
Cross-Chain Blockchain Solutions
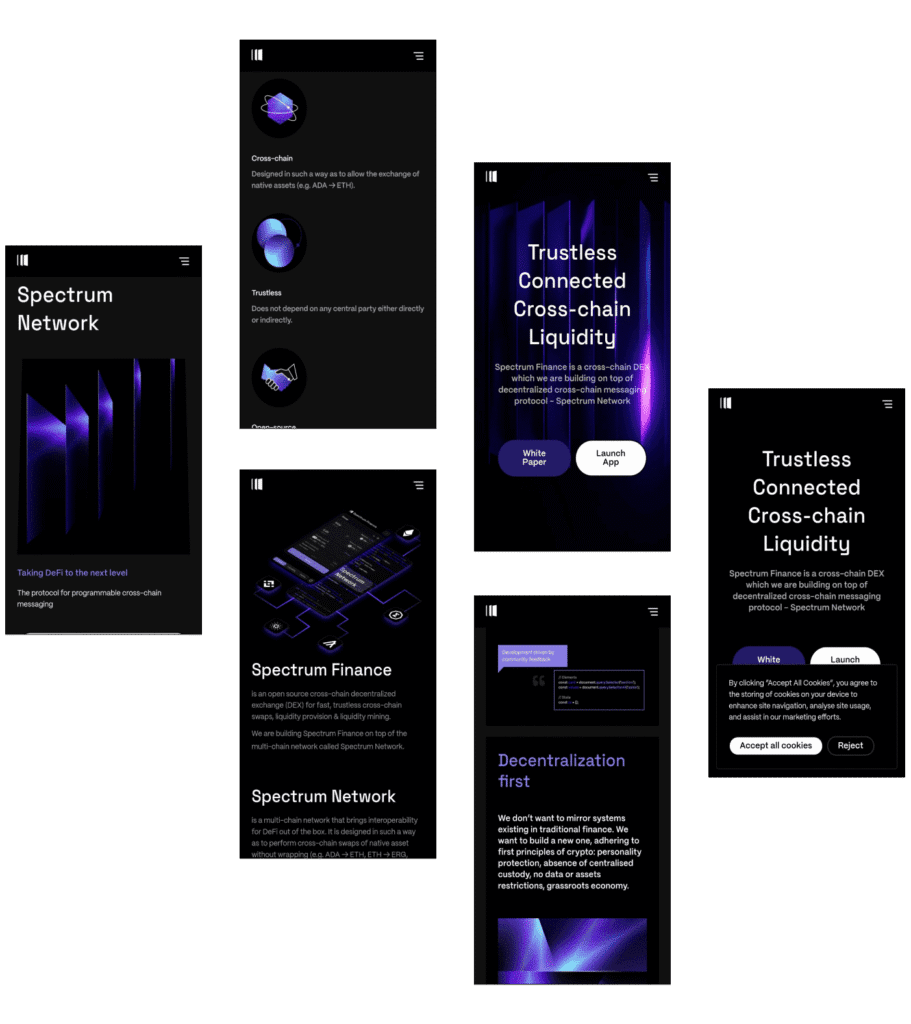
Spectrum Protocol addresses a major challenge in Blockchain Development interoperability. It provides a decentralized and secure framework for seamless cross-chain transactions and data sharing. Unlike traditional solutions that rely on centralized intermediaries, Spectrum enables direct interaction between disparate blockchain networks, eliminating the need for wrapping assets or relying on central authorities.
Get Started with this product
Spectrum enables secure communication between blockchains without central intermediaries, reducing failure risks, enhancing interoperability, and supporting seamless data and asset transfers in a fully decentralized and efficient multi-chain ecosystem.
Spectrum Protocol enables direct swaps of native assets like ADA to ETH without using wrapped tokens. This reduces transaction costs, lowers latency, enhances cross-chain liquidity, simplifies asset exchange, and promotes seamless, efficient blockchain interoperability for users globally.
Spectrum is fully open-source, ensuring transparency and community trust. Developers can audit, contribute, and build upon the code, enabling rapid innovation, increased security, and decentralized development in an inclusive ecosystem.
Spectrum’s scalable design handles high transaction volumes and growing dApp activity. It ensures stable performance, efficient cross-chain operations, and adaptability to expanding user demands and enterprise-grade blockchain solutions.
Spectrum operates without centralized intermediaries, enabling direct, peer-to-peer transactions. It enhances security, reduces manipulation risks, and preserves decentralization by removing reliance on trusted third parties for validation and control.
Developers use Spectrum to enable customizable cross-chain messaging. It supports smart contract execution, automated workflows, and seamless integration between blockchains, powering flexible, programmable, and advanced decentralized application interactions.
Spectrum supports liquidity across multiple blockchains by enabling users to participate in cross-chain liquidity mining. This increases asset accessibility, improves market efficiency, and fosters a vibrant decentralized financial ecosystem.
The SPF token empowers holders to vote, propose changes, and guide protocol development. It also reduces fees and rewards participation, promoting democratic governance and alignment with community-driven values.
Spectrum Protocol addresses the needs of developers and end-users who require seamless cross-chain functionality. These clients seek a solution that facilitates smooth and secure interactions across different blockchain networks. They demand a system that supports native asset swaps and decentralized applications, without the need for intermediaries or complex wrapping processes. The protocol must integrate effortlessly with existing blockchain infrastructures, providing a reliable and scalable platform that accommodates high transaction volumes and diverse use cases.
Additionally, clients require a solution that upholds high security and decentralization standards. The protocol must ensure trustless operations, preventing reliance on central authorities and avoiding potential vulnerabilities. With an emphasis on transparency, Spectrum’s open-source model meets the need for community-driven development and continuous improvement. Clients also expect efficient liquidity provision and governance features, allowing them to participate in protocol management and benefit from reduced fees. Overall, Spectrum Protocol must deliver a versatile and robust framework that enhances blockchain interoperability while maintaining ease of use and integration.

PoA uses trusted validators, not token staking, to secure networks. It offers high speed and efficiency, making it ideal for private or consortium blockchains with pre-established trust among participants.
PoW requires miners to solve complex problems to validate transactions. It ensures strong security but consumes significant energy, making it less efficient for scaling large decentralized blockchain networks sustainably.
Federated Consensus uses a small group of trusted nodes to validate transactions. It delivers fast, efficient performance, ideal for consortium blockchains where participants have established mutual trust and cooperation.
PoS selects validators based on staked tokens. It consumes less energy than PoW, encourages honest behavior, and supports scalability while maintaining security through financial incentives tied to validator performance.
BFT ensures reliable consensus even when some nodes act maliciously or fail. By requiring majority agreement, it strengthens security, enhances system resilience, and maintains network performance in adversarial conditions.
PoET selects validators using randomly assigned wait times enforced by trusted hardware, offering a secure, energy-efficient consensus mechanism that ensures fairness and reduces computational demands compared to PoW.
DPoS lets token holders elect delegates for consensus. It improves scalability and speed while maintaining decentralized governance through voting, ensuring delegates remain accountable to the broader token-holder community.
PoST uses storage and time commitments to validate blocks. It provides energy-efficient consensus by requiring space allocation and timed computation, offering a sustainable alternative to energy-heavy PoW systems.
Visual identity and design elements
Primary font family and usage

Brand colors
#000000
#2c1e85
Project Approach: The Spectrum project adopted a multi-faceted approach to achieve its vision of seamless blockchain interoperability. Initially, the team focused on developing a robust and scalable protocol that could handle cross-chain transactions without relying on central authorities. They designed the Spectrum Network to facilitate direct exchanges of native assets between blockchains, such as ADA to ETH, by leveraging decentralized mechanisms. The development process involved integrating multiple blockchain technologies to ensure compatibility and efficiency. Key elements of this approach included creating a decentralized exchange (DEX) framework and implementing an open-source model to encourage community collaboration and transparency.
The team also placed significant emphasis on addressing the challenges of cross-chain communication. They employed advanced consensus mechanisms, including Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority, to ensure transaction security and network reliability.
Project Results: Spectrum Finance successfully launched its cross-chain DEX and achieved notable results in enhancing blockchain interoperability. The protocol effectively enabled seamless transactions between different blockchain networks, reducing fragmentation within the crypto ecosystem. By facilitating direct exchanges of native assets without intermediaries, Spectrum Finance provided users with a more efficient and cost-effective solution. The open-source nature of the project fostered widespread adoption and innovation, allowing developers to build and integrate new applications on top of the Spectrum Network.
The implementation of decentralized consensus mechanisms contributed to the network’s robustness and security, ensuring reliable performance and minimizing the risk of attacks. The project also demonstrated scalability, accommodating increased transaction volumes and expanding its reach across various blockchain ecosystems.

One of the primary challenges for Spectrum Finance was achieving genuine decentralization in its cross-chain interoperability solution. While many existing approaches rely on centralized oracles or a fixed group of validators, which can compromise decentralization, Spectrum aimed to provide a truly decentralized network. This meant developing a system where no single entity had control over the entire network
Another significant challenge was enabling seamless interoperability between diverse blockchains with different technical standards and consensus mechanisms. Blockchain networks often have varying security models, programming languages, and operational protocols, making it difficult to create a unified system that can interact with all of them effectively. Spectrum Finance needed to develop a protocol that could handle these differences and facilitate smooth transactions between disparate blockchain environments.
Scalability and performance posed critical challenges for the Spectrum project, especially as it aimed to support a growing number of transactions and users. The protocol needed to handle high transaction volumes efficiently while maintaining quick processing times and low costs. Implementing a scalable solution involved addressing potential bottlenecks in the system and optimizing the consensus mechanisms to support large-scale operations.

Spectrum provides seamless cross-chain transactions, native asset swaps, and scalable solutions for diverse blockchain networks.





