Key Takeaways
- Over 420 million people globally owned cryptocurrencies by 2025, with exchanges serving as the essential infrastructure making crypto trading accessible, fast, and secure for mainstream adoption.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges operate in two main models: Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) like Binance and Coinbase that act as trusted intermediaries, and Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap that use smart contracts for peer-to-peer trading without middlemen.
- CEXs use order books and matching engines to pair buy/sell orders instantly, with platforms like Binance handling over $65 billion in daily trading volume, demonstrating massive scale and user trust in regulated platforms.
- DEXs replace traditional order books with liquidity pools and Automated Market Makers (AMMs), using mathematical formulas like Uniswap’s (x*y = k) to determine prices based on supply and demand dynamics.
- Exchange security relies on multi-layered protection including cold storage (98% of assets offline), hot wallets for active trading, two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, SSL certificates, and regular security audits.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges generate revenue through multiple streams: trading fees (0.1%-0.5% per trade), withdrawal fees, listing fees, margin/futures trading interest, and staking programs, with Coinbase earning over $3.1 billion in transaction revenue in 2024.
- Regulatory frameworks are tightening globally: India imposes 1% TDS and 30% tax on crypto gains, the U.S. SEC classifies certain tokens as securities, and EU’s MiCA regulation (2024) introduced comprehensive compliance standards.
- Following major failures like Mt. Gox (2014) and FTX (2022), exchanges now undergo Proof-of-Reserves (PoR) audits using blockchain data to prove they hold customer assets on a 1:1 basis, enhancing transparency and trust.
- The future of exchanges includes cross-chain swaps via bridges, AI-driven risk monitoring for fraud detection, regulated hybrid exchanges (HEXs) combining centralized liquidity with decentralized custody, and Web3 integration with NFTs and DeFi protocols.
- Global crypto trading volume is projected to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2030 (PwC forecast), positioning exchanges as the heartbeat of crypto adoption and the core engine driving digital finance innovation.
Think of buying Bitcoin as easily as you buy groceries online. That’s exactly what cryptocurrency exchanges have made possible. According to Statista, over 420 million people globally owned cryptocurrencies by 2025, and this number continues to climb as exchanges make crypto trading accessible, fast, and secure.
But have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you click “Buy Bitcoin”? What systems process your order? Who sets the price? How is your digital asset secured in a decentralized environment? Let’s unravel the inner workings of a cryptocurrency exchange, the backbone of the crypto economy.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Exchange?
A cryptocurrency exchange is a digital platform that enables users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies for other assets, such as fiat currencies (USD, INR, EUR) or digital tokens (BTC, ETH, USDT).
These exchanges act as intermediaries, much like stock exchanges, but instead of company shares, users trade digital currencies powered by blockchain technology.
There are two main types-
- Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) like Binance, Coinbase, and WazirX act as trusted intermediaries.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and PancakeSwap, which use smart contracts to allow peer-to-peer trading without a middleman.
Each type has distinct mechanisms, advantages, and risk levels, which we’ll explore next.
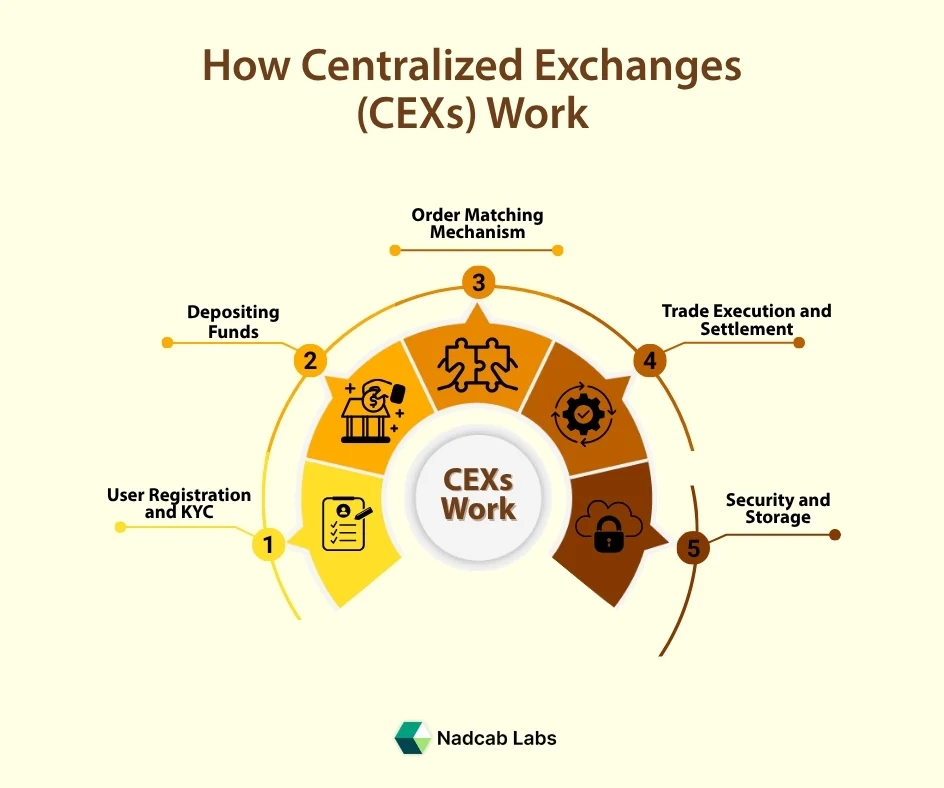
How Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) Work
1- User Registration and KYC
The first step is account creation. CEXs require users to verify their identity through KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures, uploading ID proof, selfies, and sometimes address verification.
This ensures compliance with AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws, making platforms trustworthy and legally compliant.
Fact- Binance handles over $65 billion in daily trading volume (CoinMarketCap, 2025), proving that user trust in regulated centralized exchanges remains strong.
2- Depositing Funds
Once verified, users deposit funds, either-
- Fiat currency via bank transfer or card payment, or
- Cryptocurrency from another wallet.
These funds are then stored in the exchange’s custodial wallets until a trade occurs.
3- Order Matching Mechanism
At the heart of every CEX lies an order book, a real-time digital ledger containing buy and sell orders.
- When a user places a buy order (bid) or sell order (ask), it enters the order book.
- The matching engine pairs orders of equal value and executes the trade instantly.
For example, if Alice wants to buy 1 BTC for $60,000 and Bob wants to sell 1 BTC at the same price, the exchange matches their orders, facilitating the trade.
This process ensures liquidity, the ability to quickly buy or sell assets without affecting their price.
4- Trade Execution and Settlement
Once matched-
- The exchange updates user balances.
- BTC is credited to Alice’s exchange wallet.
- USD (or other fiat) is credited to Bob.
This happens within seconds due to the exchange’s off-chain ledger system, which records trades internally before final blockchain settlement.
5- Security and Storage
CEXs secure assets through:
- Cold wallets (offline storage for large reserves),
- Hot wallets (online storage for active trading), and
- Multi-signature wallets for added protection.
Platforms like Coinbase ensure digital assets through FDIC or private coverage, a vital trust factor.
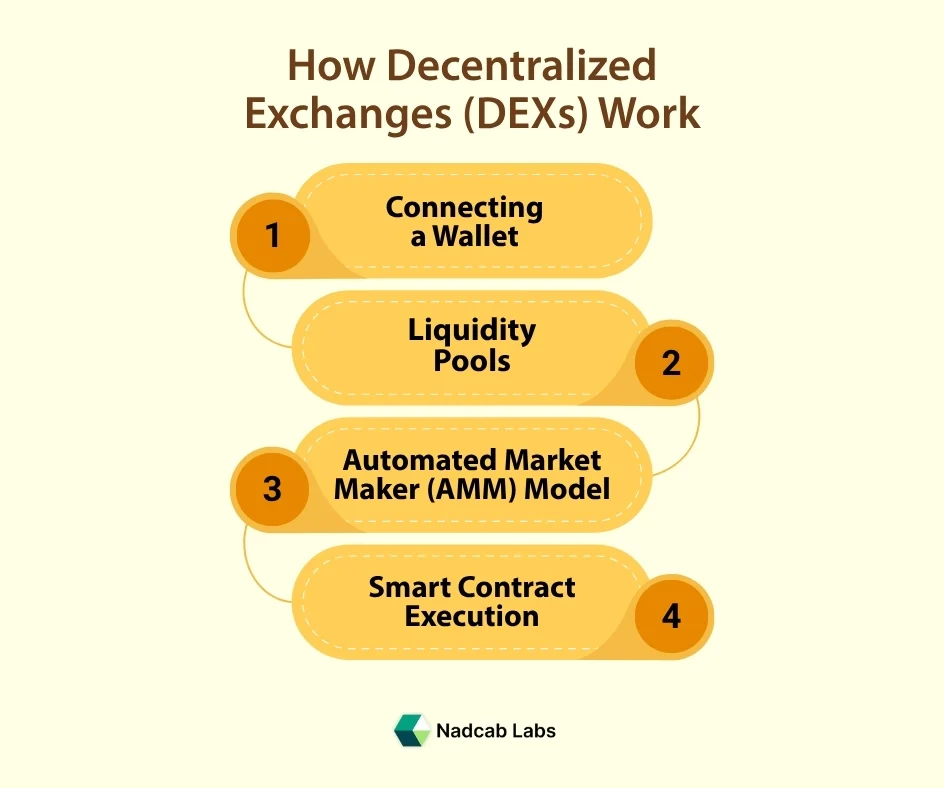
How Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) Work
Unlike CEXs, DEXs operate without intermediaries. They use smart contracts, self-executing blockchain programs, to enable peer-to-peer trading.
1- Connecting a Wallet
Users connect wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet directly to the DEX. No sign-up, no KYC, just blockchain interaction.
2- Liquidity Pools
DEXs replace order books with liquidity pools, reserves of tokens locked by users (liquidity providers).
Example: An ETH/USDT pool allows traders to swap ETH for USDT using the pool’s liquidity.
In return, liquidity providers earn fees and rewards proportionate to their contribution.
3- Automated Market Maker (AMM) Model
AMMs determine asset prices through mathematical formulas rather than through buyers and sellers.
For example, Uniswap’s formula (x*y = k) ensures the product of the two token reserves remains constant.
As more of one asset is purchased, its price increases, mimicking supply and demand.
4- Smart Contract Execution
When a trade is initiated, the smart contract automatically:
- Calculates the exchange rate,
- Executes the swap, and
- Transfers the assets between wallets.
No centralized authority ever touches user funds, offering complete decentralization but also placing responsibility for security on users.
The Technology Behind the Exchange
Cryptocurrency exchanges rely on an integrated ecosystem of technologies:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Blockchain Network | Verifies and records transactions transparently. |
| Smart Contracts | Automate trades and settlements on DEXs. |
| Order Matching Engine | Matches buy/sell orders on CEXs in milliseconds. |
| APIs and Market Data Feeds | Provide real-time pricing and chart updates. |
| Security Protocols | Include encryption, 2FA, SSL, and DDoS protection. |
| Custodial Infrastructure | Manages users’ private keys and digital assets safely. |
Many modern exchanges also integrate AI and machine learning to detect fraudulent transactions and enhance trading efficiency.
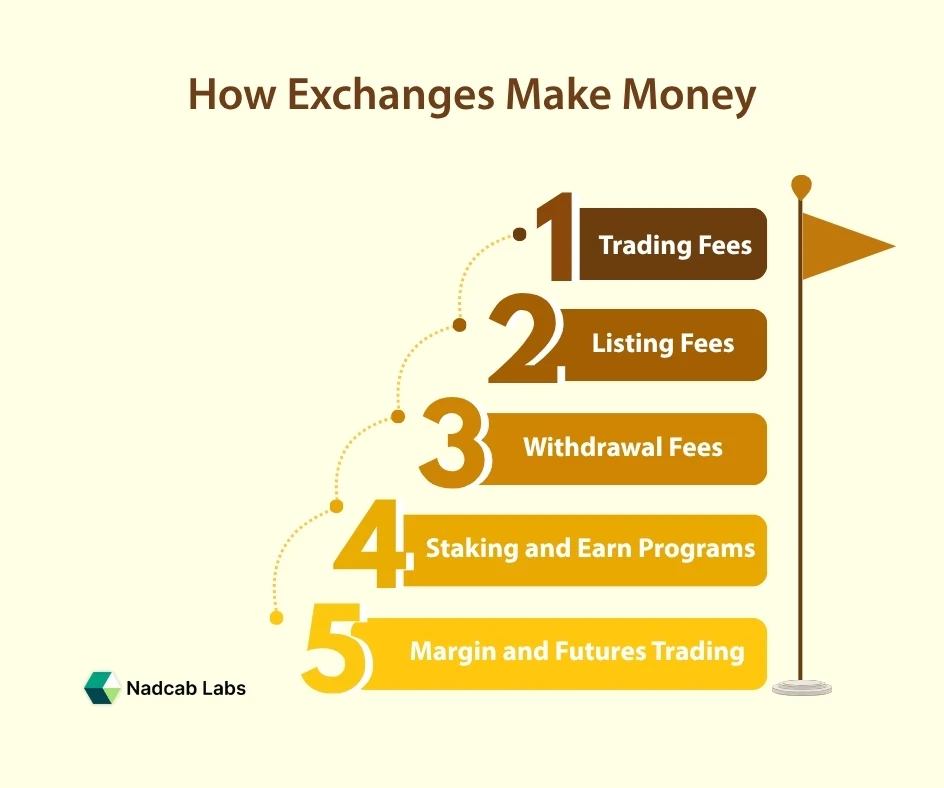
Revenue Model- How Exchanges Make Money
Crypto exchanges are profit-driven entities with multiple income sources:
- Trading Fees- A percentage of every trade (usually 0.1%–0.5%).
- Withdrawal Fees- Charged when moving assets off the exchange.
- Listing Fees- New tokens often pay to be listed.
- Margin and Futures Trading- Earns from interest and liquidation fees.
- Staking and Earn Programs- Platforms like Binance Earn or Kraken Staking share the yield with users while keeping a portion.
For instance, Coinbase earned over $3.1 billion in transaction revenue in 2024, demonstrating the massive scale of crypto trading economics.
Security- The Pillar of Trust
Given the digital nature of crypto assets, security is paramount.
Exchanges adopt multi-layered measures:
- Cold Storage (98% of assets offline)
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Encryption & SSL Certificates
- Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing mic
- Bug Bounty Programs reward ethical hackers.
Still, even top platforms aren’t immune; the Mt. Gox hack (2014) and FTX collapse (2022) highlighted why transparency and regulatory oversight are crucial.
As a result, newer exchanges now undergo Proof-of-Reserves (PoR) audits, where blockchain data proves they hold customer assets 1:1.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
In 2025, governments worldwide will continue tightening regulations:
- India imposes TDS (1%) and a 30% tax on crypto gains.
- The U.S. SEC regulation classifies certain tokens as securities, requiring registration.
- The EU’s MiCA regulation (2024) introduced clear compliance standards for crypto businesses.
Adhering to such frameworks enhances the trustworthiness and longevity of exchanges, aligning with EEAT principles of transparency and user safety.
How a Real Trade Happens
Let’s take an example:
- You open Coinbase and deposit $500.
- You place a buy order for 0.005 BTC at the market price ($100,000/BTC).
- The matching engine finds a seller instantly.
- The trade executes, and your Coinbase wallet now shows 0.005 BTC.
If this were on Uniswap, you’d connect MetaMask, swap USDC → BTC (wrapped form), and the smart contract would complete the trade without an intermediary.
Launch Your Own Crypto Exchange Today
Ready to Build the Next Big Cryptocurrency Exchange? Partner with Nadcab Labs to create a secure, scalable, and high-performance trading platform.
The Future of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
The next phase of evolution includes:
- Cross-Chain Exchanges- Seamless swaps across blockchains via bridges.
- AI-Driven Risk Monitoring- Detects suspicious trades in real time.
- Regulated Hybrid Exchanges (HEXs)- Combining centralized liquidity with decentralized custody.
- Web3 Integration- Direct crypto-to-NFT and DeFi protocol connections.
With global crypto trading volume projected to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2030 (PwC forecast), exchanges will continue driving digital finance innovation.
Read More: Step-by-Step Roadmap to Launch a Crypto Exchange
Closing Insights – The Core Engine of the Crypto Economy
A cryptocurrency exchange isn’t just a crypto trading platform; it’s a sophisticated fusion of blockchain technology, finance, and security architecture.
Whether centralized or decentralized, every exchange performs one core mission: connecting people to the future of money.
Understanding how these exchanges work helps investors trade confidently, assess platform credibility, and embrace the decentralized financial revolution responsibly.
As the digital economy grows, exchanges remain the heartbeat of crypto adoption, empowering millions to participate in the blockchain era.
Frequently Asked Questions
A cryptocurrency exchange is a digital platform where users buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies using order books (CEXs) or smart contracts and liquidity pools (DEXs).
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) act as intermediaries with KYC, custodial wallets, and order books, while decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable peer-to-peer trading using smart contracts without intermediaries.
Centralized exchanges use an order matching engine that pairs buy and sell orders at the same price from the order book, executing trades instantly with high liquidity.
Decentralized exchanges use Automated Market Makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools. Prices are calculated using formulas like x × y = k, based on supply and demand within the pool.
Yes, most reputable cryptocurrency exchanges use multi-layer security such as cold storage, hot wallets, 2FA, encryption, and regular audits, though users should still follow best security practices.
Proof-of-Reserves is a transparency method where exchanges verify on-chain that they hold customer assets 1:1, increasing trust after past exchange failures.
Crypto exchanges earn revenue through trading fees, withdrawal fees, token listing fees, margin and futures trading, staking programs, and interest on lending services.
Most centralized exchanges require KYC to comply with AML regulations, while decentralized exchanges usually do not require KYC and operate directly via connected wallets.
Exchanges store funds in custodial wallets, keeping most assets in offline cold storage and smaller amounts in hot wallets to support daily trading activity.
The future includes cross-chain trading, AI-based fraud detection, hybrid exchanges combining CEX liquidity with DEX custody, and deeper integration with Web3, NFTs, and DeFi protocols.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







