Key Takeaways
- A hybrid crypto exchange combines CEX trading speed with DEX-level custody security.
- Off-chain matching + on-chain settlement (Model A) is the most scalable hybrid exchange architecture.
- Users retain control of funds through on-chain vaults or smart contract custody.
- Low-latency order books deliver a centralized exchange–like trading experience.
- Batch on-chain settlement ensures scalability, cost efficiency, and auditability.
- A synchronized off-chain trading ledger and on-chain settlement state is mandatory.
- Non-custodial vault contracts provide the strongest hybrid exchange security guarantees.
- Risk engines protect against overtrading, abuse, and withdrawal exploits.
- Merkle proofs and Proof of Reserves increase transparency and user trust.
- Hybrid exchanges scale better than DEXs while remaining safer than custodial CEXs.
- Instant UX + self-custody withdrawals define the true hybrid exchange advantage.
- A phased hybrid exchange development roadmap enables faster launch and safer growth.
What is a Hybrid Crypto Exchange?
A hybrid crypto exchange is a trading platform that combines the speed and user experience of centralized exchanges (CEX) with the security and custody guarantees of decentralized exchanges (DEX). Users can trade quickly using traditional order books and matching engines while retaining control over their funds through on-chain vaults or smart contract custody. This approach ensures that trades are executed efficiently without compromising security.
Key benefits of a hybrid exchange include low-latency trading, instant order matching, and auditable reserves that increase trust among users. It also provides self-custody options, reducing the risk of centralized fund loss.
For traders and investors comparing platforms, a hybrid exchange vs centralized vs decentralized exchange offers a perfect balance—merging fast trading, advanced UX, and strong security in one system. This makes it an ideal choice for both professional traders and casual users.
Why Choose a Hybrid Exchange?
A hybrid exchange offers the best of both worlds by combining the speed of centralized exchanges with the security of decentralized platforms. Unlike traditional CEXs, which hold user funds centrally, or DEXs, which often suffer from slow settlement, hybrid exchanges provide fast order execution, reliable liquidity, and user-controlled custody.
The pros of the hybrid model include professional trading features like order books, margin support, and low-latency trades, along with enhanced safety via on-chain vaults or multi-signature wallets. Additionally, the platform’s UX is familiar and intuitive, making adoption easier for new traders. Scalability is another advantage, as hybrid exchanges can handle high trading volumes without sacrificing speed or security.
For anyone evaluating options, a hybrid crypto exchange delivers a balanced solution for pro trading, security, and scalability, making it a compelling choice for modern cryptocurrency markets.
Hybrid Crypto Exchange Architecture (Step-by-Step Guide)
A hybrid exchange combines CEX speed/UX (order books, matching, low latency) with DEX custody guarantees (users keep keys, settlement on-chain, auditable reserves).
1) Decide the Hybrid Model First (The Foundation)
Before building anything, the most important decision in hybrid exchange development is selecting the right hybrid model. This choice impacts architecture, custody, settlement, security, and even compliance. Broadly, there are three common hybrid exchange models used in the industry.
Model A — Off-chain Matching + On-chain Settlement
This is the most widely adopted and proven hybrid crypto exchange architecture, especially for professional trading platforms.
In this model, orders and matching happen off-chain, using a high-performance matching engine. This ensures fast execution, low latency, and smooth user experience, similar to centralized exchanges. However, funds never sit directly with the exchange operator. Instead, user assets remain locked inside a smart contract vault or protected through controlled MPC custody.
Trades are finalized through on-chain settlement, either per trade or in batches. This ensures that balances are always verifiable and aligned with on-chain reality. For platforms targeting advanced trading features like spot, margin, or futures, Model A is the ideal hybrid exchange setup.
Model B — CEX UI + DEX Liquidity (Aggregator Model)
This model focuses on providing a CEX-like user interface, but all trades are routed to decentralized exchanges for execution. There is no traditional order book or matching engine. Instead, trades are executed as swaps through liquidity pools.
This hybrid exchange model is suitable for teams looking for a quick launch with minimal infrastructure, but it has limitations. Advanced trading features, deep liquidity control, and professional order types are difficult to support. While it still qualifies as a hybrid exchange, it is not ideal for high-frequency or institutional trading.
Model C — On-chain Order Book + Off-chain Services
In this architecture, orders are stored directly on-chain or on Layer 2 networks, and matching can also occur on-chain. This makes it the most decentralized hybrid exchange model, but it comes at a cost.
On-chain order books increase complexity, gas costs, and engineering overhead. While this model appeals to decentralization-focused users, it is harder to scale for high-volume trading. For most production-grade hybrid exchanges, this model is used selectively rather than as a default design.
For a real hybrid exchange with professional trading, Model A remains the most practical and scalable choice.
2) High-Level Component Map of a Hybrid Exchange
A production-ready hybrid crypto exchange architecture can be broken down into six interconnected layers, each responsible for a specific function.
- Client Layer
Web, mobile, and API-based trading clients that interact with the exchange. - Edge & Authentication Layer
Includes WAF protection, rate limiting, session management, and device binding to secure user access. - Trading Core
This is the heart of the hybrid exchange. It includes the order service, matching engine, and risk engine, ensuring fast and secure trading operations. - Account & Wallet Core
Manages balances, internal ledger, custody logic, and withdrawal rules. This layer plays a critical role in hybrid exchange custody. - Settlement Layer
Handles on-chain vault contracts, Merkle proofs, and settlement watchers, ensuring that off-chain trades reconcile with on-chain balances. - Data, Analytics & Compliance Layer
Covers logs, monitoring, analytics dashboards, and regulatory requirements such as KYC/AML reporting.
3) Core Data Model- Standardizing Balance Management
A hybrid crypto exchange operates across two balance worlds that must always stay in sync.
A) Trading Ledger (Off-chain, UX-Authoritative)
This ledger ensures fast trading performance and real-time UI updates. It manages:
- available_balance
- locked_balance (open orders)
- positions (for margin or futures trading)
- event-sourced, append-only records for auditability
B) Settlement State (On-chain, Custody-Authoritative)
This represents the true ownership of funds. It includes:
- vault balances per user or per settlement epoch
- withdrawal rules, limits, time delays, and signatures
Golden Rule
The off-chain ledger must always reconcile with on-chain reality, ensuring trust and transparency in the hybrid exchange system.
4) Custody Architecture – The Hybrid “Truth Layer”
Custody is what truly differentiates a hybrid exchange from a centralized platform. There are three primary custody patterns used in hybrid exchange architecture.
Option 1 — Non-custodial Vault Smart Contract (Best Hybrid Model)
Users deposit funds directly into a smart contract. The contract only releases funds through verified settlement or withdrawal proofs.
- The operator cannot steal funds, even if systems are compromised.
- This model provides the strongest security guarantees for a hybrid crypto exchange.
Option 2 — MPC/TSS Hot Wallet + Proof of Reserves
This setup allows faster withdrawals while maintaining controlled access.
- Requires strong key management, audits, and Proof of Reserves reporting
- Still partially custodial, but safer than traditional CEX models
Option 3 — Account Abstraction Wallets (Per User)
Each user operates through a smart wallet with session keys and signature-based permissions.
- Excellent UX
- Higher engineering complexity
In practice, most hybrid exchange development teams start with Option 1, combined with a limited hot wallet for instant withdrawals.
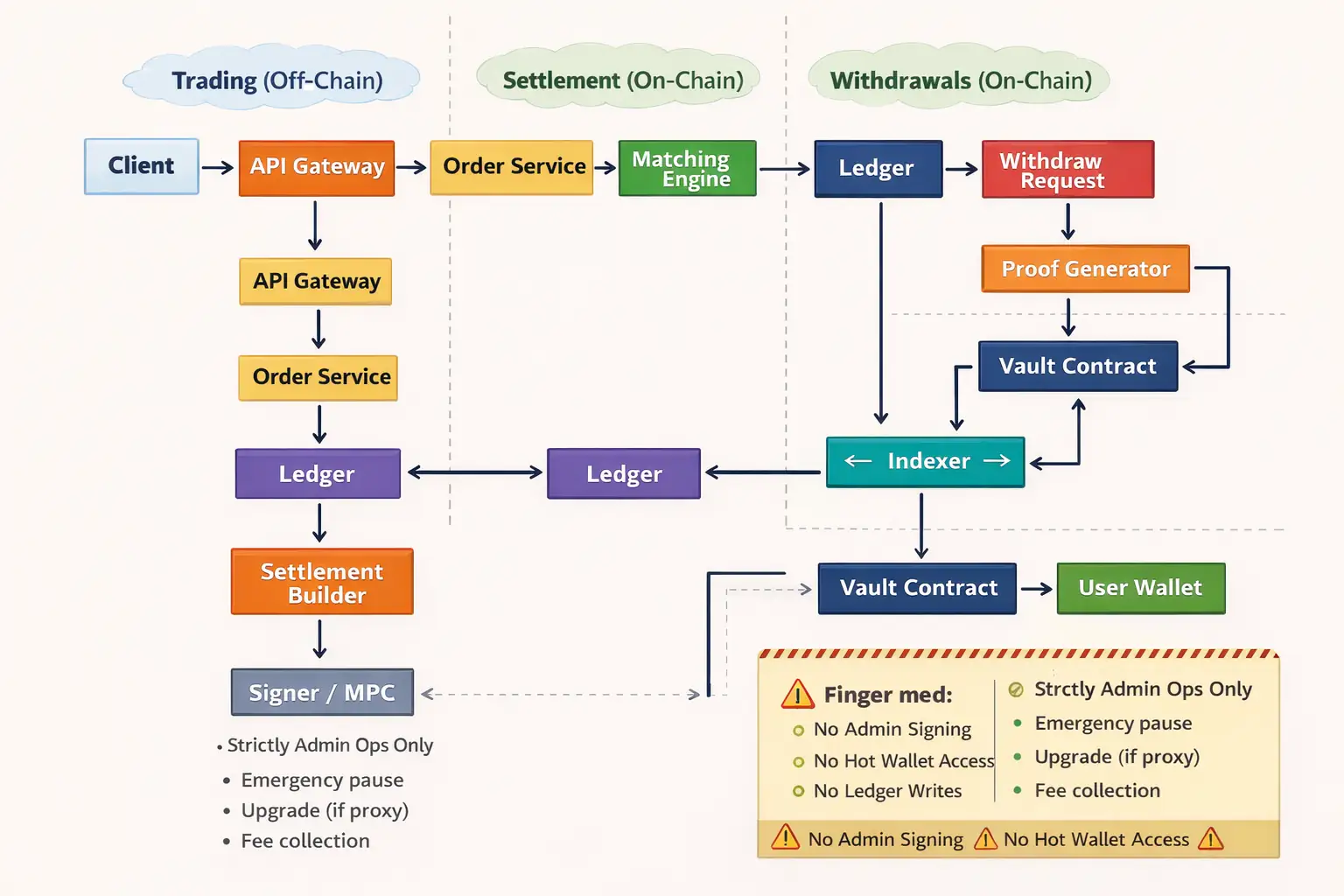
5) Step-by-Step Trading Flow in a Hybrid Crypto Exchange (Model A)
In a hybrid crypto exchange, the trading flow is designed to deliver centralized-exchange speed while preserving decentralized custody guarantees. Model A off-chain matching with on-chain settlement is the most widely adopted hybrid exchange architecture for professional spot trading.
Step 5.1 Deposit
The trading journey in a hybrid exchange begins when a user deposits funds into an on-chain vault contract.
- The user sends tokens directly to the Vault Smart Contract, retaining cryptographic ownership.
- A blockchain indexer continuously monitors deposit events.
- Once the deposit reaches finality (for example, ~12 blocks on Ethereum or fewer on Layer 2 networks), the off-chain ledger credits the user’s available balance.
- The user can now place orders instantly without waiting for further on-chain interaction.
A strict deposit finality policy is critical in a hybrid crypto exchange architecture to protect against chain reorganizations and double-spend risks.
Step 5.2 Place Order
When placing an order, the hybrid crypto exchange follows a trust-minimized approach using cryptographic authorization.
- The user signs the order using EIP-712 typed data, ensuring intent and authenticity.
- The Order API validates:
- Signature authenticity
- Nonce correctness (to prevent replay attacks)
- Balance availability in the off-chain ledger
- Risk engine checks (order size, exposure limits)
Once validated, the order is accepted and the corresponding balance is locked. This ensures the hybrid exchange custody layer always remains consistent with trading activity.
Step 5.3 Match Orders
Order matching happens entirely off-chain to achieve low latency and high throughput.
- The matching engine consumes buy and sell orders using price-time priority.
- When a match occurs, the engine generates trade events (fills).
- The off-chain ledger immediately records:
- Base and quote asset debits/credits
- Trading fees
- Maker and taker accounting
Because settlement is deferred, the trade appears instant in the UI, giving users the same experience as a centralized exchange while still operating within a hybrid crypto exchange model.
Step 5.4 — On-Chain Settlement
Settlement bridges the off-chain trading world with on-chain custody. Two approaches are commonly used in hybrid exchange architecture–
Method 1: Per-Trade Settlement
Each trade triggers an on-chain transaction.
- Simple and easy to reason about
- Very expensive and not scalable
Method 2: Batch Settlement (Recommended)
Used by most scalable hybrid crypto exchanges.
- Net balance changes are computed for each user at fixed intervals
- A Merkle tree of balance deltas or snapshots is built
- The Merkle root is committed on-chain as a settlement epoch
- Users later prove their balance using a Merkle proof
Batch settlement offers scalability, cost efficiency, and strong security guarantees, making it ideal for hybrid exchange development at scale.
6) Withdrawals – The Core Hybrid Guarantee
Withdrawals define the real trust model of a hybrid exchange. A robust system typically supports two parallel paths.
Path A — Instant Withdraw (Hot Liquidity Path)
This path provides fast withdrawals for user convenience.
- Limited withdrawal amounts
- Strict velocity rules (transactions per minute)
- Risk scoring based on behavior and device changes
- Time delays for withdrawals above thresholds
- Protected by multi-sig, MPC policies, or two-man rules
All instant withdrawals are later reconciled against the on-chain vault, ensuring the hybrid exchange custody remains auditable and secure.
Path B — Trust-Minimized Withdraw (Vault Proof Path)
This is the strongest guarantee in a hybrid crypto exchange.
- The user requests a withdrawal
- The system generates a cryptographic proof:
- Either a direct vault balance mapping
- Or Merkle inclusion proof from a settlement epoch
- The vault contract releases funds only if the proof is valid
Even if the off-chain infrastructure is compromised, attackers cannot drain funds without valid on-chain proofs. This is what truly differentiates a hybrid exchange from traditional custodial platforms.
7) Risk Engine – Mandatory for Any Hybrid Exchange
A dedicated risk engine is non-negotiable in a hybrid crypto exchange architecture, even for spot trading.
The risk engine enforces:
- Balance lock and unlock rules
- Maximum order size and notional limits
- Self-trade prevention
- Exposure caps by user and trading pair
- Circuit breakers for abnormal price movement
- Withdrawal risk detection (IP changes, behavior anomalies)
This engine acts as a gatekeeper for both order acceptance and withdrawal approval, ensuring the hybrid exchange remains stable, secure, and abuse-resistant.
Without a properly designed risk engine, even the most advanced hybrid exchange development efforts can fail under real-world conditions.
8) Market Data + Indexing Layer in a Hybrid Crypto Exchange
The Market Data and Indexing Layer is critical for delivering real-time performance and transparency in a hybrid crypto exchange. This layer ensures that traders receive accurate price discovery, instant updates, and reliable historical data, while also keeping the on-chain and off-chain worlds synchronized.
A production-grade hybrid exchange architecture must run multiple real-time data streams in parallel.
Core Market Data Services
A hybrid exchange typically operates the following services:
Order Book Streamer (WebSocket)
Streams real-time order book updates to trading clients with ultra-low latency. This is essential for professional trading and market-making on a hybrid exchange.
Trade Tape (Fills Stream)
Publishes executed trades, fills, and match events in real time. This data feeds charts, analytics, and external market data APIs.
Candles (OHLCV Data)
Aggregates trades into OHLCV candles across multiple timeframes. This enables charting, indicators, and technical analysis for hybrid crypto exchange users.
Chain Indexers (Deposits & Withdrawals)
Index on-chain events such as deposits, withdrawals, settlement confirmations, and vault balance changes. These indexers bridge blockchain activity with the hybrid exchange ledger.
Event Streaming Infrastructure
To manage this scale of real-time data, a hybrid exchange must use a robust message bus. Common choices include:
- Kafka / Redpanda / NATS for event streaming
- Enables asynchronous, fault-tolerant communication
- Decouples trading, settlement, and data consumers
This architecture allows the hybrid crypto exchange to scale horizontally without breaking real-time guarantees.
Data Storage Stack
A standard hybrid exchange data layer uses:
- PostgreSQL for the trading ledger, balances, and reference data
- Redis for ultra-low-latency order book snapshots and viewing caches
This combination ensures fast reads for trading while maintaining strong consistency for settlement and audits.
A properly designed market data layer is what allows a hybrid exchange to feel as fast as a centralized exchange while remaining verifiable like a decentralized exchange.
Build Your Own Hybrid Crypto Exchange Today
Turn Your Crypto Exchange Idea into Reality.
9) Security Architecture (Hybrid-Specific Controls)
Most hybrid crypto exchanges fail not because of trading logic, but because they copy CEX security models and ignore on-chain attack surfaces. Hybrid exchange security must cover both off-chain infrastructure and blockchain-native risks.
Must-Have Security Controls for a Hybrid Exchange
HSM / MPC Key Management
Any hot funds used for instant withdrawals must be protected using HSM or MPC/TSS systems. Private keys should never exist in plain memory.
Dedicated Signing Service
Transaction signing must run in a separate signing service, never inside API or trading pods. This isolates private keys from application-level attacks.
Contract & Token Allowlisting
A hybrid exchange must strictly allowlist supported smart contracts and tokens. This prevents exploits caused by non-standard ERC-20 behavior, fee-on-transfer tokens, or malicious callbacks.
Chain Reorg Handling
Deposits must follow finality rules rather than simple block confirmations. Hybrid exchanges should handle chain reorganizations gracefully to avoid double-crediting funds.
MEV-Aware Settlement Design
Settlement transactions must avoid predictable batch patterns. A secure hybrid exchange uses randomized timing, private relays, or MEV-aware strategies to reduce front-running risk.
Continuous Reconciliation (Ledger ↔ Chain)
The off-chain ledger must continuously reconcile against on-chain vault balances. Any mismatch should trigger alerts and automatic withdrawal halts.
Proof & Audit Layer (Optional but Powerful)
Advanced hybrid crypto exchanges add transparency layer:
- Periodic Proof of Reserves and Liabilities publication
- Merkle roots published on-chain
- Independent verification by users or third parties
This strengthens trust and clearly differentiates a hybrid exchange from a centralized exchange model.
10) Deployment Topology (Production-Grade Hybrid Exchange Setup)
A real-world hybrid exchange deployment is split into multiple isolated zones. This separation reduces blast radius, improves performance, and strengthens security.
Public Zone
This zone handles all external traffic.
- API Gateway + WAF for request filtering and DDoS protection
- WebSocket Gateway for real-time market data and order book streams
No sensitive keys or internal services live in this zone.
Core Trading Zone
This is the performance-critical heart of the hybrid crypto exchange.
- Order Service for order lifecycle management
- Matching Engine (isolated, ultra-low latency)
- Risk Service for limits, margin checks, and liquidation logic
- Ledger Service for authoritative off-chain balance tracking
The matching engine is typically deployed separately with strict resource isolation to guarantee deterministic latency.
Chain & Settlement Zone
This zone interacts directly with the blockchain.
- Signer Service (HSM/MPC)
- Blockchain Indexers
- Settlement Composer for batching, proofs, and on-chain execution
This isolation ensures that even if trading systems are compromised, custody and settlement remain protected.
Observability & Monitoring Layer
A production hybrid exchange architecture must include deep observability:
- Distributed tracing
- Structured logs
- SIEM alerts
- Anomaly detection, especially for withdrawals and settlement behavior
This allows rapid detection of suspicious activity before it escalates into a loss event.
11) Minimal Build Plan for a Hybrid Crypto Exchange
Building a hybrid crypto exchange is best done in clearly defined phases. A phased rollout allows teams to launch faster, control risk, and gradually add decentralization, scalability, and advanced trading features. Below is a practical hybrid exchange development roadmap followed by most production platforms.
Phase 1- MVP Spot Hybrid Exchange
Phase 1 focuses on launching a functional and secure spot trading hybrid exchange with core features only. The goal is speed-to-market while maintaining hybrid custody guarantees.
The foundation of this phase is a vault smart contract that handles deposits and withdrawals. Users deposit funds directly into the vault, ensuring non-custodial or trust-minimized custody. An off-chain ledger mirrors these balances to provide fast UI updates and real-time trading.
A basic order book and matching engine is deployed to enable limit and market orders with low latency. Trades are executed off-chain for performance, while batch settlement occurs on-chain every fixed interval (for example, every few minutes). This keeps gas costs low while maintaining verifiable balances.
To control risk, the MVP includes basic risk checks and limits, such as balance locking, maximum order size, and withdrawal thresholds. At this stage, the hybrid exchange already delivers CEX-like speed with DEX-level custody protection.
Phase 2- Scale and Trust Expansion
Once the MVP hybrid crypto exchange is stable, Phase 2 focuses on scalability, transparency, and user trust.
The settlement layer is upgraded to support Merkle epoch roots published on-chain. This allows users to independently verify their balances and trade history. Self-serve proof-based withdrawals are introduced, enabling users to withdraw funds even if off-chain services are degraded.
To strengthen transparency, the platform adds Proof of Reserves (PoR) and Proof of Liabilities (PoL) reporting, positioning the hybrid exchange as a trust-minimized trading venue.
On the performance side, multi-region WebSocket infrastructure is deployed to reduce latency for global traders and improve reliability during high-volume trading periods.
Phase 3- Advanced Hybrid Exchange Capabilities
Phase 3 transforms the platform into a full-scale hybrid trading ecosystem.
Advanced products such as margin trading and futures are introduced, supported by enhanced risk engines and liquidation logic. The exchange expands to cross-chain deposits, allowing users to trade assets from multiple blockchains within a single hybrid exchange.
To further improve UX and security, Account Abstraction (AA) wallets and session keys are integrated, enabling seamless trading without repeated signing. Finally, advanced surveillance and compliance automation are added to support institutional users and regulatory requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
A hybrid crypto exchange is a trading platform that combines centralized exchange speed and order books with decentralized custody, allowing users to trade fast while keeping control of their funds.
A hybrid exchange uses off-chain order matching for low-latency trading and on-chain smart contracts for custody and settlement, ensuring speed without sacrificing security.
A CEX controls user funds, a DEX trades fully on-chain with slower UX, while a hybrid exchange offers fast trading like a CEX with self-custody and transparency like a DEX.
Yes, hybrid exchanges are safer than traditional centralized exchanges because funds are held in smart contract vaults or MPC custody, reducing the risk of exchange hacks or misuse.
Off-chain matching enables instant order execution using a matching engine, while on-chain settlement ensures final ownership and balance verification through smart contracts.
Yes, users retain control of their funds through non-custodial vaults, smart contracts, or proof-based withdrawal mechanisms, even if the exchange goes offline.
Key benefits include low-latency trading, self-custody, high liquidity, professional trading features, scalable architecture, and verifiable on-chain reserves.
Hybrid crypto exchanges handle liquidity by combining internal order books with external DEX liquidity or market makers. This ensures users experience fast trades, tight spreads, and deep liquidity without compromising on security or custody. Some platforms also use automated aggregation to optimize pricing across multiple liquidity sources.
Yes, advanced hybrid exchanges can support margin, futures, and derivatives by using off-chain risk engines with on-chain settlement and collateral verification.
Hybrid exchanges solve the major problems of both CEX and DEX platforms by offering fast trading, better UX, transparent custody, and reduced counterparty risk.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






