deviations, understand arbitrage mechanisms |
| Regulatory Risk | Legal restrictions on synthetic assets | Understand local regulations, consult legal counsel, use VPN if permitted |
| Liquidity Risk | Difficulty exiting positions at fair prices | Use established platforms, check trading volumes, avoid exotic assets |
Optimizing Gas Fees During Minting
Gas fees can consume significant portions of returns on smaller synthetic asset positions, making optimization essential for profitability. Monitor network congestion through gas tracking websites before executing transactions, timing your minting during lower activity periods when fees are reduced. Many protocols support Layer 2 solutions like Optimism or Arbitrum offering dramatically lower fees than Ethereum mainnet while maintaining security. If your target protocol operates on multiple networks, compare fee structures across them.
Batch operations when possible, combining multiple actions like approvals and minting into single transactions reducing overall fee burden. Some protocols optimize this automatically, while others require manual transaction structuring. Consider that overpaying gas to rush transactions during urgent situations may prove worthwhile to prevent liquidations or capture opportunities, while routine position management can wait for low-fee periods. Calculate break-even position sizes where fees represent acceptable percentages of total position value, avoiding positions so small that fees eliminate profit potential. Understanding gas mechanics for your specific blockchain and protocol informs strategic decisions about position sizes and timing.
Build Your Own DEX with Synthetic Asset Support
Create synthetic assets on a DEX with secure smart contracts and easy minting steps.
Launch Your Exchange Now
Conclusion
Creating synthetic assets on decentralized exchanges represents one of DeFi’s most powerful innovations, enabling global access to diverse financial instruments through blockchain technology. This comprehensive guide has explored the complete journey from fundamental concepts through practical implementation, providing the knowledge necessary to confidently navigate synthetic asset creation. Whether you’re seeking exposure to traditional assets, creating custom derivatives, or building innovative financial products, understanding how to create synthetic assets on a DEX opens doors to opportunities previously accessible only through traditional financial intermediaries.
The landscape of synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges continues evolving rapidly, with new protocols, improved user experiences, and expanded asset coverage emerging constantly. Success requires not only technical understanding of minting mechanics but also appreciation for risk management, security practices, and ongoing position monitoring. Starting with established platforms, beginning with small positions, thoroughly researching protocols, and maintaining conservative collateralization ratios provides solid foundations for synthetic asset success. As you gain experience, you can explore more advanced strategies, custom asset creation, and complex DeFi integrations.
Remember that synthetic asset creation carries significant risks including liquidation, smart contract vulnerabilities, oracle failures, and regulatory uncertainties. Never invest more than you can afford to lose, and approach synthetic assets as speculative instruments requiring active management rather than passive holdings. Continuous learning, careful risk management, and strategic position sizing separate successful synthetic asset creators from those who experience losses. The tools and knowledge shared in this guide provide starting points, but your ongoing education, practice, and adaptation to market conditions determine long-term outcomes in this dynamic and exciting corner of decentralized finance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Synthetic assets on a decentralized exchange are tokenized derivatives that track the price of real-world assets like stocks, commodities, currencies, or indices without requiring direct ownership of the underlying asset. These digital tokens use smart contracts and collateralization mechanisms to maintain their peg to the target asset’s price through oracles that feed external price data onto the blockchain. When you hold a synthetic asset, you gain exposure to price movements of traditional assets while maintaining the benefits of blockchain technology including 24/7 trading, global accessibility, and reduced intermediary costs.
The collateralization ratio for minting synthetic assets on a DEX typically ranges from 150% to 750% depending on the protocol and asset volatility. For example, creating $1,000 worth of synthetic gold might require posting $1,500 to $2,000 in cryptocurrency collateral to account for price fluctuations and maintain system stability. Higher volatility assets generally require higher collateralization ratios to protect against liquidation risk. Some protocols use dynamic collateralization that adjusts based on market conditions, while others maintain fixed ratios to ensure predictable requirements for users creating synthetic derivatives on DEX platforms.
Major DEX platforms supporting synthetic asset creation include Synthetix on Ethereum and Optimism, Mirror Protocol on Terra and Ethereum, UMA Protocol across multiple chains, and Kwenta for perpetual synthetic trading. Each platform offers different asset types, collateralization models, and fee structures. Synthetix focuses on crypto-backed synthetic assets covering forex, commodities, and indices. Mirror Protocol specializes in synthetic stocks mirroring real equities. UMA enables customizable synthetic token creation with flexible parameters. The choice depends on your specific needs including target assets, preferred blockchain, collateral requirements, and technical complexity tolerance.
The legality of creating synthetic assets on a DEX varies significantly by jurisdiction and depends on asset types, user location, and regulatory interpretation. In many regions, synthetic assets representing commodities or indices exist in regulatory gray areas, while synthetic stocks may face securities law scrutiny. Some jurisdictions prohibit residents from accessing certain synthetic asset platforms, while others have not established clear frameworks. Before engaging in synthetic asset creation on decentralized exchanges, users should consult legal counsel familiar with their jurisdiction’s securities, derivatives, and digital asset regulations to ensure compliance with applicable laws and avoid potential legal consequences.
Key risks in minting synthetic assets on a DEX include liquidation risk if collateral value drops below required thresholds, smart contract vulnerabilities that could result in asset loss, oracle manipulation affecting price feeds, impermanent loss when providing liquidity to synthetic asset pools, and regulatory uncertainty potentially limiting platform access or asset tradability. Additionally, synthetic assets may experience depegging events where token prices diverge from their target asset, creating losses for holders. Gas fees during high network congestion can make position management expensive. Understanding these risks and implementing proper risk management including diversified collateral, monitoring collateralization ratios, and setting liquidation alerts proves essential for successful synthetic asset creation.
Selecting appropriate collateral for synthetic asset creation involves evaluating asset stability, liquidity, platform acceptance, and correlation with your synthetic asset. Stablecoins like USDC or DAI offer low volatility reducing liquidation risk but may provide lower yields. Major cryptocurrencies like ETH provide broader ecosystem integration and potential appreciation but carry higher volatility requiring higher collateralization ratios. Some protocols accept protocol-specific tokens offering governance benefits or reduced fees. Diversifying collateral across multiple assets can reduce risk. Consider collateral liquidity for easy liquidation if needed, smart contract risk of the collateral token itself, and potential correlation between collateral and synthetic asset to avoid compounding losses during market downturns.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






