Key Takeaways
- ✦Concentrated liquidity in DeFi allows liquidity providers to allocate funds within specific price ranges rather than spreading them across all possible prices.
- ✦This approach dramatically improves capital efficiency, meaning your funds work harder and earn more fees with less idle capital sitting unused.
- ✦Uniswap V3 was the first major protocol to introduce concentrated liquidity, setting a new industry standard for automated market makers.
- ✦Liquidity providers can customize their price ranges based on their market outlook, making it a more active and strategic form of earning.
- ✦Narrower price ranges generate higher trading fee returns but also carry more risk if the token price moves outside that range.
- ✦Concentrated liquidity reduces slippage for traders, making DeFi exchanges more competitive with centralized exchanges in terms of pricing.
- ✦Impermanent loss, a key risk in DeFi, behaves differently under concentrated liquidity and requires careful price range management.
- ✦Businesses and blockchain startups are integrating concentrated liquidity AMMs into their DeFi platforms to offer better user experiences and higher returns.
- ✦Range based liquidity positions can be represented as NFTs, making each position uniquely trackable and tradable on the blockchain.
- ✦Blockchain solution providers like Nadcab Labs help startups and enterprises build and implement DeFi protocols that leverage concentrated liquidity for real world financial products.
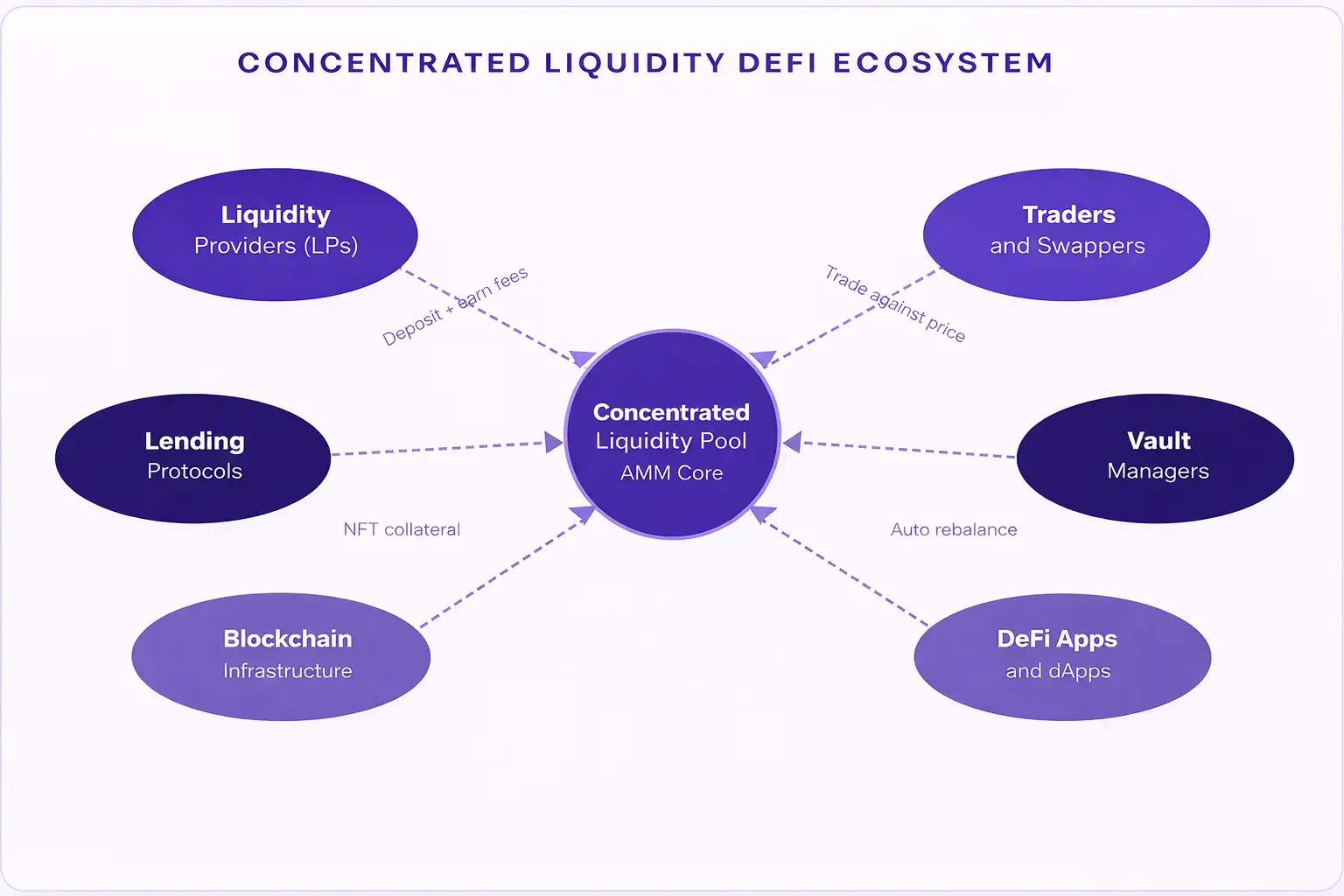
Concentrated liquidity in DeFi is one of the most powerful concepts transforming how people earn from their crypto assets today. If you have ever heard terms like liquidity pools, AMMs, or yield farming and felt confused, you are in the right place. This guide breaks it all down in plain language so that any beginner, investor, or curious learner can understand exactly what concentrated liquidity means, why it matters, and how it is quietly reshaping decentralized finance from the ground up.
What Is Concentrated Liquidity in DeFi?
To understand concentrated liquidity, it helps to first understand how traditional liquidity works in decentralized finance. In the early days of DeFi, when you deposited funds into a liquidity pool, those funds were spread uniformly across every possible price point from zero to infinity. This model is called the constant product AMM, made popular by Uniswap V2 and similar protocols.
While that model worked, it had a significant flaw: the vast majority of liquidity sat idle at price points that rarely or never got traded. Only a tiny fraction of the capital was actually doing useful work at any given moment. The result was low efficiency and lower earnings for liquidity providers.
Concentrated liquidity changes this entirely. Instead of spreading your funds everywhere, you choose a specific price range where you believe most trading will happen, and you place all your capital there. This means your money is active, generating fees, and working at full capacity within that chosen window.
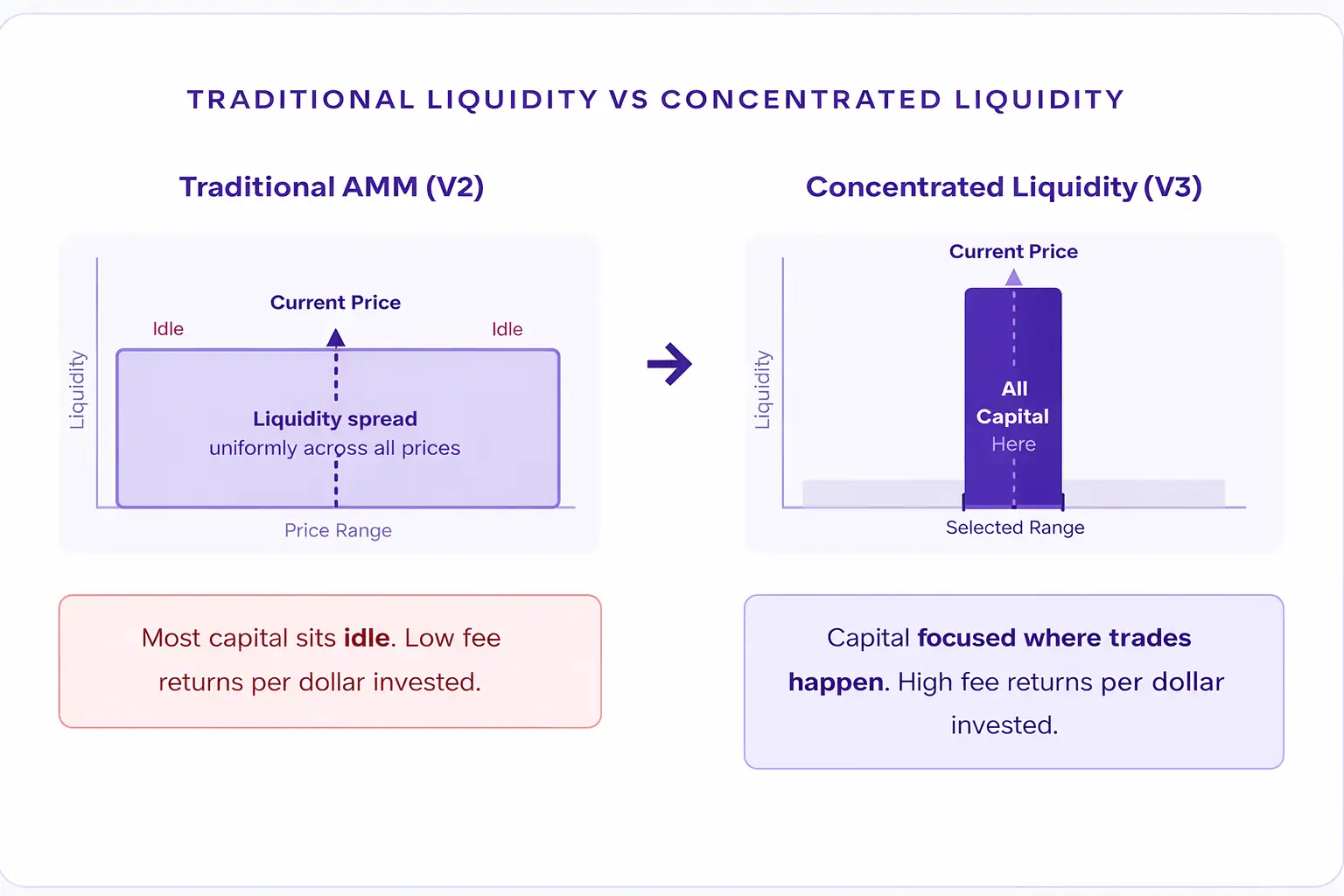
Why Concentrated Liquidity Matters for Modern AMMs
Automated market makers, or AMMs, are the smart contracts that power decentralized trading. They replace traditional order books with algorithms and liquidity pools. Before concentrated liquidity, AMMs struggled with two main problems: low capital efficiency and high slippage for large trades.
Capital efficiency means how much output or return you get from every dollar of capital you put in. In a traditional AMM liquidity pool, a liquidity provider might need to deposit one million dollars to generate the same fee revenue that a concentrated liquidity provider could achieve with just fifty thousand dollars placed in the right price range. That difference is enormous and it fundamentally changes how profitable DeFi can be.
For traders, concentrated liquidity means much tighter spreads and lower slippage, because more capital is concentrated near the current market price. This makes decentralized exchanges feel closer to centralized exchanges in terms of execution quality, which is a big deal for attracting serious traders and institutional volume.
Industry Insight: According to research published on Ethereum.org, DeFi protocols have been racing to improve capital efficiency since 2021, with concentrated liquidity emerging as the defining innovation of next generation AMM design.
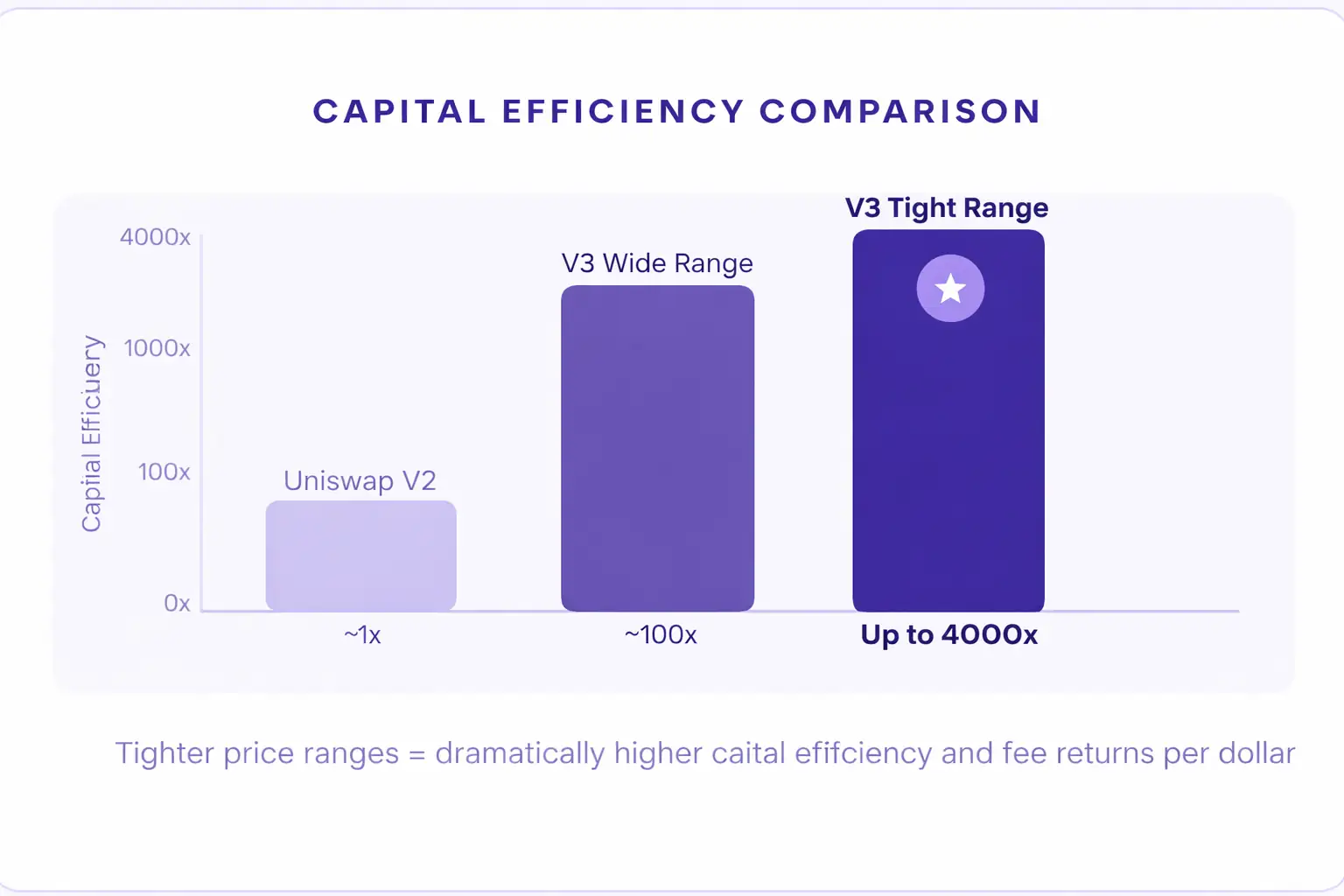
How Concentrated Liquidity Works: Step by Step
Understanding the mechanics of concentrated liquidity does not require a mathematics degree. Here is a straightforward walkthrough of how a liquidity provider interacts with a concentrated liquidity AMM.
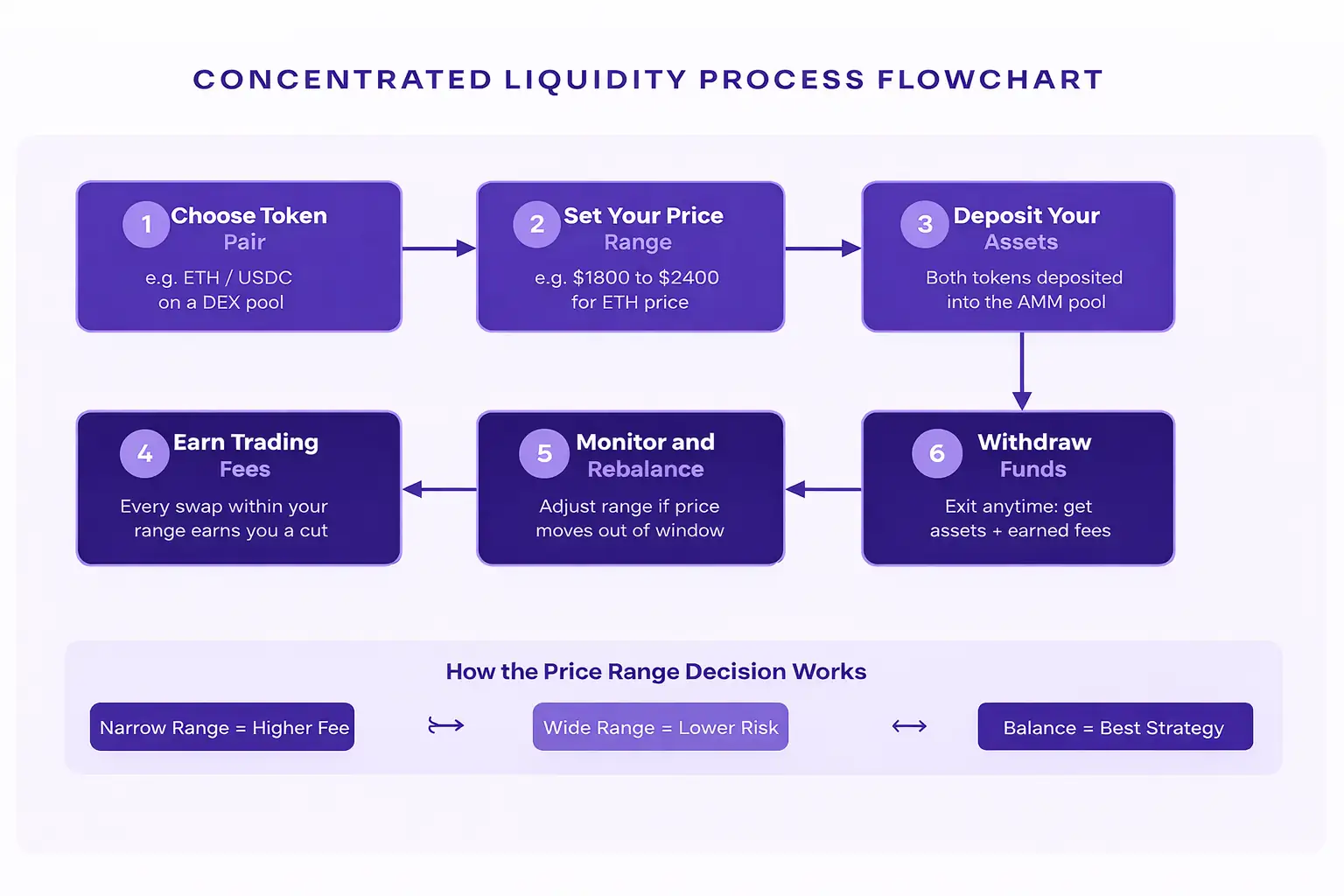
Pick your token pair and define the price window you believe will see the most trading activity.
Deposit both tokens into the pool. Your position immediately begins earning fees every time a trade hits your range.
Monitor market price, rebalance if it exits your range, and exit whenever you want to collect your assets plus fees.
The Role of Uniswap V3 in Popularizing Concentrated Liquidity
When Uniswap V3 launched in May 2021, it was a watershed moment in DeFi history. For the first time, a widely used decentralized exchange gave users the ability to control their liquidity ranges. This was not just a small feature update. It was a complete redesign of how AMMs think about capital and efficiency.
The Uniswap V3 liquidity model introduced several groundbreaking features alongside concentrated liquidity. Each liquidity position became a unique NFT rather than a fungible token, meaning every position was individually trackable because each had its own price range, fee tier, and characteristics. Uniswap V3 also introduced multiple fee tiers of 0.05%, 0.30%, and 1.00%, allowing liquidity providers to match their fee expectations to the volatility of the token pair.
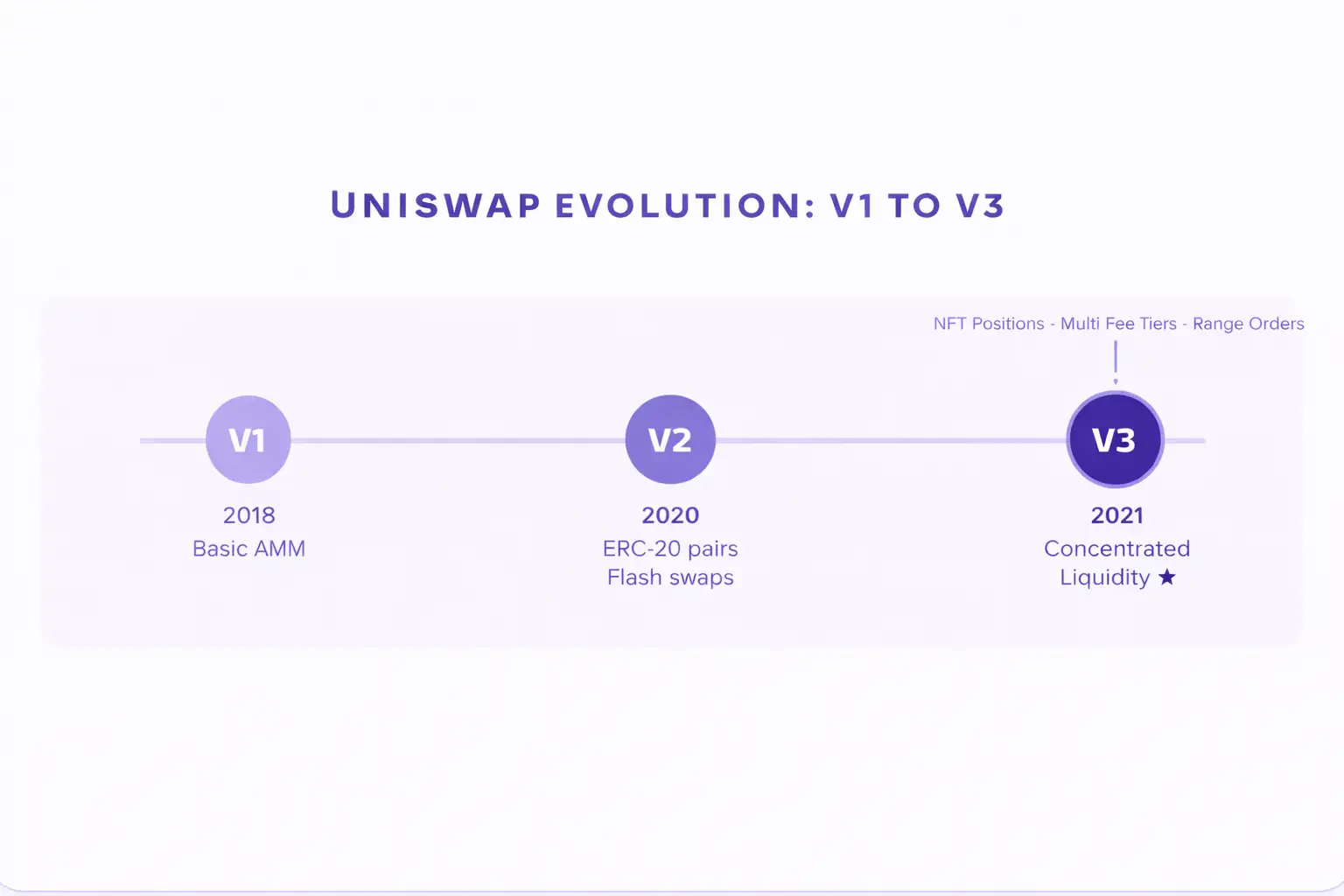
Since then, the concentrated liquidity AMM model has been adopted and adapted by dozens of other protocols across multiple blockchains, including networks like Arbitrum, Polygon, Optimism, and BNB Chain.
Real World Use Cases of Concentrated Liquidity
Concentrated liquidity is not just a concept for advanced DeFi users. It is being integrated into real products and platforms that serve millions of users worldwide. Here are some practical examples of how this technology shows up in the real world.
Protocols that handle USDC to USDT trades use very tight price ranges near 1:1, since these assets almost never deviate. High fees with minimal risk.
Lending protocols use concentrated liquidity to maintain efficient price oracles, ensuring borrowing and lending rates reflect accurate market prices.
Web3 payment processors use concentrated liquidity pools to guarantee tight spreads when converting tokens for merchants, reducing the cost of every transaction.
Vault protocols like Gamma Strategies and Arrakis Finance manage concentrated liquidity positions on behalf of users, rebalancing automatically as prices move.
Certain cross chain bridges use concentrated liquidity pools on both sides to ensure that asset swaps remain efficient and low cost for users moving funds between networks.
Options platforms use concentrated liquidity mechanics to let users effectively implement covered call or put strategies by choosing strategic price ranges.
Business Relevance: Startups building DeFi products today often integrate concentrated liquidity into their core architecture. Teams like those at Nadcab Labs work with founders and enterprises to architect these protocols correctly, ensuring that smart contract logic, fee tier selection, and range management strategies are all aligned with the product goals.
Concentrated Liquidity vs Traditional AMM: A Full Comparison
To truly appreciate the leap that concentrated liquidity represents, it helps to compare it directly against the older model across several key dimensions.
| Feature | Traditional AMM (V2 Model) | Concentrated Liquidity (V3 Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Efficiency | Low. Capital spread across all prices, most of it idle. | Very High. Capital focused where trading actually happens. |
| Fee Earnings | Lower per dollar deposited due to diluted positions. | Significantly higher per dollar, especially in tight ranges. |
| Slippage for Traders | Higher slippage on large trades near the current price. | Lower slippage due to deep liquidity near the current price. |
| Impermanent Loss | Moderate and consistent across price movements. | Can be larger within the range but zero when price exits range. |
| Complexity for LPs | Simple. Deposit and earn. No active management needed. | Active management required. Ranges must be monitored. |
| Position Representation | Fungible LP tokens. All positions of same pool are identical. | Non fungible NFTs. Each position is unique and customizable. |
| Fee Tiers | Single fixed fee across the entire pool. | Multiple fee tiers selectable by the liquidity provider. |
| Best For | Passive investors who prefer set and forget strategies. | Active managers, protocols, and professional market makers. |
Benefits and Advantages of Concentrated Liquidity
The advantages of using a concentrated liquidity model extend well beyond just higher fee earnings. Here is a full picture of why this approach is considered a major advancement in DeFi design.
- ▸Higher Returns on Invested Capital: By deploying capital only where trades occur, providers earn more fees from less money, fundamentally improving the return on every dollar invested.
- ▸Better Prices for Traders: Deep liquidity near the current market price means traders get better execution, lower fees, and tighter spreads, making decentralized exchanges more attractive.
- ▸Personalized Risk Management: Providers can choose wide ranges for safety or tight ranges for maximum yield, tailoring their exposure to match their personal risk tolerance and market view.
- ▸Supports Professional Market Making: Institutions and professional traders who previously avoided DeFi because of inefficiency can now participate with strategies similar to those used on centralized exchanges.
- ▸Reduced Protocol Liquidity Requirements: DeFi projects launching new tokens can bootstrap meaningful liquidity with a smaller total value locked, because concentrated capital is so much more effective than spread capital.
- ▸Composability with Other DeFi Protocols: Concentrated liquidity positions represented as NFTs can be used as collateral in lending protocols, staked in vaults, or managed by automated strategies, creating powerful composable financial products.
Risks and Limitations to Understand
Like every financial tool, concentrated liquidity comes with trade offs. Understanding these risks is essential before committing capital to any DeFi strategy.
In a concentrated position, because your capital is focused in a narrower range, the impact of price movement within that range is amplified. If the price moves outside your range, you end up holding a one sided position entirely in one token.
Unlike traditional AMM positions where you can deposit and forget, concentrated liquidity requires ongoing attention. If the market price drifts outside your chosen range, your position stops earning fees entirely.
Creating, adjusting, and closing concentrated liquidity positions on Ethereum mainnet can become expensive during high network activity. Many providers prefer Layer 2 networks where gas costs are a fraction of mainnet.
Choosing the right price range requires market intuition. Ranges that are too narrow might go out of range frequently, while ranges that are too wide reduce capital efficiency. Finding the optimal balance is part skill and part experience.
Industry and Business Relevance of Concentrated Liquidity
Concentrated liquidity is not limited to individual crypto enthusiasts. It has become a foundational technology for entire categories of DeFi businesses and financial products. Protocols offering decentralized options, perpetuals, lending, and structured yield products all depend on efficient price discovery and deep liquidity near market prices.
Startups entering the Web3 space in 2025 and beyond are expected to understand and integrate these mechanics from day one. Investors in blockchain startups increasingly look for teams that know how to design token economics, liquidity strategies, and AMM architecture that take full advantage of concentrated liquidity principles.
Global Finance Context: The World Economic Forum has highlighted DeFi as a major force reshaping global financial infrastructure. Concentrated liquidity is one of the core innovations making DeFi more capital efficient, scalable, and competitive with traditional finance at a global scale.
DeFi Liquidity Strategies: Which Approach Suits You?
Not every investor needs the same strategy. This table helps you match your personal profile to the right liquidity approach.
| Investor Profile | Recommended Strategy | Why It Fits |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Beginner | Traditional AMM or automated vault | Simple to use, no active management, lower risk exposure |
| Passive Crypto Holder | Wide range concentrated liquidity | Better yield than traditional AMM with manageable risk |
| Active DeFi Participant | Tight range concentrated liquidity | Maximum capital efficiency and high fee returns |
| Professional Market Maker | Multiple concentrated positions across fee tiers | Full control over exposure and returns, like traditional market making |
| DeFi Protocol Builder | Custom concentrated liquidity protocol deployment | Tailored fee structures and range logic for specific token pairs |
| Business or Startup | Expert guided DeFi liquidity infrastructure | Blockchain partners like Nadcab Labs design production grade solutions |
Future Outlook and Trends in Concentrated Liquidity
The future of concentrated liquidity is bright and rapidly evolving. Here are the key trends shaping where this technology is heading over the next few years.
Artificial intelligence tools are being developed to automatically predict optimal price ranges and rebalance concentrated liquidity positions in real time, removing the burden from individual investors.
Protocols are emerging that allow a single concentrated liquidity position to serve multiple blockchain networks simultaneously, dramatically increasing the reach and efficiency of deployed capital.
Financial institutions exploring blockchain are building products that leverage concentrated liquidity for tokenized real world assets, including bonds, real estate funds, and commodity backed tokens.
As Layer 2 adoption grows on Ethereum, concentrated liquidity pools on Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, and zkSync are seeing explosive growth with lower gas costs making frequent rebalancing economically viable.
Next generation AMMs are experimenting with fee tiers that adjust dynamically based on market volatility, ensuring liquidity providers are compensated appropriately during turbulent market conditions.
Common Myths About Concentrated Liquidity
As with any emerging technology, concentrated liquidity has attracted its fair share of misunderstandings. Let us clear up the most common ones.
Concentrated liquidity is only for expert traders and not suitable for everyday investors.
While active management requires some knowledge, automated vault protocols make concentrated liquidity accessible to anyone. You can choose a wide price range and let the protocol do the heavy lifting.
Concentrated liquidity always results in more impermanent loss than traditional AMMs.
When the price stays within your range, the higher fees earned can more than offset any impermanent loss. The key is choosing ranges that reflect realistic price behavior for the token pair you are providing liquidity for.
You need a large amount of capital to benefit from concentrated liquidity.
Because concentrated liquidity is so capital efficient, even relatively small positions can generate meaningful returns. On Layer 2 networks where gas costs are low, even modest amounts can participate effectively.
Concentrated liquidity is only available on Uniswap.
The model has been adopted by numerous protocols across many blockchains, including PancakeSwap V3, SushiSwap, Camelot, Trader Joe V2, and many others, each with their own unique variations and improvements.
Your funds are locked in a concentrated liquidity position and cannot be withdrawn.
Concentrated liquidity positions are fully non custodial and can be withdrawn at any time. You retain complete control over your assets throughout the entire process, just like with any other DeFi protocol.
Why Concentrated Liquidity in DeFi Is the Future?
Concentrated liquidity in DeFi represents one of the most significant leaps forward in how decentralized finance thinks about capital, efficiency, and earning potential. What started as a bold innovation in Uniswap V3 has grown into a defining pillar of modern AMM design, adopted across dozens of protocols, blockchains, and financial products that collectively serve millions of users around the world.
For individual investors, concentrated liquidity offers the ability to put your capital to work far more effectively than ever before. For businesses and developers, it opens the door to building DeFi products that can genuinely compete with and even surpass traditional financial infrastructure in terms of efficiency, transparency, and user experience.
The concept is evolving rapidly, with artificial intelligence, cross chain technology, and institutional adoption all pointing toward a future where concentrated liquidity becomes the default standard rather than an advanced option. Understanding it today puts you ahead of the curve in one of the most transformative financial revolutions of our generation.
Whether you are just learning about DeFi for the first time or you are preparing to build your own blockchain product, the principles of concentrated liquidity in DeFi are worth knowing deeply. They sit at the heart of how decentralized finance is becoming smarter, leaner, and more powerful with every passing year.
Frequently Asked Questions
A tick is a discrete price point on the Uniswap V3 price scale. The entire price spectrum is divided into equally spaced ticks, and liquidity providers must set their lower and upper price boundaries at valid tick positions. Think of ticks as the grid lines on a ruler where you can only mark measurements. The spacing between ticks, called tick spacing, varies by fee tier. Pools with a 0.05% fee have finer tick spacing, allowing tighter ranges, while 1% fee pools have wider spacing suited to more volatile assets.
Yes, in certain situations. If you set a price range that is entirely above the current market price, your position will be funded entirely with the base token. If your range is entirely below the current price, you fund it only with the quote token. This is called a single sided position and it behaves similarly to a limit order, converting fully into the opposite token if the price crosses your range. It is a strategic way to enter a position at a target price while earning fees along the way.
Tax treatment of DeFi liquidity positions varies significantly by country and jurisdiction. In many regions, depositing tokens into a liquidity pool may be considered a taxable disposal, earned trading fees may be treated as ordinary income, and impermanent loss may or may not be recognized as a deductible loss depending on local rules. It is strongly recommended to consult a qualified tax professional or crypto tax specialist familiar with the laws in your country before participating in any DeFi liquidity strategy.
There is no protocol-enforced minimum deposit amount. However, the practical minimum is determined by gas fees. On Ethereum mainnet, creating and managing a position can cost anywhere from a few dollars to over a hundred dollars in gas during busy periods, which makes very small positions economically unviable. On Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, or Base, gas fees are dramatically lower, sometimes just a few cents, making it practical to start with as little as fifty to one hundred dollars worth of tokens.
Yes. Because each concentrated liquidity position in Uniswap V3 and similar protocols is represented as an NFT, it lives in your wallet like any other NFT and can be transferred to another wallet address. Some DeFi protocols such as Toros, Arrakis, and certain lending platforms also accept LP NFTs as collateral, allowing you to borrow stablecoins or other assets against the value of your position without having to close it and exit your liquidity strategy.
Fee tier selection depends on how volatile the token pair is. The 0.05% tier is designed for very stable pairs like USDC and USDT where price barely moves, attracting high volume from arbitrageurs and professional traders. The 0.30% tier suits moderately volatile pairs like ETH and a major stablecoin. The 1.00% tier is appropriate for highly volatile or low liquidity pairs where providers need higher compensation for the increased risk of their position going out of range. Always check which fee tier already holds the most liquidity for your pair, as that tier generally attracts the most trading volume.
During a sudden and severe price drop, the market price will rapidly move through your range and potentially exit it entirely. As the price falls through your range, your position automatically converts from a mix of both tokens into entirely the falling token. If the price exits your range on the downside, your position becomes inactive and holds only the declining asset. While this sounds alarming, your position is not liquidated. The funds remain in the pool and you can withdraw them at any time, though you may withdraw less total value than you deposited depending on how far prices moved.
Yes, several dedicated analytics platforms exist for monitoring concentrated liquidity positions. Revert Finance provides detailed real time analytics for Uniswap V3 positions including fee earned, time in range, and return on investment calculations. DefiLlama tracks total value locked across all concentrated liquidity protocols. Dune Analytics has community built dashboards for specific pools and strategies. Additionally, the native interfaces of most AMMs show your earned fees, current price relative to your range, and uncollected rewards at a glance.
These are two separate actions in a concentrated liquidity protocol. Collecting fees means you claim only the trading fees your position has accumulated, while your principal deposit stays active in the pool and continues earning. Removing liquidity means you withdraw your actual deposited tokens and close your position or reduce its size. You can collect fees as often as you like without disturbing your position. Many liquidity providers collect fees periodically and reinvest them, a strategy known as compounding, to increase the size of their active position over time.
Automated vault managers pool deposits from many users into a shared smart contract that acts as a single large concentrated liquidity position. They continuously monitor the market price and use algorithmic rules to decide when to rebalance, meaning when to withdraw from the current range and redeploy into a new range that surrounds the current price. The manager collects fees earned, deducts a small protocol fee typically between 0.5% and 2% annually, automatically compounds the rest back into the position, and issues you a receipt token representing your proportional share. This lets you benefit from concentrated liquidity without needing to manage anything yourself.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







