Key Takeaways: What Is IoT Development?
- IoT development connects physical devices with software systems, enabling machines to collect, send, and act on data.
- IoT is not a single product; it is a complete system combining hardware, connectivity, and application logic.
- The core purpose of IoT development is automation, not just data collection or remote visibility.
- IoT development differs from traditional software because it operates across physical environments and digital platforms.
- Devices alone do not make an IoT solution; software orchestration is what turns hardware into a system.
- IoT development focuses on system behavior, not isolated apps, dashboards, or sensors.
- Scalability and reliability are fundamental requirements from the very first design decision.
- IoT development runs continuously, often 24/7, unlike user-driven web or mobile applications.
- IoT systems bridge real-world operations and digital intelligence, forming a foundation for modern enterprise automation.
- Understanding IoT development concepts is essential before exploring architecture, costs, risks, or use cases.
The physical world has always generated data. Machines vibrate. Temperatures rise and fall. Vehicles move. Equipment wears down. For decades, this information existed silently, invisible unless a human stood nearby to observe it.
IoT development changes that reality.
IoT development is the discipline that allows physical objects to sense what is happening around them, communicate that information digitally, and interact with software systems in a meaningful, automated way. It is not just about connecting devices to the internet. It is about transforming physical operations into continuously observable, measurable, and improvable systems.
At its core, IoT development brings the physical and digital worlds into a single operational loop.
Understanding IoT Beyond the Buzzword
The term “Internet of Things” is often misunderstood. Many people associate IoT with consumer gadgets, smart homes, or connected appliances. While these are visible examples, they do not define IoT development as an engineering discipline. Focusing only on gadgets hides the true scope and purpose of IoT systems.
IoT development is not about isolated products. It is about connected operational ecosystems. These ecosystems are designed to function continuously, often without direct human involvement, while maintaining reliability and accuracy over long periods of time.
The real value of IoT development lies not in connectivity alone, but in how data flows, decisions are made, and actions are triggered across an entire system.
What IoT Is Not
IoT development is often confused with simpler concepts, which leads to unrealistic expectations and failed projects. Understanding what IoT is not is just as important as understanding what it is.
-
Not just sensors
Sensors only collect raw signals. IoT development turns those signals into usable information through software-driven processing and system-level logic. -
Not just an app
A mobile or web app is only an interface. IoT development focuses on the system operating behind the interface, often without direct user interaction. -
Not just internet connectivity
Connectivity enables communication, but IoT development defines how systems behave when connectivity changes, degrades, or becomes intermittent.
Why IoT Matters in 2026
IoT has moved far beyond smart gadgets. It’s now a critical infrastructure layer for global digital transformation.
Key facts showing IoT’s growth:
- The global IoT market will hit $1.6 trillion by 2030.
- 79% of enterprises say IoT is vital for business efficiency.
- IoT in manufacturing alone is projected to cross $225 billion by 2028.
IoT’s impact spans:
- Smart homes
- Smart cities
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Agriculture
- Energy
- Logistics
- Industrial automation
From tracking cattle health to managing billion-dollar supply chains, IoT has become the invisible network powering modern systems.
Core Definition of IoT Development
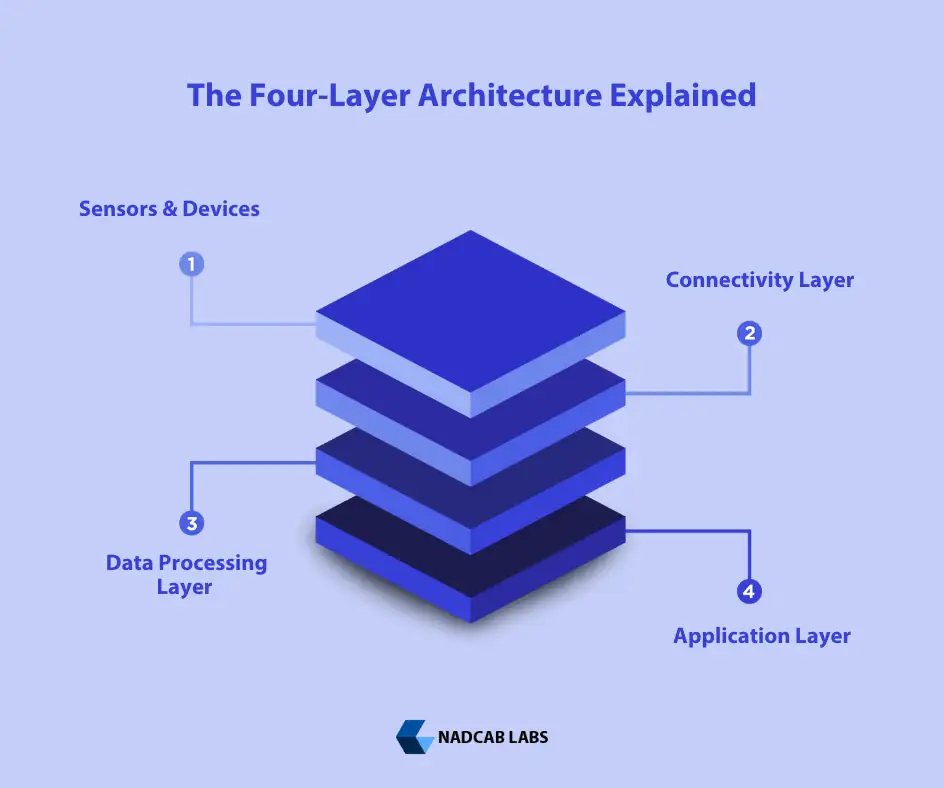
IoT development can be clearly defined as the end-to-end process of designing, building, deploying, and operating systems that enable physical devices to collect data, communicate digitally, and trigger software-driven responses over time.
This definition emphasizes process and continuity, not just implementation. IoT development is not a single event or deliverable. It is an ongoing system lifecycle that evolves as physical environments, operational needs, and data requirements change.
The discipline combines elements of software engineering, systems thinking, and operational design. What makes it unique is its responsibility for bridging two fundamentally different worlds: the unpredictable physical world and the structured digital world.
Why IoT Development Exists as a Separate Discipline
Traditional software development assumes a controlled environment. Servers are stable, networks are predictable, and user interactions are intentional. IoT development operates under very different assumptions. Physical environments are messy, devices fail, networks fluctuate, and data arrives continuously without human prompting.
Because of this, IoT development requires a different mindset. Engineers must design systems that expect inconsistency rather than perfection. They must account for long lifecycles, unattended operation, and real-world consequences of system behavior.
This is why IoT development has emerged as a separate discipline rather than an extension of web or mobile development. The problems it solves and the constraints it operates under are fundamentally different.
The Fundamental Purpose of IoT Development
The core purpose of IoT development is to enable continuous, data-driven understanding of physical systems. Instead of relying on periodic inspections or manual reporting, organizations can observe operations in real time and over long durations.
IoT development allows physical processes to speak for themselves through data. Machines no longer need to be checked; they report their own condition. Environments no longer need constant supervision; they describe their own changes.
This shift enables faster decisions, more accurate insights, and automated responses that would be impossible through manual processes alone.
While this article focuses on explaining what IoT development fundamentally means, a complete understanding of IoT requires deeper exploration of how these systems are structured, applied, evaluated, and governed at scale. For readers looking to understand how all these layers come together in real-world implementations, this complete IoT system overview explains architecture, use cases, investment drivers, and enterprise considerations in one place.
From Observation to Automation
Before IoT systems, physical operations followed a slow and reactive pattern. A problem occurred, someone noticed it, and corrective action was taken afterward. This approach often resulted in inefficiency, downtime, and preventable losses.
IoT development transforms this pattern into a continuous feedback loop. Systems observe conditions in real time, interpret changes automatically, and respond based on predefined logic or learned behavior.
Automation does not eliminate human involvement. Instead, it elevates it. Humans move from constant monitoring to strategic oversight, focusing on exceptions, insights, and improvements rather than routine checks.
What IoT Development Actually Builds
IoT development does not simply build devices or dashboards. It builds digital reflections of physical reality. These reflections allow software systems to understand what is happening in the physical world without being physically present.
Through continuous data flow, IoT systems create a living model of operations. This model evolves over time, capturing trends, anomalies, and patterns that are invisible in isolated snapshots.
The result is a system that does not just react to events but develops context around them.
The Relationship Between Devices and Software
In IoT development, devices and software play complementary roles. Devices act as the eyes, ears, and hands of the system. Software acts as the brain.
Devices sense conditions and execute actions, but they do not make complex decisions. Software processes data, applies logic, and determines what should happen next. IoT development defines how these two elements communicate, cooperate, and remain synchronized over time.
A well-designed IoT system ensures that devices and software remain aligned even as conditions change.
Continuous Operation as a Design Principle
One of the defining characteristics of IoT development is continuous operation. IoT systems are expected to run without interruption, often for years, in environments that cannot be easily accessed or reset.
This requirement shapes every design decision. Systems must handle failures gracefully, recover automatically, and continue functioning even when parts of the system are temporarily unavailable.
IoT development prioritizes resilience and longevity over short-term performance gains.
Data as the Core Asset
In IoT development, data is not a byproduct. It is the primary asset. Every data point represents a real-world observation that can inform decisions, improve processes, or reveal inefficiencies.
Over time, this data accumulates into a historical record of operations. This record becomes increasingly valuable as patterns emerge and understanding deepens.
IoT development ensures that data remains consistent, meaningful, and usable throughout the system’s lifecycle.
IoT Development vs Traditional Software Development
Although both involve writing code, IoT development and traditional software development solve different types of problems. Traditional software focuses on user workflows, interfaces, and transactional logic. IoT development focuses on system behavior, event streams, and physical interaction.
In IoT systems, users are often observers rather than operators. The system runs continuously, generating value even when no one is actively using an interface.
This fundamental difference requires a shift in how success is measured and how systems are designed.
Lifecycle Thinking in IoT Development
IoT development demands long-term thinking from the very beginning. Decisions made during early design stages influence how systems perform years later.
The lifecycle includes deployment, scaling, maintenance, updates, and eventual evolution. Each phase introduces new challenges that must be anticipated rather than reacted to.
Successful IoT development treats the system as a long-term operational asset, not a one-time project.
Why IoT Development Is Often Underestimated
Many IoT initiatives fail not because the idea is wrong, but because the complexity is underestimated. Early prototypes often work well in controlled conditions, creating a false sense of simplicity.
Real challenges emerge when systems scale, environments vary, and operations become critical. IoT development must be approached with realism, patience, and system-level thinking.
Underestimating these factors leads to fragile systems that struggle in real-world conditions.
The Role of Abstraction in IoT Systems
Abstraction is a key principle in IoT development. Raw sensor data is rarely useful on its own. IoT systems translate raw signals into higher-level information that humans and software can act upon.
This abstraction allows decision-makers to focus on outcomes rather than technical details. It also enables systems to evolve without requiring constant redesign of interfaces or workflows.
Good abstraction makes complex systems usable and scalable.
Human Interaction With IoT Systems
Even the most autonomous IoT systems involve humans at some level. IoT development defines how people interact with systems, interpret information, and intervene when necessary.
The goal is to provide clarity, not overload. Humans should receive insights, not noise. IoT systems should support decision-making rather than complicate it.
Designing this interaction is a critical part of IoT development.
IoT Development as a Strategic Capability
As organizations become more data-driven, IoT development moves from experimental projects to strategic infrastructure. It enables transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement across physical operations.
Organizations that treat IoT development as a core capability are better positioned to adapt, optimize, and innovate over time.
This strategic importance explains why IoT development is increasingly handled by specialized teams and partners.
How IoT Development Supports Digital Transformation
Digital transformation often focuses on software platforms and analytics. IoT development provides the missing link by connecting these digital tools to real-world activity.
Without IoT development, digital systems operate in isolation. With it, they gain real-time awareness of physical processes, enabling deeper insight and more effective automation.
IoT development grounds digital transformation in reality.
The Foundation for Everything Else in IoT
Architecture, costs, risks, tools, and use cases all build on the fundamental concept of IoT development. Without understanding this foundation, deeper discussions lack context and coherence.
This is why IoT development must be understood first, before moving into implementation details or strategic decisions.
IoT Development as an Ongoing Journey
IoT systems evolve. As data accumulates, understanding improves. As environments change, systems adapt. IoT development is not static; it is a continuous process of refinement and learning.
This ongoing journey is where long-term value is created.
The Role of an IoT App Development Company
Because IoT systems operate continuously in real-world environments, building them requires more than standard application development skills. Organizations often work with an enterprise IoT development partner that understands system behavior, long-term scalability, and operational reliability rather than treating IoT as a short-term software project.
IoT Development Steps – How IoT Solutions Are Built
Developing an IoT system involves various specialised stages:
1. Requirement Analysis & Strategy
This includes identifying:
- What problem needs solving?
- What data must be collected?
- What devices and sensors are needed?
- What connectivity technologies suit the environment?
For example, a hospital uses IoT to monitor patient vitals in real time.
2. Hardware & Sensor Selection
Choosing the right components:
- Microcontrollers (ESP32, Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Sensors (temperature, infrared, GPS, pressure)
- Actuators
Hardware selection impacts power usage, accuracy, and scalability.
3. Firmware Development
Firmware is the software running inside IoT devices.
Developers program instructions for:
- Data collection
- Device behavior
- Network communication
- Security protocols
This layer ensures devices operate reliably in real-world conditions.
4. Network Architecture & Integration
IoT engineers build secure communication frameworks using protocols like:
- MQTT for lightweight messaging
- CoAP for constrained environments
- HTTPS for secure web communication
5. Cloud Backend & Database Development
This step includes:
- IoT cloud setup
- Data pipelines
- Data storage architecture
- API development
Databases like InfluxDB, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL store device data streams.
6. Frontend & Mobile App Development
Users interact with IoT systems through intuitive dashboards or mobile applications.
Devices send data → the cloud processes it → the app visualises it in real time.
Activities include:
- UI/UX design
- Real-time charts
- Alerts and automation triggers
To streamline this stage, businesses often rely on an IoT platform that helps build responsive interfaces, manage device data, and ensure smooth user experiences.
7. AI & Analytics Integration
This transforms raw IoT data into intelligent actions.
Examples:
- Predicting machine failure
- Detecting abnormal user activity
- Optimizing energy usage
- Automating workflows
AI models enhance IoT’s ability to learn and adapt over time.
8. Testing & Quality Assurance
Testing validates:
- Device performance
- Communication reliability
- Security robustness
- Power and battery efficiency
IoT testing is crucial because these systems operate in critical environments like hospitals and factories.
9. Deployment & Scaling
Once ready, the IoT network is deployed and configured.
This involves:
- Device provisioning
- Edge gateway configuration
- Cloud integration
- Security setup
Monitoring tools ensure everything works smoothly.
Real-World Use Cases of IoT Development
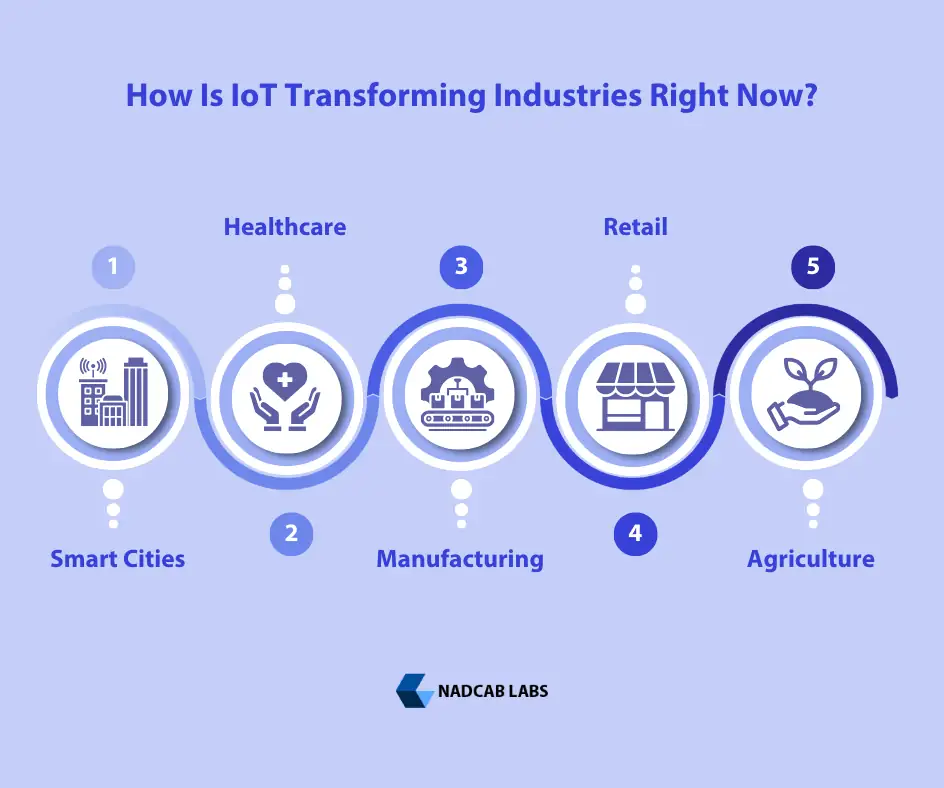
IoT is not just a futuristic idea; it’s shaping industries every day.
1. Smart Cities
Cities use IoT for:
- Traffic optimization
- Waste management
- Smart lighting
- Environmental monitoring
Example- Copenhagen reduced about 55% of streetlight energy by using IoT-connected LED lighting and dimming controls.
2. Healthcare
IoT manages:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Smart wearables
- Smart hospital equipment
Example- Wearable ECG monitors reduce hospitalisation by enabling early diagnosis.
3. Manufacturing
IoT empowers Industry 4.0:
- Predictive maintenance
- Robotics
- Real-time machine monitoring
Example- GE uses IoT sensors to reduce maintenance costs by up to 30%.
4. Retail
IoT supports:
- Smart shelves
- Automated billing
- Inventory management
Amazon Go is a perfect example of IoT-based automated shopping.
5. Agriculture
IoT enhances:
- Soil monitoring
- Irrigation automation
- Livestock tracking
Smart agriculture enhances crop yields by utilizing real-time data.
Benefits of IoT Development for Businesses
1. Operational Efficiency
IoT reduces manual tasks and increases automation.
2. Real-Time Visibility
Businesses see the live status of devices, machines, and processes.
3. Cost Reduction
Predictive maintenance prevents machine breakdowns.
4. Better Customer Experience
Smart products keep users connected and engaged.
5. Scalability
IoT systems expand easily as businesses grow.
6. Data-Driven Decisions
IoT provides actionable insights to optimize outcomes.
Challenges in IoT Development (And How They’re Solved)
1. Security Risks
IoT devices can be entry points for cyberattacks.
Solution- end-to-end encryption and secure firmware.
2. Scalability Issues
Millions of devices create data overload.
Solution- cloud-native and distributed architecture.
3. Interoperability
Different devices often use different protocols.
Solution- standardization through APIs and universal protocols.
4. Power Consumption
Battery-operated devices need optimization.
Solution- low-power communication technologies like LoRaWAN.
Transform your business with next-gen IoT
Connect your devices and run your business smarter with IoT power.
Future of IoT – What’s Coming in 2025 and Beyond
- 6G IoT enabling micro-second latency
- Digital Twins for virtual simulations
- AIoT (AI + IoT) is becoming standard
- Autonomous industrial robotics
- Smart cities are becoming mainstream
- Blockchain-integrated IoT security
- Zero-touch device configuration
IoT is evolving into an intelligent, adaptive global network.
Closing Thoughts
IoT development is the backbone of smart innovation across every industry. From sensor data collection to cloud intelligence and device automation, IoT solutions simplify operations, reduce costs, improve safety, and create futuristic user experiences.
Whether you want to build a smart home solution, monitor industrial machines, or create a connected retail system, choosing custom IoT app development helps you get a solution that fits your exact needs and scales as you grow.
In a world rapidly becoming connected, IoT isn’t just a technology; it’s the foundation of the digital future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, but only when implemented with best practices like encryption, secure firmware, strong authentication, network monitoring, and periodic updates. Security is a major focus in IoT development.
Edge computing processes data directly on the device or a nearby gateway rather than sending everything to the cloud. This makes IoT systems faster, more reliable, and ideal for real-time tasks like machine monitoring.
Yes, Digital Twins are very useful for small businesses. They make it easier to monitor machines, spot issues early, and cut maintenance costs. By creating a virtual version of your equipment, you can test ideas, prevent downtime, and make smarter decisions without spending a lot.
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, retail, and smart homes benefit the most. IoT helps automate processes, improve monitoring, reduce costs, enhance safety, and deliver real-time data insights. These advantages make IoT valuable across both consumer and industrial sectors.
IoT will advance through AI-driven automation, edge computing, faster connectivity, and improved security. Expect smarter cities, autonomous devices, intelligent supply chains, and more predictive systems. As hardware becomes affordable, IoT adoption will expand across homes, industries, and enterprise operations.
Costs depend on app complexity, hardware requirements, cloud usage, and integrations. Basic IoT apps are more affordable, while advanced platforms with automation, analytics, and multiple devices cost more. Custom features, scalability, and long-term maintenance also influence the total budget.
IoT apps require ongoing updates, bug fixes, security patches, cloud monitoring, and device health checks. Regular maintenance ensures smooth performance, prevents downtime, enhances security, and keeps your system compatible with new hardware or platform upgrades.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







