Key Takeaways
-
DAG processes transactions in parallel instead of in blocks, which significantly improves speed, scalability, and overall network efficiency.
-
Unlike traditional blockchains that face congestion as usage grows, DAG networks often become faster as more participants join the system.
-
DAG technology enables near-instant confirmations and extremely low or zero transaction fees, making it ideal for micropayments and real-time applications.
-
Blockchain remains stronger for security-focused use cases, while DAG is better suited for high-throughput environments like IoT, supply chains, and high-frequency systems.
-
Popular projects such as IOTA, Nano, Fantom, Hedera, and Avalanche demonstrate that DAG technology is viable at real-world scale.
-
Choosing between DAG and blockchain depends on business goals, where speed and cost-efficiency favor DAG, and decentralization and long-term security favor traditional blockchain.
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) represent an innovative alternative to traditional blockchain architecture, offering significant improvements in scalability, transaction speed, and cost efficiency. Unlike conventional blockchains, which process transactions sequentially in blocks, DAG technology enables the parallel processing of multiple transactions simultaneously. This fundamental difference makes DAGs particularly valuable for high-volume environments where speed and cost are critical.
This comprehensive guide explains what DAGs are, how they work, their key advantages over traditional blockchains, real-world cryptocurrency projects that utilize DAG technology, and practical applications across various industries.
What is a Directed Acyclic Graph in a Blockchain?
Definition
A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) in blockchain is a data structure that enables parallel transaction processing instead of sequential blocks, resulting in faster confirmations, higher scalability, and lower transaction costs compared to traditional blockchains.
A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) in blockchain is an advanced data structure that enhances transaction speed and efficiency compared to traditional linear blockchain architecture. Unlike conventional blockchains that arrange transactions in a sequential chain of blocks, a DAG allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, making it significantly more scalable and cost-effective.
Key Terminology:
- Directed: Transaction references have direction, and each transaction references one or more previous transactions
- Acyclic: No cycles exist in the graph structure, so you cannot traverse edges and return to the original transaction
- Graph: Multiple connection paths exist rather than a single linear chain
- Nodes: Individual transactions form nodes in the DAG structure
- Edges: Transaction references create directed connections between nodes
Core Difference from Blockchain:
| Aspect | Traditional Blockchain | DAG Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Processing | Sequential, one block at a time | In parallel, multiple transactions are simultaneously |
| Structure | Linear chain of blocks | Web-like graph network |
| Confirmation Time | Minutes to hours with block validation | Seconds to milliseconds |
| Scalability | Limited by block size and generation time | Scales naturally with network growth |
| Mining and Fees | Energy-intensive mining is required | Minimal or zero transaction fees |
For organizations implementing DAG-based solutions, professional blockchain development services provide customized architecture design, ensuring optimal performance and integration with existing systems.
The Architecture of DAG: Parallel Transaction Processing
The DAG structure in blockchain networks operates by organizing transactions in a way that enables simultaneous processing rather than sequential validation.
Step 1: Transaction Submission
Users send transactions directly to the network. Unlike traditional blockchains, transactions do not need to wait for a block to be created before they can be processed.
Step 2: Direct Referencing
Each new transaction connects to one or more previous transactions. These connections form a graph-like structure and help prove that the transaction is valid and correctly linked to the network’s history.
Step 3: Parallel Validation
Many transactions can be validated at the same time by different network nodes. Because transactions are processed independently, the system can handle higher speeds without bottlenecks.
Step 4: Consensus Achievement
The network reaches agreement using DAG-specific methods such as gossip protocols. Transactions are ordered using a process called topological sorting, which ensures every transaction is confirmed only after the transactions it references.
Step 5: Finality
Once confirmed, transactions become permanent and cannot be changed. The network continues to grow naturally as new transactions link to earlier ones.
Why Parallel Processing Matters:
Traditional blockchains create bottlenecks: A blockchain network processes one block every 10-30 seconds (Bitcoin) or 12 seconds (Ethereum), regardless of transaction volume. DAG networks process multiple transactions concurrently, so adding more participants actually increases throughput.
How DAG Technology Differs from Traditional Blockchain
Understanding the differences between DAG and blockchain is essential for choosing the right technology for specific applications.
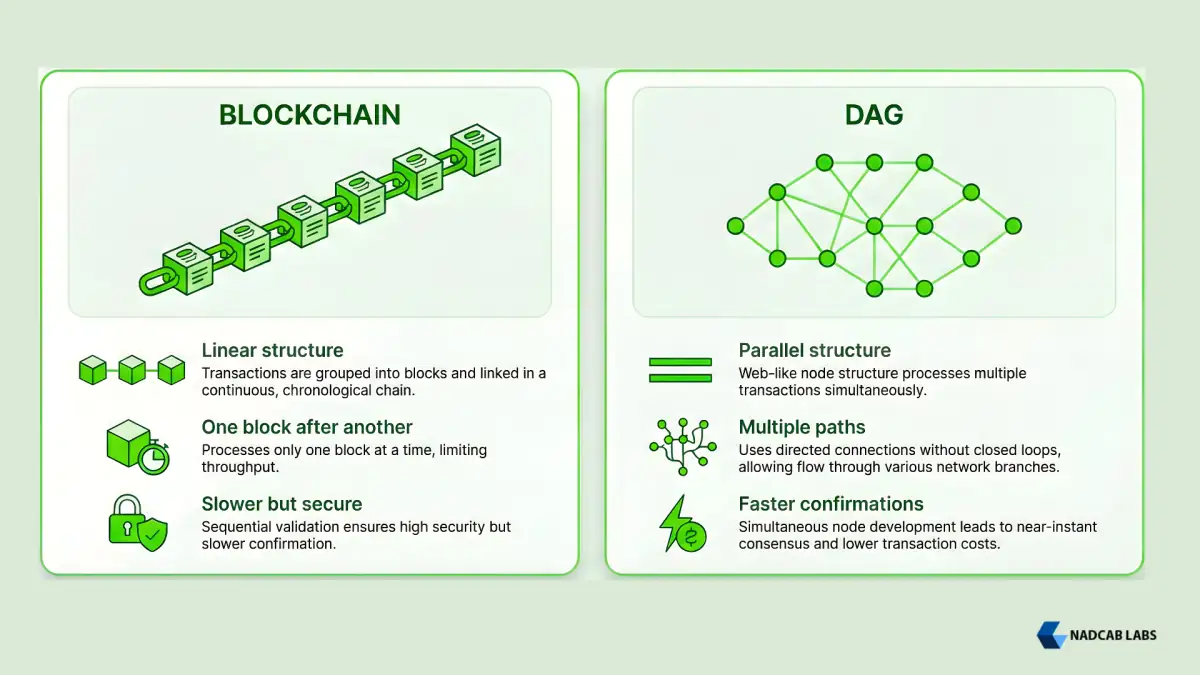
Architectural Differences
Transaction Organization:
- Blockchain: Transactions grouped into blocks; blocks form a sequential chain
- DAG: Individual transactions organized in a graph structure; multiple connection paths
Confirmation Process:
- Blockchain: Transaction waits for block creation, mining, then confirmation by subsequent blocks
- DAG: Transaction confirmed immediately upon referencing previous transactions
Consensus Mechanism:
- Blockchain: Proof-of-Work (energy-intensive) or Proof-of-Stake (capital requirements)
- DAG: Various mechanisms (gossip protocols, directed acyclic consensus, Byzantine fault tolerance)
Performance Differences Between DAG and Blockchain
| Metric | Blockchain | DAG |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | 12 to 600 TPS typical | 1,000+ TPS common |
| Confirmation Time | 10 to 30+ seconds | Less than 1 second is typical |
| Scalability | Limited due to block constraints | Scales naturally with network size |
| Transaction Costs | High due to mining or validator fees | Minimal or zero fees |
| Energy Consumption | Very high in PoW, moderate in PoS | Low, since no mining is required |
| Decentralization | High with many validators | Varies and can be more centralized |
| Finality | Probabilistic, reorgs possible | Near instant finality |
Security Comparison
Blockchain Security:
- Battle-tested for 15+ years (Bitcoin)
- Large validator networks provide security through decentralization
- Proof-of-Work provides cryptographic finality
DAG Security:
- Newer technology with less historical validation
- Depends heavily on consensus mechanism implementation
- Some DAG systems have fewer validators (centralization risk)
- Requires careful ordering and conflict resolution design
Use Case Suitability
Blockchain Better For:
- Decentralized finance requires maximum security
- Store-of-value cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin)
- Smart contract platforms require proven security
- Regulatory-compliant applications valuing decentralization
DAG Better For:
- Micropayments (fees matter)
- IoT device coordination (numerous transactions)
- Real-time applications (speed matters)
- High-frequency trading systems
- Supply chain tracking (many concurrent updates)
- Sustainability focus (energy efficiency matters)
DAG and blockchain are not direct competitors; they excel in different contexts. Blockchain prioritizes security and decentralization; DAG prioritizes speed and cost-efficiency. Organizations choose based on which properties matter most for their specific application. For organizations evaluating blockchain technology selection or implementing DAG-based solutions, consulting with blockchain experts helps ensure architectural alignment with business requirements.
Build Powerful Blockchain Solutions with Experts
From smart contracts to enterprise-grade Web3 platforms, our blockchain development team helps businesses launch scalable, secure, and future-ready products.
Which Crypto Projects Use DAG Technology?
Several crypto projects have adopted DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) technology to enhance scalability, speed, and efficiency in their networks. Here are some notable projects:
IOTA – The Tangle
Structure: DAG-based structure called “The Tangle.”
Focus: Internet of Things (IoT) and micropayments
Key Feature: Feeless transactions designed for device-to-device payments
Use Case: IoT sensors and connected devices exchanging value without intermediaries
Status: Active mainnet with a growing ecosystem
Nano – Block Lattice
Structure: DAG architecture called “Block Lattice.”
Key Feature: Each account maintains its own blockchain; accounts operate independently
Benefits: Instant transactions without mining; high scalability
Focus: Peer-to-peer cryptocurrency and instant payments
Status: Established network with 7 years of operational history
Fantom – Lachesis Protocol
Structure: DAG-based protocol called “Lachesis.”
Key Feature: Fast, scalable smart contract execution
Benefits: Solves traditional blockchain issues (slow confirmation, high costs)
Smart Contracts: Supports EVM-compatible dApps
Status: Major DeFi ecosystem with $1B+ TVL
Hedera Hashgraph
Structure: Technically a Hashgraph (related to DAG, not pure DAG)
Key Feature: The gossip protocol achieves a fast consensus mechanism
Benefits: Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus without mining
Applications: Enterprise applications, micropayments, supply chain
Status: Governed network with institutional backing
Avalanche
Structure: DAG-based consensus mechanism
Key Feature: Multiple blockchain networks within the ecosystem
Benefits: High throughput, fast finality, true decentralization
Scalability: Supports subnets for specific use cases
Status: Major Layer 1 blockchain with a strong DeFi ecosystem
Constellation Network
Structure: DAG architecture with Hypergraph Transfer Protocol (HGTP)
Key Feature: Processing 11,000+ TPS with minimal nodes
Focus: Enterprise solutions and scalable dApps
Enterprise Ready: Integrates with existing IT infrastructure
Status: Growing ecosystem focused on business adoption
Why DAG is a Game-Changer: Core Advantages
1. Exceptional Scalability
DAG allows multiple transactions to process simultaneously, enabling the network to handle high transaction volumes without slowing down. Unlike blockchains constrained by block generation time, DAG throughput can exceed 10,000 TPS.
Scalability Property: As network size grows, DAG performance often improves (more nodes = more parallel processing capacity). This is the opposite of traditional blockchains, which can become congested.
2. Ultra-Fast Transactions
Transaction confirmation happens in milliseconds to seconds, not minutes or hours. Users do not wait for block mining; transactions are confirmed as they reference existing transactions and achieve consensus through the DAG’s consensus mechanism.
Real Impact: An international payment settles instantly instead of 1-3 business days (traditional banking) or 10+ minutes (Bitcoin).
3. Minimal or Zero Transaction Fees
DAG networks eliminate energy-intensive mining, removing the primary fee component. Many DAG systems operate with zero fees or fractions of a cent per transaction.
Economic Impact: Enables business models impossible on blockchain (micropayments, high-frequency operations, IoT automation).
4. Superior Energy Efficiency
DAG does not rely on mining (Proof-of-Work), making it vastly more energy-efficient than traditional blockchains. A DAG transaction consumes orders of magnitude less electricity than a Bitcoin transaction.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable alternative for organizations prioritizing carbon footprint reduction.
5. No Network Bottlenecks
Traditional blockchains hit performance ceilings as networks grow. DAG architecture scales horizontally; adding more participants increases overall throughput rather than causing congestion.
Practical Result: Network performance remains consistent during peak demand periods.
6. Deterministic Finality
DAG transactions achieve final settlement deterministically (not probabilistically like blockchain). Once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed, providing certainty that blockchains cannot match.
Key Advantages of Blockchain DAG
Blockchain DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) offers several key advantages that make it an attractive alternative to traditional blockchain structures:
-
Scalability
DAG allows multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, enabling the network to handle a high volume of transactions without slowing down.
-
Faster Transactions
Since there’s no need to wait for blocks to be mined, transactions in a DAG-based system are confirmed much more quickly, leading to faster processing times.
-
Lower Fees
Without the need for miners to validate transactions, the costs associated with transactions in a DAG network are significantly reduced, often leading to lower or even zero fees.
-
Energy Efficiency
DAG doesn’t rely on energy-intensive mining processes, making it a more eco-friendly option compared to traditional blockchains.
-
No Bottlenecks
The parallel structure of DAG ensures that as the network grows, it doesn’t experience the bottlenecks that can occur in traditional blockchains, maintaining consistent performance.
Final Take
Directed Acyclic Graphs represent a significant innovation in distributed ledger technology, addressing fundamental limitations of traditional blockchains. By enabling parallel transaction processing, DAGs achieve superior scalability, faster settlement, and lower costs, making them ideal for applications where speed and efficiency matter most.
The choice between DAG and blockchain depends on application requirements. Blockchain excels at decentralized security and store-of-value applications. DAG excels at high-throughput, low-cost applications where instant settlement is critical. Real-world cryptocurrency projects, IOTA, Nano, Fantom, Hedera, and Avalanche, demonstrate DAG’s viability at scale. Emerging applications in IoT, supply chain, autonomous vehicles, and DeFi showcase DAG’s practical value.
As blockchain technology matures, DAG-based systems will likely coexist with traditional blockchains, each serving its optimal use cases. Organizations evaluating distributed ledger technology should consider both architectures when designing solutions.
For detailed guidance on implementing DAG-based solutions or integrating DAG technology with existing systems, professional blockchain consulting services provide expertise, ensuring proper architecture selection and deployment.
Frequently Asked Questions
A DAG is a data structure where transactions connect like a web instead of a chain. Each transaction references previous transactions, creating a graph where you can move forward but never loop back. This allows multiple transactions to be processed at the same time, making DAG faster and cheaper than traditional blockchains.
Blockchain processes transactions sequentially in blocks; DAG processes multiple transactions in parallel. Blockchain requires mining and takes minutes to confirm; DAG confirms in seconds with minimal fees. Blockchain excels at security and decentralization; DAG excels at speed and scalability. Both are valid technologies optimized for different purposes.
DAG’s main advantages are:
(1) Handles 10,000+ transactions per second
(2) Fast confirmation in milliseconds to seconds
(3) Minimal fees, such as zero or near-zero
(4) Energy efficiency with no mining required
(5) No bottlenecks, improves as the network grows
(6) Deterministic finality: Transactions cannot be reversed.
These advantages make DAG ideal for high-volume, time-sensitive applications.
DAG is not universally “better”—it’s better for specific use cases. DAG excels for micropayments, IoT, high-frequency operations, and speed-critical applications. Blockchain excels for decentralized finance, store-of-value cryptocurrencies, and applications requiring maximum security. Choose DAG if speed and cost matter most; choose blockchain if decentralization and security matter most.
Major DAG-based cryptocurrencies include: IOTA (Tangle, IoT focus), Nano (instant payments, zero fees), Fantom (smart contracts, DeFi), Hedera Hashgraph (enterprise applications), Avalanche (multiple blockchains), and Constellation Network (11,000 TPS). Each implements DAG differently but shares the core benefits of parallel processing, fast confirmation, and low fees.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







