Key Takeaways
- ▸Tokenization vendor red flags include missing regulatory compliance documentation, absent security audits, and unclear asset backing, collectively responsible for over $2 billion in investor losses across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets since 2020.
- ▸Lack of third-party security audits from recognized firms like CertiK or OpenZeppelin represents critical tokenization vendor red flags, as unaudited smart contracts have caused $3 billion+ in DeFi exploits requiring $30,000-$150,000 investment for proper verification.
- ▸Weak KYC/AML frameworks expose tokenization platforms to regulatory enforcement, potential shutdown, and investor fund seizure, with penalties reaching $100 million+ for serious violations across major jurisdictions globally.
- ▸Marketing claims promising guaranteed returns exceeding 15-20% annually or zero-risk investments represent immediate tokenization vendor red flags indicating potential Ponzi schemes, as legitimate real estate tokenization typically yields 6-12% returns.
- ▸Centralized control disguised as decentralized systems creates significant tokenization vendor red flags, enabling rug pulls and unauthorized fund access affecting 40% of failed tokenization projects since 2021 across global markets.
- ▸Absence of proven track record with verifiable client references, documented transaction history, and named completed projects indicates tokenization vendor red flags requiring enhanced due diligence before any capital commitment.
- ▸Infrastructure concerns including single-server architectures, absent disaster recovery planning, and no uptime guarantees represent tokenization vendor red flags potentially causing permanent data and fund loss during system failures.
- ▸Professional due diligence identifying tokenization vendor red flags costs $10,000-$50,000 but prevents potential losses of $500,000-$50 million, delivering 10-100x return on investment for serious institutional and individual investors.
Introduction to Tokenization Vendors and Trust Risks
The rapid growth of asset tokenization has attracted hundreds of vendors offering platforms, services, and technology solutions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets. However, this explosive growth has also brought numerous fraudulent, incompetent, and undercapitalized operators creating significant risks for investors and asset owners. With over eight years of experience evaluating tokenization partners, our agency has identified critical tokenization vendor red flags that distinguish legitimate providers from those posing unacceptable risks to capital, compliance, and long-term investment success.
Understanding tokenization vendor red flags protects against substantial financial losses, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. Failed tokenization projects have cost investors over $2 billion since 2020 through security breaches, regulatory shutdowns, fraudulent schemes, and operational failures. Professional due diligence identifying warning signs before engagement costs $10,000-$50,000 but prevents potential losses of $500,000-$50 million, delivering exceptional return on investment for serious institutional and individual investors seeking blockchain-based asset exposure while maintaining appropriate risk management.
Why Tokenization Vendor Due Diligence Matters
Tokenization vendor due diligence extends beyond traditional procurement assessment because blockchain-based systems create unique risks including immutable transaction records, smart contract vulnerabilities, and regulatory complexity spanning multiple jurisdictions. Identifying tokenization vendor red flags early prevents engagement with providers whose technical capabilities, compliance frameworks, or financial stability cannot support successful project execution. The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions means errors or fraud cannot be easily corrected, making upfront verification essential rather than optional across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Institutional investors increasingly mandate formal vendor assessment processes before allocating capital to tokenized assets, recognizing that platform risks directly impact investment security. Regulatory bodies across major markets have intensified enforcement against non-compliant tokenization providers, creating secondary risks for investors using problematic platforms. Comprehensive due diligence evaluating tokenization vendor red flags across security, compliance, operational, and financial dimensions protects capital while ensuring access to legitimate blockchain-based investment opportunities with appropriate risk-reward characteristics.
Lack of Regulatory Compliance as a Major Red Flag
Regulatory non-compliance represents the most severe tokenization vendor red flags category because it exposes investors to enforcement actions, fund seizures, and platform shutdowns without recourse. Tokenized securities require proper registration or exemptions under SEC regulations in USA, FCA authorization in UK, VARA licensing in UAE, and provincial securities compliance in Canada. Vendors unable to demonstrate current regulatory status, provide compliance documentation, or articulate their legal framework likely operate illegally, creating existential risks for all platform participants regardless of individual investment merit.
| Jurisdiction | Required Compliance | Red Flag Indicators | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | SEC Reg D, Reg A+, or Reg S exemptions | No Form D filing, missing legal opinion | SEC EDGAR database search |
| UK | FCA authorization for security tokens | Missing FRN number, no sandbox approval | FCA Register verification |
| UAE (Dubai) | VARA licensing for virtual assets | No VARA registration, unclear jurisdiction | VARA public registry check |
| Canada | Provincial securities registration | No CSA recognition, missing prospectus | SEDAR+ filing verification |
Weak Smart Contract Security Practices
Smart contract vulnerabilities have caused over $3 billion in losses across blockchain applications, making weak security practices critical tokenization vendor red flags requiring immediate attention during due diligence. Vendors should demonstrate secure development lifecycle implementation including code reviews, automated testing, formal verification where applicable, and adherence to established security patterns. Inability to articulate security practices, provide technical documentation, or demonstrate vulnerability management processes indicates either incompetence or deliberate negligence threatening investor funds across all platform operations.
Professional tokenization vendors employ experienced Solidity or Rust developers with verifiable credentials, implement test coverage exceeding 90% of contract functionality, use established libraries like OpenZeppelin for standard patterns, and maintain bug bounty programs incentivizing external security research. Request evidence of development team qualifications, code review processes, test coverage reports, and dependency management practices. Vendors dismissing security concerns or providing vague assurances without documentation represent unacceptable tokenization vendor red flags warranting immediate disqualification from consideration.
Absence of Third-Party Security Audits
Missing third-party security audits constitute definitive tokenization vendor red flags because independent verification represents the only reliable method for identifying smart contract vulnerabilities that internal teams may miss or deliberately overlook. Professional audits from recognized firms like CertiK, Trail of Bits, OpenZeppelin, Quantstamp, or ConsenSys Diligence cost $30,000-$150,000 depending on contract complexity and provide critical assurance that code functions as intended without exploitable weaknesses. Vendors refusing to invest in audits either lack financial resources indicating instability or intentionally hide security problems.
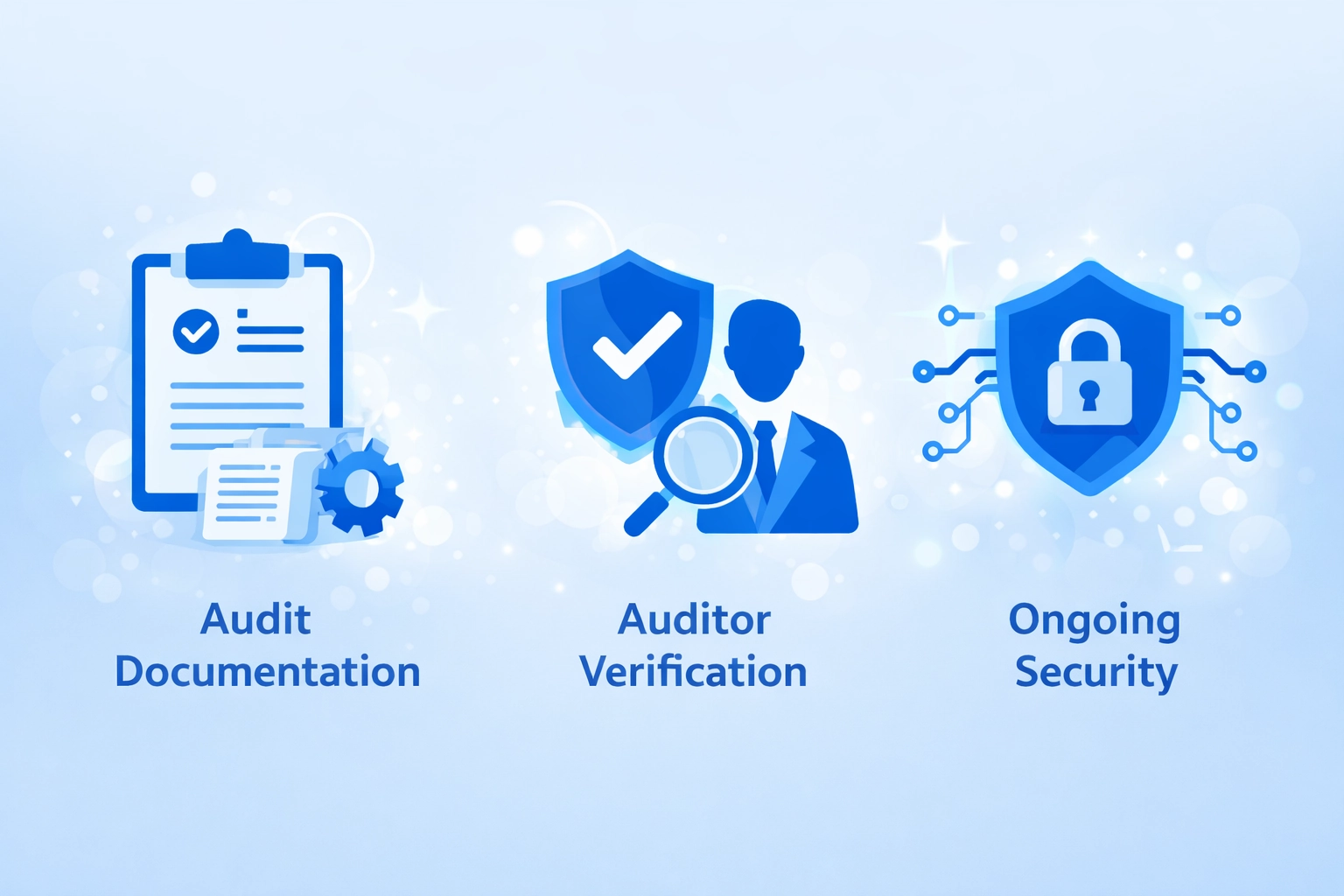
Security Audit Verification Checklist
Audit Documentation
- Complete audit report with findings
- Severity classification of issues
- Remediation confirmation for critical bugs
- Re-audit results after fixes
- Date and version audited matches deployment
Auditor Verification
- Confirm auditor firm legitimacy
- Verify report authenticity directly
- Check auditor reputation and history
- Review other projects audited
- Confirm no auditor conflicts of interest
Ongoing Security
- Active bug bounty program
- Security monitoring systems
- Incident response procedures
- Regular re-audits for updates
- Penetration testing schedule
Poor Transparency in Tokenization Architecture
Architectural opacity represents significant tokenization vendor red flags because legitimate blockchain implementations derive value from transparency enabling independent verification. Vendors should publish smart contract addresses on block explorers, provide verified source code for independent review, document system architecture comprehensively, and clearly explain data flows between on-chain and off-chain components. Refusal to disclose technical details, vague explanations avoiding specifics, or claims of proprietary technology preventing disclosure suggest either incompetence or intentional concealment of problematic implementations across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian deployments.
Comprehensive architectural documentation should include blockchain network selection rationale, smart contract functionality descriptions, oracle integration methods for external data, custody solution specifications, and disaster recovery procedures. Fee structures should be completely transparent with no hidden costs or unexplained charges. Legitimate vendors welcome technical scrutiny because robust architectures withstand examination. Opacity inversely correlates with trustworthiness, making transparency evaluation essential for identifying tokenization vendor red flags before capital commitment.
Inadequate Data Privacy and User Protection Measures
Data privacy deficiencies create serious tokenization vendor red flags given the sensitive personal and financial information collected during KYC processes and ongoing platform usage. Vendors must comply with GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, PIPEDA in Canada, and data protection requirements across all operating jurisdictions. Missing privacy policies, unclear data retention practices, inadequate encryption standards, and absence of data processing agreements indicate insufficient protection for user information potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and regulatory penalties.
Centralized Control Hidden Behind Decentralized Claims
Centralized control disguised as decentralized systems represents dangerous tokenization vendor red flags enabling rug pulls, unauthorized fund access, and unilateral terms changes affecting investor security. Analysis indicates 40% of failed tokenization projects since 2021 involved centralized control despite decentralization claims. Examine smart contract admin functions, upgrade authority ownership, multi-signature requirements, and time-lock mechanisms. Single-key admin access, unilateral upgrade capabilities, and immediate execution of sensitive functions without delays indicate centralization risks despite marketing claims across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian platforms.
Legitimate decentralized tokenization implementations distribute control through multi-signature wallets requiring multiple approvals, implement governance mechanisms enabling token holder participation, use time-locks providing advance notice of changes enabling user exit, and employ gradual decentralization roadmaps with verifiable milestones. Request detailed explanations of control mechanisms, admin key management procedures, and governance frameworks. Vague responses or inability to articulate decentralization architecture confirm tokenization vendor red flags warranting immediate concern.
Unclear Asset Backing and Ownership Verification
Unclear asset backing creates fundamental tokenization vendor red flags because tokens derive all value from underlying assets requiring verifiable ownership, proper custody, and legal enforceability of investor rights. Request title documents, property valuations from accredited appraisers, legal opinions confirming token-holder rights, and custody arrangements with regulated custodians. Absence of these documents suggests assets may be encumbered, non-existent, or legally problematic with tokens representing worthless claims. Professional verification through independent attorneys and title companies costs $5,000-$20,000 but prevents potential total loss of investment capital.[1]
| Asset Verification Element | Required Documentation | Red Flag Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Property Ownership | Title deed, ownership chain, lien search | Refusal to provide title documentation |
| Asset Valuation | Accredited appraiser report, comparable analysis | Inflated valuations without support |
| Legal Structure | SPV documents, operating agreements, legal opinion | Vague ownership structure explanations |
| Custody Arrangements | Custodian agreements, insurance certificates | Assets held in vendor personal accounts |
| Token Rights | Legal opinion on token-asset connection | Unclear token holder legal rights |
Weak KYC and AML Frameworks
Weak KYC/AML frameworks create serious tokenization vendor red flags exposing platforms to regulatory enforcement, potential shutdown, and investor fund seizure without recourse. Inadequate identity verification enables money laundering, terrorist financing, and sanctions violations triggering severe penalties potentially reaching $100 million+ for serious violations. Regulators across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada actively prosecute non-compliant platforms, creating risks for all users regardless of their individual compliance. Request detailed KYC procedures, AML policy documentation, compliance officer credentials, and third-party verification provider information.
Protect Your Tokenization Investment
Our experts identify vendor red flags before you commit capital. Get comprehensive due diligence across security, compliance, and operational risk factors.
Institutional-grade KYC/AML frameworks include document validation using multiple verification sources, biometric authentication, sanctions screening against OFAC, EU, and UN lists, ongoing transaction monitoring for suspicious activity, and suspicious activity reporting procedures. Vendors should employ dedicated compliance officers with relevant certifications and experience. Minimal verification processes accepting self-declarations, missing ongoing monitoring, and absent suspicious activity procedures indicate tokenization vendor red flags creating unacceptable regulatory exposure for platform participants.
Limited Incident Response and Breach Handling Plans
Absent incident response capabilities represent significant tokenization vendor red flags because security breaches inevitably occur requiring rapid, coordinated response to minimize damage and protect investor assets. Vendors should maintain documented incident response plans, dedicated security personnel or retainer relationships with cybersecurity firms, communication protocols for affected users, and relationships with law enforcement. Request incident response documentation, ask about previous security events and remediation actions, verify cyber insurance coverage, and confirm breach notification procedures comply with applicable regulations across operating jurisdictions.
Vendor Due Diligence Assessment Lifecycle
Initial Screening
Review public information, verify company registration, check team credentials on LinkedIn, search for news coverage and regulatory actions.
Compliance Verification
Request regulatory documentation, verify registrations with authorities, review legal opinions, assess KYC/AML frameworks comprehensively.
Technical Assessment
Review smart contract audits, verify audit authenticity, examine architecture documentation, assess security practices and infrastructure.
Asset Verification
Confirm asset ownership through title search, verify valuations independently, review legal structure connecting tokens to underlying assets.
Reference Checks
Contact named client references, verify project completion claims, assess industry reputation through professional networks and forums.
Financial Stability
Review financial statements, assess funding sources, verify insurance coverage, evaluate long-term operational viability and runway.
Legal Review
Engage securities attorney to review offering documents, assess investor protections, verify contract enforceability across jurisdictions.
Final Decision
Compile findings, assess aggregate risk profile, make engagement decision based on comprehensive evaluation of all red flag categories.
Overpromising ROI and Misleading Marketing Claims
Marketing-related tokenization vendor red flags include guaranteed returns exceeding 15-20% annually, promises of zero-risk investments, claims of revolutionary technology without technical substance, and aggressive urgency tactics pressuring immediate investment decisions. Legitimate real estate tokenization involves physical assets generating 6-12% typical yields with associated market, liquidity, and operational risks. Vendors promising exceptional returns above market rates likely operate Ponzi schemes, fraudulent offerings, or fundamentally misrepresent investment characteristics creating unrealistic expectations leading to investor losses across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets.
Professional tokenization vendors provide realistic projections based on comparable market data, clearly disclose all risks, present audited financial information supporting claims, and welcome investor scrutiny. Request independent verification of return claims, examine historical performance data where available, and compare projections against market benchmarks. Unrealistic promises, pressure tactics emphasizing limited availability, and refusal to provide supporting documentation confirm tokenization vendor red flags indicating potential fraud requiring immediate disengagement regardless of apparent opportunity attractiveness.
No Proven Track Record or Industry References
Track record absence represents major tokenization vendor red flags because blockchain tokenization requires specialized expertise across legal, technical, and financial domains developed through practical experience. Vendors without verifiable completed projects, named client references with permission to contact, and documented transaction history lack proven capability to execute complex tokenization implementations successfully. Request specific project examples, verify team member credentials independently, check company registration history, and search for news coverage, industry recognition, or conference presentations demonstrating thought leadership.
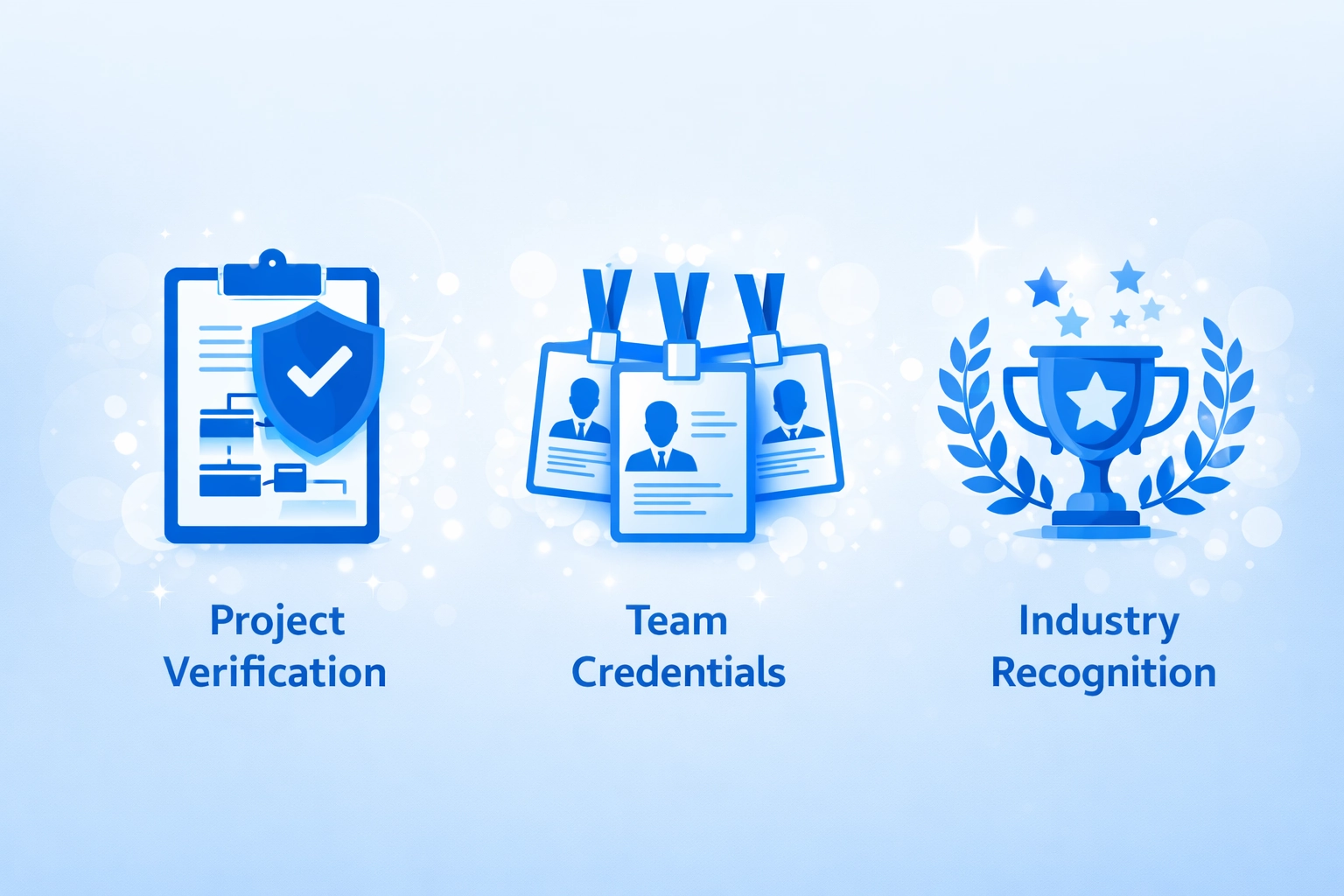
Track Record Verification Methods
Project Verification
- Request specific project names and details
- Verify blockchain transactions on explorers
- Contact named clients for references
- Review project documentation samples
- Confirm completion and outcomes
Team Credentials
- Verify LinkedIn profiles independently
- Check previous employer references
- Confirm educational credentials
- Review professional certifications
- Assess relevant industry experience
Industry Recognition
- Search for news coverage and press
- Check conference speaking history
- Review published thought leadership
- Verify industry association memberships
- Assess professional network connections
Scalability and Infrastructure Reliability Concerns
Infrastructure-related tokenization vendor red flags include single-server architectures without redundancy, absence of disaster recovery planning, reliance on single cloud providers, lack of uptime guarantees, and missing service level agreements. Legitimate platforms employ multi-region deployment ensuring geographic redundancy, automatic failover systems maintaining availability during component failures, regular backup procedures protecting data integrity, and 99.9%+ uptime commitments with financial remedies for failures. Request infrastructure documentation, penetration testing results, and historical incident data demonstrating operational maturity.
Vendors unable to articulate scalability plans, demonstrate load testing results, or provide infrastructure documentation may collapse under increased usage potentially losing investor data and funds. Cloud provider selection, database architecture, API design, and monitoring systems all impact platform reliability. Professional operations require 24/7 monitoring, documented escalation procedures, and capacity planning ensuring continued service as usage grows. Technical opacity regarding infrastructure indicates tokenization vendor red flags warranting careful evaluation before entrusting assets to platform operations across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets.
How Vendor Red Flags Impact Investor Confidence and Long-Term Trust
Tokenization vendor red flags directly impact investor confidence, market development, and long-term trust in blockchain-based investment products. Platform failures, security breaches, and regulatory shutdowns affect not only direct victims but also damage broader market perception, increasing skepticism and slowing adoption. Institutional investors mandate rigorous vendor assessment, and retail investors increasingly research platform security before committing capital. Vendors demonstrating strong compliance, security, transparency, and track record attract more investors and higher valuations, while those exhibiting red flags face declining participation and eventual market exit.
Protecting Your Investment Through Comprehensive Due Diligence
Identifying tokenization vendor red flags before capital commitment protects investments while supporting development of legitimate blockchain-based markets. Professional due diligence costs $10,000-$50,000 but prevents potential losses of $500,000-$50 million, delivering exceptional return on investment for serious investors. Comprehensive assessment should evaluate regulatory compliance, security practices, audit documentation, asset backing, KYC/AML frameworks, track record, and infrastructure reliability across all vendor engagement decisions.
Our eight years of tokenization industry experience across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada enables identification of tokenization vendor red flags that less experienced evaluators might miss. The convergence of blockchain technology, securities regulation, and real estate investment creates unique complexity requiring specialized assessment capabilities. As tokenization markets mature, vendors demonstrating excellence will capture growing institutional allocations while those exhibiting red flags face increasing marginalization. Protecting capital through rigorous due diligence supports both individual investment security and broader market development benefiting all participants in the tokenized asset ecosystem.
People Also Ask
Tokenization vendor red flags include absence of regulatory compliance documentation, missing third-party security audits, unclear asset backing verification processes, weak KYC/AML frameworks, and overpromising returns without evidence. Vendors lacking proven track records, refusing to share smart contract audit reports, or demonstrating centralized control behind decentralized marketing claims pose significant risks. Organizations across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada should verify vendor licensing, examine security certifications, request client references, and assess incident response capabilities before engagement to protect investments and maintain regulatory compliance.
Verifying regulatory compliance requires examining vendor licensing documentation for specific jurisdictions including SEC registration or exemptions in USA, FCA authorization in UK, VARA licensing in UAE, and provincial securities compliance in Canada. Request evidence of legal opinions from recognized law firms, verify claimed registrations through regulatory databases, examine compliance officer credentials, and assess ongoing reporting capabilities. Tokenization vendor red flags include inability to produce compliance documentation, vague responses about regulatory status, or claims of operating in regulatory grey areas without proper legal frameworks supporting operations.
Third-party security audits from recognized firms like CertiK, Trail of Bits, or OpenZeppelin provide independent verification that smart contracts and platform infrastructure meet security standards. Audits identify vulnerabilities before exploitation, verify code matches documented functionality, and demonstrate vendor commitment to security. Tokenization vendor red flags include refusal to share audit reports, audits from unknown firms, outdated audits not covering current code versions, or audits revealing critical vulnerabilities without evidence of remediation. Professional audits costing $50,000-$300,000 protect billions in tokenized assets across global implementations.
Legitimate tokenization vendors demonstrate comprehensive security through published smart contract audits, bug bounty programs, encryption standards for data protection, multi-signature wallet controls, penetration testing reports, and SOC 2 Type II compliance. Vendors should maintain incident response plans, employ dedicated security teams, implement continuous monitoring, and provide transparent security documentation. Tokenization vendor red flags include absence of security certifications, unwillingness to discuss security architecture, single-point-of-failure key management, and lack of insurance coverage protecting against losses from security breaches across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian operations.
Misleading marketing claims from tokenization vendors include guaranteed returns, unrealistic yield projections, claims of regulatory immunity, promises of liquidity without established secondary markets, and exaggerated technology capabilities. Tokenization vendor red flags include inability to substantiate claims with evidence, pressure tactics creating artificial urgency, testimonials from unverifiable sources, and comparisons to successful projects without similar fundamentals. Legitimate vendors provide conservative projections, acknowledge risks transparently, offer verifiable references, and comply with securities advertising regulations across jurisdictions including USA, UK, UAE, and Canada.
Essential due diligence questions include requesting smart contract audit reports, regulatory compliance documentation, client references with contact information, insurance coverage details, incident response procedures, key management practices, and financial stability evidence. Ask about team credentials, technology architecture, data protection measures, exit strategies, and dispute resolution processes. Tokenization vendor red flags appear when vendors evade questions, provide vague responses, refuse documentation requests, or demonstrate discomfort discussing security and compliance topics essential for protecting investor interests across global markets.
Tokenization vendor red flags directly impact investor confidence by creating uncertainty about asset security, regulatory exposure, and long-term viability. Institutional investors across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada conduct extensive due diligence, and discovering red flags typically results in immediate deal termination. Red flags suggesting compliance failures may expose investors to regulatory penalties, while security concerns indicate potential for asset loss. Market reputation damage from red flag associations can reduce token liquidity, decrease valuations, and limit future fundraising capabilities for projects associated with questionable vendors.
Warning signs of hidden centralization include single-entity control over smart contract upgrades, admin keys held by small teams without multi-signature requirements, governance token concentration enabling unilateral decisions, and platform dependencies on proprietary infrastructure. Tokenization vendor red flags include inability to explain decentralization mechanisms, vague responses about key management, absence of time-locked upgrades, and marketing emphasizing decentralization without technical evidence. True decentralization requires distributed governance, transparent key management, community oversight, and verifiable on-chain mechanisms across global implementations
Track record and references provide crucial evidence of vendor capability, reliability, and integrity demonstrated through successful project completions. Legitimate vendors maintain portfolios showcasing implemented projects, provide client references willing to discuss experiences, and demonstrate industry recognition through awards and certifications. Tokenization vendor red flags include absence of verifiable completed projects, reluctance to provide references, claims of confidentiality preventing disclosure, and inability to demonstrate relevant experience in target jurisdictions including USA, UK, UAE, and Canada where specific regulatory expertise matters significantly.
Professional tokenization vendors maintain documented incident response plans covering security breaches, smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory investigations, and operational failures. Capabilities include 24/7 monitoring, defined escalation procedures, communication protocols for affected parties, forensic investigation resources, and insurance coverage for incident-related losses. Tokenization vendor red flags include absence of incident response documentation, inability to describe breach handling procedures, no dedicated security personnel, and lack of insurance protecting investors from losses caused by vendor failures across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian operations.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






