Key Takeaways
- Government blockchain solutions transform public sector operations through immutable record-keeping, enhanced transparency, and automated processes reducing administrative overhead across agencies.
- Blockchain-based identity systems enable secure citizen authentication eliminating redundant verification while protecting privacy through cryptographic proofs and selective disclosure mechanisms.
- Decentralized public records management ensures tamper-proof documentation for vital statistics, property titles, and official certificates accessible across jurisdictional boundaries.
- Smart contract automation in procurement streamlines tendering processes, enforces compliance rules automatically, and accelerates vendor payments through programmable business logic.
- Budget transparency initiatives leverage blockchain to track public spending allocation in real-time, enabling citizens to monitor Government blockchain solutions expenditure and accountability.
- Permissioned blockchain networks facilitate secure cross-agency data sharing while maintaining governance controls and regulatory compliance across Government blockchain solutions departments.
- Land registry implementations provide definitive ownership proof preventing property fraud, streamlining title transfers, and reducing dispute resolution costs through immutable records.
- Blockchain voting systems enhance electoral integrity through verifiable voter authentication, tamper-proof ballot recording, and transparent counting processes building public trust.
- Supply chain traceability for defense contracts and infrastructure projects ensures authentic materials, prevents counterfeiting, and maintains complete procurement audit trails.
- Regulatory compliance automation via distributed ledgers reduces manual auditing requirements while providing real-time verification of Government blockchain solutions operations against policy frameworks.
Government blockchain solutions represent a fundamental reimagining of how public sector organizations deliver services, manage records, and build citizen trust in the digital age. Across jurisdictions in USA, UK, UAE, and Canada, forward-thinking Government blockchain solutions are implementing distributed ledger technology to address longstanding challenges in transparency, efficiency, and service accessibility. These implementations span diverse applications from identity verification and land registries to procurement automation and voting systems, each leveraging blockchain’s core strengths of immutability, transparency, and decentralization. Understanding the strategic opportunities, technical architectures, and implementation challenges surrounding government blockchain solutions provides essential insights for policymakers, technology leaders, and citizens navigating public sector digital transformation. This comprehensive analysis examines proven applications, emerging use cases, and best practices derived from years of experience implementing blockchain across government contexts globally.
Strategic Role of Blockchain in Digital Government blockchain solutions Transformation
Government blockchain solutions occupy a strategic position in broader digital transformation initiatives aimed at modernizing public sector operations for 21st-century citizen expectations. Traditional government IT systems suffer from fragmentation across agencies, redundant data entry requiring citizens to provide identical information multiple times, and opacity preventing public verification of government claims. Blockchain Technology addresses these systemic challenges through distributed architectures enabling secure data sharing, cryptographic proofs eliminating trust dependencies, and transparent audit trails restoring public confidence. Strategic adoption requires careful consideration of which government functions benefit most from blockchain characteristics versus alternative digital solutions, avoiding technology-first approaches that force blockchain into inappropriate contexts.
The transformation potential extends beyond operational efficiency to fundamental shifts in government-citizen relationships, moving from opaque bureaucratic processes toward transparent, verifiable, and citizen-centric service delivery. Early adopter Government blockchain solutions demonstrate blockchain’s capacity to reduce corruption through immutable transaction records, streamline cross-border coordination via shared ledgers, and enable new service models impossible with centralized databases. Strategic implementation demands executive leadership commitment, cross-agency coordination mechanisms, and long-term investment horizons recognizing that blockchain benefits accrue gradually as network effects build across interconnected government services. Jurisdictions across North America, Europe, and Middle East increasingly view government blockchain solutions as essential infrastructure for competitive advantage in attracting talent, investment, and citizen satisfaction in an interconnected global economy.
Blockchain-Based Identity Systems for Secure Citizen Authentication
Digital identity represents perhaps the most impactful application of government blockchain solutions, addressing fundamental challenges in authentication, privacy, and service accessibility across public sector interactions. Traditional identity systems require citizens to maintain separate credentials for each government service, creating friction in service access while generating redundant identity verification costs across agencies. Blockchain-based identity solutions establish self-sovereign identity models where citizens control personal credentials stored in digital wallets, sharing only necessary attributes through zero-knowledge proofs during service interactions. Government blockchain solutions verify identity claims against blockchain-anchored credentials without accessing underlying personal data, protecting privacy while ensuring authentication integrity. This architectural approach reduces identity fraud, streamlines onboarding for government services, and enables seamless authentication across agency boundaries.
Implementation experiences from Estonia, Switzerland, and Dubai demonstrate blockchain identity’s capacity to transform citizen experiences while reducing Government blockchain solutions costs through shared verification infrastructure. Estonia’s e-residency program leverages blockchain to provide digital identities for global entrepreneurs, enabling company formation and banking without physical presence. Dubai’s blockchain strategy aims to make the emirate paperless by 2026 through universal digital identity integrated across all government services. These pioneering implementations reveal critical success factors including robust enrollment processes ensuring identity uniqueness, strong privacy protections addressing citizen concerns, and interoperability standards enabling cross-border identity recognition. Technical architectures typically combine on-chain identity anchors with off-chain personal data storage, balancing transparency benefits against privacy requirements while maintaining cryptographic linkage between credentials and authorized holders.
Decentralized Public Records Management Using Immutable Ledgers
Public records management constitutes a core Government blockchain solutions function where blockchain’s immutability characteristics deliver substantial value through tamper-proof documentation and verifiable provenance chains. Birth certificates, marriage licenses, educational credentials, and professional certifications issued on blockchain platforms gain permanent verification capability without requiring contact with issuing authorities. Citizens maintain cryptographic proofs of record authenticity, presenting credentials to third parties who independently verify against blockchain state without intermediary involvement. This architecture eliminates document forgery, reduces verification costs for employers and institutions, and prevents Government blockchain solutions record tampering that undermines public trust. Records remain accessible even if issuing agencies reorganize or systems migrate, ensuring long-term preservation independent of specific technology platforms.
Decentralized records management extends beyond individual credentials to encompass corporate registries, property records, and regulatory compliance documentation requiring multi-party coordination and verification. Business registration systems using blockchain enable real-time verification of corporate good standing, authorized representatives, and beneficial ownership, supporting anti-money laundering efforts and procurement due diligence. The architectural shift from centralized databases to distributed ledgers introduces complexity around data migration from legacy systems, ensuring accessibility for citizens lacking digital literacy, and maintaining performance at scale serving millions of verification requests. Successful implementations balance blockchain’s strengths with practical realities through hybrid approaches combining blockchain anchors for critical verification with traditional databases for high-volume transactional processing.[1]
Smart Contract Automation in Government blockchain solutions Procurement and Tendering
Government blockchain solutions procurement processes represent high-value targets for blockchain automation given their complexity, multi-stakeholder coordination requirements, and vulnerability to corruption and inefficiency. Traditional procurement involves manual document handling, sequential approvals creating delays, and limited transparency enabling favoritism or fraud. Smart contract implementations codify procurement rules into self-executing programs that automatically verify vendor qualifications, evaluate bids according to predetermined criteria, and trigger payments upon delivery confirmation without manual intervention. This automation reduces procurement cycle times from months to weeks, eliminates manual errors in bid evaluation, and creates complete audit trails documenting decision rationale. Transparency benefits extend to vendors who gain visibility into procurement status and fair treatment assurance, while taxpayers access spending data verifying Government blockchain solutions accountability.
Procurement automation initiatives in jurisdictions including UK, Canada, and UAE demonstrate substantial efficiency gains alongside challenges requiring careful management. The UK’s Digital Marketplace explores blockchain for framework agreements, automating vendor onboarding and contract management across Government blockchain solutions departments. Implementation complexity arises from integrating blockchain systems with existing procurement software, training procurement officers on new processes, and ensuring legal validity of smart contract executions under administrative law. Successful deployments typically begin with simpler procurement categories like office supplies before expanding to complex construction or IT projects requiring sophisticated contract logic. The combination of transparency, automation, and immutability positions blockchain-enabled procurement as a powerful tool for reducing Government blockchain solutions waste and restoring public confidence in spending decisions.
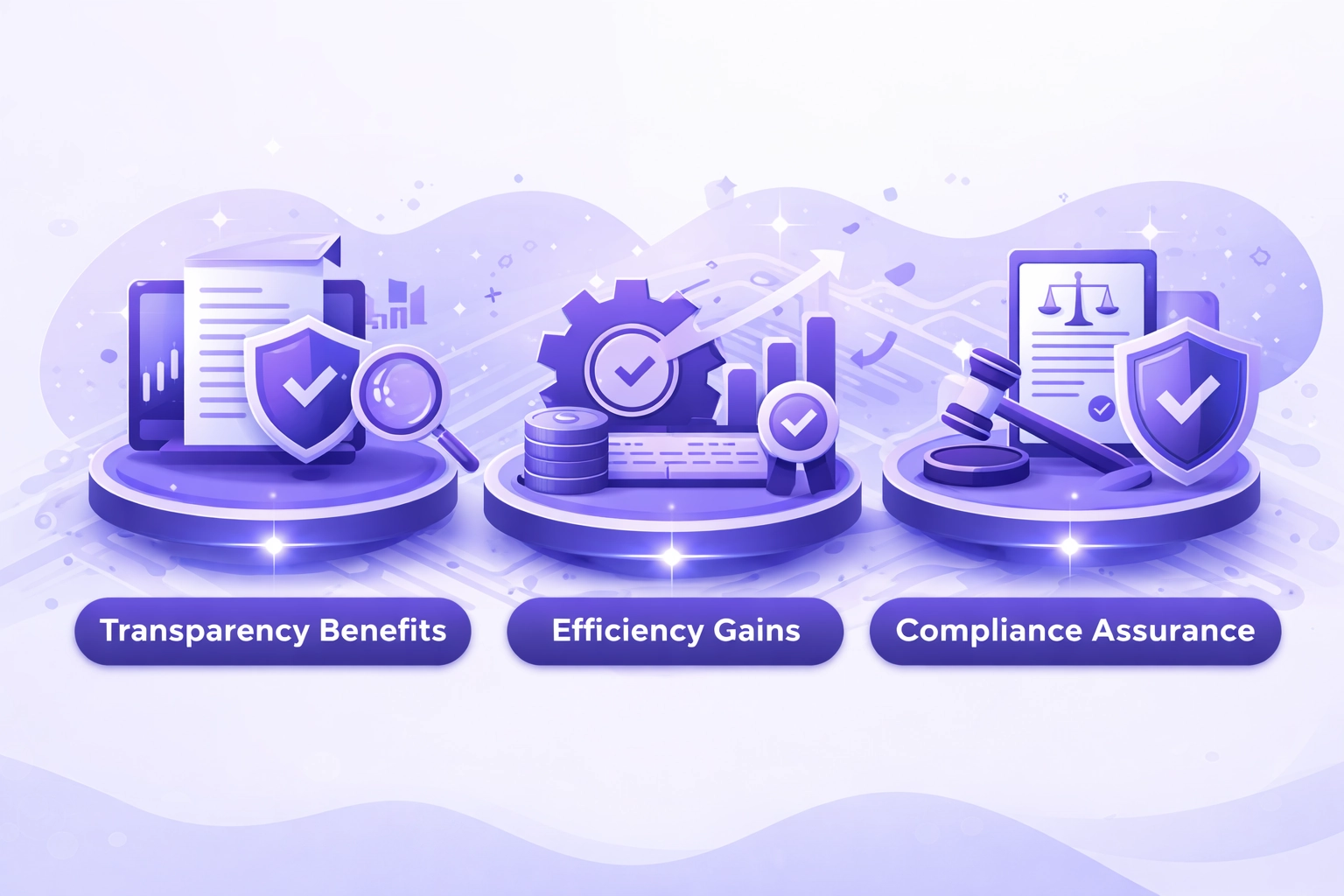 Government Blockchain Solutions Procurement Blockchain Benefits
Government Blockchain Solutions Procurement Blockchain Benefits
Transparency Benefits
- Complete audit trails documenting procurement decisions
- Public visibility into contract awards and spending
- Reduced opportunities for corruption and favoritism
- Enhanced vendor confidence in fair competition
Efficiency Gains
- Automated bid evaluation reducing manual processing
- Accelerated payment cycles through smart contracts
- Elimination of redundant documentation requests
- Streamlined vendor qualification verification
Compliance Assurance
- Automated policy enforcement through coded rules
- Real-time compliance monitoring and alerting
- Immutable records supporting regulatory audits
- Standardized processes across Government blockchain solutions agencies
Blockchain for Transparent Budget Allocation and Public Spending
Budget transparency initiatives leveraging government blockchain solutions address fundamental accountability challenges by enabling real-time public tracking of spending from appropriation through final disbursement. Traditional budget systems provide limited visibility into fund flows, creating opportunities for misallocation and preventing citizens from verifying that spending aligns with stated priorities. Blockchain-based budget tracking records every transaction in immutable ledgers accessible to citizens, journalists, and oversight bodies, creating unprecedented transparency in public finance management. Smart contracts can encode spending limits and approval requirements, automatically preventing unauthorized transactions while generating alerts when expenditures approach thresholds. This real-time visibility transforms budget oversight from retrospective audit exercises into continuous monitoring enabling proactive intervention when irregularities emerge.
Implementation experiences reveal both substantial benefits and implementation challenges requiring careful navigation. Brazil’s transparency portal experiments with blockchain to track federal spending, while several US states explore blockchain for municipal budgets and bond issuance. Technical challenges include integrating blockchain systems with existing financial management platforms, ensuring appropriate access controls balancing transparency against security, and maintaining performance processing thousands of daily transactions. Privacy considerations arise when spending data could reveal sensitive Government blockchain solutions operations or individual employee information requiring careful data design. Successful implementations typically focus on high-level budget allocations initially, gradually expanding granularity as technical capabilities mature and stakeholder confidence builds. The combination of transparency, immutability, and programmable controls positions blockchain as powerful infrastructure for restoring public trust in Government blockchain solutions financial stewardship.
Cross-Agency Data Sharing Through Permissioned Blockchain Networks
Cross-agency data sharing represents a persistent challenge in Government blockchain solutions operations where autonomous agencies maintain separate databases creating information silos that degrade service quality and inflate costs through redundant data collection. Citizens repeatedly provide identical information to different agencies, while Government blockchain solutions workers lack access to data held by other departments needed for informed decision-making. Permissioned blockchain networks address these challenges by establishing shared ledgers where authorized agencies can contribute and access data according to defined governance rules. Smart contracts encode data sharing policies, automatically enforcing access controls and audit logging without requiring central administrators mediating every data request. This architecture enables seamless information flow while maintaining agency autonomy and accountability for data quality within respective jurisdictions.
Technical implementations typically employ permissioned platforms like Hyperledger Fabric or R3 Corda providing fine-grained access controls, private channels for sensitive data, and performance characteristics suitable for Government blockchain solutions transaction volumes. Governance frameworks establish processes for onboarding new agencies, resolving data quality disputes, and evolving shared data standards as requirements change. Successful deployments in Singapore, Australia, and Canada demonstrate cross-agency blockchain’s capacity to reduce duplicate data collection, accelerate case processing through instant information availability, and improve service coordination across organizational boundaries. Implementation challenges include establishing inter-agency governance mechanisms, migrating legacy data into shared formats, and managing change resistance from agencies protective of data control. The long-term vision encompasses government-wide data infrastructure enabling holistic citizen service delivery transcending traditional agency silos.
Government Blockchain Solutions Implementation Lifecycle
Use Case Identification
Analyze Government blockchain solutions processes to identify high-value blockchain applications considering stakeholder complexity, transparency needs, and fraud risks requiring immutable records.
Stakeholder Alignment
Engage agencies, technology vendors, legal advisors, and citizen groups establishing shared objectives and governance frameworks for blockchain initiative.
Technical Architecture Design
Select appropriate blockchain platform, design data models, define access controls, and plan integration with existing Government blockchain solutions IT infrastructure and databases.
Pilot Implementation
Execute limited-scope pilot with controlled user group validating technical assumptions, testing workflows, and gathering feedback before broader deployment.
Security and Compliance Validation
Conduct comprehensive security audits, penetration testing, privacy impact assessments, and regulatory compliance verification before production deployment.
Scaled Production Deployment
Roll out blockchain system to full user population with phased approach, monitoring performance metrics and providing extensive user training and support.
Performance Monitoring
Track system usage, transaction volumes, user satisfaction, and cost savings metrics to demonstrate value and identify optimization opportunities.
Continuous Improvement
Iterate on system capabilities based on user feedback, extend to additional use cases, and share lessons learned across Government blockchain solutions community.
Securing National Land Registries with Blockchain-Based Ownership Proof
Land registry implementations represent among the most mature and impactful government blockchain solutions, addressing critical challenges in property rights protection, transaction fraud, and title dispute resolution. Traditional paper-based or centralized digital registries suffer from vulnerability to manipulation, destruction through natural disasters or conflict, and opacity enabling fraudulent conveyances. Blockchain-based land registries create immutable ownership records cryptographically linked to property identifiers, making title tampering computationally infeasible while providing complete transaction histories from original surveys through current ownership. Smart contracts can automate title transfers upon escrow completion, reducing transaction costs and timeframes while eliminating manual processing errors. This transformation particularly benefits developing nations where weak property rights infrastructure constrains economic activity and vulnerable populations lack secure tenure.
Pioneering implementations in Georgia, Sweden, and United Arab Emirates demonstrate blockchain land registry’s capacity to enhance transaction security while streamlining property transfers. Georgia’s blockchain land registry processes property transactions in days rather than weeks, with complete audit trails increasing buyer confidence and foreign investment. Sweden’s pilot reduces processing time from months to hours for straightforward residential transfers. Technical architectures typically combine blockchain for ownership records with traditional databases for property characteristics and spatial data, balancing immutability requirements against update frequency for non-ownership attributes. Implementation challenges include digitizing historical paper records, resolving existing title disputes before blockchain migration, and ensuring legal recognition of blockchain-based ownership proofs in judicial proceedings. The combination of fraud prevention, transaction efficiency, and transparent provenance positions blockchain land registries as foundational infrastructure for property markets and economic security.
Blockchain-Driven Voting Systems and Electoral Integrity Frameworks
Electoral systems utilizing government blockchain solutions address fundamental challenges in voter authentication, ballot secrecy, and result verification that undermine public confidence in democratic processes. Traditional voting methods face tradeoffs between verifiability and secrecy, with paper ballots providing tangible verification but enabling vote buying, while electronic systems offer convenience but raise manipulation concerns. Blockchain voting architectures employ cryptographic techniques enabling voters to verify their ballot was correctly recorded and counted without revealing vote choices to others. Zero-knowledge proofs allow election authorities to tally results while maintaining individual ballot privacy. Immutable records prevent retroactive ballot manipulation while transparent counting processes enable independent verification by candidates, parties, and civil society organizations. This combination addresses core electoral integrity requirements: ensuring eligible voters cast one ballot each, maintaining ballot secrecy, enabling result verification, and preventing post-election tampering.
Implementation experiences from Switzerland, Estonia, and several US jurisdictions reveal both promise and persistent challenges requiring careful management. Switzerland’s blockchain voting pilots in local referenda demonstrate technical feasibility while highlighting usability challenges for non-technical voters. Estonia’s internet voting system, while not pure blockchain, incorporates distributed architecture principles serving as a model for digital democracy. Critical concerns include ensuring accessibility for citizens lacking internet access or digital literacy, preventing coercion in uncontrolled voting environments outside polling stations, and maintaining public trust in cryptographic verification mechanisms most citizens cannot directly validate. Security requirements exceed typical Government blockchain solutions systems given election outcomes’ political significance and adversary sophistication. Despite challenges, blockchain voting’s potential to increase participation through convenient remote voting while enhancing transparency positions it as important infrastructure for future democratic governance, particularly for overseas voters and supplemental participation mechanisms beyond traditional election day voting.
Supply Chain Traceability for Defense and Public Infrastructure Projects
Supply chain traceability applications for Government blockchain solutions procurement leverage blockchain to verify material authenticity, prevent counterfeiting, and maintain complete audit trails from raw material sourcing through final installation. Defense procurement particularly benefits given security implications of counterfeit components in weapons systems and critical infrastructure. Blockchain-based supply chain platforms record every custody transfer, quality inspection, and origin certification in immutable ledgers, enabling procurement officers to verify supplier claims and detect anomalies indicating counterfeit infiltration. Smart contracts can automatically verify supplier certifications and quality documentation before accepting deliveries, reducing manual verification costs while improving compliance. This transparency extends to tracking materials in public infrastructure projects, ensuring concrete strength certifications, steel origin documentation, and subcontractor licensing verification throughout construction lifecycles.
Government implementations in USA, UK, and Canada demonstrate blockchain supply chain’s capacity to enhance procurement security while supporting domestic sourcing preferences and conflict mineral regulations. The US Department of Defense explores blockchain for critical component tracking, while Canadian infrastructure projects pilot blockchain for materials verification. Technical architectures integrate IoT sensors generating automated custody records, supplier systems publishing certifications, and Government blockchain solutions inspection databases recording quality verifications. Implementation challenges include onboarding diverse supplier ecosystems with varying technical capabilities, ensuring data accuracy from upstream suppliers, and maintaining system security against sophisticated adversaries seeking supply chain infiltration. The combination of provenance verification, counterfeit detection, and regulatory compliance positions blockchain as essential infrastructure for Government blockchain solutions procurement security in an era of global supply chain complexity and geopolitical uncertainty.
Government Blockchain Solutions Use Case Comparison
| Application Domain | Primary Benefits | Implementation Complexity | Maturity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Identity | Privacy protection, fraud reduction, service access | High – requires cross-agency coordination | Mature with production deployments |
| Land Registry | Fraud prevention, transaction speed, transparency | Medium – focused domain with clear use case | Advanced with multiple national implementations |
| Procurement | Cost reduction, transparency, compliance automation | High – complex workflows and integrations | Emerging with pilot projects |
| Voting Systems | Integrity assurance, accessibility, verifiability | Very High – security and trust requirements | Experimental with limited trials |
| Supply Chain | Counterfeit prevention, compliance, traceability | Medium – requires supplier ecosystem participation | Developing with defense sector focus |
Regulatory Compliance and Audit Automation via Government Blockchain Solutions
Regulatory compliance automation represents a high-value application of government blockchain solutions, transforming manual audit processes into continuous automated monitoring reducing costs while improving compliance effectiveness. Traditional compliance regimes require periodic audits consuming substantial resources while providing only point-in-time assurance between audit intervals. Blockchain-based compliance systems embed regulatory rules into smart contracts that continuously monitor transactions, automatically flagging non-compliant activities and preventing prohibited actions before execution. Immutable audit trails provide regulators with complete transaction histories enabling efficient investigation when anomalies arise. This architectural shift from retrospective audit to real-time compliance reduces regulatory burden on compliant organizations while improving detection of violations requiring enforcement action.
Implementation examples span financial regulation, environmental compliance, and professional licensing across jurisdictions in North America, Europe, and Middle East. Financial regulators explore blockchain for anti-money laundering monitoring, automatically analyzing transaction patterns against suspicious activity criteria. Environmental agencies pilot blockchain for emissions tracking, recording pollution data from certified sensors in tamper-proof ledgers. Professional licensing boards use blockchain for credential verification, enabling instant license status checks while preventing practice by unlicensed individuals. Technical architectures integrate regulatory business rules engines with blockchain platforms, balancing automated enforcement against flexibility for legitimate edge cases requiring human judgment. The combination of continuous monitoring, automated enforcement, and complete audit trails positions blockchain as transformative infrastructure for regulatory modernization in an era of increasing compliance complexity across Government blockchain solutions jurisdictions.
Blockchain Applications in Social Welfare and Subsidy Distribution
Social welfare programs utilizing government blockchain solutions address persistent challenges in benefit distribution including fraud, administrative overhead, and delayed payments to vulnerable populations. Traditional welfare systems suffer from identity fraud where ineligible recipients claim benefits, duplicate enrollments across programs, and complex verification processes delaying assistance to legitimate beneficiaries. Blockchain-based welfare platforms link benefits to verified digital identities, preventing duplicate claims while enabling instant eligibility verification across programs. Smart contracts can automatically disburse benefits upon eligibility confirmation, eliminating manual processing delays and reducing administrative costs. Transparent audit trails enable fraud detection while protecting recipient privacy through appropriate access controls. This combination improves service delivery to vulnerable populations while reducing program costs and fraud losses.
Pioneering implementations in developing nations demonstrate blockchain welfare’s capacity to transform social protection systems. India’s Aadhaar biometric identity system, while not pure blockchain, demonstrates large-scale digital identity infrastructure enabling subsidy delivery to hundreds of millions. Several Latin American nations pilot blockchain for conditional cash transfer programs, automatically verifying school attendance or health checkups before releasing payments. Technical architectures typically combine blockchain for payment authorization and audit with traditional banking infrastructure for actual fund disbursement, balancing innovation against financial inclusion requirements for populations lacking smartphone access. Implementation challenges include ensuring accessibility for digitally excluded populations, protecting privacy of sensitive welfare data, and maintaining system reliability given vulnerable beneficiaries’ dependence on timely assistance. Despite challenges, blockchain welfare’s potential to reduce fraud while accelerating assistance positions it as critical infrastructure for social protection system modernization globally.
Enhancing Tax Collection and Fraud Detection Using Blockchain Analytics
Tax administration represents a high-impact domain for government blockchain solutions given revenue significance, fraud vulnerability, and compliance cost burdens on taxpayers and Government blockchain solutions alike. Traditional tax systems rely on self-reporting with periodic audits creating opportunities for evasion while imposing compliance costs on honest taxpayers maintaining records and filing returns. Blockchain-based tax platforms can automatically capture transaction data from point-of-sale systems, financial institutions, and business ledgers, creating tamper-proof income and expense records reducing evasion opportunities. Smart contracts can calculate tax liabilities automatically based on recorded transactions, simplifying compliance for taxpayers while ensuring accurate collection. Real-time data availability enables tax authorities to identify anomalies indicating fraud or errors requiring investigation, shifting resources from routine processing to high-value enforcement activities.
Implementation pilots in several jurisdictions demonstrate blockchain tax administration’s potential while revealing significant implementation challenges. Value-added tax systems particularly benefit from blockchain given multi-party transaction chains where blockchain can track tax credits and prevent fraudulent reclaims. Technical challenges include integrating blockchain with diverse business accounting systems, ensuring data accuracy from source systems, and protecting taxpayer privacy while providing authorities necessary visibility. Legal frameworks require updating to recognize blockchain records as valid documentation for tax purposes and establish liability for incorrect automated calculations. Despite challenges, the combination of reduced evasion, simplified compliance, and automated processing positions blockchain as transformative infrastructure for tax administration in an increasingly digital economy where traditional compliance mechanisms struggle with cross-border commerce and intangible assets.
Interoperable Blockchain Frameworks for Smart City Governance
Smart city initiatives increasingly leverage government blockchain solutions to coordinate diverse urban systems including transportation, utilities, public safety, and environmental monitoring. Traditional smart city architectures suffer from vendor lock-in, data silos preventing cross-system optimization, and centralized control creating single points of failure. Blockchain-based smart city platforms establish interoperable frameworks where autonomous systems can securely share data and coordinate actions without centralized orchestration. IoT devices record sensor data to blockchain, creating tamper-proof records of traffic flows, air quality, energy consumption, and infrastructure conditions. Smart contracts enable automated coordination like adjusting traffic signals based on congestion data or triggering emergency responses when environmental sensors detect hazardous conditions. This distributed architecture enhances resilience, enables data-driven optimization, and supports innovation through open data access.
Smart city blockchain implementations in Dubai, Singapore, and Toronto demonstrate the technology’s potential to transform urban governance while revealing significant coordination challenges. Dubai’s Smart Dubai initiative aims to make the emirate the world’s first blockchain-powered Government blockchain solutions by leveraging distributed ledgers across transportation, health, and business licensing. Singapore’s Smart Nation program employs blockchain for identity, payments, and logistics coordination. Technical challenges include ensuring interoperability across heterogeneous IoT devices and legacy systems, maintaining performance processing millions of sensor readings, and protecting citizen privacy in pervasive sensing environments. Governance complexity increases when coordinating autonomous agencies, private utilities, and technology vendors around shared blockchain infrastructure. Despite challenges, smart city blockchain’s potential to enhance efficiency, resilience, and livability positions it as foundational infrastructure for sustainable urban futures serving growing global populations.
Legal Validity and Policy Challenges in Government Blockchain Solutions Adoption
Legal and policy frameworks governing government blockchain solutions lag technological capabilities, creating uncertainty around record admissibility, smart contract enforceability, and liability allocation when automated systems make errors. Traditional legal systems assume human decision-makers whose judgment and intent can be evaluated, while blockchain smart contracts execute automatically based on code logic potentially inconsistent with legislative intent. Questions arise around whether blockchain records satisfy legal requirements for original documents, how to handle immutability when courts order record corrections, and who bears liability when multi-party blockchain transactions cause harm. Privacy regulations designed for centralized databases may conflict with blockchain’s distributed architecture and transparency characteristics. These legal uncertainties constrain Government blockchain solutions adoption as risk-averse public sector lawyers advise against implementations lacking clear legal foundations.
Progressive jurisdictions in USA, UK, UAE, and Canada address these challenges through legislative reforms establishing blockchain record legal status and clarifying smart contract treatment under existing contract law. Vermont and Arizona pioneered blockchain-specific legislation, while UK Government blockchain solutions explores regulatory sandboxes allowing controlled blockchain experimentation. International coordination through organizations like the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law develops model laws facilitating cross-border blockchain interoperability. Policy challenges extend beyond legal frameworks to include digital divide concerns where blockchain adoption could exclude populations lacking internet access, workforce displacement as automation reduces administrative employment, and geopolitical considerations around foreign technology dependence. Successful government blockchain adoption requires balancing innovation benefits against legitimate regulatory concerns through thoughtful policy development engaging diverse stakeholders including technologists, lawyers, civil society, and affected populations.
Cybersecurity Resilience in Government Blockchain Solutions Systems Using Distributed Ledgers
Cybersecurity considerations drive government blockchain adoption as distributed architectures offer resilience advantages over centralized databases vulnerable to single-point attacks. Traditional Government blockchain solutions IT systems present attractive targets for nation-state adversaries and criminal organizations given sensitive data concentration and critical service dependencies. Successful attacks can destroy records, steal identities, or disrupt essential services affecting millions. Blockchain’s distributed nature eliminates single points of failure, with data replicated across multiple nodes ensuring service continuity even if some nodes are compromised. Cryptographic linkage between blocks makes tampering detectable, preventing silent data modification that centralized databases struggle to prevent. Immutability provides forensic evidence enabling post-incident investigation and attribution. These characteristics position blockchain as foundational infrastructure for Government blockchain solutions cybersecurity strategies addressing increasingly sophisticated threats.
Implementation requires careful security architecture balancing blockchain’s inherent advantages against new attack vectors introduced by distributed systems. Consensus mechanisms must resist byzantine attacks where compromised nodes behave maliciously. Smart contracts require rigorous security auditing preventing exploitation through code vulnerabilities. Key management becomes critical as cryptographic keys provide absolute authority without password recovery mechanisms familiar from centralized systems. Network-level attacks targeting node availability or partitioning blockchain networks require mitigation through redundant connectivity and monitoring. Security benefits increase with decentralization, creating tension with permissioned government blockchains maintaining some centralization for governance and compliance. Successful government blockchain security requires defense-in-depth approaches combining blockchain’s inherent advantages with traditional security controls including access management, encryption, monitoring, and incident response capabilities addressing the complete threat landscape facing critical Government blockchain solutions infrastructure.
Authoritative Government Blockchain Solutions Implementation Standards
Standard 1: Conduct comprehensive use case analysis before blockchain implementation ensuring technology appropriateness versus alternative solutions.
Standard 2: Establish clear governance frameworks defining decision rights, dispute resolution, and evolution processes for multi-agency blockchain networks.
Standard 3: Implement privacy-by-design principles protecting personally identifiable information while leveraging blockchain transparency for accountability.
Standard 4: Ensure legal compliance through regulatory review addressing record admissibility, smart contract enforceability, and liability frameworks.
Standard 5: Deploy comprehensive security controls including access management, encryption, monitoring, and incident response protecting blockchain infrastructure.
Standard 6: Maintain accessibility ensuring blockchain solutions do not exclude populations lacking digital literacy or internet connectivity.
Standard 7: Plan for scalability designing architectures supporting nationwide services processing millions of daily transactions with acceptable performance.
Standard 8: Monitor outcomes measuring efficiency gains, cost savings, fraud reduction, and citizen satisfaction validating blockchain investment returns.
Public-Private Blockchain Collaboration Models for National Platforms
Public-private collaboration models prove essential for government blockchain solutions given the technical expertise, infrastructure investment, and innovation velocity private sector brings to partnerships with public sector governance and service delivery missions. Government blockchain solutions agencies typically lack in-house blockchain expertise and struggle with procurement processes designed for established technologies rather than emerging platforms. Private technology companies provide platforms, consulting, and managed services enabling Government blockchain solutions to leverage blockchain without building capabilities from scratch. Collaboration models range from outsourced platform operation where governments use private blockchain-as-a-service, to public-private consortia governing shared networks, to competitive marketplaces where multiple vendors provide interoperable services on government-defined standards. Successful models balance private sector efficiency and innovation against public sector accountability and citizen protection requirements.
Implementation experiences reveal critical success factors including clear contractual frameworks establishing performance requirements and liability allocation, transparent procurement preventing favoritism, and exit strategies avoiding vendor lock-in threatening long-term sustainability. UK Government Digital Service’s approach to blockchain procurement emphasizes open standards and interoperability preventing dependence on specific vendors. Canadian provinces explore consortium models where Government blockchain solutions and private partners jointly govern blockchain infrastructure. Challenges include protecting sensitive Government blockchain solutions data while leveraging cloud infrastructure, ensuring vendor stability for critical long-term platforms, and managing intellectual property when government-funded innovation generates commercial opportunities. The evolution toward mature public-private collaboration models will determine whether government blockchain solutions achieve their transformative potential or remain niche pilots failing to scale across public sector enterprises serving citizens globally.
Scalability and Performance Constraints in Government Blockchain Solutions
Scalability constraints represent fundamental challenges for government blockchain solutions serving nationwide populations with millions of daily transactions across diverse services. Early blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum process only single-digit transactions per second, inadequate for Government blockchain solutions applications requiring thousands of transactions per second during peak periods. Permissioned government blockchains achieve higher throughput through limiting validator sets and optimizing consensus mechanisms, but still face scaling challenges as transaction volumes grow. Storage requirements accumulate as blockchain state expands with every transaction, creating operational challenges maintaining nodes with terabytes of historical data. Network bandwidth constraints limit propagation speed particularly in jurisdictions with limited internet infrastructure. These technical limitations force difficult tradeoffs between decentralization providing resilience and centralization enabling performance.
Scaling solutions under exploration include layer-2 architectures processing transactions off-chain while anchoring summaries to primary blockchain, sharding distributing transaction processing across parallel chains, and hybrid approaches combining blockchain for critical verification with traditional databases for high-volume operational data. Performance optimization techniques include transaction batching, state pruning removing old data while maintaining verification capabilities, and specialized consensus mechanisms optimized for permissioned Government blockchain solutions contexts. Implementation experiences suggest starting with focused use cases having manageable transaction volumes, gradually expanding as scaling solutions mature and operational experience accumulates. The ongoing evolution of blockchain scalability technologies will determine whether government blockchain solutions can serve as foundational infrastructure for digital government transformation or remain specialized tools for specific high-value applications requiring immutability characteristics despite performance constraints.
Government Blockchain Slutions Technology Selection Criteria
| Selection Criteria | Key Considerations | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Permission Model | Public transparency vs controlled access | Permissioned for most government applications |
| Consensus Mechanism | Transaction throughput and energy efficiency | BFT-based for performance and sustainability |
| Smart Contract Support | Automation requirements and complexity | Turing-complete for complex workflows |
| Privacy Features | PII protection and selective disclosure | Zero-knowledge proofs and private channels |
| Interoperability | Cross-agency and international integration | Standards-based APIs and data formats |
| Vendor Ecosystem | Support availability and lock-in risk | Open source with commercial support options |
Future Roadmap for Blockchain Integration Across Government Blockchain Solutions
The future trajectory of government blockchain solutions points toward comprehensive digital transformation where distributed ledgers become foundational infrastructure underlying diverse public services. Current implementations focus on specific high-value applications like identity and land registries, but the vision encompasses integrated blockchain ecosystems where data flows seamlessly across agencies and services without redundant collection or reconciliation. Interoperability standards will enable cross-border service delivery where citizens can access government services regardless of physical location, using verified credentials from home jurisdictions. Artificial intelligence integration will enhance blockchain systems through automated anomaly detection, predictive analytics optimizing resource allocation, and intelligent agents executing complex multi-party transactions on citizen behalf. These technological advances will combine with evolving governance models balancing transparency against privacy, and automation against human oversight.
Realization of this vision requires sustained investment in blockchain infrastructure, workforce training building public sector blockchain expertise, and regulatory frameworks providing legal certainty enabling innovation. International coordination through organizations fostering standards adoption and best practice sharing will accelerate progress while avoiding fragmentation into incompatible national systems. Citizen engagement remains critical, ensuring blockchain implementations address real service delivery challenges rather than pursuing technology for its own sake. The transition from pilot projects to production deployments serving millions marks the maturation phase where government blockchain solutions demonstrate sustainable value justifying ongoing investment. Success metrics will ultimately measure not technical sophistication but tangible improvements in service quality, cost efficiency, transparency, and citizen trust that blockchain enables across government operations serving populations in USA, UK, UAE, Canada, and globally.
Transform Your Government Services with Blockchain
Partner with experienced blockchain specialists to design and implement secure, scalable solutions for digital government transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Government blockchain solutions refer to distributed ledger technology implementations designed specifically for public sector applications including identity management, records keeping, procurement, and service delivery. These systems provide tamper-proof transaction records, enhanced transparency, and reduced administrative costs compared to traditional government databases. Importance stems from blockchain’s ability to restore public trust through verifiable audit trails, eliminate redundant data entry across agencies, and prevent fraud in subsidy distribution and voting systems. Governments worldwide recognize blockchain as foundational infrastructure for digital transformation initiatives addressing citizen expectations for efficient, transparent, and secure public services in the digital age.
Government blockchain solutions prioritize different objectives than private implementations, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and regulatory compliance over speed and cost efficiency. Public sector blockchains typically employ permissioned architectures where known entities operate nodes, balancing decentralization benefits with governance requirements and legal accountability. Privacy protections must accommodate public records laws and freedom of information requests while protecting personally identifiable information. Government solutions require extensive stakeholder coordination across agencies, longer procurement cycles, and higher security standards given sensitive data handled. Additionally, government blockchains must ensure accessibility for all citizens regardless of technical sophistication, requiring user-friendly interfaces and multi-channel service delivery.
Identity management, land registries, and procurement systems demonstrate highest blockchain value given their requirements for tamper-proof records and multi-party verification. Digital identity solutions reduce fraud in benefit distribution while enabling seamless authentication across government services. Land title systems prevent property disputes and corruption by maintaining immutable ownership chains. Procurement platforms using smart contracts ensure transparent bidding, automated compliance checking, and timely payments to vendors. Other high-impact applications include voting systems ensuring electoral integrity, supply chain tracking for defense contracts, tax collection with automated audit trails, and cross-border document verification for customs and immigration. Benefits concentrate in processes involving multiple stakeholders, high fraud risk, or significant public trust requirements.
Technical challenges include integrating blockchain systems with legacy databases, ensuring scalability for nationwide services processing millions of transactions, and maintaining performance during peak usage. Regulatory obstacles arise from unclear legal frameworks around blockchain records admissibility, smart contract enforceability, and cross-border data flows. Organizational barriers include resistance from employees fearing job displacement, lack of blockchain expertise in government IT departments, and coordination complexity across autonomous agencies. Budget constraints limit pilot project funding and long-term maintenance commitments. Additionally, citizen adoption requires overcoming digital literacy gaps and establishing trust in unfamiliar technology, particularly among vulnerable populations skeptical of government digitization initiatives potentially excluding those lacking internet access.
Security measures include permissioned blockchain architectures restricting node operation to vetted government agencies or contractors, encryption of sensitive personal data before blockchain storage, and multi-signature requirements for critical transactions preventing unilateral actions. Privacy techniques employ zero-knowledge proofs allowing verification without revealing underlying data, selective disclosure enabling citizens to share only necessary information, and off-chain storage of detailed records with blockchain containing only cryptographic hashes. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and incident response planning address emerging threats. Compliance frameworks ensure alignment with data protection regulations like GDPR while maintaining blockchain’s transparency benefits. Access controls implement role-based permissions determining which government employees can view specific data types based on legitimate operational needs.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







