Key Takeaways
- Smart contracts in USA are revolutionizing digital transformation by automating complex business processes across finance, real estate, and healthcare industries.
- US businesses achieve 40-80% cost reductions through Smart contracts in USA implementation by eliminating intermediaries and reducing administrative processing overhead significantly.
- Multiple US states including Arizona, Wyoming, Nevada, and Tennessee have enacted legislation providing legal recognition for smart contract agreements.
- Cryptographic security and immutable transaction records make Smart contracts in USA significantly more secure than traditional paper-based agreement systems in the USA.
- Real estate transactions in the USA using smart contracts reduce closing times from weeks to hours while ensuring transparent ownership transfer records.
- Supply chain optimization through smart contracts provides end-to-end visibility and automated compliance verification for US manufacturers and distributors.
- Healthcare systems across the United States leverage smart contracts for secure patient data management and automated insurance claims processing.
- Integration of smart contracts with AI, IoT, and Web3 technologies creates new opportunities for automated decision-making in American enterprises.
- Security auditing and professional risk management are essential requirements before deploying smart contracts in production environments across US markets.
- US startups and enterprises both benefit from Smart contracts in USA cost savings, with implementation timelines ranging from 4-16 weeks based on complexity.
What Smart Contracts Mean for Digital Transformation in the USA
The United States stands at the forefront of blockchain innovation, with smart contract technology driving unprecedented digital transformation across every major industry sector. These self-executing programs represent a fundamental shift in how American businesses structure agreements, process transactions, and manage complex operational workflows. From Wall Street financial institutions to Silicon Valley startups, organizations are discovering that Smart contracts in USA deliver automation, security, and transparency that traditional systems simply cannot match.
Our agency has spent over eight years helping enterprises across the USA, UK, UAE, and Canada implement Smart contracts in USA solutions that transform their operations. During this time, we have witnessed the technology mature from experimental applications to mission-critical infrastructure powering billions of dollars in transactions annually. American businesses that embrace smart contracts gain competitive advantages through faster execution, reduced costs, and enhanced trust with their customers and partners.
Digital transformation powered by Smart contracts in USA extends beyond simple automation. These blockchain-based programs enable entirely new business models, including decentralized finance platforms, tokenized real estate investments, and automated supply chain management systems that were impossible with traditional technology infrastructure.
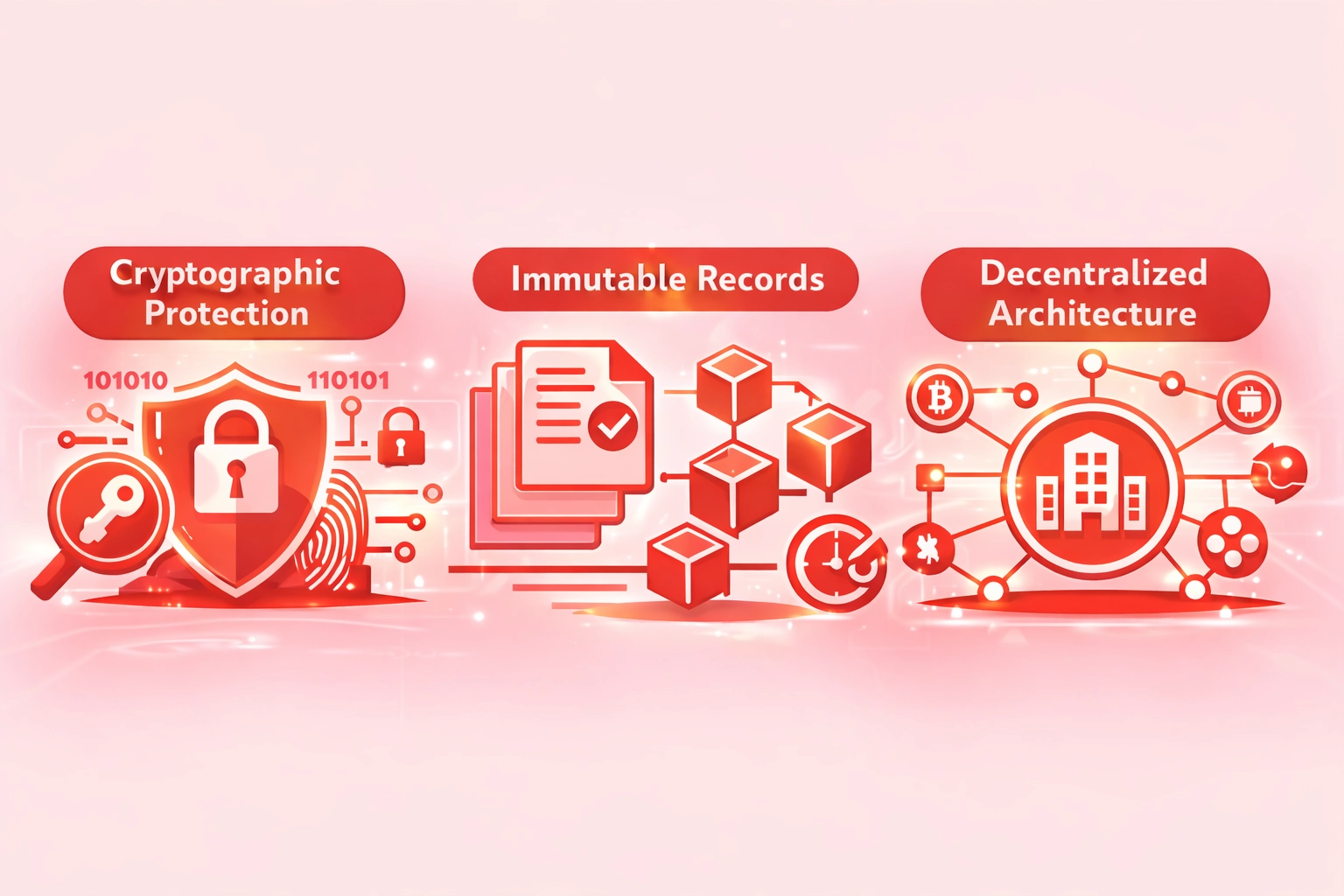
Security Benefits of Smart Contracts in the US Digital Ecosystem
Smart contracts in USA provide multi-layered security that traditional systems cannot match.
Cryptographic Protection
- 256-bit encryption standards
- Digital signature verification
- Tamper-proof transaction records
- Secure key management
Immutable Records
- Permanent transaction history
- No unauthorized modifications
- Complete audit trails
- Regulatory compliance support
Decentralized Architecture
- No single point of failure
- Distributed data storage
- Network consensus validation
- Resilient infrastructure
Transparency Through Smart Contracts in the United States
Transparency represents one of the most significant advantages smart contracts in USA bring to business operations. Every transaction executed through a smart contract creates an immutable record visible to all authorized participants. This visibility eliminates information asymmetry that traditionally advantages certain parties in business relationships. American enterprises using Smart contracts in USA report substantially improved trust with partners, customers, and regulatory bodies.
The public nature of blockchain transactions means that Smart contracts in USA logic itself can be verified by any interested party. Businesses can demonstrate their operational integrity by pointing to verifiable on-chain records. This transparency is particularly valuable in industries facing regulatory scrutiny or public trust challenges. Financial services firms, healthcare organizations, and government contractors increasingly leverage Smart contracts in USA transparency to build stakeholder confidence.
Real-time visibility into contract execution status eliminates the uncertainty that plagues traditional agreement monitoring. Participants can verify performance without relying on counterparty reports or third-party auditors.
Cost Efficiency Achieved With Smart Contracts in the USA
American businesses implementing smart contracts consistently report significant cost reductions across multiple operational categories. The elimination of intermediaries, automated compliance verification, and reduced dispute resolution requirements deliver measurable financial benefits that justify implementation investments within months rather than years.
| Cost Category | Traditional Process | Smart Contract | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediary Fees | 2-5% per transaction | 0.1-0.5% gas fees | 80-95% |
| Processing Time | 3-5 business days | Minutes to hours | 95-99% |
| Legal Review | $5,000-50,000 | One-time audit | 60-80% |
| Dispute Resolution | $10,000-100,000+ | Automated execution | 90-100% |
| Compliance Auditing | $20,000-200,000/year | Automated trails | 70-85% |
Blockchain Technology as the Foundation of Smart Contracts in the US
Smart contracts in USA operate on blockchain networks that provide the underlying infrastructure for secure, decentralized execution. Ethereum remains the dominant platform for smart contract deployment, though alternatives like Polygon, Avalanche, and Solana have gained significant American enterprise adoption. Each platform offers different tradeoffs between transaction speed, cost, and decentralization levels.
The blockchain foundation ensures that smart contract execution cannot be manipulated by any single party. Consensus mechanisms require network-wide agreement before transactions are confirmed, preventing fraud and unauthorized modifications. This distributed validation process is what makes smart contracts trustworthy even between parties who have no prior relationship or reason to trust each other.
American enterprises increasingly deploy on Layer 2 solutions that inherit Ethereum security while providing faster and cheaper transaction processing. These scaling solutions enable smart contract applications that would be economically impractical on mainnet Ethereum alone.
Smart Contracts Compared to Traditional Legal Agreements in the USA
Understanding the differences between smart contracts and traditional legal agreements helps American businesses determine appropriate use cases. While smart contracts excel at automating executable terms, traditional contracts remain necessary for complex arrangements requiring subjective interpretation or human judgment.
| Feature | Smart Contracts | Traditional Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Automatic when conditions met | Manual enforcement required |
| Modification | Immutable once deployed | Amendable by agreement |
| Interpretation | Code-based, deterministic | Subject to legal interpretation |
| Dispute Resolution | Automated or on-chain arbitration | Courts and legal proceedings |
| Cost Structure | Upfront audit, minimal ongoing | Ongoing legal fees |
Impact of Smart Contracts on the US Financial Services Industry
The American financial services industry has emerged as the leading adopter of smart contracts in USA, with applications spanning lending, trading, insurance, and asset management. DeFi protocols built on Smart contracts in USA manage over $50 billion in total value locked, providing services that compete directly with traditional banks. Major institutions including Goldman Sachs, Fidelity, and BlackRock have established blockchain divisions focused on smart contract integration.
Automated lending protocols demonstrate smart contract capabilities in financial services. These systems process loans without human underwriters, using algorithmic risk assessment and collateral management. Borrowers receive funds within minutes rather than days, while lenders earn yields without counterparty default risk through over-collateralization requirements enforced by smart contract code.[1]
Insurance applications are expanding rapidly, with parametric policies that automatically pay claims when trigger conditions are verified. Flight delay insurance, crop coverage, and weather derivatives execute instantly based on oracle-provided data.
Supply Chain Optimization in the USA Using Smart Contracts
American manufacturers and distributors are implementing smart contracts in USA supply chain operations to achieve end-to-end visibility and automated compliance verification. Walmart’s blockchain initiative for food traceability demonstrates enterprise-scale smart contract deployment, tracking products from farm to shelf with immutable records. This transparency enables rapid response to quality issues and regulatory inquiries.
Smart contracts automate payment release upon delivery confirmation, eliminating disputes over goods receipt and condition. IoT sensors provide real-time data feeds that trigger contract execution when shipments reach destinations or temperature conditions are maintained throughout transit. This automation reduces working capital requirements and accelerates cash flow across supply networks.
Provenance verification through Smart contracts in USA enables premium pricing for goods with verified origins. American consumers increasingly demand transparency about product sourcing, and smart contract records provide the immutable proof that traditional documentation cannot match.
Smart Contracts Enhancing Data Security in US Healthcare Systems
Healthcare organizations across the United States face enormous challenges managing patient data securely while enabling appropriate information sharing. Smart contracts in USA healthcare applications provide granular access control that patients themselves can manage. Rather than trusting healthcare providers to protect sensitive information, patients can authorize specific data access through cryptographic permissions enforced by smart contract logic.
Insurance claims processing represents another major healthcare application. Smart contracts in USA can automatically verify coverage, calculate benefits, and trigger payments when claims meet policy criteria. This automation reduces the administrative burden that consumes significant healthcare spending while accelerating reimbursement timelines for providers.
Clinical trial management through Smart contracts in USA ensures data integrity that regulatory bodies require. Patient consent, data collection, and result reporting can all be managed through immutable blockchain records that satisfy FDA requirements for trial documentation.
Legal Recognition of Smart Contracts in the United States
Multiple US states have enacted legislation providing explicit legal recognition for smart contracts and blockchain records. Arizona’s Electronic Transactions Act amendments, passed in 2017, established that smart contracts cannot be denied legal effect solely because they operate on distributed ledger technology. Wyoming has gone further with comprehensive blockchain legislation covering smart contracts, DAOs, and digital asset custody.
Tennessee, Nevada, and several other states have followed with similar recognition statutes. These laws provide clarity that encourages enterprise adoption by removing legal uncertainty about smart contract enforceability. Businesses operating across state lines can structure agreements to take advantage of blockchain-friendly jurisdictions.
Federal recognition continues developing, with regulatory agencies including the SEC, CFTC, and OCC issuing guidance on smart contract applications in their respective domains. This evolving framework provides increasing clarity for American businesses seeking to implement smart contract solutions.
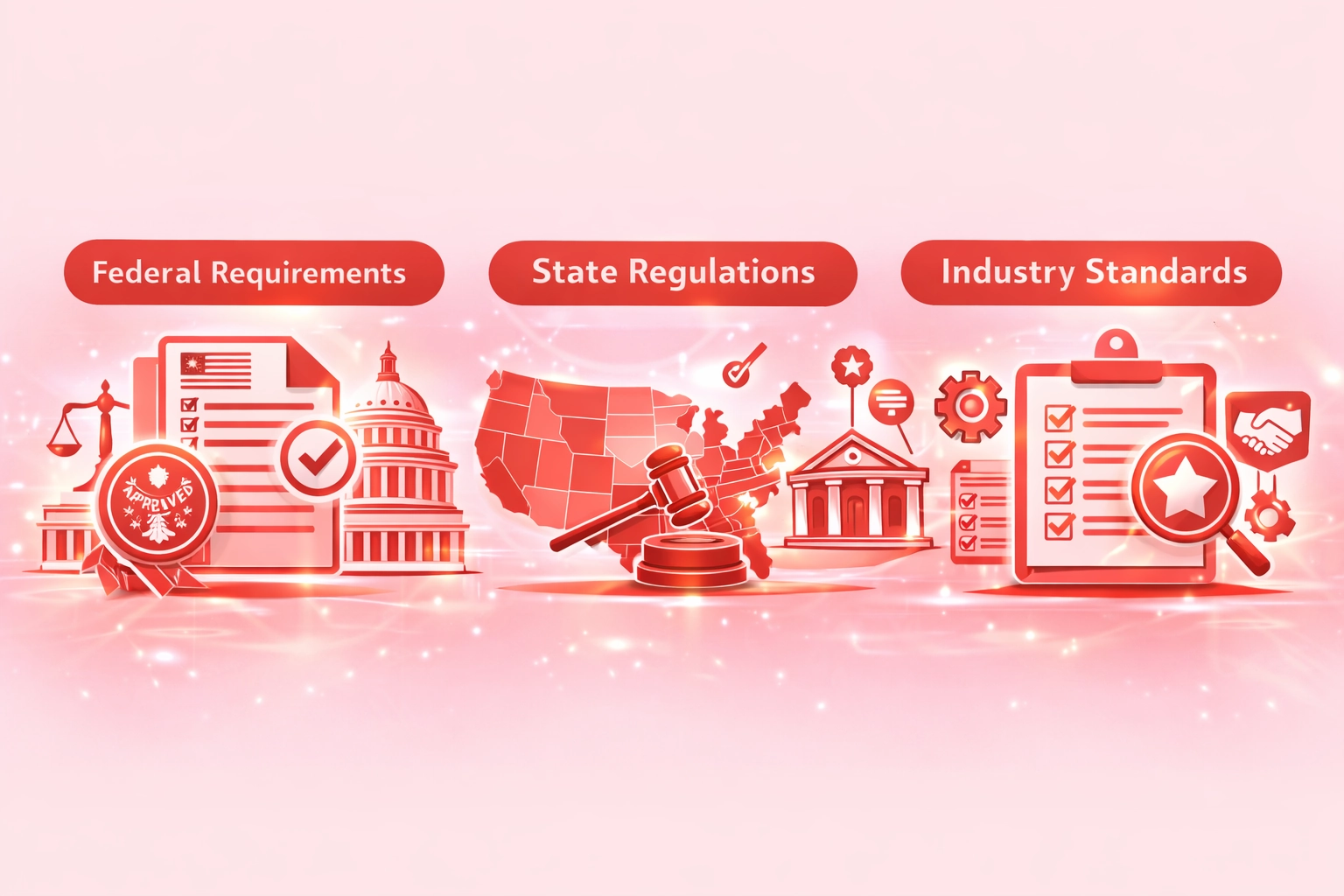
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations for Smart Contracts in the USA
Selecting the right compliance approach requires understanding the regulatory landscape across different jurisdictions and industries.
Federal Requirements
SEC securities regulations, CFTC commodity oversight, and FinCEN AML requirements apply to smart contracts handling regulated assets or transactions.
State Regulations
Money transmitter licenses, contract law requirements, and industry-specific regulations vary significantly across US states requiring careful analysis.
Industry Standards
HIPAA for healthcare, PCI-DSS for payments, and SOC 2 for technology services establish baseline requirements for smart contract implementations.
Fraud Prevention and Risk Reduction Using Smart Contracts in the US
Smart contracts in USA provide powerful fraud prevention capabilities through their immutable, transparent, and automatically executing nature. Traditional fraud schemes relying on document forgery, false claims, or unauthorized modifications become impossible when transactions are recorded on blockchain. American businesses report substantial fraud reduction after implementing Smart contracts in USA systems for high-risk processes.
Identity verification through cryptographic signatures ensures that only authorized parties can initiate transactions. Multi-signature requirements for high-value operations distribute control and prevent any single actor from committing fraud. These security mechanisms operate automatically without human oversight, eliminating opportunities for insider collusion.
Insurance fraud prevention represents a particularly compelling use case. Parametric policies that pay automatically based on verified external data eliminate false claims entirely. The trigger conditions are defined in code and verified by oracle networks, leaving no room for fraudulent manipulation.
Smart Contracts as a Cost-Saving Tool for US Startups and Enterprises
1. Requirements Analysis
Identify business processes suitable for smart contract automation and calculate potential cost savings.
2. Architecture Design
Design smart contract architecture optimized for gas efficiency and operational requirements.
3. Contract Creation
Build smart contracts following security best practices and industry standards for the US market.
4. Security Auditing
Conduct comprehensive security audits to identify vulnerabilities before production deployment.
5. Testnet Deployment
Deploy to test networks for validation in production-like environments without financial risk.
6. Mainnet Launch
Deploy verified contracts to production blockchain with monitoring and incident response plans.
7. Integration
Connect smart contracts with existing business systems, user interfaces, and external data sources.
8. Ongoing Optimization
Monitor performance, optimize gas usage, and implement upgrades to maximize cost savings continuously.
Security Auditing and Risk Management for US Smart Contracts
Professional security auditing is essential before deploying smart contracts in USA production environments. The immutable nature of blockchain means that vulnerabilities cannot be patched after deployment without complex upgrade mechanisms. Leading American enterprises require comprehensive audits from reputable firms before launching smart contract systems that handle significant value or critical operations.
Audit processes examine smart contract code for common vulnerability patterns including reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, access control flaws, and logic errors. Automated analysis tools scan for known issues, while manual review by experienced auditors identifies subtle vulnerabilities that tools miss. The best audits combine both approaches for comprehensive coverage.
Risk management extends beyond initial audits to ongoing monitoring and incident response planning. Bug bounty programs incentivize external researchers to identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. American enterprises deploying smart contracts should budget for continuous security investment rather than treating audits as one-time events.
Integration of Smart Contracts With AI, IoT, and Web3 in the USA
Convergence of emerging technologies creates powerful new capabilities for smart contracts in USA applications.
AI Integration: Machine learning models provide intelligent inputs for smart contract decisions, enabling adaptive automation based on pattern recognition.
IoT Connectivity: Sensor networks feed real-world data to smart contracts, triggering automated responses to physical events and conditions.
Web3 Ecosystems: Decentralized applications combine smart contracts with token economics and community governance for new business models.
Oracle Networks: Decentralized data providers bring off-chain information on-chain, expanding smart contract capabilities beyond blockchain data.
DePIN Networks: Decentralized physical infrastructure networks coordinate real-world resources through smart contract incentive mechanisms.
Cross-Chain Bridges: Interoperability protocols enable smart contracts to operate across multiple blockchain networks simultaneously.
Emerging Trends in the US Smart Contract Ecosystem
The smart contracts in USA ecosystem continues evolving rapidly, with new technologies and applications emerging across industries. Understanding these trends helps American businesses position themselves for competitive advantage as the technology matures.
| Trend | Description | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Account Abstraction | Smart contract wallets with improved UX | 2024-2026 |
| Zero-Knowledge Proofs | Privacy-preserving contract execution | 2025-2027 |
| Intent-Based Systems | User-centric transaction optimization | 2025-2026 |
| Regulatory Clarity | Federal smart contract frameworks | 2026-2028 |
| Enterprise Adoption | Fortune 500 production deployments | Ongoing |
The Role of Smart Contracts in Shaping the Future of Digital Transformation in the USA
Industry standards and best practices guide successful smart contract implementation across American enterprises.
Standard 1: Conduct comprehensive security audits before any production deployment of smart contracts handling value or sensitive operations.
Standard 2: Implement upgrade mechanisms using proven proxy patterns for contracts requiring future modifications or bug fixes.
Standard 3: Design access control systems with multi-signature requirements for administrative functions and emergency operations.
Standard 4: Establish monitoring and alerting systems to detect anomalous contract behavior indicating potential security issues.
Standard 5: Document smart contract logic thoroughly for regulatory compliance, user understanding, and maintenance requirements.
Standard 6: Maintain bug bounty programs to incentivize responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities discovered after deployment.
Standard 7: Follow regulatory guidance from SEC, CFTC, and state agencies for smart contracts involving regulated activities.
Standard 8: Optimize gas usage through efficient code patterns to minimize transaction costs for users and operations.
Smart Contract Compliance Checklist for US Businesses
Security Requirements
- Professional security audit completed
- Bug bounty program established
- Monitoring systems deployed
Legal Compliance
- State-specific requirements reviewed
- Federal regulations assessed
- Terms of service documented
Operational Readiness
- Incident response plan prepared
- Upgrade procedures documented
- Support team trained
Documentation
- Technical documentation complete
- User guides published
- Audit reports available
Transform Your Business With Expert Smart Contract Solutions!
Our team delivers secure, compliant smart contract solutions for US businesses. With 8+ years experience, we help enterprises achieve digital transformation goals efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on blockchain networks that automatically enforce agreement terms when predefined conditions are met. In the USA, businesses use them to automate transactions, reduce intermediaries, and ensure transparent execution. They operate across industries including finance, real estate, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Yes, smart contracts have gained legal recognition across multiple US states including Arizona, Tennessee, Wyoming, and Nevada. These states have enacted legislation acknowledging blockchain signatures and smart contract validity. However, legal enforceability depends on meeting traditional contract requirements including offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual intent to be bound.
Financial services, real estate, healthcare, supply chain, and insurance industries benefit significantly from smart contracts in the USA. DeFi platforms, property transactions, medical records management, logistics tracking, and automated claims processing represent primary use cases driving adoption across American enterprises and startups.
Smart contracts enhance security through cryptographic protection, immutable transaction records, and elimination of single points of failure. Once deployed on blockchain networks, contract code cannot be altered, preventing unauthorized modifications. Automated execution removes human error and manipulation risks that plague traditional agreement processes.
US businesses report 40-80% cost reductions through smart contract implementation by eliminating intermediaries, reducing administrative overhead, and accelerating transaction processing. Automated execution removes manual verification requirements, while transparent audit trails reduce compliance costs and dispute resolution expenses significantly.
Smart contracts in the USA fall under multiple regulatory jurisdictions including SEC for securities, CFTC for commodities, and state-level contract laws. Federal agencies continue developing frameworks while states like Wyoming lead with comprehensive blockchain legislation. Compliance requirements vary based on contract purpose and industry application.
Implementation timelines range from 4-16 weeks depending on complexity, integration requirements, and security audit needs. Simple token contracts may deploy within weeks, while enterprise systems requiring extensive testing, compliance reviews, and legacy system integration typically require 3-6 months for full production deployment.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







