Key Takeaways
- The blockchain interoperability market was valued at USD 0.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.9 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 28.3%, fueled by rising demand for cross-chain asset transfers across enterprises.
[1] - Cross-chain bridges now facilitate over $1.3 trillion in annual asset movement, and the total value locked in bridges reached approximately $19.5 billion by early 2025, contributing to 54% of all DeFi activity.
[2] - Polkadot leads the blockchain interoperability space with 26% market share, followed by Cosmos Hub at 19%, Chainlink at 13%, and Ethereum Layer 2s collectively holding 16% of the interoperability market share.
[3] - The Cosmos IBC protocol has never been exploited since its launch in 2021, and it currently connects over 115 chains with more than 35 million annual cross-chain transactions on average.
[4] - Cross-chain bridge protocols collectively hold over $60 billion in total value locked as of 2025, with DeFi’s total value locked hitting nearly $247 billion by Q2 2025, up 31% year on year.
[5] - Cross-chain bridge hacks have resulted in more than $2.8 billion in stolen funds, representing approximately 40% of the entire value hacked in Web3, according to DefiLlama and Chainlink security reports.
[6] - Wormhole alone has moved over $52 billion in lifetime transfers across 35+ supported chains, while LayerZero now processes over $5 billion monthly in cross-chain transactions.
[7] - Cross-chain stablecoin bridges transferred over $12.6 billion in value in the first half of 2025, and cross-chain DeFi activity grew by 52%, driven by bridges and Layer 2 expansion.
[8] - North America dominated the blockchain interoperability market with 45.80% share, while the BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) vertical led adoption, followed by healthcare and supply chain management.
[9] - Interoperability is required for 75% of IoT blockchain projects, and cross-chain IoT transactions increased by 127%, while sidechain interoperability adoption is projected to expand by 43%.
[10]
Blockchain technology has changed how businesses think about data, transactions, and digital ownership. But there is one major limitation that has held back its full potential for years: most blockchain networks cannot talk to each other. Ethereum, Bitcoin, Solana, Polkadot, and dozens of other chains all operate in isolation, each with their own rules, consensus mechanisms, and ecosystems. This fragmentation creates bottlenecks in liquidity, limits the functionality of decentralized applications, and forces users to rely on workarounds just to move assets from one chain to another.
This is where interoperability in blockchain becomes a fundamental necessity rather than just a technical upgrade. When different blockchain networks can communicate, share data, and enable token transfers across blockchains, the entire decentralized ecosystem becomes far more powerful and useful. Think of it like the early days of the internet, when different email systems could not send messages to each other. Once standardized communication protocols were adopted, the internet became the transformative force we know today. Blockchain interoperability is heading toward that same inflection point.
Interoperability in blockchain networks has moved from theoretical discussions to real-world implementations. Protocols like Cosmos IBC, Polkadot’s XCMP, Chainlink’s CCIP, and various cross-chain bridges are already enabling billions of dollars in token transfers across blockchains every month. The question is no longer whether interoperability matters but how quickly the industry can implement it at scale. In this article, we will break down exactly why blockchain interoperability is important, how it works, what challenges remain, and what the future looks like for a truly connected blockchain ecosystem.
What Does Interoperability in Blockchain Actually Mean?
At its core, interoperability in blockchain refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to exchange information, data, and value with each other without needing a centralized intermediary. When two or more blockchains are interoperable, a user on one network can send tokens, trigger smart contracts, or access applications on another network directly.
Without interoperability, each blockchain operates like a closed system. A user holding assets on Ethereum cannot directly use those assets in a Solana-based DeFi protocol. They would need to sell their Ethereum tokens on a centralized exchange, buy Solana tokens, transfer them to a Solana wallet, and then interact with the protocol. This process is time-consuming, expensive, and introduces unnecessary risk.
Blockchain interoperability eliminates these friction points through various technical approaches. Some solutions use cross-chain bridges that lock assets on one chain and mint equivalent tokens on another. Others rely on messaging protocols that allow smart contracts on different chains to communicate directly. The growth of these solutions has accelerated dramatically, with cross-chain protocols now facilitating over $1.3 trillion in annual asset movement across networks. The growth of these solutions reflects how critical interoperability in blockchain networks has become for the entire Web3 ecosystem.
The Market Growth Behind Blockchain Interoperability
The numbers behind blockchain interoperability tell a compelling story. The global blockchain interoperability market was valued at USD 0.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.9 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28.3%. This growth is driven by increasing cross-chain asset transfer requirements across enterprises, growing adoption of blockchain technology, and regulatory support from governments worldwide.
North America currently dominates this market with approximately 45.80% share, thanks to widespread blockchain adoption across finance, healthcare, and supply chain sectors. The BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) vertical leads adoption, as financial institutions recognize that serving customers across multiple blockchain networks requires robust interoperability infrastructure.
On the DeFi side, cross-chain bridge protocols collectively hold over $60 billion in total value locked as of 2025. DeFi’s total value locked hit nearly $247 billion by Q2 2025, up 31% year on year, and this growth has only been possible because of cross-chain bridges connecting dozens of blockchains. Cross-chain stablecoin bridges alone transferred over $12.6 billion in value in the first half of 2025, and cross-chain DeFi activity grew by 52% during the same period. These figures show that building interoperability solutions is not just a theoretical priority but a market-driven necessity.
Recommended Reading:
Cross-Chain Bridges and Interoperability Protocols: The Future of Blockchain Connectivity
Why Interoperability in Blockchain Networks Is Critical
Understanding why interoperability matters requires looking at the practical problems it solves. Here are the most important reasons why blockchain interoperability has become a top priority for the industry:
1. Breaking Down Liquidity Silos
One of the biggest challenges in decentralized finance is liquidity fragmentation. Billions of dollars are locked on separate blockchain networks like Ethereum, BNB Chain, Avalanche, and Solana, with limited ability to flow between them. When liquidity is trapped on individual chains, each pool becomes smaller, prices swing more with every trade, and users face higher slippage and wider spreads. Blockchain interoperability connects these isolated liquidity pools into a larger, more efficient network. The development of cross-chain liquidity aggregation has been transformative. According to DeFiLlama data, bridging assets across chains helped lift the total value locked in top cross-chain bridges from around $27.8 billion to over $35.1 billion between Q3 and Q4 2024, roughly a 26% increase in capital utilization. This directly benefits traders, liquidity providers, and DeFi protocols alike.
2. Expanding DeFi Possibilities
Interoperable DeFi platforms now contribute 38% of interoperability usage, driven by user demand for lending, staking, and decentralized exchange flexibility across chains. Without interoperability, a user who wants to lend on Aave (Ethereum), trade on Jupiter (Solana), and stake on Osmosis (Cosmos) would need to manage separate wallets, pay multiple transaction fees, and manually bridge assets between each network. The progress of cross-chain protocols allows users to access the best opportunities across the entire blockchain ecosystem from a single interface.
3. Enabling Token Transfers Across Blockchains
Token transfers across blockchains are among the most direct applications of interoperability. Whether it is moving USDC from Ethereum to Polygon, transferring NFTs between chains, or executing cross-chain swaps, the ability to move digital assets freely is fundamental to a functioning multi-chain ecosystem. Wormhole alone has moved over $52 billion in lifetime transfers across 35+ supported chains, while LayerZero processes over $5 billion monthly. These protocols have made token transfers across blockchains a routine operation rather than a technical challenge.
4. Supporting Enterprise Blockchain Adoption
Enterprises exploring blockchain for supply chain management, identity verification, and cross-border payments often need to interact with multiple blockchain platforms. A pharmaceutical company tracking drug shipments might use one blockchain for manufacturing records, another for logistics, and a third for retail distribution. Interoperability in blockchain networks allows these different systems to share data and verify transactions across the entire supply chain without requiring a single centralized database.
5. Strengthening the Multi-Chain Future
The blockchain industry has moved past the idea that one chain will dominate everything. Instead, the future is multi-chain, with specialized blockchains optimized for different use cases. Ethereum excels at smart contract creation, Solana offers high-speed transactions, Cosmos provides modular chain-building tools, and Polkadot delivers shared security across parachains. Blockchain interoperability ensures that users do not have to choose just one ecosystem but can leverage the unique strengths of each network.
Market Share of Leading Blockchain Interoperability Platforms
| Platform | Market Share | Key Interoperability Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Polkadot | 26% | Parachain architecture with XCMP protocol for cross-chain messaging and shared security through the Relay Chain |
| Cosmos Hub | 19% | Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol enabling trustless communication across 115+ independent chains |
| Ethereum Layer 2s (Optimism, Arbitrum) | 16% | Rollup-based scaling with cross-chain compatible transactions and low-cost bridging to the Ethereum mainnet |
| Chainlink | 13% | Oracle-based interoperability layer connecting blockchains to external data sources and cross-chain smart contract communication via CCIP |
| Avalanche Bridge | 11% | Multi-chain asset transfer facilitation with growing DeFi and dApp usage through subnet architecture |
| Binance Smart Chain (BSC) | 8% | Cross-chain swaps with Ethereum, Polygon, and other major networks through bridge integrations |
| Quant Network (Overledger) | 6% | Enterprise-grade interoperability gateway connecting blockchains for finance and supply chain applications |
How Token Transfers Across Blockchains Actually Work
Understanding how token transfers across blockchains function helps explain why building interoperability protocols is so technically demanding. There are several approaches, each with different trade-offs in terms of security, speed, and decentralization.
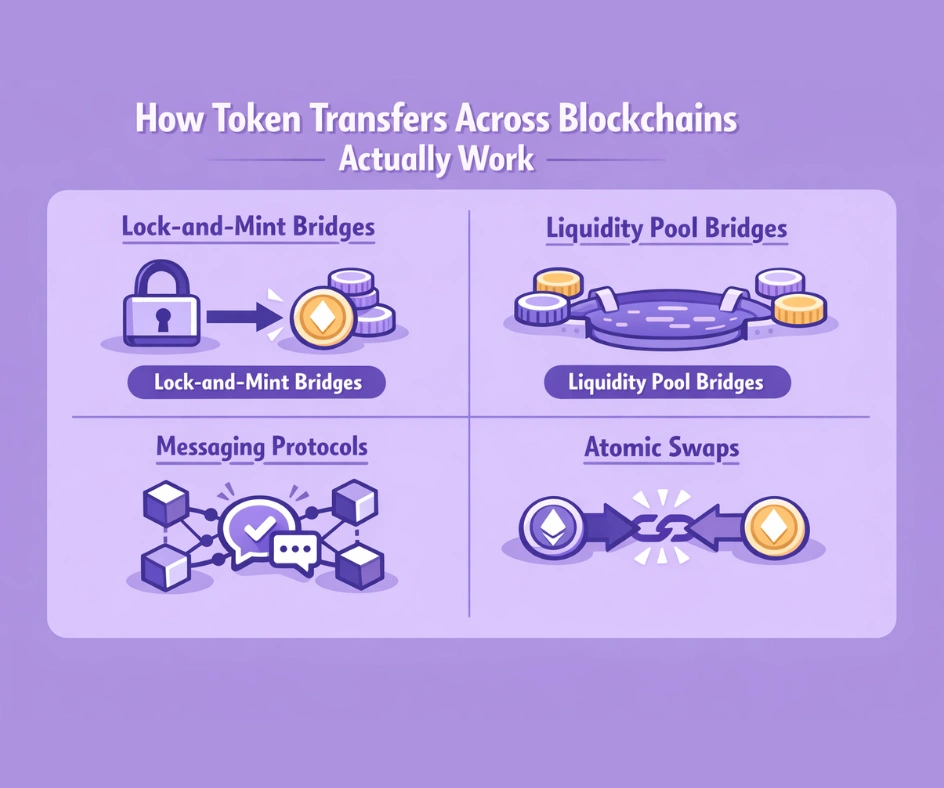
1. Lock-and-Mint Bridges
This is the most common approach. When a user wants to move tokens from Chain A to Chain B, the bridge locks the original tokens in a smart contract on Chain A and mints an equivalent number of “wrapped” tokens on Chain B. When the user wants to move back, the wrapped tokens are burned on Chain B, and the original tokens are unlocked on Chain A. Wormhole’s Portal Bridge uses this model and has processed over $52 billion in cross-chain volume using this approach. Building these bridges requires careful smart contract design to ensure that the locked and minted tokens always remain in balance.
2. Liquidity Pool Bridges
Instead of locking and minting, these bridges maintain liquidity pools of native tokens on both chains. When a user transfers assets, the bridge draws from its existing pool on the destination chain rather than creating new wrapped tokens. Stargate Finance popularized this model, which reduces the risk of wrapped token depegging and often offers faster transfers. Building liquidity pool bridges requires deep initial capitalization and ongoing incentives to maintain pool depth.
3. Messaging Protocols
Protocols like Cosmos IBC and Polkadot’s XCMP go beyond simple token transfers. They enable arbitrary data and messages to be sent between chains, allowing smart contracts on one chain to trigger actions on another. The IBC protocol, which has never been exploited since its launch in 2021, connects over 115 chains and processes more than 35 million annual cross-chain transactions. This approach to interoperability in blockchain is the most versatile, as it supports not just token transfers but also cross-chain governance, smart contract calls, and data verification. The ongoing development of these messaging standards is pushing the boundaries of what cross-chain communication can achieve.
4. Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps use hashed timelock contracts (HTLCs) to enable peer-to-peer exchanges between two blockchains without any intermediary. If either party fails to complete their side of the transaction within the timelock period, both transactions are automatically reversed. While atomic swaps offer true trustlessness, they are limited to simple token exchanges and do not support the broader data sharing that other interoperability solutions enable.
Recommended Reading:
Real-World Applications of Blockchain Interoperability
Interoperability in blockchain networks is not just a DeFi story. It has practical applications across multiple industries that are already changing how organizations handle data, assets, and transactions.
1. Healthcare Data Exchange
Healthcare systems worldwide struggle with data silos, where patient records are scattered across different providers and systems that cannot communicate with each other. Blockchain interoperability offers a way to create unified patient data access without centralizing storage. Different healthcare providers can maintain records on separate blockchain networks, but interoperability protocols allow authorized parties to access and verify patient information across systems. Research published in Frontiers in Digital Health has identified that blockchain can improve the efficiency, dependability, and security of electronic health records by enabling decentralized data exchange across healthcare institutions. Building interoperable health data solutions using blockchain has the potential to reduce medical errors caused by incomplete patient histories.
2. Supply Chain Management
A single product moving from manufacturer to consumer might pass through supply chains managed on different blockchain networks. A pharmaceutical company might track production on one blockchain, logistics on another, and retail distribution on a third. Supply chain interoperability solutions account for 22% of the blockchain interoperability market, supporting real-time logistics and supplier transparency. IBM’s collaboration with Walmart on the DSCSA (Drug Supply Chain Security Act) pilot demonstrated that blockchain-based product traceability could cut medication recall notification processes from days to seconds. This kind of cross-chain coordination requires the development of interoperability solutions in blockchain that can verify data across different networks simultaneously.
3. Cross-Border Payments and CBDC Integration
Central banks around the world are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), and interoperability between these national digital currencies is a major consideration. The mBridge project, a collaboration among central banks from Hong Kong, Thailand, the UAE, and China, is developing a multiple CBDC platform to support real-time, peer-to-peer cross-border payments. This initiative directly relies on blockchain interoperability development to enable different national digital currency systems to communicate and settle transactions across borders.
4. Gaming and NFT Ecosystems
Gaming interoperability has risen to 12% of the interoperability market, reflecting growing player demand for cross-platform in-game asset mobility. Multi-chain NFTs have surged by 133% since 2022, as artists and creators embrace network-agnostic ownership and visibility. The growth of cross-chain gaming infrastructure means that a sword earned in a game on Ethereum could potentially be used in a game on Polygon or Immutable X, creating a truly interconnected gaming economy. Token transfers across blockchains in the gaming context are about more than just financial assets; they encompass entire digital identities and inventories.
5. IoT and Decentralized Infrastructure
The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly intersecting with blockchain technology, and interoperability is essential for this convergence. According to IEEE research, interoperability is required for 75% of IoT blockchain projects, and cross-chain IoT transactions increased by 127%. As IoT devices generate data across different networks and platforms, the ability to aggregate, verify, and act on this data across multiple blockchains becomes a fundamental requirement for decentralized infrastructure.
Comparison of Cross-Chain Interoperability Approaches
| Approach | How It Works | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lock-and-Mint Bridges | Locks tokens on the source chain and mints wrapped equivalents on the destination chain | Broad chain support, relatively simple to implement, widely adopted | Wrapped token depegging risk, smart contract vulnerabilities, centralization in validator sets |
| Liquidity Pool Bridges | Uses native token pools on both chains, drawing from existing liquidity for transfers | No wrapped tokens, faster transfers, reduced depegging risk | Requires deep liquidity pools, higher initial capital, slippage during low liquidity |
| Messaging Protocols (IBC, XCMP) | Enables arbitrary data and message passing between chains using light clients and relayers | Most versatile, supports data and governance beyond tokens, strong security track record | Technically complex, requires compatible chain architectures, slower development cycle |
| Atomic Swaps (HTLC) | Peer-to-peer exchange using hashed timelock contracts that auto-reverse if conditions are not met | Fully trustless, no intermediary needed, true decentralization | Limited to simple token swaps, no broader data sharing, requires both parties to be online |
| Oracle-Based Interoperability | Connects blockchains to external data sources and other chains through decentralized oracle networks | Connects on-chain and off-chain worlds, broadens smart contract use cases, and enhances data trust | Dependency on Oracle accuracy, potential latency, and additional infrastructure overhead |
| Sidechain and Rollup Bridges | Transfers between main chain and associated sidechains or Layer 2 rollups with shared security | Low cost, high speed, benefits from parent chain security, growing ecosystem | Typically limited to specific chain pairs, withdrawal delays on optimistic rollups |
Security Challenges in Blockchain Interoperability
While interoperability in blockchain has brought tremendous benefits, it has also introduced significant security concerns. Cross-chain bridges have become one of the most targeted attack vectors in the entire Web3 space.
According to Chainlink’s security analysis, cross-chain bridges have been hacked for more than $2.8 billion, representing approximately 40% of the entire value hacked in Web3 per DefiLlama data. Chainalysis reported that bridge hacks accounted for 69% of total funds stolen in crypto during 2022 alone. The Ronin Bridge exploit saw $625 million stolen through compromised validator keys. The Wormhole bridge lost $325 million due to a smart contract vulnerability. The Nomad Bridge suffered a $190 million exploit. These incidents demonstrate that while interoperability solutions in blockchain are necessary, their creation requires extreme attention to security.
The primary vulnerabilities in cross-chain bridges include private key compromises, where attackers gain control of the keys managing bridge operations. Smart contract exploits, where flaws in the bridge code allow unauthorized minting or withdrawal of tokens. And validator collusion, where a small number of validators controlling a bridge can be compromised through social engineering or direct attack. Centralized bridge architectures, where a single network of validators handles all bridging operations, create disproportionate risk. As the Polkadot Wiki notes, centralized entities controlling bridges can be compromised or act maliciously, which is why the industry is moving toward more decentralized bridge designs.
The good news is that security is improving. The Cosmos IBC protocol has maintained zero exploits since its launch in 2021, proving that well-designed interoperability protocols can achieve strong security records. The rise of zero-knowledge proof-based bridges, multi-signature validation schemes, and decentralized relayer networks is all contributing to a more robust security landscape for blockchain interoperability.
Recommended Reading:
Leading Interoperability Protocols Shaping the Industry
Several protocols have emerged as leaders in the blockchain interoperability space, each taking a distinct approach to solving the cross-chain communication challenge.
1. Polkadot and the Parachain Model
Polkadot holds the largest market share at 26% in the interoperability space. Its architecture uses a central Relay Chain that provides shared security and consensus for all connected parachains. Each parachain can maintain its own specific functionality, governance, and token economics while benefiting from the shared security model. Polkadot’s Cross-Consensus Message Passing (XCMP) protocol facilitates communication between parachains, enabling token transfers, smart contract interactions, and arbitrary data sharing. The Snowbridge project also enables trustless bridging between Polkadot and Ethereum. As of mid-April 2025, all parachains on Polkadot had a combined TVL of approximately $196 million, with the progress of new parachains and bridge connections ongoing.
2. Cosmos and the IBC Protocol
Cosmos, often called the “Internet of Blockchains,” holds 19% market share and takes a different approach through its Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. IBC allows independent blockchains called “zones” to communicate trustlessly using light clients and relayers, without needing a central authority. As of 2025, IBC connects over 115 chains, processes over 35 million annual cross-chain transactions, and has secured tens of billions in annual value transfer without a single exploit since launch. The IBC Eureka upgrade (v2) launched in early 2025, extending IBC connectivity beyond Cosmos SDK chains to Ethereum and other ecosystems. The total value of IBC transfers between January 2022 and February 2023 alone reached $29 billion. All Zones on Cosmos had a combined TVL of approximately $2.35 billion as of mid-April 2025, making it one of the most active interoperable ecosystems. The development of IBC represents one of the most successful implementations of blockchain interoperability to date.
3. Chainlink CCIP
Chainlink commands 13% of the interoperability market through its Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP). Unlike Polkadot and Cosmos, which focus primarily on chain-to-chain communication, Chainlink also bridges on-chain and off-chain worlds through its decentralized oracle network. CCIP enables smart contracts on different blockchains to send messages, transfer tokens, and initiate actions on other chains. The protocol uses multiple independent decentralized oracle networks to verify cross-chain transactions, reducing the risk of a single point of failure that has plagued other bridge solutions.
4. LayerZero and Wormhole
LayerZero and Wormhole are two of the most active cross-chain messaging protocols in terms of volume. LayerZero processes over $5 billion monthly and has been adopted by major DeFi protocols for omnichain application building. Wormhole supports 35+ chains and has processed over $52 billion in lifetime volume, plus over one billion cross-chain messages. Both protocols raised significant venture capital, with Wormhole and LayerZero raising over $500 million combined from investors like a16z and Sequoia. The success of these protocols shows that institutional capital is increasingly backing interoperability solutions in blockchain as critical infrastructure.
Challenges Standing in the Way of Full Blockchain Interoperability
Despite the impressive progress, several challenges continue to slow the progress of full interoperability in blockchain networks.
1. Technical Complexity
Every blockchain has its own consensus mechanism, data structure, transaction format, and communication protocol. Building bridges or messaging layers that can translate between these fundamentally different architectures is extremely challenging. Building cross-chain solutions requires deep expertise in multiple blockchain platforms simultaneously, and the available talent pool is limited.
2. Security and Trust Trade-offs
As the $2.8 billion in bridge exploits demonstrates, interoperability introduces new attack surfaces. The more chains a bridge connects, the more potential vulnerabilities it creates. Developers face constant trade-offs between speed, decentralization, and security. A bridge that relies on a small set of validators can process transactions quickly but introduces centralization risk. A fully decentralized bridge with many validators offers better security but may sacrifice speed.
3. Lack of Standardization
There is no universal standard for blockchain interoperability. Different protocols use different approaches, making it difficult for developers to build applications that work across all interoperability solutions. While IBC has become a de facto standard within the Cosmos ecosystem and XCMP within Polkadot, cross-ecosystem standardization remains an ongoing challenge. The creation of common standards would significantly accelerate the adoption of interoperability in blockchain networks.
4. Regulatory Uncertainty
Cross-chain transactions can make it more difficult for regulators to track the flow of funds, which raises compliance concerns. Bridges have been used to process $1.5 billion in stolen funds for laundering during the first half of 2025 alone. This has prompted regulators to pay closer attention to cross-chain infrastructure, and the regulatory frameworks for interoperability protocols are still evolving across jurisdictions.
5. Awareness and Education Gaps
A major barrier to blockchain interoperability adoption is the lack of knowledge and understanding of the technology, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises. Many businesses are not familiar with how interoperability solutions work or what benefits they could bring. A more business-focused approach to education, combined with user-friendly interfaces, is needed to drive broader adoption.
Cross-Chain Interoperability Implementations in the Real World
The following projects reflect how cross-chain interoperability is already being applied across DeFi, token exchanges, blockchain connectivity, and multi-network ecosystems. Each implementation showcases the same distributed infrastructure principles discussed throughout this article, from cross-chain messaging and token bridging to trustless validation and community-driven protocol development.
🔗
Spectrum Finance: Cross-Chain Blockchain Interoperability
Built a decentralized protocol enabling direct native asset swaps like ADA to ETH without wrapped tokens. Spectrum reduces transaction costs, enhances cross-chain liquidity, and supports programmable cross-chain messaging for smart contract execution across multiple blockchain networks, directly reflecting the interoperability principles discussed in this article.
🌐
Optopia: AI-Driven Layer 2 with Cross-Chain Bridge
Developed a next-generation Layer 2 network featuring a cross-chain bridge that enables asset transfers between different blockchain networks. The platform integrates AI with decentralized governance and staking, allowing users to connect with multiple blockchain ecosystems without compromising security or decentralization.
Build Your Cross-Chain Blockchain Solution Today:
We bring 8+ years of blockchain expertise to cross-chain bridge development and interoperability protocol implementation. Our specialized team handles everything from smart contract design and multi-chain integration to security audits and protocol optimization, ensuring your platform can connect with multiple blockchain networks. Whether you need a custom cross-chain bridge, interoperable DeFi infrastructure, or enterprise blockchain connectivity, we deliver solutions built for performance, security, and long-term growth.
Conclusion
Interoperability in blockchain is not a luxury feature or a distant aspiration. It is a fundamental requirement for the blockchain industry to reach its full potential. The numbers speak for themselves: a market growing at 28.3% CAGR toward $7.9 billion by 2034, cross-chain bridges facilitating over $1.3 trillion in annual transfers, and DeFi ecosystems that are increasingly dependent on multi-chain connectivity for growth. Protocols like Cosmos IBC, Polkadot XCMP, Chainlink CCIP, LayerZero, and Wormhole are already proving that token transfers across blockchains can work at scale.
But the journey is far from over. Security remains a critical concern, with over $2.8 billion lost to bridge exploits. Standardization across different interoperability approaches is still evolving. And many enterprises and users still lack the understanding needed to take full advantage of cross-chain capabilities. The development of more robust security frameworks, universal interoperability standards, and user-friendly interfaces will determine how quickly the industry moves from today’s fragmented landscape to a truly connected blockchain ecosystem.
For businesses, developers, and investors, the message is clear: blockchain interoperability development is where the next wave of growth and innovation will come from. Understanding how it works, what protocols are leading the space, and what risks to watch for is essential for anyone building or participating in the decentralized economy. The blockchains that prioritize interoperability will thrive. The ones that remain isolated will be left behind.
Frequently Asked Questions
Interoperability in blockchain refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer value with each other without relying on a centralized intermediary. It allows users and applications on one blockchain to interact with smart contracts, tokens, and data on another blockchain directly. This capability is achieved through cross-chain bridges, messaging protocols like Cosmos IBC, and oracle-based solutions like Chainlink CCIP. Without interoperability, each blockchain operates as an isolated system with limited connectivity to other networks.
Cross-chain bridges are critical for DeFi because they connect liquidity pools across different blockchain networks, allowing users to access lending, staking, trading, and yield farming opportunities across multiple ecosystems. Without bridges, liquidity remains fragmented on individual chains, leading to higher slippage, fewer trading options, and inefficient capital utilization. Bridges facilitate over $1.3 trillion in annual token transfers across blockchains, and cross-chain DeFi activity grew by 52% in 2025, demonstrating how central these tools have become to the decentralized finance ecosystem.
The biggest risks include cross-chain bridge exploits, which have resulted in over $2.8 billion in stolen funds across Web3. Private key compromises, smart contract vulnerabilities, and validator collusion are the primary attack vectors. Additionally, the complexity of managing transactions across different blockchain architectures introduces potential for errors, and the lack of universal interoperability standards creates inconsistencies between different cross-chain solutions. Regulatory uncertainty around cross-chain fund flows also presents compliance challenges for both protocols and users.
The Cosmos IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) protocol enables independent blockchains called “zones” to communicate trustlessly using light clients and relayers. Light clients on each chain track the consensus state of the other chain, verifying that transactions have been properly finalized. Relayers are off-chain processes that relay data between chains by scanning each chain’s state and constructing appropriate messages. IBC supports token transfers, NFT transfers, interchain accounts, and cross-chain smart contract calls. It connects over 115 chains and has maintained zero exploits since its launch in 2021.
Polkadot currently holds the largest market share at 26% in the blockchain interoperability space, followed by Cosmos Hub at 19% and Ethereum Layer 2 solutions (Optimism, Arbitrum) collectively at 16%. Each platform takes a different approach: Polkadot uses parachain architecture with shared security, Cosmos employs the IBC protocol for independent chain communication, and Ethereum Layer 2s use rollup-based bridging. The choice of platform depends on specific use case requirements, with each offering unique strengths in the cross-chain ecosystem.
The future of blockchain interoperability is moving toward an “omnichain” model where users can interact across multiple blockchains without even being aware of the underlying infrastructure. Zero-knowledge proof-based bridges are expected to improve security while maintaining speed. Universal interoperability standards will likely emerge to reduce fragmentation between different cross-chain solutions. Sidechain interoperability adoption is projected to expand by 43%, and the overall market is expected to grow from $0.65 billion in 2024 to $7.9 billion by 2034. The development of these solutions will increasingly support enterprise adoption across finance, healthcare, supply chain, and government sectors.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






