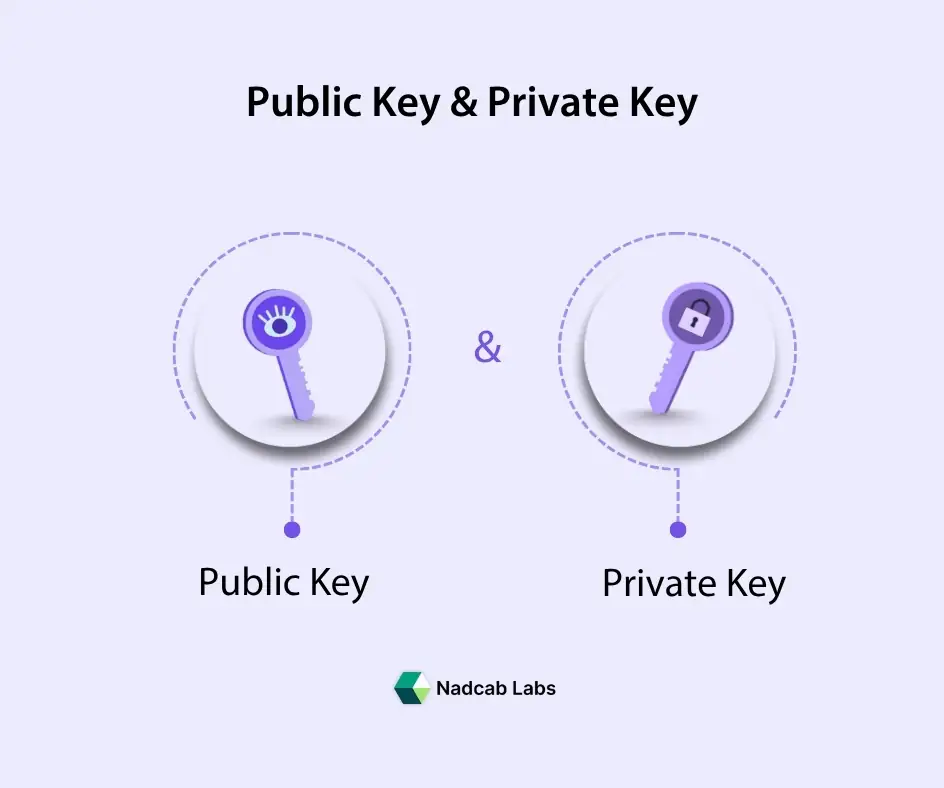
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool either software or hardware that securely stores the cryptographic keys you need to access and use your crypto assets on a blockchain network. The most important components of a crypto wallet are the public key and the private key. The public key (or address) functions like an account number you can share with others to receive crypto, while the private key is a secret alphanumeric code that authorizes spending and signing transactions. Official guidance from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) consumer protection site explains that the private key cannot be changed once generated, and if it is lost, access to the crypto is lost forever. [1]
You can think of a crypto wallet like a digital keyring: it doesn’t actually “hold” your cryptocurrency but protects the keys that prove you own crypto recorded on a blockchain. There is no central authority that can restore a lost private key unless you use a custodial cryptocurrency wallet where a service provider manages keys for you. [2]
What is Cryptocurrency Wallet?
At its core, a cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive digital assets securely. But contrary to what its name might suggest, the wallet doesn’t actually “store” cryptocurrencies. The coins themselves are always on the blockchain, a decentralized digital ledger that records every transaction ever made.
What the wallet does store are the private and public keys, which are the cryptographic credentials that allow you to access your digital assets.
According to Britannica on cryptocurrency wallets,[3] a crypto wallet acts like a “digital keychain,” enabling users to interact with blockchain networks. Every wallet, regardless of its design, fulfills one key purpose: it connects you to your crypto holdings on the blockchain securely and privately.
How Cryptocurrency Wallets Work
Wallet Creation and Seed Phrases
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, it generates a seed phrase, usually a set of 12–24 words, which serves as a master backup from which all the wallet’s private keys can be derived. Government-linked documents on crypto basics describe seed phrases as the foundational backup that allows you to recover your private keys and crypto wallet if you lose access to the device or software where the wallet was first created. [4]
Receiving Cryptocurrency
To receive cryptocurrency, the crypto wallet uses your public key or address, which you share publicly with senders. Others can send funds to that address, and the blockchain records the incoming transaction tied to your key. [5]
Sending Cryptocurrency
Sending crypto requires use of your private key. The cryptocurrency wallet uses this key to digitally sign a transaction, proving you have the authority to move the assets from your address. This signed transaction is then broadcast to the blockchain network for validation. [6]
Blockchain Validation
Blockchain network nodes, independent computers running the blockchain software, verify the digital signature and record the transaction in a block once it is confirmed. Because your crypto wallet only interfaces with decentralized blockchains, all transactions are transparent, auditable and irreversible after confirmation. [7]
Key Security Principles
Official financial regulators and government investor protection sites emphasize two important points:
- Your public key allows others to send you cryptocurrency but cannot be used to access or spend the funds. FINRA
- Your private key is essential for signing and accessing your crypto assets, and there is no recovery mechanism through a central authority if it’s lost. Investor.gov
In simple terms: you never store crypto “inside” the cryptocurrency wallet itself, your crypto always remains on the blockchain. Your wallet holds the keys that allow you to prove ownership and control of the crypto associated with your blockchain address. Using a secure crypto wallet ensures these keys remain protected against cyber threats and accidental loss.
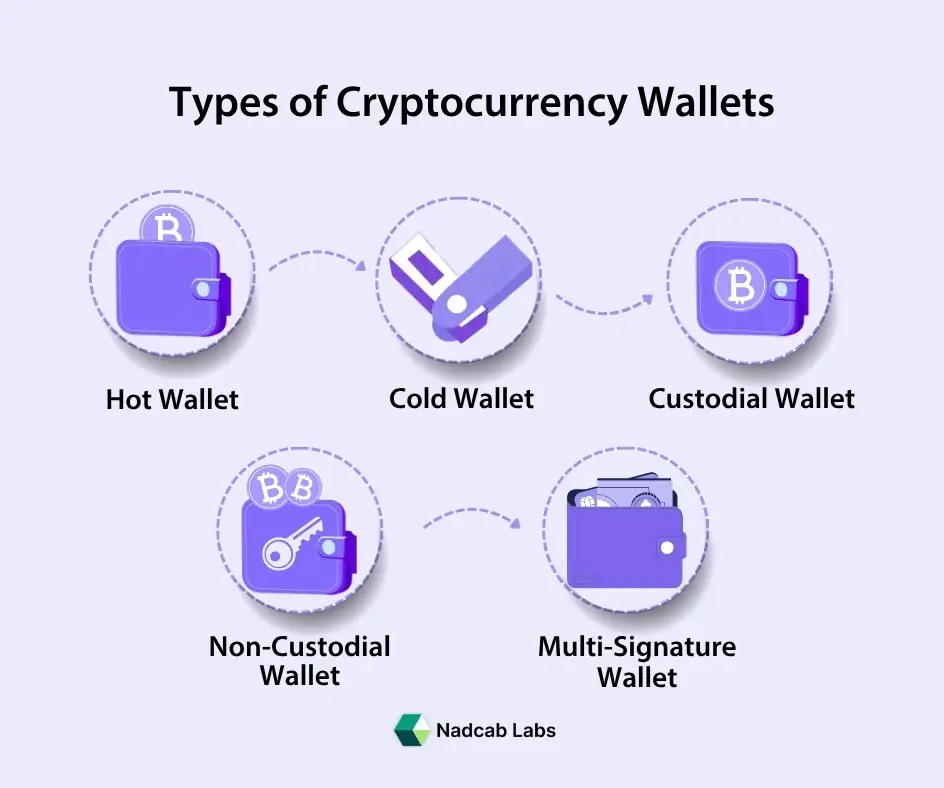
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallets
A crypto wallet is a tool that holds the cryptographic keys (private and public) that allow users to access, send, and receive digital assets on a blockchain. Official guidance from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission’s retail investor bulletin explains that cryptocurrency wallets store private keys needed for ownership and transaction authorization, and also manage public keys used to receive assets. (investor.gov Investor.gov).The following crypto wallet types are –
1. Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are crypto wallets that remain connected to the internet, offering quick access and convenience for frequent transactions or trading. According to the U.S. Investor Bulletin from the U.S. government’s investor protection site, hot wallets can be software or apps on desktop, mobile, or browser environments. These cryptocurrency wallets make it easy to interact with blockchains for daily payments, DApps, and decentralized finance activities, but because they are online they face higher cybersecurity risks, such as hacking or malware exposure. (investor.gov Investor.gov)
2. Cold Wallets
Cold wallets are cryptocurrency wallets that keep private keys completely offline, meaning they are not continuously connected to the internet. Official regulatory guidance describes cold wallets as physical devices (like hardware USB drives) or entirely offline storage, which provide significantly higher security by isolating keys from remote cyber threats. Because cold wallets are disconnected from networks, they are widely recommended for holding large amounts of crypto or for long-term storage where immediate access is not required. Using a secure crypto wallet in cold storage is considered the best practice for safeguarding large holdings. (investor.gov Investor.gov)
3. Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets are those where a third-party service such as a cryptocurrency exchange or platform holds and manages your private keys on your behalf. The U.S. Government Accountability Office highlights this distinction by noting that custodial wallets involve a service provider storing the keys for the user, meaning the provider technically controls access to the crypto assets and may have contractual obligations regarding their use. (gao.gov Government Accountability Office) Government-level tax guidance from the U.S. Internal Revenue Service also categorizes hosted wallets as custodial, explaining that such wallets may provide additional services like fiat-on/off-ramps but place key management in the hands of the service provider. (irs.gov IRS)
4. Non-Custodial Wallets
In contrast, non-custodial cryptocurrency wallets give the user full control over their private keys and crypto assets without reliance on a third party. Official definitions from U.S. government regulatory documents describe non-custodial (sometimes called un-hosted or self-custodial) wallets as those where only the wallet owner holds the cryptographic keys, enabling direct interaction with the blockchain and ensuring full control of the assets. In this case, if keys or seed phrases are lost, access to the crypto is irrevocably lost because there is no intermediary to recover them. (gao.gov Government Accountability Office)
5. How Governments View Wallet Types
Government and regulatory bodies emphasize the security and responsibility differences between wallet types. For example, U.S. regulatory guidance notes that self-custody (non-custodial) requires users to manage and protect private keys, while custodial services may reduce some user responsibility but increase reliance on the service provider for security and access. (investor.gov Investor.gov) International standards bodies like the Financial Stability Board (FSB) also recognize wallet classifications as part of broader crypto-asset regulatory frameworks, distinguishing hot vs cold storage and custodial vs non-custodial as relevant to consumer protection and regulatory oversight of virtual asset activities. (fsb.org Financial Stability Board)
Popular Wallets in 2025
| Wallet Type | Examples | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Hot Wallet | MetaMask, Trust Wallet | Everyday transactions |
| Desktop Wallet | Exodus, Electrum | Portfolio view & small trades |
| Hardware Wallet | Ledger, Trezor | Long-term storage, high security |
| Exchange Wallet | Coinbase, Binance (custodial) | Trading access + fiat rails |
| Web3 Smart Wallet | Argent, Safe (Gnosis) | DeFi & multi-sig governance |
Global Adoption Snapshot (Wallet Usage & Crypto Ownership)
While official government websites rarely publish wallet counts, industry data and adoption estimates show broad global trends in how people use cryptocurrency wallets and crypto:
Top countries by adoption rates (2025)
- UAE: 30.4% of the population owns crypto (3 million users).
- Vietnam: 21.2% of the population (17 million).
- United States: 15.6% adoption rate (53 million users).
- India: Significant adoption with exploding tax revenue from crypto gains.
- Philippines and Brazil: Strong middle-income market adoption.
- Ukraine & Venezuela: Adoption driven by economic conditions. CoinLaw
These ownership rates imply widespread crypto wallet use for storing and transacting crypto. CoinLaw
Country Wise Deep Breakdowns
Below are some of the most important country-level analyses you can use with facts, figures and government/regulatory context.
🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Crypto Adoption:
The UAE has among the highest adoption rates globally (30.4% of the population). CoinLaw
Policy & Regulation:
The UAE’s Payment Token Services Regulations govern how stablecoins and wallets are used domestically, including restrictions on acceptance of stablecoins for regular payments unless licensed. Wikipedia
Wallet Implications:
Popular cryptocurrency wallets see strong adoption due to advanced digital infrastructure. The government supports regulated frameworks to integrate blockchain into financial systems. Users often interact with licensed custodial wallets for compliance and fiat gateways.
Why It Matters:
The UAE’s blend of innovation and regulation creates both a safe environment for secure crypto wallet users and strong compliance standards for service providers.
🇻🇳 Vietnam
Vietnam ranks among the top five countries in crypto adoption, with an estimated 20.69% of the population using digital assets as of 2025 and annual transaction volumes exceeding $100 billion.
Wallet Implications:
High retail participation drives mobile crypto wallet use for trading, remittances, and DeFi. Regulation is evolving; crypto is recognized in digital tech frameworks, but financial regulators continue to clarify oversight.
User Behavior:
Vietnamese crypto users often convert wallets into local utility and international remittance tools, especially for cross-border payments and DeFi opportunities.
🇺🇸 United States of America
Ownership & Policy:
The US remains one of the largest absolute markets for crypto adoption, and regulators treat digital assets as taxable property. National agencies such as the IRS and FinCEN provide guidance on reporting and AML obligations. (irs.gov)
Wallet Context:
Wallet users must report digital asset transactions for tax compliance. Custodial wallet providers are subject to AML/KYC and money-transmission laws. Recent government interest includes executive orders to formalize strategic bitcoin holdings and oversight. AP News
User Insights:
Millions of Americans use cryptocurrency wallets for trading, investment, and DeFi, often through regulated custodial or self-custody solutions.
🇮🇳 India
India has seen a dramatic rise in crypto activity, exchanges collected nearly ₹1,100 crore in TDS from crypto gains, with Maharashtra state accounting for about 57% of that revenue. The Economic Times
Government Stance:
India does not ban cryptocurrency ownership, but regulation continues to evolve. The Finance Ministry and RBI focus on taxation, anti-money-laundering compliance, and CBDC (the Digital Rupee).
Wallet Implications:
Wallet users must be prepared for fiscal reporting and transparency. Adoption is driven by speculative investing and cross-border remittances.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
The UK is redesigning its crypto regulatory framework to extend oversight to wallet providers and exchanges, with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) playing a central role. Financial Times
Key Takeaways:
The UK’s rules aim for strong consumer protection and innovation support. Wallets that offer custodial services must comply with FCA regulations.
User Reality:
Many UK users choose crypto wallets connected to regulated exchanges or service providers to ensure compliance.
🇨🇳 China
China’s policy on private cryptocurrencies remains strict, with widespread bans on retail trading. However, the digital yuan (e-CNY), a government-issued digital currency, uses wallet infrastructure supported by authorized financial institutions. (See general PBOC CBDC disclosures warranting centralized wallet use.) arXiv
Wallet Reality:
Private crypto wallets aren’t broadly legal for trading. Centralized digital wallets linked to the e-CNY are widely used in mainland China.
🇵🇰 Pakistan
Pakistan established the Pakistan Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (PVARA) in 2025 to supervise and license virtual asset services and digital wallets. Wikipedia
Key Moves:
- A government-mandated council and regulatory body are shaping national crypto policy.
- This could lead to regulated wallets and clearer compliance frameworks.
🇺🇦 Ukraine
Ukraine stands out for significant crypto adoption and strategic interest in integrating crypto into national economic systems including proposals to include digital assets in reserve planning. Adoption surged amid geopolitical uncertainty, with donation wallets receiving large inflows. Coinpedia Fintech News
Wallet Trends:
Strong use for remittances and international aid flows. Regulatory strategy is evolving rapidly.
Government Bitcoin Holdings, What We Know
Some governments hold significant Bitcoin reserves often from seizures or strategic policy decisions:
- United States-198,000 BTC (~$22.8B)
- China-190,000 BTC (~$17.6B)
- UK-61,245 BTC (~$7.05B)
- Ukraine-46,351 BTC (~$5.33B)
- UAE, El Salvador, Venezuela, Bhutan, Finland also hold various amounts. Trading View
These holdings give insight into government engagement with crypto at a national reserve or asset level though most aren’t directly tied to retail wallet usage.
Security and Best Practices for Wallet Users
Whether you’re in the UAE, the United States, India or any other region, secure crypto wallet practices remain universally important. Users should store significant holdings in cold storage or hardware cryptocurrency wallets to reduce exposure to online threats, enable multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security and back up seed phrases offline in a safe location to prevent permanent loss of access. In regions where regulations apply, it is also advisable to use licensed custodial crypto wallets that comply with local laws and security standards. Additionally, always stay informed about local tax and reporting requirements, as many countries require disclosure of digital asset transactions or holdings. Considering compliance and regulatory obligations alongside secure crypto wallet best practices helps ensure both the safety and legality of your cryptocurrency usage.
Why Country Context Matters
Understanding how different governments treat cryptocurrency wallets helps you design better wallet strategies, tailor content and comply with legal obligations. Countries like the UAE and Vietnam show high adoption, while the US and UK illustrate strong regulatory frameworks. India and Pakistan are evolving rapidly and China’s e-CNY shows how central bank wallets can differ from private crypto wallets.
Frequently Asked Questions - Wallet
A cryptocurrency wallet is a secure digital tool that helps users store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies safely. It doesn’t physically hold coins but stores the private keys that provide access to your assets on the blockchain. In simpler words, it’s like a digital keychain that keeps your crypto safe and accessible whenever you need it.
Every crypto wallet has two keys — a public key and a private key. The public key acts like your wallet address (which you can share to receive funds), while the private key is your secret password that allows you to access and transfer your assets. When a transaction occurs, the wallet uses your private key to sign it, verifying that you are the rightful owner. This transaction is then recorded permanently on the blockchain network.
Hot wallets are connected to the internet, making them ideal for frequent trading and instant transactions. They include web, mobile, and desktop wallets. Cold wallets, on the other hand, stay offline — such as hardware or paper wallets — offering higher security for long-term storage. Hot wallets are about convenience, while cold wallets are all about maximum safety.
Unfortunately, if you lose your private key or recovery phrase, it’s nearly impossible to regain access to your funds. The blockchain system is designed to be decentralized and secure, which means there’s no central authority to help you recover lost keys. That’s why experts always recommend backing up your recovery phrase and storing it in multiple safe locations.
Yes, crypto wallets are safe when handled responsibly. The level of security depends on the type of wallet and how you protect it. Hardware wallets are considered the most secure because they’re offline, while mobile and web wallets require additional security measures like strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and awareness against phishing attempts.
Beginners should start with simple and user-friendly wallets that offer clear navigation and basic security features. Mobile or web wallets are great starting points since they are easy to set up and help you understand how crypto transactions work. As you gain experience, you can switch to more secure options like hardware or multi-signature wallets for larger investments.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.