
Overview of the Supply Chain Industry
The global supply chain industry plays a pivotal role in ensuring products reach consumers with authenticity, safety, and efficiency. From agriculture to pharmaceuticals, the demand for transparency has become a top priority. With rising consumer awareness and regulatory requirements, businesses are increasingly exploring digital solutions such as Smart Contract Provenance to prove authenticity, build trust, and reduce fraud.
Supply chains today span multiple countries, involving countless suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers. This complexity makes it difficult to track the origin of raw materials, verify ethical sourcing practices, and ensure compliance with global standards. Increasing cases of counterfeiting, product recalls, and regulatory scrutiny highlight the urgent need for systems that guarantee end-to-end traceability.
Consumers are no longer satisfied with simply receiving a product they want to know where it was made, how it was handled, and whether it aligns with environmental and ethical standards. Governments, too, are tightening regulations to ensure companies demonstrate accountability throughout their supply networks. This shift has transformed provenance from being a competitive advantage into a business necessity.
Problems in Smart Contract Provenance
Ensuring product provenance is one of the biggest challenges for modern supply chain businesses. Traditional systems often fall short in providing accuracy, speed, and transparency, leading to inefficiencies and risks. Below are the most pressing problems:
Counterfeiting
The infiltration of fake goods into supply chains is a global issue, costing businesses billions each year. Counterfeits not only damage brand reputation but also pose serious safety risks especially in sectors like pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics. Without a reliable system of verification, it becomes difficult to differentiate genuine products from fraudulent ones.
Lack of Transparency
Many supply chains still rely on fragmented and siloed systems. Traditional paper based documentation is vulnerable to manipulation, loss, or errors, leaving gaps in accountability. When records are scattered across multiple parties, visibility becomes limited, and businesses cannot guarantee authenticity to customers or regulators.
Manual Verification
Human driven processes create bottlenecks. Verifying product documents, shipment receipts, and certifications often requires days or weeks. This manual approach slows the flow of goods, increases operational costs, and leaves room for inaccuracies. For time sensitive industries like healthcare or perishable goods, such delays can have severe consequences.
Trust Deficit
Suppliers, logistics providers, and customers often find it hard to fully trust one another. Without a single, tamper proof source of truth, doubts around authenticity remain. This lack of confidence affects long term business relationships and reduces overall efficiency in global trade networks.
Compliance Risks
Global regulations demand strict traceability to ensure consumer safety and fair trade. However, businesses relying on outdated systems struggle to meet these standards. Non compliance can result in heavy fines, trade restrictions, or damaged credibility in international markets.
Data Fragmentation
Supply chains often span multiple countries and involve numerous intermediaries. Each party may use its own system for record keeping, making integration and synchronization extremely difficult. This fragmentation prevents seamless tracking and creates blind spots that counterfeiters can exploit.
High Error Rates
Human error in manual entries, mismatched documentation, and data duplication can create costly mistakes. These errors accumulate over time and compromise the overall integrity of the supply chain’s provenance records.
Limited Consumer Access
Even when businesses attempt to track provenance, consumers rarely get direct access to this data. Shoppers want assurance that products are ethical, sustainable, and authentic. When transparency tools are missing, trust in the brand weakens.
Solving Provenance Challenges Through Smart Contract Provenance Automation
A Smart Contract Provenance offers a transparent and automated way to ensure every product in the supply chain can be trusted. Instead of relying on manual paperwork or third-party intermediaries, the system automatically validates each step, creating a tamper proof record of product history.
Authenticity Tracking
Every item can be given a digital identity, such as a unique QR code or serial number. This identity is logged at each stage from sourcing raw materials to final delivery providing an unbroken chain of authenticity that is easily verified by all stakeholders.
Immutable Records
One of the strongest features is that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This prevents fraudulent changes, ensures accountability, and builds confidence for regulators, partners, and end customers.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
By removing redundant paperwork and reducing dependency on intermediaries, processes become faster and less prone to human error. Automated checks and verifications lower administrative costs, minimize delays, and enable smoother cross border movement of goods.
Compliance and Audit Readiness
Global supply chains must adhere to strict regulatory frameworks. Automated record keeping ensures businesses remain compliant with international standards, while also making audits quicker and more reliable.
End-to-End Visibility
The combined effect of authenticity tracking, immutable data, and automated checks creates complete visibility. This means customers can trace the journey of their purchases with confidence, businesses can strengthen trust, and the entire ecosystem benefits from greater transparency.
Barriers to Adoption
While the benefits of proving provenance through Smart Contract Provenance are clear, many businesses still face practical hurdles that slow down large scale adoption. These challenges are less about the technology itself and more about the readiness of organizations and regulatory ecosystems to adapt.
- High Initial Costs
Integrating blockchain based systems with existing supply chain infrastructure often requires a significant upfront investment. Companies must upgrade software, train staff, and sometimes overhaul legacy systems, which can be costly for small and mid sized firms. - Complex Infrastructure Requirements
Smart contract solutions do not operate in isolation they need to work seamlessly with IoT sensors, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and logistics platforms. Many organizations lack the digital infrastructure to support this kind of integration, creating technical barriers before full adoption is possible. - Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the biggest hurdles is the lack of clear legal frameworks. Different countries treat blockchain based contracts differently, and in some regions, they have limited or no legal recognition. This creates uncertainty for businesses that operate globally and must remain compliant with multiple jurisdictions. - Skills Gap
The supply chain industry still faces a shortage of skilled professionals who understand both blockchain technology and supply chain operations. Without trained experts to manage, monitor, and optimize these systems, adoption becomes challenging for many organizations. - Scalability Challenges
When used across large global supply chains, blockchain networks can face issues with transaction speed, high processing costs, and energy consumption. Ensuring scalability without compromising speed or security remains one of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
Best Practices for Implementing Smart Contract Provenance
For supply chain businesses, simply adopting Smart Contract Provenance is not enough their effectiveness depends on how they are implemented and managed. The following best practices help ensure successful adoption and long term reliability:
- Stakeholder Collaboration
Engaging suppliers, logistics providers, distributors, and regulators from the beginning ensures alignment and trust. When all parties agree on standards and expectations, the transition to automated provenance tracking becomes seamless. - Pilot Programs Before Scaling
Rather than overhauling an entire supply chain at once, businesses should begin with smaller pilot programs focused on high value or high risk product lines. This controlled approach minimizes risks and provides measurable insights before scaling to full operations. - Data Standardization
Using recognized global standards, such as GS1, guarantees that digital product identities remain consistent across geographies and industries. Standardization also reduces errors and improves interoperability between different systems. - Hybrid Integration with IoT
Pairing blockchain-based contracts with Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as temperature sensors, GPS trackers, and RFID tags enhances real time product authentication. This hybrid system strengthens transparency while reducing the chances of fraudulent activity. - Continuous Auditing and Monitoring
Regular audits ensure that contracts remain secure and aligned with evolving regulations. Continuous monitoring also helps detect anomalies early, safeguarding both product integrity and business reputation.
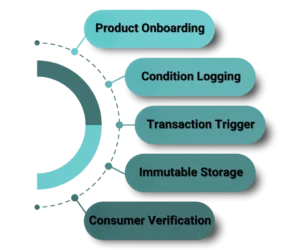
Provenance Process Using Smart Contracts
Implementing Smart Contract Provenance for supply chain provenance involves a series of structured steps that ensure every product’s journey is transparent, verifiable, and tamper-proof. The typical process includes:
- Product Onboarding – Assign a digital identity to each batch.
- Condition Logging – Use IoT sensors to capture details like temperature, storage, and location.
- Transaction Trigger – Smart Contract Provenance verify conditions before moving goods to the next stage.
- Immutable Storage – Records are stored on blockchain, accessible to all authorized parties.
- Consumer Verification – Customers scan QR codes to trace authenticity.
Protecting Product Integrity Through Secure and Compatible Systems
Smart Contract Provenance provide tamper-proof provenance, but maintaining security and ensuring seamless compatibility across systems are critical for supply chain success. Key considerations include:
- Data Encryption
All sensitive shipment details, including supplier information and product specifics, are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access and ensure confidentiality throughout the supply chain. - Cross-Chain Compatibility
Smart Contract Provenance should integrate smoothly with multiple blockchain networks, allowing interoperability between different platforms, partners, and logistics systems. - Access Controls
Role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication prevent unauthorized modifications, ensuring that only trusted parties can interact with the contract. - Resilience Against Hacks
Robust cybersecurity measures protect against tampering, ensuring that transaction data remains secure, accurate, and unaltered. - Data Integrity Checks
Regular verification routines, such as cryptographic proofs, validate that the recorded information is accurate and consistent across the network.
Market Growth and Trends
The global smart contract market within supply chains is experiencing exponential growth.
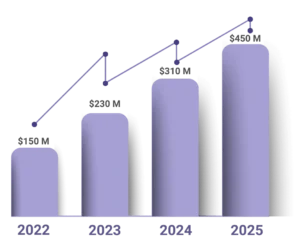
Market Growth Share % of Smart Contract Provenance (2022–2025)
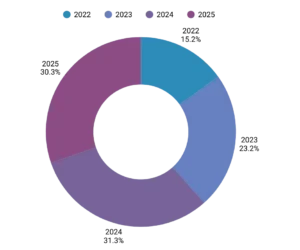
This growth is driven by consumer demand for traceability, regulatory mandates, and corporate sustainability commitments.
Current Applications of Smart Contract Provenance Across Industries
Smart Contract Provenance are used across industries to improve transparency and traceability in supply chains:
- Food & Agriculture (United States) – Track produce from farms to stores, monitoring conditions and ensuring safety.
- Pharmaceuticals (Global) – Record medicine movement to prevent counterfeits and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Diamonds & Luxury Goods (Worldwide) – Trace diamonds and high-value items for ethical sourcing and verification.
- Electronics (Asia) – Track components from manufacturers to retailers, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Automotive Parts (Europe) – Record the journey of critical auto parts to verify origin and improve quality control.
These examples show how Smart Contract Provenance provide immutable records that support verification, accountability, and transparency across multiple sectors.
Recommendations for Businesses
- Start Small – Pilot programs with high-risk products like food or medicine ensure quicker ROI.
- Invest in Training – Upskill employees in blockchain and digital traceability systems.
- Engage Regulators – Collaborate with policymakers to ensure compliance.
- Leverage IoT – Integrating sensors maximizes data accuracy and security.
- Focus on Consumer Engagement – Provide easy verification methods like QR codes for end users.
The Path Forward for Transparent and Secure Supply Chains
Provenance in supply chains is no longer optional it is a necessity. Smart Contract Provenance offer a reliable way to track products, enhance trust, and eliminate fraud. While adoption barriers exist, industry trends and successful use cases demonstrate their potential. As businesses embrace transparency, smart contracts will become the backbone of global trade, securing both businesses and consumers in an increasingly connected world.
Looking ahead, smart contracts are expected to become a foundational element of supply chain operations worldwide, not just for tracking products but also for enhancing efficiency, security, and collaboration across all stakeholders. In a world increasingly focused on accountability and sustainability, the adoption of Smart Contract Provenance represents a major step toward transparent and resilient supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions
Got questions about smart contracts and provenance in supply chains? Here’s a quick FAQ to help you understand how they build trust, improve authenticity, and ensure transparency across industries.
How do smart contracts improve product provenance?
Smart contracts track goods automatically, create immutable records, prevent fraud, and ensure product authenticity, offering transparency and trust across every supply chain stage without manual errors.
Which industries gain from smart contract provenance?
Pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, electronics, and luxury goods benefit most, as smart contracts help prevent counterfeiting, improve authenticity checks, and provide transparency demanded by consumers and regulators globally.
What trends drive future adoption of provenance solutions?
Increasing consumer awareness, stricter regulations, and integration with IoT and AI technologies will drive adoption, offering greater efficiency, competitive advantage, and enhanced supply chain transparency globally.
Are smart contracts compatible with supply chain systems?
Yes, they integrate seamlessly with ERP software, IoT devices, and global standards, ensuring interoperability and enhancing transparency while maintaining smooth operations without disrupting existing infrastructure.
What barriers limit smart contract adoption in supply chains?
Adoption faces challenges like high costs, lack of expertise, unclear regulations, and scalability concerns, though ongoing innovation and supportive policies are steadily reducing these limitations.
Can smart contracts reduce global supply chain compliance risks?
Absolutely. Automated execution ensures compliance, accurate documentation, reduced errors, and minimized penalties, enabling businesses to meet international regulations with efficiency, transparency, and improved operational trust.







