Key Takeaways
- Ripple Blockchain execution framework delivers real-time gross settlement with 3-5 second finality, processing 1,500 transactions per second for enterprise payment operations at scale.
- Enterprise architects leverage RippleNet APIs and XRP Ledger protocols to build compliant payment systems integrating seamlessly with existing banking infrastructure.
- Liquidity routing through XRP bridges eliminates pre-funded nostro accounts, reducing capital requirements by 60% while enabling instant cross-border currency conversion.
- Smart pathfinding algorithms automatically discover optimal payment routes across distributed validator networks, minimizing costs and maximizing settlement speed.
- Compliance-aware execution frameworks embed KYC/AML validation, transaction monitoring, and regulatory reporting directly into payment workflows without manual intervention.
- Enterprise wallet architectures support high-volume operations through multi-signature security, hierarchical key management, and institutional-grade custody solutions.
- Fault-tolerant retry logic and atomic settlement strategies ensure payment reliability across multi-currency corridors with cryptographic proof of immutability.
- Real-time monitoring dashboards provide operational visibility into transaction flows, validator performance, and system health metrics for proactive issue resolution.
- Disaster recovery architectures maintain 99.99% uptime through redundant validator infrastructure, automated failover mechanisms, and geographic distribution strategies.
Enterprise payment systems require infrastructure capable of processing cross-border transactions with speed, security, and regulatory compliance that traditional banking rails cannot deliver. Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative solution, with Ripple leading enterprise adoption through purpose-built payment execution frameworks. RippleNet’s distributed ledger architecture enables financial institutions to settle transactions in 3-5 seconds compared to the multiple days required by correspondent banking networks. The XRP Ledger processes 1,500 transactions per second while maintaining cryptographic security and immutable audit trails. Major banks and payment providers worldwide have integrated Ripple’s technology to reduce operational costs, eliminate capital tied up in nostro accounts, and provide customers with instant settlement capabilities. As cross-border payment volumes continue growing 8% annually, enterprises demand robust execution frameworks that handle institutional-scale throughput while satisfying stringent regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions.[1]
Architectural Overview of Ripple’s Enterprise Payment Execution Model
Ripple’s enterprise payment architecture separates into distinct layers handling messaging, validation, settlement, and reconciliation. The messaging layer accepts payment instructions through REST APIs and WebSocket connections supporting both synchronous and asynchronous communication patterns. Transaction validation occurs across a distributed network of independent validators running the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm, achieving agreement on ledger state without proof-of-work mining. The settlement layer executes atomic transfers updating account balances with cryptographic finality once consensus reaches 80% validator agreement. Reconciliation components synchronize ledger state with internal banking systems ensuring consistency between blockchain records and traditional accounting platforms. This modular architecture allows enterprises to customize execution flows while maintaining interoperability with the broader RippleNet ecosystem. Payment channels enable high-frequency micro-transactions off-ledger with periodic on-chain settlement reducing transaction costs for specific use cases. The framework supports multi-currency operations where XRP serves as bridge asset facilitating instant liquidity between currency pairs lacking direct markets. Enterprise deployments typically implement hybrid architectures integrating Ripple for international settlement while utilizing domestic payment rails for local transactions, optimizing both speed and cost efficiency.
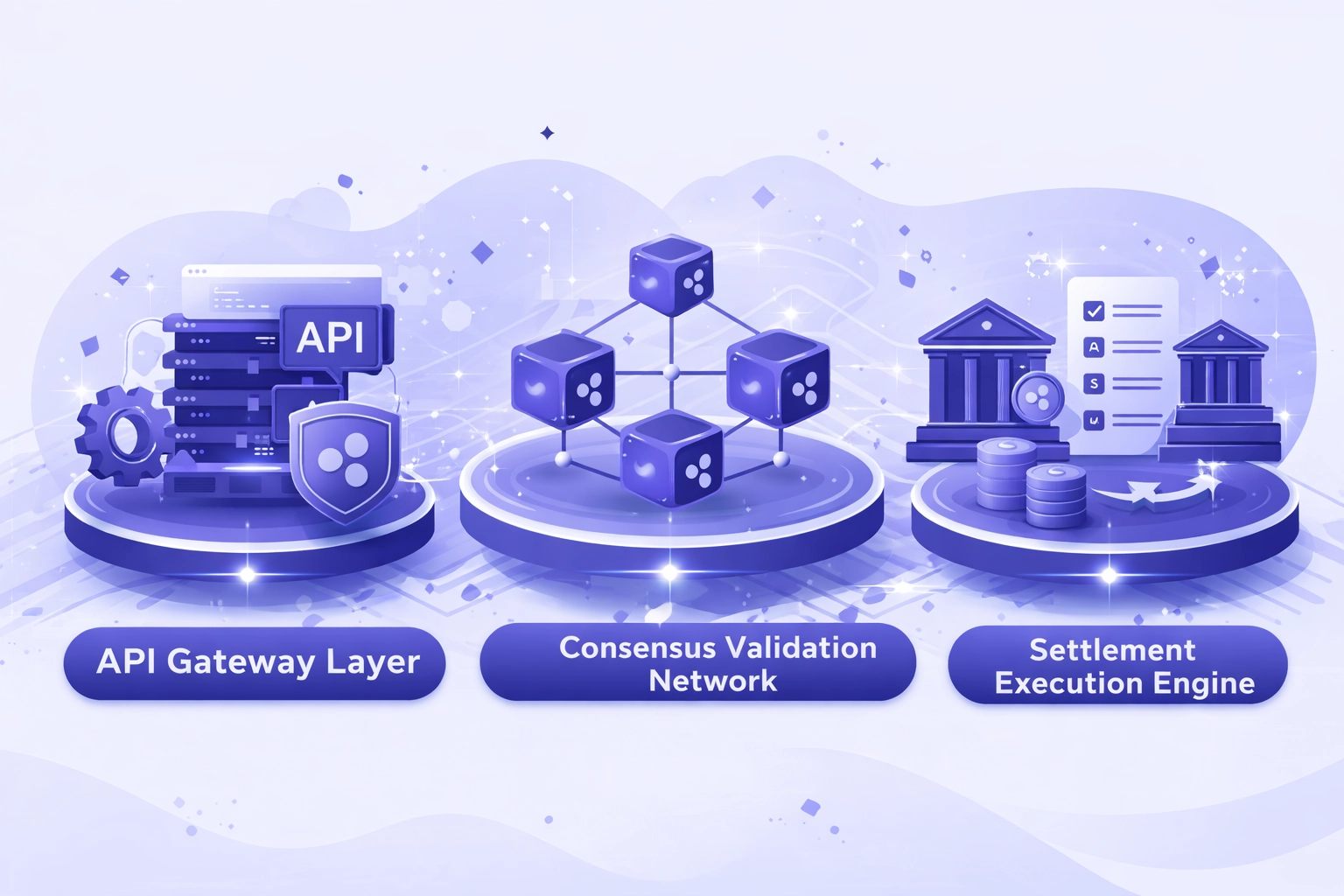 Core Architectural Components
Core Architectural Components
API Gateway Layer
RESTful endpoints and WebSocket interfaces accept payment instructions from enterprise applications with authentication, rate limiting, and request validation ensuring secure system access.
Consensus Validation Network
Distributed validators execute the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm achieving Byzantine fault-tolerant agreement on transaction ordering and ledger state updates.
Settlement Execution Engine
Atomic transfer mechanisms update account balances with cryptographic finality once consensus threshold reaches, ensuring irreversible settlement without intermediary clearing.
Transaction Lifecycle Design in RippleNet-Based Payment Systems
Payment transactions in RippleNet follow a structured lifecycle from initiation through final settlement and reconciliation. The process begins when enterprise applications submit payment instructions containing sender, receiver, amount, and currency details. Transaction construction components validate input parameters, calculate fees, and generate cryptographically signed transaction blobs ready for ledger submission. Once submitted, transactions enter a queuing system where they await inclusion in the next ledger version based on fee priority and submission timestamp. Validator nodes receive transaction proposals and execute preliminary validation checking signature authenticity, account balances, and transaction format compliance. Consensus rounds occur approximately every 3-5 seconds where validators exchange proposals and vote on which transactions to include in the next validated ledger. Transactions achieving 80% validator agreement become immutably recorded in the ledger with a unique hash identifier. Post-settlement, monitoring systems emit events triggering downstream processes including balance updates, notification delivery, and accounting system synchronization. Failed transactions receive detailed error codes enabling automated retry logic or manual intervention. The entire lifecycle maintains comprehensive audit trails recording every state transition for compliance reporting and dispute resolution purposes.
Transaction Lifecycle Stages
Initiation and Validation
Payment requests undergo parameter validation, fee calculation, and cryptographic signing before submission to validator network for consensus processing.
Consensus Agreement
Validators exchange transaction proposals and vote through consensus rounds achieving 80% agreement threshold for ledger inclusion within 3-5 seconds.
Settlement Finality
Atomic balance updates execute with cryptographic immutability once consensus achieves, providing irreversible settlement without clearing intermediaries or delays.
Reconciliation and Reporting
Post-settlement processes synchronize ledger state with internal systems while generating audit trails, notifications, and compliance reports automatically.
Message Validation and Settlement Finality in Ripple Consensus
The Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm validates payment messages through multi-stage verification ensuring transaction integrity before ledger commitment. Initial validation checks transaction format compliance including properly formed field structures, valid account addresses, and cryptographic signature authenticity. Validators verify that transaction fees meet minimum network requirements and accounts possess sufficient balances to cover transfer amounts plus fees. Trust line verification ensures recipient accounts have established currency issuance relationships when receiving non-XRP assets. Sequence number validation prevents transaction replay attacks by confirming each transaction increments the sender’s sequence counter appropriately. During consensus rounds, validators independently execute transaction logic in a deterministic sandbox environment computing resultant state changes. Proposals containing identical transaction sets and state transformations receive votes from validators observing consistent outcomes. Once 80% of trusted validators agree on a transaction set, that ledger version becomes permanently validated and appended to the blockchain. Settlement finality occurs immediately upon validation with no subsequent confirmation periods required unlike proof-of-work systems needing multiple block confirmations. This design provides enterprises with certainty that payments are irreversible and final within seconds enabling real-time business process integration.
Liquidity Routing Logic Using XRP for Cross-Border Transfers
XRP serves as a bridge currency enabling instant liquidity for cross-border payments between currency pairs lacking direct exchange markets. When enterprises initiate payments from one fiat currency to another, liquidity routing engines analyze available pathways determining optimal conversion strategies. Direct currency markets receive priority when available, but most currency corridors lack sufficient depth for institutional-scale transfers. XRP bridges solve this by decomposing transfers into two atomic steps: source currency to XRP conversion followed by XRP to destination currency conversion. This approach accesses deep XRP liquidity pools maintained by market makers globally ensuring competitive exchange rates regardless of currency pair. Auto-bridging logic automatically detects when XRP pathways offer better pricing than direct routes, dynamically selecting the most cost-effective settlement method. Enterprises eliminate the need to pre-fund nostro accounts in destination currencies, reducing capital requirements by 60% while maintaining instant settlement capabilities. Liquidity providers earn spreads by maintaining order books in both XRP and various fiat currencies, creating economic incentives for deep market liquidity. The routing algorithms consider multiple factors including exchange rates, transfer fees, slippage impact, and settlement speed to optimize total transaction cost while meeting enterprise service level requirements for payment execution.
XRP Bridge vs Traditional Correspondent Banking
| Attribute | XRP Liquidity Bridge | Traditional Correspondent |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement Speed | 3-5 seconds real-time settlement | 2-5 business days delayed settlement |
| Capital Requirements | No pre-funded nostro accounts needed | Billions locked in correspondent accounts |
| Transaction Cost | Under $0.01 per transaction average | $25-50 per transaction typical fees |
| Currency Pair Coverage | Any currency pair via XRP bridge | Limited to established banking relationships |
| Transparency | Real-time tracking with cryptographic proof | Limited visibility until final settlement |
Smart Pathfinding Algorithms in Ripple Payment Execution
Pathfinding algorithms automatically discover optimal routes for payment execution across complex networks of currency relationships and liquidity pools. The XRP Ledger maintains a decentralized exchange where accounts establish trust lines authorizing specific counterparties to hold issued currencies. When enterprises submit cross-currency payments, pathfinding engines explore all possible conversion pathways considering direct currency trades, XRP bridges, and multi-hop chains through intermediary currencies. Depth-first search algorithms traverse the trust line graph identifying viable routes while pruning paths exceeding cost thresholds. Cost functions incorporate multiple variables including exchange rates, transfer fees, slippage estimates based on order book depth, and counterparty risk scores. Advanced implementations utilize machine learning models trained on historical transaction data predicting optimal routes based on time of day, currency pair volatility, and market maker availability patterns. Real-time pathfinding occurs during transaction submission as market conditions change continuously requiring dynamic route recalculation. Payment channels provide alternative pathways for high-frequency transfers between parties maintaining bidirectional channels settling net positions periodically on-chain. The pathfinding system implements fairness algorithms preventing any single liquidity provider from monopolizing transaction flow ensuring competitive pricing through market maker distribution.
Route Optimization Parameters
Exchange Rate Quality: Algorithms compare conversion rates across multiple pathways selecting routes offering best overall pricing for currency conversions required.
Liquidity Depth: Order book analysis estimates slippage impact for large transfers ensuring sufficient liquidity exists at competitive pricing levels throughout execution.
Transaction Fees: Total cost calculations include all intermediate transfer fees and exchange costs providing accurate end-to-end pricing for route comparison.
Counterparty Risk: Trust line analysis evaluates intermediary reliability using historical performance metrics and credit ratings when selecting multi-hop payment pathways.
Enterprise Wallet Architecture for High-Volume Ripple Payments
Enterprise wallet architectures must support millions of transactions daily while maintaining institutional-grade security and regulatory compliance. Hot wallets connected to the internet handle operational payments requiring immediate access for transaction signing and submission. Warm wallets maintain intermediate security balances with offline key storage but accessible within hours for liquidity management. Cold storage vaults secure the majority of institutional holdings using hardware security modules and multi-signature schemes requiring physical presence for access. Hierarchical deterministic wallet structures generate unlimited addresses from master seeds enabling organized account management and backup procedures. Address derivation follows BIP-32 and BIP-44 standards ensuring compatibility with industry wallet infrastructure. Transaction signing occurs in isolated environments preventing private key exposure to networked systems vulnerable to remote attacks. Multi-signature configurations require multiple authorized parties to approve high-value transfers implementing separation of duties and preventing unilateral fund movements. Automated sweeping mechanisms consolidate small balances from deposit addresses into centralized hot wallets optimizing fee efficiency and simplifying liquidity management. Enterprise wallet systems integrate with hardware security modules providing FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certified key protection meeting banking industry security requirements for custody operations.
Enterprise Wallet Security Requirements
Implement hardware security modules for cryptographic key generation and storage meeting FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certification standards
Deploy multi-signature transaction approval workflows requiring multiple authorized parties to execute high-value transfers above threshold limits
Maintain segregated hot, warm, and cold wallet infrastructure allocating funds based on access requirements and risk tolerance levels
Establish hierarchical deterministic wallet structures enabling unlimited address generation from encrypted master seeds with secure backup procedures
Configure automated balance monitoring and sweeping mechanisms consolidating fragmented deposits into centralized operational wallets for efficiency
Implement transaction signing in air-gapped environments preventing private key exposure to internet-connected systems vulnerable to remote attacks
Compliance-Aware Execution Frameworks on Ripple Blockchain
Regulatory compliance integrates directly into Ripple payment execution through programmable validation rules and automated monitoring systems. Know Your Customer processes verify participant identities before authorizing account access using cryptographic identity proofs linked to validated credentials. Anti-money laundering checks screen transactions against sanctions lists including OFAC, UN, and EU databases rejecting transfers involving prohibited parties or jurisdictions. Transaction monitoring engines analyze payment patterns in real-time flagging suspicious activity based on velocity thresholds, geographic anomalies, and behavioral analytics. Configurable rule engines enable financial institutions to define custom compliance policies reflecting their risk appetites and regulatory obligations. Automated reporting generates regulatory filings including Suspicious Activity Reports and Currency Transaction Reports from blockchain data without manual compilation. Travel Rule compliance embeds originator and beneficiary information within payment metadata ensuring cross-border transfers include required identifying details. Geographic restrictions prevent transactions with embargoed countries enforced programmatically during transaction validation. Address whitelisting restricts payment destinations to pre-approved counterparties meeting due diligence requirements. Audit trails maintain immutable records of all compliance decisions and policy applications enabling regulatory examination and internal oversight. These frameworks reduce compliance costs by 40% compared to manual processes while improving accuracy and response times for regulatory inquiries.
Build Enterprise Payment Infrastructure
Deploy production-ready Ripple payment systems with expert guidance on architecture design, regulatory compliance, and institutional security standards.
Integrating Core Banking Systems with RippleNet APIs
Integration between traditional core banking systems and RippleNet requires middleware layers translating between legacy payment formats and blockchain protocols. RESTful APIs provide standard interfaces for payment submission, status queries, and ledger synchronization accessible from any programming environment. WebSocket connections stream real-time events including transaction confirmations, balance updates, and system notifications enabling reactive application architectures. Message translation services convert between industry payment formats like ISO 20022 and SWIFT MT messages into RippleNet’s native transaction structure. Authentication mechanisms implement OAuth 2.0 and API key management ensuring secure access control for system integrations. Rate limiting protects backend infrastructure from excessive request loads while prioritizing critical payment operations during peak processing periods. Webhook endpoints enable callback-based integration patterns where RippleNet pushes transaction events to banking systems eliminating polling overhead. Database synchronization adapters maintain consistency between blockchain ledger state and internal accounting systems through reconciliation processes. Batch processing interfaces handle high-volume payment file uploads during nightly settlement windows complementing real-time transaction capabilities. Error handling frameworks provide detailed diagnostic information when integration failures occur enabling automated retry logic and manual intervention workflows. Connection pooling and circuit breaker patterns ensure resilient integration surviving temporary network disruptions without transaction loss or duplicate processing.
RippleNet Integration Patterns
| Integration Method | Use Case | Implementation Approach |
|---|---|---|
| REST API | Synchronous payment submission and query | HTTP endpoints for transaction operations with JSON payloads |
| WebSocket Streaming | Real-time event notification and ledger monitoring | Bidirectional persistent connections with subscription management |
| Message Queue | Asynchronous batch processing and load balancing | Kafka or RabbitMQ integration with durable message persistence |
| Webhook Callbacks | Push-based transaction confirmations to core systems | Registered HTTP endpoints receiving event-triggered notifications |
| File Transfer | Bulk payment uploads during scheduled processing windows | SFTP or API-based file ingestion with format translation |
Fault Tolerance and Retry Logic in Ripple Transaction Execution
Enterprise payment systems require sophisticated fault tolerance mechanisms ensuring transaction completion despite temporary infrastructure failures. Idempotency guarantees prevent duplicate transaction submission when retry logic activates after communication failures. Unique transaction identifiers enable systems to detect previously processed payments avoiding double-spending scenarios. Exponential backoff algorithms space retry attempts progressively longer intervals preventing system overload during recovery periods. Circuit breaker patterns detect sustained failure conditions temporarily halting retry attempts while infrastructure stabilizes. Transaction status polling monitors pending payments checking ledger state periodically until definitive outcomes emerge. Timeout configurations define maximum waiting periods before declaring transactions failed and initiating compensating workflows. Dead letter queues capture permanently failed transactions for manual review and resolution preventing data loss. Compensation transactions reverse partially completed multi-step operations when subsequent steps fail maintaining consistency across distributed systems. Transaction logs record every retry attempt with timestamps and error details enabling root cause analysis and system optimization. Health check endpoints monitor validator connectivity and ledger synchronization status proactively detecting infrastructure degradation before it impacts payment processing. Automated failover switches transaction submission to backup validator nodes when primary connections fail ensuring continuous operation.
Transaction Retry Strategy Timeline
Immediate Retry (0-5s)
Transient network failures receive immediate retry attempts with minimal delay assuming rapid recovery from temporary connectivity issues.
Exponential Backoff (5s-5m)
Subsequent retries increase intervals exponentially preventing system overload while allowing infrastructure time to recover from degradation.
Circuit Breaker Activation (5-15m)
Sustained failures trigger circuit breaker temporarily halting retry attempts while alerting operations teams for manual intervention.
Failover Switching (15-30m)
Extended outages activate automated failover routing transactions to backup validator infrastructure ensuring continuous payment processing.
Manual Queue (30m+)
Persistently failed transactions move to manual review queues where operations teams investigate root causes and execute compensating actions.
Post-Mortem Analysis
Complete transaction logs enable detailed failure analysis identifying systemic issues requiring infrastructure improvements or configuration adjustments.
Security Models for Enterprise-Grade Ripple Payment Systems
Enterprise security architectures implement defense-in-depth strategies protecting payment systems across multiple layers. Network segmentation isolates blockchain infrastructure from public internet access requiring VPN or private network connectivity for system administration. Firewall rules whitelist specific validator IP addresses preventing unauthorized network participants from influencing consensus. API authentication enforces OAuth 2.0 token-based access control with fine-grained permission scoping limiting capabilities by client application. Transport layer security encrypts all network communications using TLS 1.3 preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Transaction signing occurs in dedicated signing services maintaining private keys in hardware security modules never exposing them to application code. Address verification algorithms detect typosquatting and invalid destinations preventing funds from sending to incorrect recipients. Anomaly detection systems monitor transaction patterns flagging unusual activity including velocity spikes, geographic anomalies, and deviation from historical norms. Penetration testing and security audits occur quarterly identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. Incident response procedures define escalation paths and remediation steps when security breaches occur minimizing impact duration. Compliance frameworks align with industry standards including PCI DSS for payment processing and SOC 2 for operational controls ensuring institutional-grade security posture.
Throughput Optimization Techniques for Ripple-Based Payments
Maximizing payment throughput requires optimization across transaction construction, network communication, and validator infrastructure. Transaction batching combines multiple payments into single ledger submissions reducing per-transaction overhead and fee costs. Parallel processing architectures submit transactions concurrently to multiple validator nodes increasing effective throughput beyond single-threaded limits. Connection pooling maintains persistent WebSocket connections to validator infrastructure eliminating handshake overhead for each transaction. Transaction prevalidation checks locally before submission filtering invalid transactions that would waste network resources and ledger space. Fee optimization algorithms calculate minimum viable fees based on current network congestion ensuring fast processing without overpayment. Payment channels enable high-frequency micro-transactions off-ledger with periodic on-chain settlement reducing ledger load for specific use cases. Database query optimization ensures balance checks and transaction history retrieval complete quickly preventing bottlenecks in payment workflows. Caching strategies store frequently accessed data like exchange rates and account configurations in memory reducing database query loads. Load balancing distributes transaction submission across multiple validator nodes preventing any single node from becoming overwhelmed. Infrastructure scaling provisions additional compute resources during peak periods maintaining consistent performance as transaction volumes fluctuate. These optimizations enable production systems to process sustained loads of thousands of transactions per second approaching the theoretical limits of Ripple’s consensus protocol.
Performance Optimization Strategies
| Optimization Technique | Performance Impact | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Batching | 40-60% throughput increase for bulk operations | Medium – requires queue management logic |
| Connection Pooling | 25-35% latency reduction eliminating handshakes | Low – standard library implementations available |
| Payment Channels | 100x throughput for micro-transaction scenarios | High – requires channel management infrastructure |
| Parallel Submission | 2-3x throughput utilizing concurrent processing | Medium – asynchronous programming patterns needed |
| Query Caching | 50-70% reduction in database load and latency | Low – Redis or similar caching layer integration |
Atomic Settlement Strategies Across Multi-Currency Corridors
Atomic settlement ensures multi-step currency conversions execute completely or fail entirely without partial state changes creating inconsistencies. Cross-currency payments decompose into source currency deduction, currency conversion, and destination currency credit operations. Atomicity guarantees all three steps complete successfully or none execute preventing scenarios where funds deduct from sender without reaching recipient. The XRP Ledger implements atomicity through transaction preconditions checking all requirements before applying any state changes. Trust line verification confirms recipients can accept destination currencies before initiating conversions preventing stuck transactions. Balance checks ensure all intermediate conversions have sufficient liquidity avoiding partial execution scenarios. Escrow mechanisms temporarily lock funds during multi-step processes releasing them only upon successful completion of all dependent operations. Time-based holds provide automatic rollback for operations exceeding maximum execution windows preventing indefinite resource locks. Cryptographic proofs of payment provide recipients with mathematical certainty that funds transferred successfully eliminating reconciliation delays. Settlement finality occurs within single ledger versions typically 3-5 seconds providing near-instant confirmation for complex multi-currency transfers. These atomic guarantees enable enterprises to reliably execute sophisticated payment flows without developing complex error recovery and compensation logic for partial failures.
Real-Time Monitoring and Auditing in Ripple Payment Frameworks
Comprehensive monitoring provides operational visibility into payment system health, performance, and compliance status. Dashboard interfaces display real-time metrics including transaction throughput, success rates, average settlement times, and fee costs. Alert systems trigger notifications when key performance indicators deviate from expected ranges enabling proactive issue resolution. Ledger monitoring tracks validator consensus status detecting forks or synchronization delays impacting settlement reliability. Account balance tracking monitors liquidity across operational wallets alerting when reserves fall below configured thresholds. Transaction tracing follows payment journeys from submission through settlement capturing timing breakdowns for performance analysis. Error rate monitoring identifies systematic failures requiring infrastructure attention or code corrections. Compliance monitoring screens transactions against regulatory rules generating alerts for suspicious activity patterns. Audit trail generation creates immutable records of all system actions including configuration changes, access events, and operational decisions. Performance trending analyzes historical metrics identifying capacity constraints before they impact service levels. Geographic monitoring maps transaction flows across jurisdictions ensuring compliance with regional regulations. Cost analytics track fee expenditures optimizing transaction submission strategies to minimize operating expenses. Integration with enterprise monitoring platforms enables centralized visibility across payment infrastructure and traditional banking systems.
Deploy Production Payment Systems
Leverage proven expertise in Ripple infrastructure design, implementation, and optimization for institutional-grade cross-border payment solutions.
Scalable Node Infrastructure for Enterprise Ripple Deployments
Enterprise validator infrastructure requires horizontal scaling capabilities supporting growing transaction volumes without performance degradation. Containerized validator deployments using Docker and Kubernetes enable dynamic resource allocation based on workload demands. Auto-scaling policies provision additional validator instances during peak processing periods maintaining consistent settlement times. Load balancers distribute transaction submissions across validator pools preventing hotspots and maximizing throughput. Geographic distribution deploys validators across multiple data centers and cloud regions providing disaster recovery and reduced latency for global operations. High-availability configurations implement active-active clusters where multiple validators process transactions simultaneously with automatic failover. Storage optimization uses SSD arrays for ledger data ensuring fast transaction validation and historical query performance. Network optimization implements dedicated bandwidth provisioning between validator nodes reducing consensus latency. Database partitioning distributes account data across multiple shards enabling parallel processing of independent transactions. Monitoring infrastructure tracks resource utilization triggering capacity planning before constraints impact operations. Version management systems coordinate validator software upgrades minimizing downtime while maintaining consensus compatibility. Configuration management tools ensure consistent settings across distributed validator infrastructure preventing consensus failures from configuration drift.
Key Management and Custody Design for Institutional Use
Institutional key management implements multi-layered security controls protecting cryptographic assets from theft and unauthorized access. Hardware security modules generate and store private keys in tamper-resistant environments meeting FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certification standards. Multi-signature schemes require multiple parties to authorize transactions implementing separation of duties preventing unilateral fund movements. Key ceremony procedures document master key generation with multiple witnesses and notarization establishing legal accountability. Backup and recovery systems maintain encrypted key copies in geographically distributed safe deposit boxes enabling restoration after catastrophic failures. Access control implements role-based permissions limiting key operations to authorized personnel with audit trails of all access events. Time-delayed transactions provide cooling-off periods for large transfers allowing security teams to review and potentially cancel suspicious operations before execution. Key rotation policies periodically generate new keys transferring balances to fresh addresses limiting exposure from potential historical compromises. Secure enclaves isolate signing operations from general computing infrastructure preventing malware from extracting keys during transaction signing. Third-party custody services provide institutional-grade key management for organizations lacking internal security expertise. Insurance coverage protects against key loss or theft providing financial recourse when security controls fail.
Custody Solution Comparison
| Custody Type | Security Level | Operational Flexibility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Wallet | Medium – internet connected | Immediate automated access | Operational funds for daily transactions |
| Warm Wallet | High – offline key storage | Hours to access for transfers | Reserve funds for liquidity management |
| Cold Storage | Maximum – air-gapped vaults | Days to access with procedures | Long-term asset holding and insurance |
| Third-Party Custody | Institutional grade insured | API-based programmatic access | Enterprises lacking internal capabilities |
Regulatory Controls Embedded in Ripple Payment Execution
Embedding regulatory controls directly into payment execution ensures compliance without manual oversight. Sanctions screening integrates with OFAC, UN, and EU watchlists blocking transactions involving prohibited individuals or entities. Geographic restrictions prevent payments to embargoed countries enforced through IP geolocation and account registration data. Transaction limits implement daily and monthly caps on individual and aggregate payment volumes satisfying anti-money laundering requirements. Velocity checks flag unusual transaction patterns including rapid successive transfers or sudden volume increases. Customer due diligence workflows verify identity documents before authorizing account access maintaining KYC compliance. Travel Rule implementation embeds originator and beneficiary information within payment messages satisfying cross-border information exchange requirements. Source of funds verification requires documentation for large transfers preventing illicit fund movement. Enhanced due diligence applies to politically exposed persons and high-risk jurisdictions with additional approval workflows. Automated reporting generates regulatory filings including Suspicious Activity Reports when patterns match defined criteria. Record retention maintains seven years of transaction history accessible for regulatory examination and audit requests. These controls satisfy requirements from FinCEN, FATF, and international payment regulations while maintaining operational efficiency through automation.
Disaster Recovery and High Availability in Ripple Systems
Disaster recovery planning ensures payment system continuity despite catastrophic infrastructure failures. Geographic redundancy deploys validator infrastructure across multiple cloud regions and data centers preventing single location failures from disrupting operations. Automated failover switches traffic to backup infrastructure within seconds when primary systems experience outages. Regular backup procedures capture ledger state and configuration data enabling rapid restoration after data loss events. Recovery time objectives define maximum acceptable downtime durations guiding infrastructure investment decisions. Recovery point objectives specify acceptable data loss windows informing backup frequency requirements. Disaster simulation exercises test recovery procedures identifying gaps before actual incidents occur. Documentation procedures maintain detailed runbooks guiding operations teams through recovery workflows. Communication plans define escalation paths and stakeholder notification procedures during outage events. Alternative processing sites maintain ready standby capacity activated during extended primary site unavailability. Database replication maintains synchronized copies across geographically distributed infrastructure enabling instant failover. Health monitoring detects degraded infrastructure triggering proactive failover before complete failures impact service. These capabilities enable enterprises to achieve five-nines availability approaching 99.999% uptime annually.
Future Evolution of Ripple Execution Frameworks for Enterprises
Ripple’s execution framework continues evolving with enhanced features addressing emerging enterprise requirements. Federated sidechains enable private transaction processing while maintaining connectivity to the main XRP Ledger for settlement. Smart contract capabilities expand payment logic beyond simple transfers supporting complex conditional payments and programmable money. Central bank digital currency integration positions Ripple as settlement infrastructure for sovereign digital currencies. Automated market making protocols provide algorithmic liquidity provisioning reducing reliance on manual market maker operations. Privacy enhancements implement zero-knowledge proofs concealing transaction details while maintaining regulatory compliance through selective disclosure. Interoperability bridges connect Ripple with other blockchain networks enabling seamless value transfer across ecosystems. Quantum-resistant cryptography prepares payment infrastructure for post-quantum security requirements protecting long-term asset holdings. Machine learning integration optimizes pathfinding algorithms and fraud detection improving system intelligence over time. Governance mechanisms enable decentralized protocol upgrades reducing reliance on central coordination. These advancements position Ripple as foundation for next-generation payment infrastructure serving financial institutions globally.
Enterprise payment systems built on Ripple’s execution framework deliver transformative capabilities for cross-border financial services. The architecture enables real-time gross settlement with cryptographic finality in 3-5 seconds, processing 1,500 transactions per second at institutional scale. XRP liquidity bridges eliminate capital trapped in nostro accounts reducing requirements by 60% while maintaining instant settlement. Smart pathfinding algorithms discover optimal routes across complex currency networks minimizing costs automatically. Compliance controls embed directly into execution workflows satisfying KYC, AML, and sanctions requirements without manual oversight. Fault-tolerant retry logic and atomic settlement strategies ensure reliable payment completion across multi-currency corridors. Enterprise wallet architectures implement hierarchical key management with multi-signature security meeting institutional custody standards. Integration patterns enable seamless connectivity between RippleNet and traditional core banking systems through standard APIs. Real-time monitoring provides operational visibility into payment flows, validator performance, and compliance status. Scalable infrastructure supports horizontal growth handling increasing transaction volumes without performance degradation. These capabilities position Ripple as premier blockchain platform for enterprise payment modernization delivering speed, efficiency, and reliability impossible with legacy correspondent banking networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ripple’s execution framework operates on distributed ledger technology enabling real-time gross settlement without intermediary banks. Unlike traditional systems requiring multiple days for cross-border transfers, Ripple achieves settlement finality within 3-5 seconds through consensus validation across independent validator nodes. The framework eliminates pre-funded nostro accounts by utilizing XRP as bridge currency, reducing capital requirements by up to 60% while providing cryptographic proof of payment immutability. Enterprise developers integrate directly with RippleNet APIs accessing atomic settlement, instant liquidity, and transparent transaction tracking unavailable in legacy payment rails.
Building enterprise payment systems on Ripple requires proficiency in RESTful API integration, WebSocket protocols for real-time event streaming, and cryptographic signing libraries for transaction authentication. Developers utilize languages like JavaScript, Python, Java, and C++ alongside Ripple’s official SDKs. Understanding XRP Ledger’s transaction types including Payment, TrustSet, and OfferCreate proves essential. Knowledge of asynchronous programming patterns handles concurrent payment processing while database expertise manages transaction reconciliation. Familiarity with enterprise integration patterns, message queuing systems, and microservices architecture ensures robust production deployments handling thousands of transactions per second.
Ripple embeds compliance controls directly into execution frameworks through programmable transaction validation rules. The system supports KYC/AML verification through cryptographic identity proofs before payment authorization. Transaction monitoring engines analyze patterns in real-time flagging suspicious activity based on configurable risk parameters. Regulatory reporting generates automatically from immutable ledger data ensuring audit trails meet jurisdictional requirements. Financial institutions implement address whitelisting, transaction limits, and multi-signature authorization satisfying regulatory frameworks including BSA, FinCEN, and international payment standards while maintaining operational efficiency through automated compliance workflows.
Ripple’s XRP Ledger processes 1,500 transactions per second with settlement finality in 3-5 seconds, substantially exceeding traditional payment networks. Enterprise implementations achieve higher effective throughput through payment batching and channel optimization. The consensus protocol scales horizontally as validator networks expand without performance degradation. Production deployments demonstrate sustained processing of millions of daily transactions with sub-second latency. Payment queuing mechanisms handle traffic spikes while load balancing across validator infrastructure ensures consistent performance. Organizations report 99.99% uptime with transaction costs under $0.01 making Ripple viable for high-frequency payment operations.
Enterprise integration utilizes RippleNet’s REST APIs and messaging protocols compatible with core banking platforms. Middleware layers translate between legacy payment formats like ISO 20022, SWIFT MT messages, and Ripple’s native transaction structure. Connection frameworks support both batch processing for scheduled settlements and real-time streaming for instant payments. Database adapters synchronize ledger state with internal accounting systems ensuring consistency. Organizations implement hybrid architectures where Ripple handles cross-border settlement while domestic systems manage local operations. Standardized integration patterns reduce implementation timelines to weeks rather than months typical of traditional payment network integrations.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







