Key Takeaways
- 1. DeFi governance is the process through which decentralized communities make decisions about protocol upgrades, treasury spending, and rule changes.
- 2. On chain governance records every vote and proposal directly on the blockchain, making it transparent and tamper proof.
- 3. Off chain governance happens outside the blockchain through forums, social discussions, and signaling tools like Snapshot voting.
- 4. Governance tokens give holders the power to vote on proposals, similar to how shareholders vote in a traditional company.
- 5. Both models have unique advantages: on chain offers automation, while off chain offers flexibility and lower costs.
- 6. Many leading DeFi protocols use a hybrid approach that combines elements of both on chain and off chain governance.
- 7. Understanding governance helps investors and builders evaluate the long term health and decentralization of a DeFi project.
- 8. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) are the primary structures that implement these governance systems in practice.
- 9. Voter participation and token distribution remain major challenges for fair decentralized governance.
- 10. Blockchain solution providers like Nadcab Labs help startups and enterprises design and deploy secure DAO governance frameworks.
In the world of decentralized finance, every protocol faces one important question: who gets to make decisions, and how? This is where the debate around On Chain vs Off Chain Governance in DeFi becomes truly important. Unlike traditional banks or financial institutions where a handful of executives call the shots, DeFi platforms aim to give power directly to their communities. But the way that power is exercised can vary dramatically.
If you have ever wondered what DeFi governance really means, how proposals get voted on, or why some platforms use tokens while others rely on discussion forums, this guide is for you. Whether you are a curious beginner, an early crypto investor, or a business founder exploring blockchain, understanding governance is the key to navigating the decentralized world with confidence.
In this article, we will break down both governance models in simple, everyday language. We will explore how they work, where they are used, their strengths and weaknesses, and why they matter for the future of finance and technology. Let us get started.
What Is DeFi Governance? A Simple Explanation
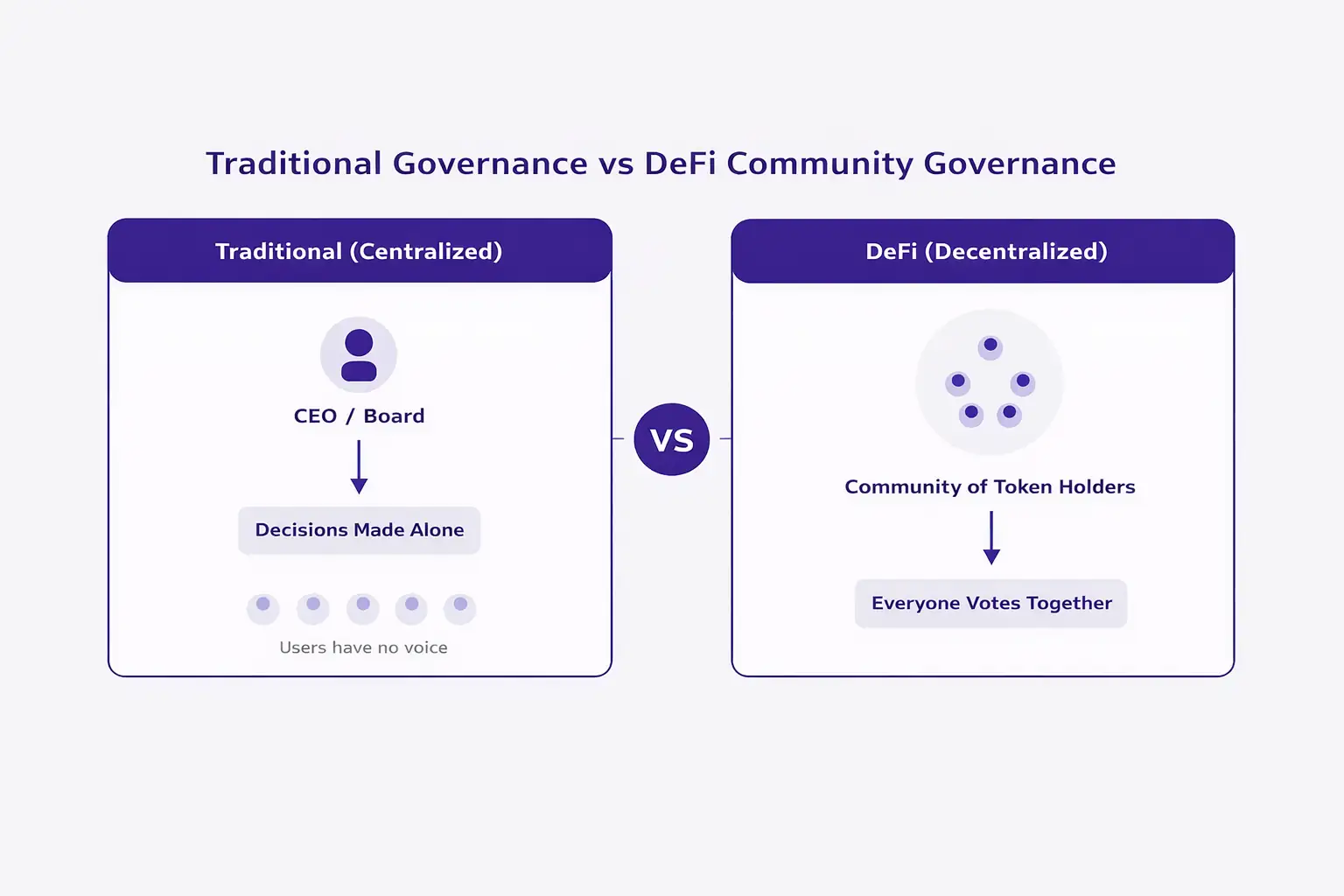
Think of DeFi governance like a town hall meeting for the internet. In a traditional company, the board of directors decides the future direction of the business. In DeFi, there is no board. Instead, the users, developers, and token holders collectively decide how the protocol should evolve.
DeFi governance covers a wide range of decisions. These can include changing interest rates on a lending platform, allocating funds from a community treasury, adding new features, adjusting security parameters, or even deciding which blockchain network to expand to. Essentially, any rule change or upgrade that affects the protocol goes through a governance process.
This is what makes decentralized finance truly revolutionary. It shifts power from centralized institutions to distributed communities. But for this system to work fairly and efficiently, there need to be clear rules about how decisions are proposed, discussed, and finalized. That is where on chain and off chain governance come in.
What Is On Chain Governance? Everything You Need to Know
On chain governance is a system where every part of the decision making process happens directly on the blockchain. This means that proposals are submitted as transactions, votes are recorded on the ledger, and if a proposal passes, the changes are automatically executed through smart contracts.
Imagine a school election where every single vote is written on a public board that nobody can erase or alter. That is essentially what on chain governance does. It creates a permanent, transparent, and verifiable record of every governance action.
How On Chain Governance Works in Practice:
- A token holder creates a formal proposal on the blockchain
- The proposal enters a review or discussion period
- Token holders cast their votes using governance tokens
- Votes are recorded as immutable transactions on the chain
- If the proposal meets the required threshold, a smart contract automatically executes the change
Platforms like Tezos and Polkadot are well known examples of on chain governance. In these ecosystems, protocol upgrades are proposed, voted on, and implemented entirely through the blockchain itself. There is no need for a central authority to approve or deny anything.
The biggest strength of on chain governance is automation and trust. Since smart contracts handle the execution, there is no room for human error or manipulation once a vote passes. The code does exactly what the community decided.
What Is Off Chain Governance? Understanding the Informal Approach
Off chain governance takes a different path. Instead of recording everything on the blockchain, discussions and decisions happen through external channels. These can include community forums, social media platforms, GitHub discussions, Discord servers, and specialized signaling tools like Snapshot.
Think of it like a group of friends deciding where to go for dinner. They discuss options in a group chat, someone creates a poll, and the group agrees on a plan. The conversation is not recorded in a formal system, but the outcome is still valid because everyone participated.
In off chain governance, the voting itself does not cost gas fees and does not create blockchain transactions. Instead, it acts as a signaling mechanism. Once the community reaches a clear consensus, developers or a multisig wallet (a wallet that requires multiple signatures to authorize transactions) implements the change manually.
Bitcoin is the most famous example of off chain governance. Changes to the Bitcoin protocol are discussed through Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs), debated on mailing lists and forums, and eventually implemented by core developers if there is broad agreement. There is no formal on chain voting mechanism.
In the DeFi world, many protocols like Uniswap and Aave use a combination where initial discussions and temperature checks happen off chain (often through Snapshot voting), and only final binding votes happen on chain.
Why Governance Matters in Decentralized Finance
Governance is not just a technical detail. It is the foundation of trust and sustainability in any DeFi protocol. Without proper governance, a decentralized platform is really just a centralized product wearing a decentralized mask.
Here is why governance matters so much:
- Security: Governance allows communities to respond quickly to security threats, patch vulnerabilities, and upgrade smart contracts.
- Fairness: It ensures that no single party can make unilateral decisions that affect millions of users and billions of dollars in assets.
- Adaptability: DeFi protocols need to evolve with market conditions, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. Governance makes this possible.
- Community Ownership: Good governance gives users a real stake in the platform’s future, which increases loyalty and long term engagement.
- Transparency: Governance processes, especially on chain ones, create a public record that anyone can audit and verify.
For business founders and investors evaluating DeFi projects, the governance model is one of the most important factors to examine. A protocol with strong, fair governance is far more likely to succeed in the long run than one controlled by a small group of insiders.
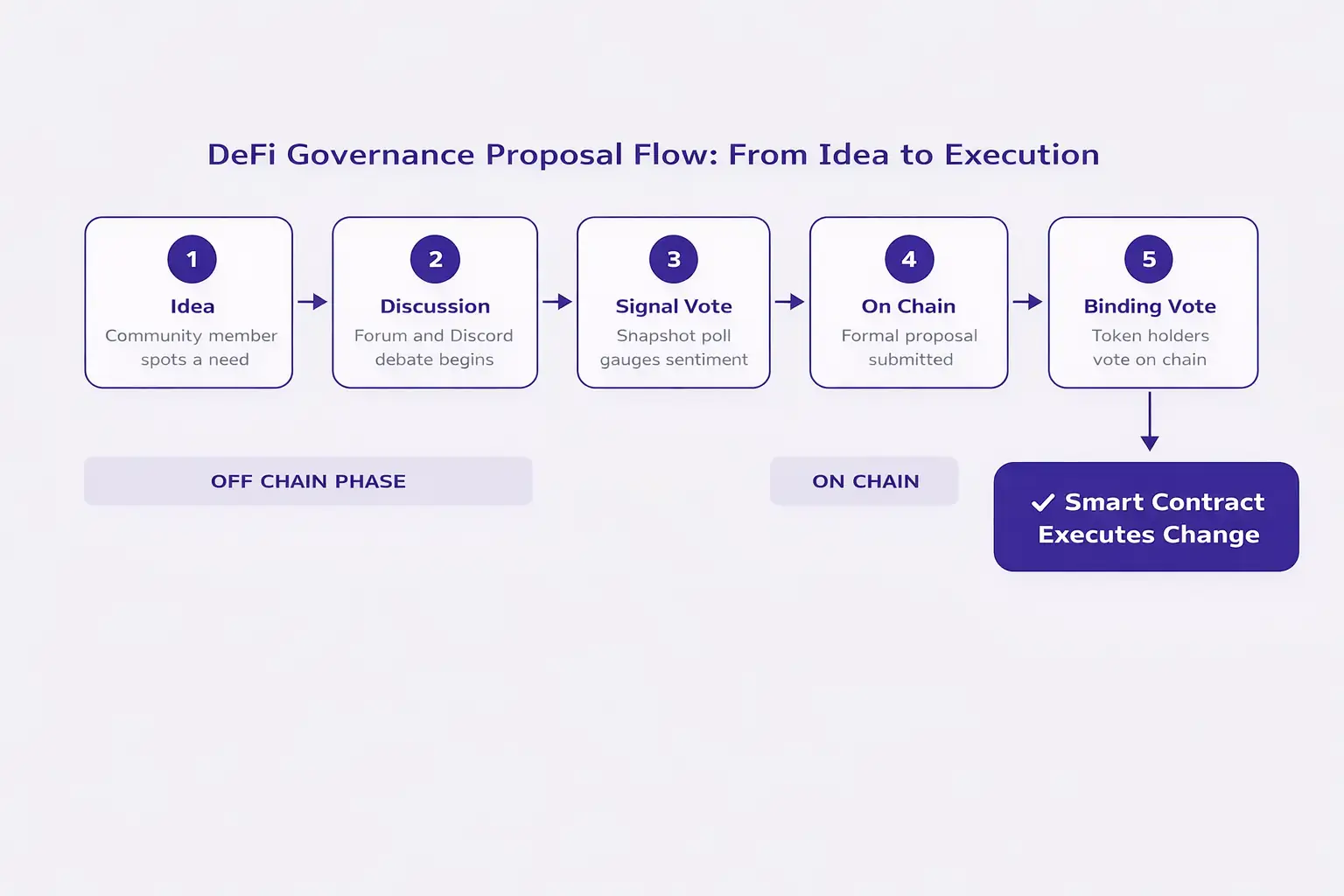
Step by Step: How a DeFi Governance Proposal Goes from Idea to Execution
Understanding how a governance proposal actually works can feel confusing at first, but the process is surprisingly similar to how decisions are made in everyday organizations. Here is a simplified walkthrough that applies to many popular DeFi protocols:
A community member identifies a problem or improvement. For example, a user might suggest lowering the collateral ratio on a lending protocol to attract more borrowers.
The idea is posted on a governance forum, Discord channel, or community platform. Other members discuss the pros, cons, and potential risks. This stage filters out weak proposals before they reach the voting stage.
Many protocols use tools like Snapshot for a preliminary off chain vote. This gasless vote gauges community sentiment without spending any money on transaction fees.
If the temperature check passes, the proposal is formalized and submitted on chain. This usually requires the proposer to hold a minimum number of governance tokens.
Token holders cast their votes during a defined time window. Each token typically represents one vote. Some protocols also use delegation, where holders can assign their voting power to trusted representatives.
If the proposal meets the quorum (minimum participation) and passes the required majority, a smart contract automatically executes the change. In some cases, there is a time lock period before execution to allow for final review.
Real World Use Cases of On Chain and Off Chain Governance
Understanding theory is great, but seeing how governance plays out in real platforms makes it truly click. Here are some notable examples:
On Chain Governance Examples
- Tezos: One of the pioneers of on chain governance. Token holders vote on protocol upgrades, and approved changes are automatically applied to the network without requiring hard forks.
- Polkadot: Uses a sophisticated on chain governance system with a council, technical committee, and public referendum mechanism to manage upgrades.
- MakerDAO: MKR token holders vote on critical parameters like stability fees and collateral types. Approved changes are executed through smart contracts.
Off Chain Governance Examples
- Bitcoin: All protocol changes are discussed through BIPs and community forums. There is no formal on chain voting system. Consensus is reached through developer agreement and miner signaling.
- Ethereum (historically): Major upgrades like the transition to proof of stake were debated extensively through off chain channels like Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) and community calls.
- Yearn Finance: Uses off chain discussions and Snapshot voting for many governance decisions before final implementation.
Benefits of On Chain Governance
On chain governance has gained popularity because it brings several powerful advantages to decentralized ecosystems:
- Full Transparency: Every proposal, vote, and outcome is permanently recorded on the blockchain. Anyone can verify the process at any time.
- Automated Execution: Smart contracts remove the need for human intermediaries. Once a vote passes, the code handles the rest.
- Tamper Proof Records: Since votes live on the blockchain, they cannot be altered, deleted, or manipulated after the fact.
- Direct Democracy: Every token holder has the opportunity to participate in decisions, creating a more inclusive governance structure.
- Reduced Centralization Risk: No single entity can override or ignore the community’s decision once it is recorded on chain.
Benefits of Off Chain Governance
Off chain governance also brings unique strengths, especially when it comes to flexibility and accessibility:
- Lower Cost: Off chain voting does not require gas fees, making it accessible to token holders regardless of their wallet size.
- Faster Iteration: Discussions and votes can happen quickly without waiting for blockchain confirmations or dealing with network congestion.
- Richer Discussion: Forums, Discord channels, and community calls allow for nuanced debate that is difficult to capture in on chain transactions.
- Flexibility: Off chain systems can be adapted and improved without requiring smart contract upgrades or protocol changes.
- Broader Participation: Because there is no cost to vote, smaller holders and community members without large token positions can still have their voices heard.
Risks and Limitations of Each Governance Model
No governance system is perfect. Both on chain and off chain models come with challenges that communities must navigate carefully.
Limitations of On Chain Governance
- High gas fees can discourage participation, especially for smaller token holders
- Whale dominance: large token holders can disproportionately influence outcomes
- Smart contract bugs in governance contracts can lead to catastrophic failures
- Slower process due to blockchain confirmation times and mandatory voting periods
- Low voter turnout is a common issue across many on chain governance systems
Limitations of Off Chain Governance
- Votes are not binding and can be ignored by the implementing team
- Less transparent since records may not be permanently stored
- Potential for manipulation through social engineering or coordinated campaigns
- Relies on trust in the core team or multisig holders to honor voting outcomes
- Fragmented discussions across multiple platforms can create confusion
Key Differences Between On Chain and Off Chain Governance in DeFi
| Feature | On Chain Governance | Off Chain Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Where Voting Happens | Directly on the blockchain | Forums, Snapshot, social platforms |
| Transparency | Fully transparent and verifiable | Varies by platform |
| Execution | Automated via smart contracts | Manual by core team or multisig |
| Cost | Requires gas fees | Usually free or very low cost |
| Speed | Slower due to blockchain processing | Faster and more flexible |
| Binding Nature | Votes are binding and enforceable | Votes are advisory or signaling |
| Immutability | Records are permanent | Records may not be permanent |
| Participation Barrier | Higher due to transaction costs | Lower and more accessible |
| Examples | Tezos, Polkadot, MakerDAO | Bitcoin, Snapshot, Yearn Finance |
The Role of Governance Tokens in DeFi Voting Power
Governance tokens are the backbone of DeFi voting systems. These are special tokens that give holders the right to participate in governance decisions. Think of them as digital voting shares. The more tokens you hold, the more voting power you have.
Popular governance tokens include UNI (Uniswap), AAVE (Aave), COMP (Compound), and MKR (MakerDAO). Each of these tokens allows holders to propose changes, vote on proposals, and shape the future of their respective protocols.
However, this model raises an important question about fairness. If voting power is tied to token ownership, wealthier participants naturally have more influence. This is why many protocols are exploring alternative models such as quadratic voting (where the cost of additional votes increases exponentially) and delegation systems (where smaller holders can delegate their votes to trusted community representatives).
For businesses and startups building in the DeFi space, designing a fair and effective token governance system is one of the most critical decisions. The tokenomics and distribution model directly affect how decentralized and democratic the governance process will be. This is an area where working with experienced blockchain development partners like Nadcab Labs can make a significant difference, ensuring the governance framework is robust, secure, and genuinely community driven.
How DAOs Use Hybrid Governance Systems
In practice, most successful DAOs do not rely on a single governance model. Instead, they blend on chain and off chain elements to create a hybrid system that captures the best of both worlds.
A typical hybrid governance flow looks like this:
- ▶ Phase 1 (Off Chain): A community member posts an idea or proposal on a governance forum like Discourse or Commonwealth.
- ▶ Phase 2 (Off Chain): The community discusses the proposal, suggests modifications, and builds consensus.
- ▶ Phase 3 (Off Chain): A Snapshot vote is conducted to measure community sentiment without gas costs.
- ▶ Phase 4 (On Chain): If the Snapshot vote passes, a formal on chain proposal is submitted.
- ▶ Phase 5 (On Chain): Token holders cast binding votes on the blockchain, and the smart contract executes the approved changes.
This hybrid approach is used by major protocols including Uniswap, Aave, and Compound. It reduces unnecessary on chain transactions for proposals that may not have community support while ensuring that final decisions are binding, transparent, and automated.
As noted in Ethereum’s governance documentation, effective blockchain governance often requires a combination of formal mechanisms and informal coordination to function well at scale.
Business and Startup Relevance of DeFi Governance
If you are a business founder or startup exploring blockchain technology, understanding governance is not optional. It is essential. The governance model you choose for your decentralized application or protocol will directly impact user trust, regulatory compliance, and long term viability.
Here are some practical ways governance affects businesses in the blockchain space:
- Investor Confidence: Protocols with transparent, community driven governance attract more investment because they demonstrate accountability.
- Regulatory Alignment: As regulators worldwide begin examining DeFi, having a well structured governance system can help demonstrate responsible operation.
- User Retention: Users are more likely to stay engaged with platforms where they have a voice in decision making.
- Risk Management: Good governance enables faster response to security incidents, market changes, and operational challenges.
For startups that want to build DAO governance models, deploy governance smart contracts, or create custom voting mechanisms, partnering with an experienced blockchain solutions company is critical. Nadcab Labs, for instance, works with startups and enterprises globally to design, develop, and deploy governance frameworks that are tailored to specific business requirements and community goals.
Future Trends in DAO and DeFi Governance
The governance landscape in DeFi is evolving rapidly. Here are some trends that are shaping the future of decentralized decision making:
- Quadratic Voting: This system makes it increasingly expensive to accumulate voting power, reducing whale dominance and encouraging broader participation.
- Vote Delegation and Liquid Democracy: Token holders can delegate their voting power to trusted representatives who are more active or knowledgeable about specific proposals.
- Reputation Based Governance: Some protocols are exploring governance systems that consider a user’s history, contributions, and engagement, not just their token balance.
- Cross Chain Governance: As DeFi expands across multiple blockchains, governance systems that work seamlessly across chains are becoming increasingly important.
- AI Assisted Governance: Emerging tools are helping communities analyze proposals, predict outcomes, and summarize complex discussions to improve voter participation and decision quality.
- Legal DAO Frameworks: Jurisdictions like Wyoming and the Marshall Islands are creating legal structures for DAOs, which will shape how governance interacts with traditional legal systems.
According to research by the World Economic Forum, decentralized governance models are gaining attention not just in crypto but also in traditional industries looking to improve transparency and stakeholder participation.
Common Misconceptions About DeFi Governance
As governance becomes a bigger topic in the crypto world, several misconceptions have emerged. Let us clear up the most common ones:
“Governance means every user gets equal say.”
In most DeFi protocols, voting power is proportional to token holdings. This means larger holders have more influence. While some protocols are working toward more equitable models, true equal voting is rare in the current landscape.
“On chain governance is always better than off chain.”
Both models have strengths and weaknesses. On chain governance offers transparency but can be expensive and slow. Off chain governance is faster and cheaper but relies on trust. The best approach depends on the protocol’s needs and community.
“Governance tokens are just for voting.”
While voting is the primary function, many governance tokens also carry economic value, staking rewards, and access to exclusive protocol features. Some even represent a share of protocol revenue.
“DeFi governance is fully decentralized.”
In reality, many DeFi protocols still have significant centralization in their governance. Core teams, foundations, and large venture capital holders often control a majority of governance tokens, especially in early stages.
Conclusion
The debate around On Chain vs Off Chain Governance in DeFi is not about choosing a winner. It is about understanding two complementary approaches to decentralized decision making and knowing when each one works best.
On chain governance brings transparency, immutability, and automated execution. Off chain governance provides flexibility, lower costs, and richer community discussions. The most successful DeFi protocols recognize this and adopt hybrid models that leverage both approaches strategically.
For beginners stepping into the world of decentralized finance, understanding governance is a fundamental skill. It helps you evaluate which projects are truly decentralized, which ones give their communities genuine power, and which ones are built to last.
For builders and entrepreneurs, governance is not just a feature to add later. It should be a core part of your protocol design from day one. Working with experienced blockchain development partners ensures that your governance framework is robust, secure, and aligned with your community’s long term interests.
As DeFi continues to grow and reshape the financial world, governance will remain at the heart of what makes decentralization meaningful. The more you understand about on chain and off chain governance models, the better positioned you will be to participate in, invest in, and build the decentralized future.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are several aggregator tools designed for this. Platforms like Boardroom, Tally, and Messari Governance track live and upcoming proposals across multiple DeFi protocols in one dashboard. You can also follow individual protocol governance forums or set up notifications through Snapshot to stay updated on new proposals relevant to your holdings.
If a vote fails to reach quorum, meaning not enough token holders participated, the proposal is typically rejected regardless of whether the majority of actual voters supported it. Some protocols allow the proposer to resubmit the proposal for another round after a waiting period, sometimes with adjusted parameters or additional community outreach to increase participation.
On chain governance votes are pseudonymous, not anonymous. Every vote is linked to a wallet address and is publicly visible on the blockchain. While your real world identity is not directly attached, anyone can see which wallet voted and how. This transparency is intentional, as it allows the community to audit the voting process and hold large voters accountable.
Generally, once a smart contract executes an approved governance change, it cannot be undone automatically. However, the community can submit a new proposal to reverse or modify the previous decision. In emergency situations, some protocols have a guardian or emergency multisig that can pause changes temporarily, but this is considered a last resort and is often debated within the community.
It depends on the protocol. Some DeFi platforms offer voting incentives such as token rewards, fee sharing, or boosted staking yields for active governance participants. Others do not offer direct financial rewards but may provide reputation scores or increased influence in future governance rounds. Protocols like Curve Finance are known for rewarding active voters through their gauge voting system.
Flash loan governance attacks occur when someone borrows a massive amount of tokens temporarily to sway a vote. To prevent this, most protocols use snapshot mechanisms that record token balances at a specific block before the vote begins. This means tokens acquired after the snapshot do not count. Additional safeguards include time locks on execution, minimum proposal thresholds, and multi stage voting processes.
Yes. Governance tokens are subject to market volatility just like any other cryptocurrency. Their value can decline due to factors like low voter participation, poor governance decisions, token inflation from excessive minting, or broader market downturns. A token’s governance utility alone does not guarantee its price stability, so investors should evaluate the overall health and activity of the protocol before purchasing.
While both systems give token or share holders voting rights, there are key structural differences. Corporate voting is regulated by securities law, conducted through centralized intermediaries, and often limited to annual meetings. DeFi governance is permissionless, operates around the clock, and can be fully automated through smart contracts. Additionally, DeFi governance is open for anyone to observe and audit in real time, whereas corporate voting records are typically private.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







