Blockchain technology is changing how people handle digital transactions, store records, and build trust without middlemen. But most people only interact with it as end users. They buy crypto on an exchange, check their balance in a wallet app, and call it a day. What they miss is that the real backbone of any blockchain network is the nodes. Without people running nodes, no blockchain can function. So the question is, should you be running one yourself? This article will walk you through everything you need to know about blockchain nodes, why running one matters, what types exist, how to set one up, and whether you can earn rewards for doing it.
Key Takeaways
- Running a blockchain node gives you direct control over transaction verification without depending on any third party.
- Full nodes store the complete blockchain ledger and are the most important type for network health and decentralization.
- Different node types serve different purposes, from lightweight nodes on mobile devices to mining nodes that create new blocks.
- Setting up a node requires choosing a network, meeting hardware requirements, and keeping the software updated.
- Nodes protect the network from attacks by distributing data and validating every transaction independently.
- Some nodes earn rewards through mining, staking, or providing network services, depending on the consensus mechanism used.
- Running your own node aligns with the core principle of blockchain, which is eliminating the need for centralized control.
What Is a Blockchain Node and What Does It Do?

A blockchain node is simply a computer that connects to a blockchain network and follows its rules. That is the most basic definition. But what it actually does behind the scenes is far more involved than most people realize.
Every node keeps a copy of the blockchain ledger, either the full version or a partial one. This ledger contains a record of every transaction that has ever happened on that network. When someone sends cryptocurrency, the transaction does not just go from point A to point B. It first gets broadcast to the network, where nodes pick it up, check it against the rules, and then pass it along to other nodes. This process of checking and forwarding is what keeps the whole system honest.
Think of it this way. In traditional banking, a central server owned by the bank keeps track of who has what. If that server goes down, gets hacked, or the bank decides to freeze your account, you are stuck. With blockchain, there is no single server. Instead, thousands of nodes across the world each hold a copy of the same information. No single party controls it, and no single failure can bring it down.
The job of a node breaks down into a few core tasks. It validates transactions by checking that the sender has enough funds and that the transaction follows the cryptographic rules. It validates blocks, which are bundles of transactions grouped together. And it shares new data with neighboring nodes so the entire network stays in sync. This is how blockchain technology achieves its promise of being tamper-proof and trustless.
Without nodes, a blockchain is just a concept on paper. The more nodes a network has, the stronger and more resistant it becomes to manipulation, censorship, and downtime.
How Does a Node Function Within a Blockchain Network?
When you break down how a node actually works, the process is straightforward, even if the technology behind it is complex. Here is what happens step by step.
Someone initiates a transaction. Maybe they are sending Bitcoin to a friend or interacting with a smart contract on Ethereum. That transaction gets broadcast to the network. Your node, if it is connected, receives this broadcast. The first thing it does is check whether the transaction is valid. Does the sender actually have the funds they claim to have? Does the digital signature check out? Are all the protocol rules being followed?
If the answer to all of those is yes, the node marks the transaction as valid and passes it on to other nodes it is connected to. If the transaction fails any of these checks, the node rejects it. This is a critical filter that prevents bad actors from flooding the network with fake transactions.
Valid transactions sit in a waiting area called the mempool until a miner or validator picks them up and groups them into a block. Once a block is proposed, nodes again check everything. They verify that each transaction in the block is valid and that the block itself follows the consensus rules. Only after this second round of checks does the block get added to the chain.
This two-layer verification, first at the transaction level and then at the block level, is what makes blockchain so reliable. It is also why having more nodes matters. Every additional node is one more independent checker that a bad actor would need to fool. If you are working with smart contract-based logic in decentralized systems, understanding how nodes validate these interactions is especially important because smart contracts execute automatically once conditions are met, and nodes are the ones confirming those conditions.
Types of Nodes in a Blockchain Network
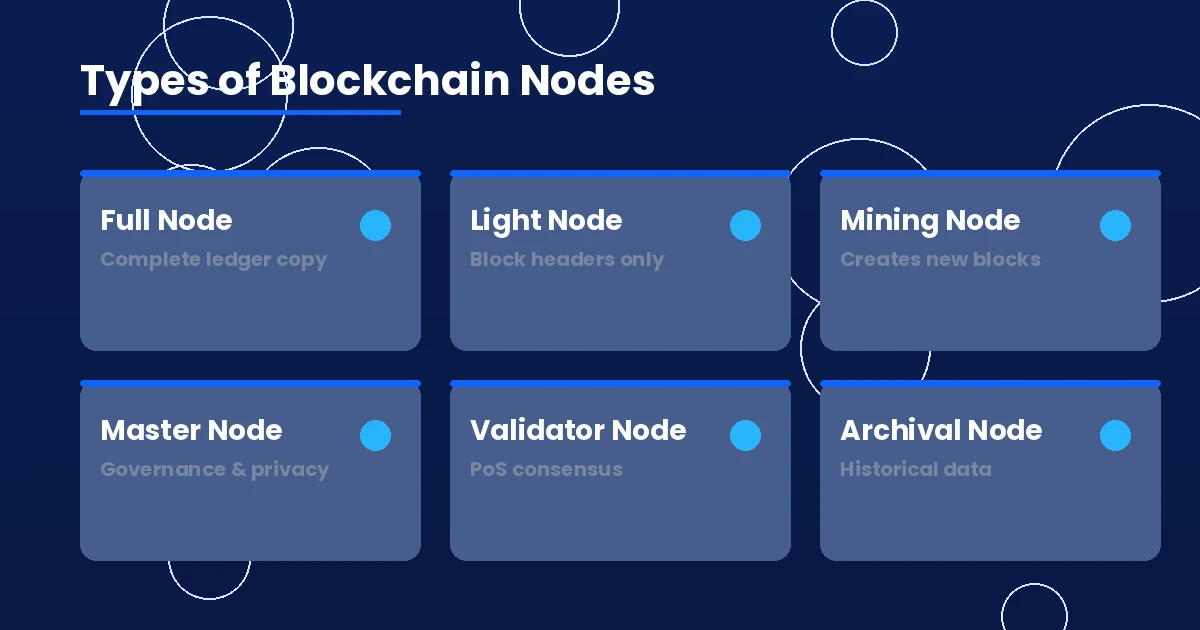
Not all nodes are created equal. Different types of nodes exist because different people and organizations have different needs, hardware, and goals. Understanding these types helps you figure out which one makes sense for you.
Full Nodes
Full nodes are the workhorses of any blockchain. They download and store the entire blockchain from the very first block (called the genesis block) to the most recent one. They independently verify every transaction and block without trusting anyone else. If every other node on the network told a full node that a fraudulent transaction was valid, the full node would still reject it because it checks everything against the actual rules. This independence is what makes full nodes so important for decentralization.
Lightweight Nodes (SPV Nodes)
Lightweight nodes, sometimes called Simplified Payment Verification nodes, take a shortcut. Instead of downloading the whole blockchain, they only grab the block headers. These headers contain enough information to verify that a transaction was included in a block, but not enough to fully validate everything independently. Lightweight nodes rely on full nodes for the detailed data. This trade-off makes them ideal for mobile devices and applications where storage and processing power are limited.
Mining Nodes
Mining nodes are full nodes that go a step further. They compete to create new blocks by solving cryptographic puzzles in Proof of Work systems. This process requires significant computational power and electricity. The first mining node to solve the puzzle gets to propose the next block and earns a reward for doing so. Mining nodes are essential for networks like Bitcoin, where they serve as the mechanism for both creating new coins and securing the network.
Master Nodes
Master nodes carry extra responsibilities beyond what regular full nodes handle. In some networks, they manage governance decisions, facilitate private transactions, or enable instant transaction processing. Running a master node typically requires locking up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral. In return, operators receive a portion of the block rewards. Dash is one of the more well-known networks that uses master nodes.
Validator Nodes
Validator nodes exist in Proof of Stake networks. Instead of competing through computational power, validators are chosen to create blocks based on how much cryptocurrency they have staked. The more you stake, the higher your chances of being selected. Validator nodes are central to networks like Ethereum (after its move to PoS) and play a growing role as more blockchains move away from energy-intensive mining.
Archival Nodes
Archival nodes store everything. While a standard full node might prune old data to save space, an archival node keeps the entire history, including every past state of the blockchain. This is invaluable for developers, researchers, and services that need to look up historical information. If you are exploring concepts like state trie structures, archival nodes are where that historical state data lives.
| Node Type | Stores Full Ledger | Validates Independently | Creates Blocks | Special Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Node | Yes | Yes | No | Core network backbone |
| Lightweight (SPV) | No | Partial | No | Mobile and low-resource use |
| Mining Node | Yes | Yes | Yes (PoW) | Earns block rewards |
| Master Node | Yes | Yes | Sometimes | Governance and privacy |
| Validator Node | Yes | Yes | Yes (PoS) | Stake-based block creation |
| Archival Node | Yes + historical | Yes | No | Research and data access |
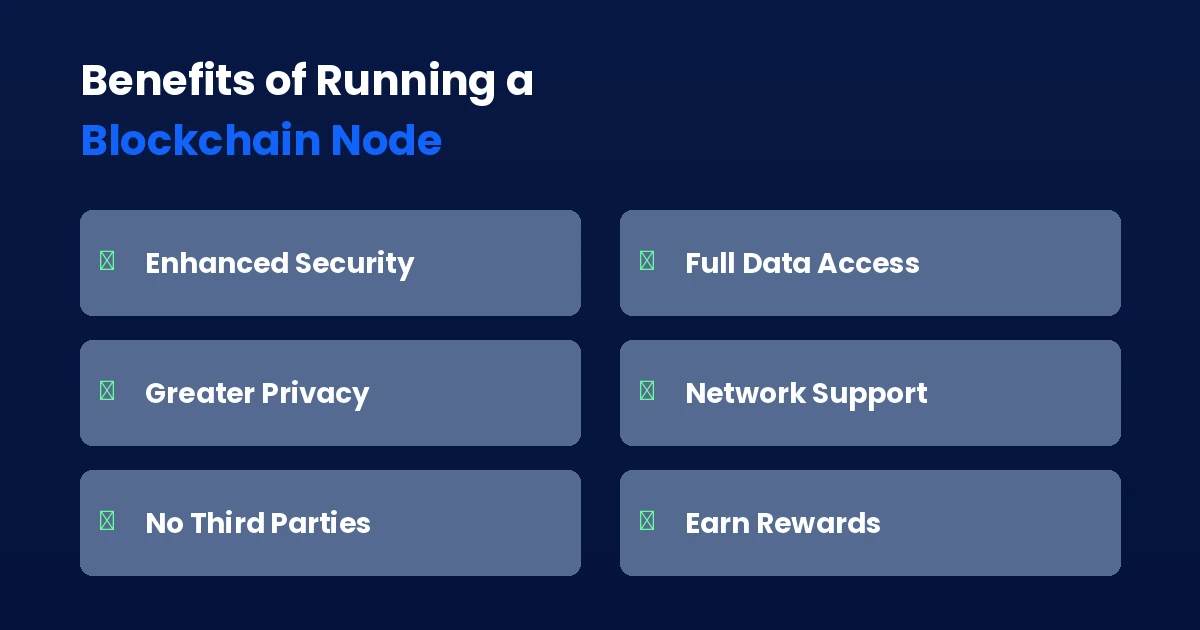
Why Should You Run a Blockchain Node?
This is the central question, and the answer goes deeper than most people expect. Running a node is not just a technical exercise. It is a way to participate directly in a system that is designed to operate without gatekeepers.
You Verify Your Own Transactions
When you use a third-party service to check your balance or confirm a transaction, you are trusting that service to tell you the truth. Running your own node removes that trust requirement entirely. You verify everything yourself, directly against the blockchain. This is especially relevant for businesses and individuals who deal with large volumes of transactions. If you are involved in platforms that handle financial operations at scale, such as those described in the cryptocurrency MLM software market analysis, having your own node means you never have to wonder if the data you are seeing is accurate.
You Strengthen the Network
Every node that joins a blockchain network makes it harder to attack. If a bad actor wants to manipulate the blockchain, they need to overpower a majority of the network. More nodes means a higher bar for any attack. Your single node might not seem like much on its own, but collectively, nodes are what prevent any form of centralized control or censorship.
You Protect Your Privacy
Using someone else’s node means routing your transactions through their infrastructure. This gives them visibility into your activity. With your own node, your transactions go directly to the network. No middleman sees what you are doing. For anyone who values financial privacy, this is a significant advantage.
You Get Complete Data Access
Running a full node means you have the entire blockchain stored locally. You can query any transaction, check any address balance, and trace any flow of funds without relying on external block explorers or APIs. This level of access is particularly useful for developers, auditors, and analysts who need accurate and unrestricted data.
You Support Decentralization
Decentralization is the foundational principle of blockchain. But it does not happen automatically. It requires people to actually run nodes. If too few people run nodes, the network effectively becomes centralized around whoever is running them. By running a node, you are making a practical contribution to keeping the system decentralized, which protects everyone who uses it.
For organizations building on blockchain, particularly those exploring decentralized MLM structures, understanding node participation is not optional. It is foundational to how the technology they depend on actually works.
Build Your Blockchain Node Infrastructure
Need a custom blockchain node setup that is secure, scalable, and built to your specifications? Get expert guidance and development support from a team that understands the technology inside and out.
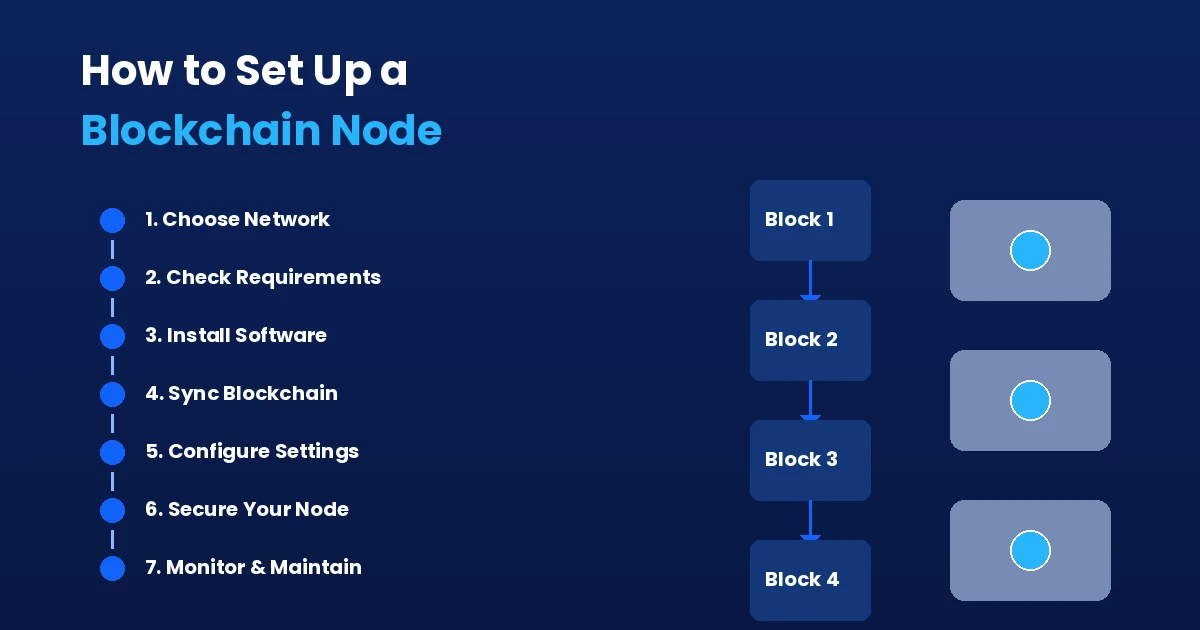
How to Set Up Your Own Blockchain Node: Step by Step
Setting up a blockchain node is less complicated than it sounds, but it does require some preparation. Here is a practical breakdown.
Step 1: Pick Your Blockchain Network
The first decision is which network you want to run a node on. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most common choices, but there are dozens of other options depending on your interests. Each network has its own client software, system requirements, and community. If you are new to this, starting with a well-documented network like Bitcoin or Ethereum is a solid choice because the community support is strong and the software is mature.
Step 2: Meet the Hardware Requirements
Different blockchains need different hardware. A Bitcoin full node, for example, currently needs at least 7 GB of RAM, a solid-state drive with at least 1 TB of storage, and a reliable internet connection that can handle significant data transfer. Ethereum has similar requirements. Check the official documentation for your chosen network before buying or allocating hardware. Using a dedicated machine or a VPS (Virtual Private Server) is recommended over running a node on your daily-use computer.
Step 3: Install the Node Software
Each network has one or more client software options. For Bitcoin, the standard choice is Bitcoin Core. For Ethereum, popular options include Geth and Nethermind. Download the software from the official source only. Using unofficial downloads creates security risks. Follow the installation guides provided by the project.
Step 4: Synchronize With the Network
Once the software is installed, your node needs to download the entire blockchain. This is called the initial sync, and it can take anywhere from a few hours to several days depending on the network and your internet speed. During this time, your node is catching up on every block and transaction that has ever occurred. Be patient and make sure your system does not shut down during this process.
Step 5: Configure Network and Security Settings
After syncing, you will want to configure your node properly. This includes setting up port forwarding on your router so other nodes can connect to yours, adjusting firewall rules, and enabling any specific features you need. On the security side, use strong passwords, keep the software updated, and consider running the node behind a firewall or on a dedicated network segment. Gas costs and transaction processing efficiency are also factors worth understanding, especially on networks like Ethereum. You can read more about gas optimization strategies to understand how transaction fees work at the protocol level.
Step 6: Monitor and Maintain
Running a node is not a set-and-forget activity. You need to monitor its health, ensure it stays synced, and update the software whenever new versions are released. Most blockchain clients offer dashboards or command-line tools for monitoring. Some third-party services also provide monitoring dashboards that alert you if your node falls behind or goes offline.
Hardware Requirements for Popular Blockchain Nodes
| Requirement | Bitcoin Full Node | Ethereum Full Node | Solana Validator |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAM | 7 GB+ | 16 GB+ | 128 GB+ |
| Storage | 1 TB SSD | 2 TB+ SSD | 2 TB+ NVMe SSD |
| CPU | Multi-core | 4+ cores | 12+ cores |
| Internet | 50 Mbps+ | 25 Mbps+ | 300 Mbps+ |
| Initial Sync Time | 1 to 3 days | 2 to 7 days | 1 to 2 days |
These numbers change as blockchains grow. Always check the latest official documentation before setting up your node. The Ethereum network, for instance, has seen its storage requirements increase significantly after years of transaction history accumulation.
The Lifecycle of a Blockchain Node
A blockchain node goes through several stages during its operational life. Understanding this lifecycle helps you plan for long-term operation and avoid common pitfalls.
Phase 1 Setup and Installation – You select your network, install the client software, and configure your system. This is where you make decisions about what type of node to run and what hardware to use.
Phase 2 Initial Synchronization – Your node downloads the entire blockchain history. This is the most time-consuming phase and requires a stable internet connection. During this stage, your node is catching up to the current state of the network.
Phase 3 Active Operation – Once synced, your node begins participating in the network. It receives new transactions, validates them, verifies new blocks, and relays information to peer nodes. This is the steady-state phase where your node contributes to the network continuously.
Phase 4 Maintenance and Updates – Software updates, security patches, and protocol upgrades require attention. Hard forks or significant network changes may require you to update your client software or adjust your configuration. Governance decisions can also affect how your node operates, a topic explored further in smart contract governance models.
Phase 5 Scaling or Decommissioning – Over time, you may choose to upgrade your hardware to handle a growing blockchain, switch to a different node type, or shut down your node. Each of these decisions should be made based on your ongoing goals and the network’s evolving requirements.
How Do Nodes Keep a Blockchain Secure?
Security in blockchain does not come from a firewall or an antivirus program. It comes from the distributed nature of the network itself, and nodes are the ones making that happen.
Here is a practical example. Suppose an attacker tries to submit a fake transaction that says they have 1,000 Bitcoin when they actually have none. That transaction gets broadcast to the network. But every node that receives it checks the transaction against the blockchain record. Since the attacker’s balance does not match the claim, every honest node rejects the transaction. For the attack to succeed, the attacker would need to control a majority of the nodes on the network, which is referred to as a 51% attack. On a large network with thousands of independently operated nodes, this is extraordinarily difficult and expensive to pull off.
Nodes also protect against double-spending. If someone tries to spend the same cryptocurrency twice, nodes will catch it because they keep track of which funds have already been spent. The first valid transaction gets accepted, and any subsequent attempt to spend the same funds is rejected.
Another layer of security comes from the fact that the blockchain data is distributed across all nodes. There is no single database to hack. Even if several nodes are compromised or go offline, the rest of the network continues operating normally because each remaining node still has a complete copy of the ledger. This resilience through redundancy is one of the most powerful features of blockchain architecture.
The consensus mechanism adds yet another dimension. Whether a network uses Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or another method, the consensus process requires nodes to agree on the current state of the blockchain before any changes are accepted. This collective agreement makes unilateral manipulation practically impossible. If your work involves smart contract architecture, the security provided by node consensus is what ensures your contracts execute exactly as written.
Do Blockchain Nodes Earn Rewards?
The short answer is: it depends on the type of node and the network you are on.
In Proof of Work networks like Bitcoin, mining nodes earn rewards. When a mining node successfully creates a new block, it receives newly minted coins (the block reward) plus the transaction fees from all the transactions included in that block. This is the primary financial incentive for miners and is what keeps the network running.
In Proof of Stake networks, validator nodes earn rewards for staking their cryptocurrency and participating in block creation. The rewards typically come from transaction fees and, in some networks, newly issued tokens. Staking rewards vary by network but can provide a steady return on the cryptocurrency you lock up. The concept of verifiable credentials is also gaining traction in these ecosystems as a way to verify validator identities and reputations.
Master nodes in networks like Dash earn a share of the block rewards in exchange for providing additional network services. The requirement to lock up collateral means there is a financial barrier to entry, but the ongoing rewards can be significant.
Regular full nodes, on the other hand, typically do not earn direct financial rewards. Their value comes from the benefits discussed earlier: independent verification, privacy, data access, and supporting the network. Some people compare running a full node to maintaining infrastructure. You do not get paid directly, but you gain reliability and independence.
| Node Type | Earns Rewards? | Reward Source | Collateral Needed? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Node | No | N/A | No |
| Mining Node | Yes | Block rewards + tx fees | No (hardware cost) |
| Validator Node | Yes | Staking rewards + tx fees | Yes (staked crypto) |
| Master Node | Yes | Block reward share | Yes (locked collateral) |
| Lightweight Node | No | N/A | No |
Real-World Example: What Happens When Node Count Drops
To understand why node participation matters, consider what happens when it declines. In 2017, the Bitcoin network had over 12,000 reachable full nodes. Over the years, this number has fluctuated. During periods when fewer nodes are online, the network becomes more centralized around a smaller group of operators. This does not immediately break anything, but it creates concentration risk. If a handful of large entities control most of the nodes, they could theoretically coordinate to influence the network in ways that benefit them at the expense of regular users.
This is not a hypothetical concern. Smaller blockchain networks with fewer nodes have experienced attacks and manipulation because there were not enough independent operators to prevent it. The lesson is clear: the health of any blockchain depends on a diverse and distributed set of node operators. Every additional independent node makes the network more resilient and harder to compromise.
For businesses building on blockchain, especially those developing platforms for financial operations like cryptocurrency MLM software solutions, running your own nodes is not just good practice. It is a way to ensure that the infrastructure your business depends on remains secure and available.
Who Should Run a Blockchain Node?
Running a node is not for everyone, but it is for more people than you might think. Here is a breakdown of who benefits most.
Developers who build applications on blockchain need local access to the full ledger. Running a node gives them the ability to test, debug, and deploy without depending on external services that may be unreliable or rate-limited.
Businesses that accept cryptocurrency or build products on blockchain benefit from having their own node for transaction verification, data access, and operational independence. If your revenue depends on the blockchain, you should not be trusting someone else’s node to tell you what is happening on it.
Privacy-conscious individuals who want to make transactions without exposing their activity to third parties benefit directly from running their own node.
Crypto enthusiasts and supporters who believe in the mission of decentralization can contribute by running a node, even if they do not earn direct financial rewards for doing so. The broader trading and financial ecosystem built around blockchain depends on robust node infrastructure.
Researchers and analysts who need access to complete and accurate blockchain data will find that running an archival node is the most reliable way to get it.
“The strength of any blockchain is not measured by the number of users it has, but by the number of independent nodes verifying its integrity. Every node is a vote for decentralization.”
This idea captures why individual participation at the node level matters. Running a node is the most direct way to back up your belief in what blockchain technology represents.
Common Challenges of Running a Blockchain Node
Being honest about the challenges is important. Running a node is not all upside, and going in with realistic expectations will help you stay committed long-term.
Storage requirements grow over time. The Bitcoin blockchain was around 500 GB in 2023 and continues to grow. Ethereum is even larger. You need to plan for increasing storage needs, which may mean upgrading your hardware periodically.
Internet bandwidth can be significant. Nodes constantly send and receive data. If you have data caps on your internet plan, running a node could cause you to exceed them. A stable, unmetered connection is ideal.
Initial sync takes time. Depending on the network and your hardware, the first synchronization can take days. This requires patience and a system that can run uninterrupted for that period.
Software updates require attention. When a network undergoes a hard fork or protocol upgrade, you may need to update your node software promptly. Falling behind on updates can cause your node to fall out of sync with the rest of the network.
Power costs are ongoing. Running a node 24/7 uses electricity. While the cost for a full node is not comparable to mining, it is still a continuous expense to factor into your planning.
PoW vs PoS: How Consensus Affects Node Operation
| Factor | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
|---|---|---|
| How blocks are created | Solving cryptographic puzzles | Selected based on stake |
| Energy consumption | Very high | Low |
| Hardware requirement | Specialized mining rigs (ASICs) | Standard server hardware |
| Entry barrier | High (hardware and electricity) | Medium (requires staked crypto) |
| Reward structure | Block rewards + fees | Staking yields + fees |
| Example networks | Bitcoin, Litecoin | Ethereum, Cardano, Solana |
The shift from PoW to PoS, which Ethereum completed in September 2022, has made running a validator node accessible to more people by removing the need for expensive mining equipment. According to Investopedia’s overview of Proof of Stake, this transition also reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by over 99%, making it a more sustainable option for node operators.
Get Expert Blockchain Node Development
Whether you need a full node, validator node, or custom blockchain infrastructure, our development team delivers secure and scalable solutions tailored to your needs.
Final Thoughts
Running a blockchain node is one of the most practical ways to participate in the blockchain ecosystem beyond simply buying and holding cryptocurrency. It gives you independence, strengthens the network you rely on, and aligns your actions with the decentralized principles that make blockchain technology valuable in the first place.
Whether you are a developer building applications, a business processing transactions, or an individual who values privacy and self-sovereignty, running a node is worth serious consideration. The technical barriers have come down significantly in recent years, and the benefits, both personal and collective, remain substantial.
The blockchain space is still growing. As it matures, the networks that thrive will be the ones with the broadest and most independent set of node operators. By running a node today, you are not just helping yourself. You are helping build the infrastructure for a more open and resilient digital future.
Frequently Asked Questions
A full node downloads and stores the entire blockchain ledger and independently validates every transaction and block using the network consensus rules. A lightweight node, also called an SPV node, stores only block headers and depends on full nodes for detailed verification. Full nodes offer better security and independence, while lightweight nodes are designed for mobile devices and systems with limited storage and processing power. Choosing between them depends on your goals and available hardware resources.
The cost of running a blockchain node at home varies based on the network you choose and your existing hardware. For a Bitcoin full node, you generally need a computer with at least 1 TB of SSD storage and a reliable internet connection. Electricity costs for keeping the machine running around the clock are typically modest. If you already have suitable hardware, the primary ongoing costs are electricity and bandwidth. If you need to buy dedicated hardware or a VPS, expect to spend anywhere from a few hundred to over a thousand dollars upfront.
It depends on the type of node you operate and the blockchain network. Mining nodes on Proof of Work networks earn block rewards and transaction fees for creating new blocks. Validator nodes on Proof of Stake networks earn staking rewards by locking up cryptocurrency and participating in consensus. Master nodes earn a share of block rewards for providing extra services. However, standard full nodes do not receive direct financial compensation. The benefits of running a full node are primarily independence, privacy, and contributing to network security rather than monetary rewards.
Running a blockchain node is legal in most countries, but cryptocurrency regulations vary significantly around the world. In countries where cryptocurrency is legal and regulated, operating a node is generally permitted and may even be encouraged. However, some jurisdictions have restrictions or outright bans on cryptocurrency activities, which could extend to running nodes. Before setting up a node, research the specific cryptocurrency regulations in your country or region. Regulatory environments are also evolving, so staying updated on local laws is advisable for long-term node operators.
The initial setup and synchronization time depends on the blockchain network and your hardware. Installing the node software itself takes just a few minutes. However, the initial sync, where your node downloads the complete blockchain history, can range from several hours to several days. Bitcoin full nodes typically take one to three days to sync on modern hardware with a fast connection. Ethereum nodes can take two to seven days or even longer. Using a fast SSD and a stable, high-speed internet connection significantly reduces sync time for any network.
If your node goes offline temporarily, the blockchain network continues functioning normally because other nodes maintain the ledger. When your node comes back online, it will need to catch up by downloading and validating all the blocks that were added while it was offline. This re-sync process usually takes much less time than the initial full sync. However, extended downtime may cause your node to fall significantly behind. For validator or master nodes, prolonged absence could result in missed rewards or penalties depending on the specific network rules and consensus mechanism in place.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.