Key Takeaways
- Testnets are sandbox environments that replicate mainnet conditions using valueless test tokens for safe development and testing.
- Sepolia and Holesky have replaced older Ethereum testnets like Ropsten and Rinkeby as the primary testing environments.
- Each blockchain ecosystem maintains its own testnet with unique characteristics suited for different development needs.
- Testnet deployment reduces financial risk and helps identify bugs before launching on production networks.
- Understanding consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake and Delegated Proof of Stake is essential for effective testnet usage.
- Professional blockchain development requires thorough testnet validation to ensure smart contract security and performance.
Building blockchain applications without proper testing is like constructing a skyscraper without checking the foundation. Testnets serve as the practice grounds where developers can experiment, fail, learn, and perfect their projects before putting real assets at risk. In 2025, the blockchain landscape has evolved significantly, and understanding which testnet fits your project has become more important than ever.
This guide walks you through seven widely used testnets across different blockchain networks. Whether you are building decentralized applications, deploying smart contracts, or creating token systems, these testing environments provide the safety net every serious developer needs. Companies like Nadcab Labs, with over 8 years of hands-on blockchain development experience, emphasize that proper testnet deployment forms the backbone of successful blockchain projects.
The transition from legacy testnets to newer alternatives has reshaped how developers approach testing. Networks like Ethereum Foundation regularly update their recommended testing environments to match mainnet upgrades and security improvements.
What is a Testnet in Blockchain Development?
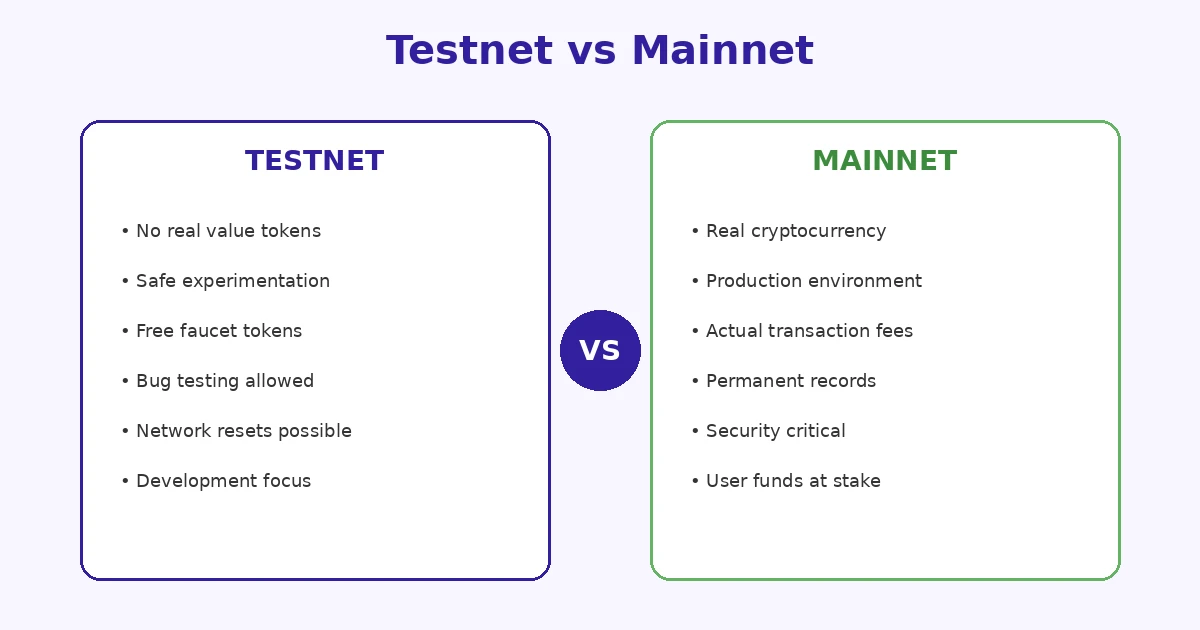
A testnet is a separate blockchain network designed specifically for development and testing purposes. It operates independently from the mainnet, which handles real transactions with actual monetary value. The primary distinction lies in the tokens used. Testnet tokens have zero financial worth, allowing developers to execute transactions, deploy contracts, and test features without spending real cryptocurrency.
Think of a testnet as a flight simulator for pilots. Just as pilots practice maneuvers without risking passengers or aircraft, blockchain developers use testnets to practice deployments without risking user funds or network stability. This controlled environment mirrors production conditions while eliminating financial consequences of errors.
The architecture of most testnets closely resembles their corresponding mainnets. They use identical or similar consensus mechanisms, support the same programming languages for smart contracts, and process transactions using comparable protocols. This similarity ensures that code tested on a testnet behaves predictably when moved to production. Understanding concepts like node synchronization becomes practical through hands-on testnet experience.
Obtaining testnet tokens typically involves faucets, which are web services that distribute free test tokens to developer wallets. Some networks require social verification or rate-limit distributions to prevent abuse, while others offer generous allocations for serious testing needs.
How Does a Testnet Work?
Testnets function through the same fundamental blockchain mechanics as mainnets but with important modifications for development purposes. When you deploy a smart contract on a testnet, the network validates and records the transaction just like on the main network. Blocks get created, transactions get confirmed, and state changes get recorded permanently on the test chain.
The consensus mechanism determines how the testnet validates transactions and creates new blocks. Some testnets use Proof of Work, others use Proof of Stake, and some employ Proof of Authority where designated validators control block production. The choice affects transaction speed, network stability, and how closely the testnet mimics mainnet behavior.
Testnet Operation Cycle
Step 1: Developer obtains test tokens from a faucet by providing their wallet address.
Step 2: Smart contract or dApp code gets compiled and prepared for deployment.
Step 3: Developer broadcasts the deployment transaction to the testnet.
Step 4: Testnet validators process and confirm the transaction.
Step 5: Contract becomes active on testnet for functional testing.
Step 6: Developer runs tests, identifies issues, and iterates until satisfied.
Network explorers for testnets work identically to mainnet explorers. Developers can track transactions, verify contract deployments, check wallet balances, and debug issues using these tools. This transparency helps identify problems quickly and verify that applications behave as expected. Exploring blockchain data becomes second nature when you understand how to use tools similar to blockchain explorers.
Gas fees on testnets exist but cost nothing real. This allows developers to test gas optimization strategies and understand how transaction costs scale without financial pressure. The experience translates directly to mainnet deployment planning and cost estimation.
7 Popular Testnets for Blockchain Development
The blockchain ecosystem offers numerous testing environments, each serving different networks and development requirements. Here is a detailed examination of seven testnets that developers frequently use in their projects.
| Testnet | Network | Consensus | Status | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sepolia | Ethereum | Proof of Stake | Active | dApp Testing |
| Holesky | Ethereum | Proof of Stake | Active | Protocol Testing |
| BSC Testnet | Binance Smart Chain | Proof of Authority | Active | BSC Development |
| Amoy | Polygon | Proof of Stake | Active | Layer 2 Testing |
| Fuji | Avalanche | Avalanche Consensus | Active | High-Speed Apps |
| Fantom Testnet | Fantom | Lachesis | Active | DeFi Projects |
| Solana Devnet | Solana | Proof of History | Active | High Throughput |
1. Sepolia Testnet (Ethereum)
Sepolia has become the primary testnet recommended by the Ethereum Foundation for application developers. Following the deprecation of older testnets like Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Goerli, Sepolia emerged as the go-to environment for testing smart contracts and decentralized applications on Ethereum.
The network uses Proof of Stake consensus, matching the current Ethereum mainnet configuration since The Merge upgrade. This alignment means developers can test their applications under conditions that closely mirror production. Block times average around 12 seconds, and the network maintains consistent stability for reliable testing workflows.
Sepolia tokens are available through various faucets, though some require authentication through services like Alchemy or Infura. The permissioned validator set keeps the network predictable, which benefits developers who need consistent testing conditions without unexpected network disruptions.
For projects focusing on smart contract deployment, token creation, or dApp development on Ethereum, Sepolia provides the most straightforward path from testing to mainnet. The blockchain development services offered by experienced firms typically include comprehensive Sepolia testing as part of their deployment pipeline.
2. Holesky Testnet (Ethereum)
Holesky launched in September 2023 as a replacement for the Goerli testnet, specifically designed for staking and infrastructure testing. While Sepolia serves application developers, Holesky caters to those working on protocol-level features, validator setups, and staking mechanisms.
The network boasts a significantly larger supply of test ETH compared to Sepolia, making it suitable for testing scenarios that require substantial token amounts. This design choice supports testing of staking protocols, which require 32 ETH deposits on mainnet.
Validators on Holesky can test their infrastructure without financial risk, an important consideration for those preparing to run mainnet validators. The network configuration closely tracks Ethereum mainnet upgrades, ensuring that protocol-level testing remains relevant and accurate.
Understanding scaling solutions like Plasma and state channels becomes practical through Holesky testing, where developers can experiment with Layer 2 integrations in a safe environment.
3. Binance Smart Chain Testnet
The BSC Testnet mirrors the Binance Smart Chain mainnet, providing developers with an environment to test BNB-based applications. It uses a Proof of Authority consensus mechanism with a limited set of validators, resulting in fast block times and predictable network behavior.
Developers building on BSC benefit from the testnet’s compatibility with Ethereum tooling. Wallets like MetaMask, development frameworks like Hardhat and Truffle, and programming languages like Solidity work seamlessly across both networks. This compatibility reduces the learning curve for developers transitioning between ecosystems.
Test BNB tokens are freely available through the official BSC faucet. The generous distribution allows for extensive testing without worrying about token shortages. Transaction confirmation happens quickly, enabling rapid iteration during development cycles.
According to Wikipedia’s documentation on Binance, the BSC network has grown to become one of the most active blockchain ecosystems, making its testnet an essential tool for developers targeting this user base.
4. Polygon Amoy Testnet
Polygon Amoy replaced the Mumbai testnet in early 2024, continuing the tradition of providing a testing ground for Polygon-based development. The transition followed Goerli’s deprecation since Mumbai depended on Goerli as its root chain.
Amoy uses Sepolia as its Ethereum layer, maintaining compatibility with the current Ethereum testing infrastructure. This setup allows developers to test bridging operations, Layer 2 transactions, and cross-chain functionality with modern tooling.
The testnet supports the full range of Polygon features including fast transactions, low fees, and Ethereum compatibility. Developers can deploy ERC-20 tokens, NFT contracts, DeFi protocols, and other applications with confidence that behavior will translate to mainnet.
Layer 2 scaling solutions represent a growing segment of blockchain development. Testing on Amoy helps developers understand the nuances of working with sidechain technology and its integration points with the main Ethereum network.
5. Avalanche Fuji C-Chain Testnet
Fuji serves as the primary testnet for Avalanche development, supporting all three chains in the Avalanche ecosystem: X-Chain, P-Chain, and C-Chain. Most smart contract developers focus on the C-Chain, which provides Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility.
The Avalanche consensus protocol delivers sub-second finality on Fuji, allowing developers to experience the network’s speed advantages during testing. This rapid confirmation time significantly improves the development experience compared to slower networks.
Test AVAX tokens power transactions on Fuji. The faucet system provides sufficient tokens for most testing needs, and the network rarely experiences congestion or stability issues. For projects exploring Avalanche blockchain solutions, Fuji provides the essential testing infrastructure.
Developers can test subnet creation, cross-chain transfers, and custom virtual machine deployments on Fuji before committing resources to mainnet. This flexibility makes Avalanche attractive for projects requiring customized blockchain configurations.
6. Fantom Testnet
The Fantom testnet replicates the mainnet’s Lachesis consensus mechanism, an asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant system that enables high throughput and quick finality. This environment suits developers building DeFi applications and other transaction-heavy systems.
Fantom’s Opera chain supports Ethereum tooling, making migration between networks straightforward. Solidity contracts deploy without modification, and developers can use familiar tools throughout the development process.
The testnet maintains good uptime and provides reliable infrastructure for continuous integration and testing pipelines. Test FTM tokens are available through community faucets, supporting ongoing development work.
Performance testing on Fantom’s testnet helps developers understand how their applications will handle real-world transaction loads. The network’s speed makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring rapid state changes and frequent user interactions.
7. Solana Devnet
Solana Devnet provides a testing environment for the Solana ecosystem, which uses a unique Proof of History consensus mechanism combined with Proof of Stake. The network processes thousands of transactions per second, giving developers a taste of Solana’s performance capabilities.
Unlike EVM-compatible chains, Solana uses its own programming model with Rust and the Anchor framework. The Devnet allows developers to learn and practice these tools without financial risk while building familiarity with Solana’s account model and program architecture.
Airdrop commands in the Solana CLI provide unlimited test SOL, removing any friction from the testing process. The network resets periodically, so developers should not rely on persistent state for long-term testing scenarios.
For projects requiring maximum transaction throughput, Solana Devnet offers an opportunity to validate performance assumptions before mainnet deployment. The learning curve is steeper than EVM chains, but the testing infrastructure supports developers throughout their journey.
Launch Your Blockchain Project with Confidence
Get expert guidance on testnet deployment and blockchain development. Our team ensures thorough testing before your mainnet launch.
Testnet Feature Comparison
Selecting the right testnet depends on your project requirements, target blockchain, and specific testing needs. The following comparison highlights technical differences that affect development workflows.
| Feature | Sepolia | BSC Testnet | Polygon Amoy | Fuji |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block Time | ~12 seconds | ~3 seconds | ~2 seconds | ~2 seconds |
| EVM Compatible | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (C-Chain) |
| Faucet Availability | Multiple | Official | Multiple | Official |
| Network Stability | High | High | High | High |
| Mainnet Similarity | Very High | High | High | Very High |
Testnet Development Lifecycle
Professional blockchain development follows a structured approach to testnet usage. Understanding this lifecycle helps teams plan their projects effectively and avoid common pitfalls that delay mainnet launches.
Phase 1: Local Development
Development begins with local blockchain instances using tools like Hardhat Network or Ganache. This phase focuses on rapid iteration and basic functionality testing. Smart contracts get written, compiled, and tested in isolation before any network deployment.
Phase 2: Testnet Deployment
Once local testing passes, contracts move to a public testnet. This phase tests network interactions, gas costs, transaction timing, and integration with external services. Multiple deployment cycles refine the application.
Phase 3: Integration Testing
Testnet deployments enable testing with other protocols, oracles, and services. DeFi applications test liquidity pool interactions. NFT projects verify marketplace compatibility. Cross-chain applications confirm bridge functionality.
Phase 4: Security Audit Preparation
Testnet deployments provide auditors with working code to examine. Security teams can interact with live contracts, probe for vulnerabilities, and verify fixes without affecting production systems.
Phase 5: Mainnet Migration
Final testnet verification confirms readiness for mainnet. Deployment scripts, gas estimates, and operational procedures get validated before committing real funds to the deployment process.
Problems like orphan blocks and other blockchain anomalies can be safely studied and understood through testnet experimentation without any financial consequences.
Importance of Testnet Token Development
Creating tokens on testnets serves multiple purposes beyond simple functionality testing. Token economics, distribution mechanisms, and governance features require thorough validation before mainnet deployment. Mistakes in token design can be costly or impossible to fix once real value is involved.
Testnet token development allows teams to verify that transfer functions work correctly across different wallet types. Testing reveals edge cases in approval mechanisms, burning functions, and minting controls that might otherwise cause issues after launch.
Projects building complex token systems benefit from extended testnet periods. Governance tokens need testing of voting mechanisms. Utility tokens require verification of access control functions. Security tokens must demonstrate compliance features work as intended.
The principle of atomicity in blockchain transactions ensures that token operations either complete fully or fail entirely. Testing this behavior under various conditions builds confidence in the system’s reliability.
New blockchain platforms continue emerging, each with unique characteristics. Developers exploring networks like Sui can practice creating tokens on newer blockchains using their respective testnets before committing to production deployments.
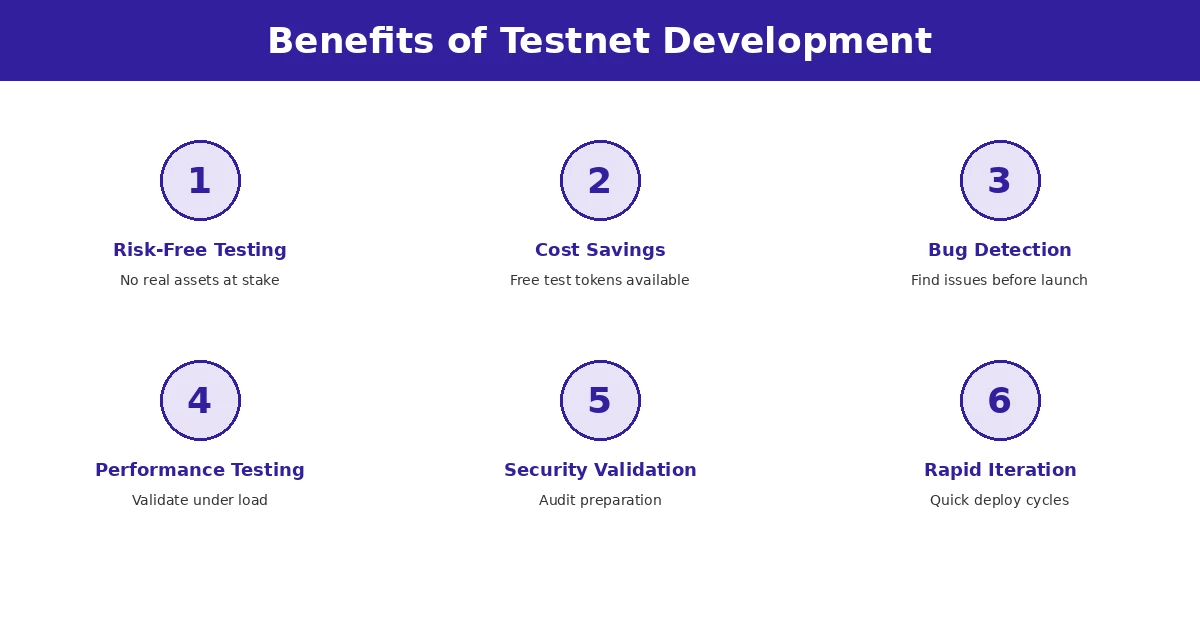
Essential Features of Testnet Deployment
Effective testnet deployment incorporates several features that maximize testing value while minimizing wasted effort. Understanding these features helps development teams extract maximum benefit from their testing investments.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Risk-Free Environment | No real assets at stake during testing | Encourages experimentation and learning |
| Mainnet Simulation | Replicates production network conditions | Accurate behavior prediction |
| Free Test Tokens | Faucets provide unlimited testing resources | No budget constraints on testing |
| Network Explorers | Full transaction visibility and debugging | Fast problem identification |
| Rapid Iteration | Quick deployment and testing cycles | Faster development timelines |
| Tool Compatibility | Standard development tools work seamlessly | No additional learning required |
Understanding consensus mechanisms like Proof of Elapsed Time for permissioned blockchains helps developers choose appropriate testing strategies for different network types.
Overcoming Testnet Challenges
While testnets provide valuable testing environments, they come with limitations that developers must understand and work around. Awareness of these challenges leads to more effective testing strategies.
Faucet rate limits can slow development when projects require large token amounts for testing. Planning token acquisition ahead of time and maintaining reserves prevents workflow interruptions. Some faucets offer larger allocations for verified developers or established projects.
Network differences between testnets and mainnets occasionally cause unexpected behavior during migration. Gas price dynamics, block timing variations, and validator behavior may differ. Thorough testing across multiple scenarios helps identify potential issues.
Testnet deprecation creates migration challenges for long-running projects. The transitions from Ropsten to Sepolia and Mumbai to Amoy required developers to redeploy contracts and update infrastructure. Staying informed about network roadmaps helps teams prepare for such changes.
The broader challenges of blockchain adoption often surface during testnet phases, providing early warning of issues that could affect mainnet success.
Professional Testnet Development with Nadcab Labs
Nadcab Labs brings over 8 years of hands-on blockchain development experience to testnet deployment and smart contract testing. This extensive background spans multiple blockchain generations, from the early days of Ethereum to today’s multi-chain ecosystem.
The team has deployed and tested contracts across all major testnets, accumulating practical knowledge about each network’s quirks and capabilities. This experience translates directly into efficient testing strategies that identify issues quickly and comprehensively.
Customized testnet environments form part of Nadcab Labs’ service offering. For projects requiring specific configurations or isolated testing conditions, the team creates private test networks that replicate target mainnet characteristics exactly.
Documentation and knowledge transfer accompany every project. Development teams receive detailed guides on testnet usage, deployment procedures, and troubleshooting approaches. This investment in client capability ensures long-term project success beyond the initial engagement.
Security-first testing methodologies guide every Nadcab Labs project. Testnet phases include comprehensive vulnerability assessments, gas optimization reviews, and performance benchmarking. These practices established through years of professional development set projects up for successful mainnet launches.
Partner with Blockchain Testing Experts
From testnet deployment to mainnet launch, our experienced team guides your project through every phase of blockchain development.
Final Thoughts
Testnets remain fundamental infrastructure for responsible blockchain development. The seven networks covered in this guide represent the most active and well-supported testing environments across major blockchain ecosystems. Choosing the right testnet depends on your target blockchain, testing requirements, and development workflow.
Modern blockchain development demands thorough testing before any mainnet deployment. The cost of bugs in production, whether measured in lost funds, damaged reputation, or security breaches, far exceeds the investment in proper testing. Testnets eliminate financial barriers to comprehensive testing.
As blockchain technology continues evolving, testnets evolve alongside mainnets. Staying current with testnet updates, deprecations, and new features ensures your development practices remain effective. Professional development teams make testnet proficiency a core competency, recognizing its role in delivering secure and reliable blockchain applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
A testnet is a separate blockchain network used for development and testing where tokens have no real monetary value. The mainnet is the production blockchain where real transactions occur with actual cryptocurrency. Testnets mirror mainnet functionality, allowing developers to test smart contracts, dApps, and token systems before deploying them to production. This separation protects users from bugs and vulnerabilities that could cause financial losses on the live network.
Ethereum testnet tokens are available through faucet websites that distribute free test ETH to developer wallets. For Sepolia, popular faucets include those provided by Alchemy, Infura, and the official Sepolia faucet. You need to connect your wallet, enter your address, and request tokens. Some faucets require social verification through Twitter or Discord to prevent abuse. Token amounts vary by faucet, but most provide enough for extensive testing needs.
Sepolia is the recommended testnet for most Ethereum application development in 2025. The Ethereum Foundation officially supports Sepolia for dApp testing and smart contract deployment. Holesky serves staking and infrastructure testing needs. Older testnets like Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Goerli have been deprecated and should not be used for new projects. Sepolia offers stable network conditions and reliable faucet access for development teams.
No, testnet transactions cannot affect the mainnet blockchain in any way. Testnets operate as completely separate networks with their own blocks, transactions, and state. There is no connection between testnet and mainnet systems. Actions taken on a testnet stay on that testnet only. This isolation is what makes testnets safe for experimentation, allowing developers to make mistakes without any real-world consequences or impact on production networks.
Testnet deployment duration varies based on project complexity and team experience. Simple smart contracts might need one to two weeks of testing. Complex DeFi protocols or token systems typically require four to eight weeks of thorough testnet validation. Projects involving security audits extend this timeline further. Professional development teams often maintain continuous testnet deployments throughout development cycles to catch issues early and validate every change before mainnet deployment.
Testnets get deprecated when they can no longer effectively mirror mainnet conditions or when maintenance becomes impractical. Ethereum deprecated Ropsten, Rinkeby, and Goerli after The Merge upgrade changed the consensus mechanism to Proof of Stake. Maintaining multiple testnets with different configurations became inefficient. New testnets like Sepolia and Holesky were designed specifically for post-Merge Ethereum, ensuring accurate testing environments that match current mainnet behavior and security assumptions.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






