Key Takeaways
- Decentralization distributes control across networks, eliminating single points of failure and making censorship nearly impossible while ensuring no single entity can manipulate the system.[1]
- The Web3 ownership model provides true digital asset ownership through cryptographic keys, where users maintain exclusive control without platform dependency.
- Trustless systems replace institutional trust with cryptographic verification and smart contracts that automatically execute agreements without human intermediaries.
- Web3 governance models through DAOs enable collective decision-making where community members vote on protocol changes and resource allocation.
- The Web3 vs Web2 trust model shifts from trusting centralized platforms to verifying transactions independently through transparent, immutable code.
- NFTs and tokens provide verifiable proof of ownership that exists independently of any platform, enabling new models for digital collectibles, gaming assets, and creator economies.
- Web3 identity and ownership create portable digital identities where your reputation and assets follow you across applications without centralized control.
- Businesses adopting Web3 principles benefit from increased transparency, reduced intermediary costs, and innovative customer engagement models through tokenization.
Introduction to Web3 Principles
The internet has undergone remarkable transformations since its inception, evolving from static web pages to interactive platforms that billions rely on daily. Now, we stand at the threshold of another significant shift. The key principles of Web3 represent not merely a technological upgrade but a fundamental reimagining of how we interact with digital systems, own digital assets, and establish trust in online environments.
Understanding Web3 fundamentals has become essential for anyone looking to navigate the future of digital interactions. Whether you are a business leader exploring new opportunities, a creator seeking to monetize your work directly, or simply a curious individual wanting to understand where technology is heading, grasping these core concepts of Web3 will prove invaluable.
What Is Web3
Web3 refers to the next generation of internet services built on blockchain technology and decentralized protocols. Unlike the current internet (often called Web2), which relies heavily on centralized platforms and intermediaries, Web3 aims to create a more open, transparent, and user-centric digital environment.
At its foundation, Web3 integrates blockchain networks, smart contracts, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized storage to create applications where users maintain control over their data and digital assets. This represents a departure from the model where tech giants accumulate vast amounts of user data and exercise significant control over digital experiences.
The term “Web3” encompasses a broad ecosystem of technologies and applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and various blockchain-based applications that prioritize user sovereignty and peer-to-peer interactions.
Why Web3 Principles Matter
The significance of Web3 principles extends far beyond technical innovation. These principles address fundamental concerns about privacy, ownership, and power distribution in our increasingly digital lives. As more of our economic activity, social interactions, and creative expression moves online, the question of who controls these digital spaces becomes critically important.
The Web3 ownership model offers creators and users the ability to truly own their digital creations and assets, rather than merely licensing them from platforms that can change terms or revoke access at any time. This shift has profound implications for artists, musicians, writers, and anyone who creates value in digital spaces.
Understanding Decentralization in Web3
Decentralization stands as perhaps the most fundamental of all Web3 principles. It represents a structural shift in how digital systems operate, moving away from centralized control toward distributed networks where no single entity holds disproportionate power.
What Decentralization Means in Web3
In the context of Web3, decentralization refers to the distribution of power, data, and decision-making across a network of participants rather than concentrating these elements in a single authority. This is achieved through blockchain technology, where thousands of nodes maintain identical copies of transaction records and collectively validate new entries.
True decentralization encompasses multiple dimensions. Network decentralization means that no single server or company controls the infrastructure. Governance decentralization ensures that protocol decisions are made collectively by stakeholders. Data decentralization guarantees that information is stored across multiple locations rather than in proprietary databases.
The degree of decentralization varies across different blockchain networks and applications. Some prioritize maximum decentralization at the cost of speed and efficiency, while others make calculated trade-offs to achieve better performance while maintaining meaningful distribution of control.
How Decentralization Removes Intermediaries
Traditional digital systems rely heavily on intermediaries: banks process payments, social media platforms host content, and cloud providers store data. These intermediaries often charge fees, impose rules, and can deny service based on their own policies or external pressures.
Web3 technologies eliminate or minimize the need for these intermediaries through peer-to-peer protocols and smart contracts. When you send cryptocurrency to another person, the transaction is validated by the network itself rather than a bank. When you interact with a decentralized application, you connect directly through your wallet without creating an account with a centralized service.
This removal of intermediaries has practical implications: lower fees for financial transactions, resistance to censorship, and the elimination of platform risk where a company’s decisions can suddenly affect millions of users. However, it also shifts responsibility to individuals, who must now manage their own security and cannot rely on customer service departments to reverse mistakes.
Benefits of Decentralization
The benefits of decentralization extend across multiple dimensions, creating value for users, creators, and the broader ecosystem. Understanding these benefits helps explain why Web3 fundamentals are attracting significant attention from technologists, entrepreneurs, and investors worldwide.
Security and Censorship Resistance
Decentralized networks offer inherent security advantages through their distributed architecture. To compromise a centralized system, an attacker needs to breach a single point of failure. To compromise a well-designed decentralized network, they would need to simultaneously attack thousands of independent nodes, making such attacks practically infeasible.
Censorship resistance emerges as a natural property of decentralization. When content or transactions exist across thousands of nodes worldwide, no single government or organization can effectively suppress them. This property is particularly valuable in regions where free expression faces restrictions or where citizens have limited access to stable financial services.
However, censorship resistance also raises legitimate concerns about illegal content and activities. The Web3 ecosystem continues to grapple with how to maintain these benefits while developing appropriate mechanisms to address harmful uses.
Transparency and Network Resilience
Blockchain networks operate with unprecedented transparency. All transactions are recorded on a public ledger that anyone can audit. Smart contract code is typically open source and verifiable. This transparency creates accountability and allows users to verify exactly how systems operate rather than trusting company claims.
Network resilience comes from having no single point of failure. When centralized services experience outages, millions of users lose access. Decentralized networks continue functioning even if significant portions experience problems, as the remaining nodes maintain network operations. This resilience has proven valuable during various stress tests and attack attempts on major blockchain networks.
| Aspect | Centralized Systems | Decentralized Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Single entity makes decisions | Distributed among participants |
| Data Storage | Proprietary servers | Distributed across nodes |
| Failure Risk | Single point of failure | Highly resilient |
| Transparency | Limited, controlled by operator | Full, publicly auditable |
| Censorship | Easily implemented | Highly resistant |
| User Trust | Trust in institution required | Verify through code and math |
Ownership as a Core Principle of Web3
The Web3 ownership model fundamentally transforms what it means to own something in digital spaces. For decades, digital “ownership” has been largely illusory, with users essentially renting access to content and services under terms that platforms can modify unilaterally.
User Ownership of Data and Assets
In Web3, ownership is established through cryptographic keys rather than accounts with centralized platforms. When you hold cryptocurrency or an NFT, you possess the private key that controls those assets. No company can freeze your account, no terms of service can revoke your access, and no platform shutdown can eliminate your holdings.
This ownership extends to personal data as well. Emerging Web3 identity and ownership solutions allow users to control their personal information, choosing what to share with applications and maintaining the ability to revoke access. This contrasts sharply with current models where platforms harvest and monetize user data with limited user control.
The implications are profound for creators especially. Musicians can sell directly to fans without record label intermediaries. Artists can receive royalties automatically whenever their work is resold. Writers can monetize their content without platform algorithms determining their reach and revenue.
Digital Asset Ownership Using Blockchain
Blockchain technology enables verifiable scarcity and provable ownership for digital assets. Before blockchain, digital items could be infinitely copied, making true ownership meaningless. Now, blockchain records create unique, verifiable digital assets that can be owned, transferred, and traded with the same certainty as physical property.
Smart contracts govern the rules of this ownership. They can enforce royalty payments, restrict transfers, or enable complex ownership arrangements like fractional ownership of expensive assets. The code defines the asset’s behavior, and users can verify these rules before acquiring any asset.
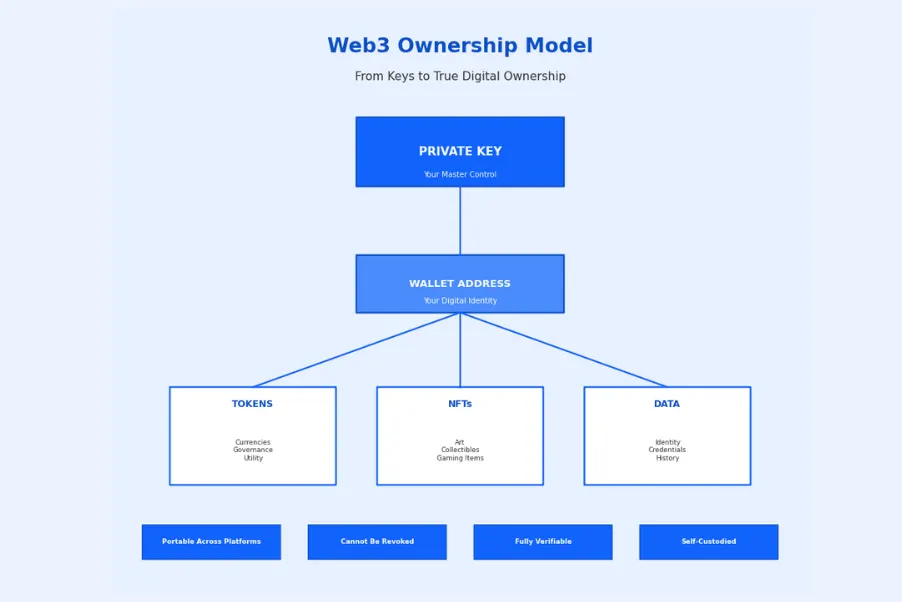
Role of Tokens and NFTs in Ownership
Tokens and NFTs serve as the primary vehicles for expressing ownership in Web3 ecosystems. Understanding these instruments is essential for grasping how the Web3 ownership model functions in practice.
Token-Based Ownership Models
Tokens in Web3 represent various forms of value and utility. Fungible tokens like cryptocurrencies are interchangeable, with each unit identical to another. Governance tokens grant voting rights in decentralized protocols. Utility tokens provide access to specific services or features within applications.
These tokens enable new ownership models impossible in traditional systems. Community members can own stakes in protocols they use. Users can earn tokens through participation, aligning their incentives with platform success. Token holders can collectively govern protocol changes through voting mechanisms.
The programmatic nature of tokens allows for sophisticated ownership arrangements. Vesting schedules can automatically release tokens over time. Revenue sharing can occur automatically through smart contracts. Complex financial instruments can be created and traded without institutional intermediaries.
NFTs and Proof of Digital Ownership
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) provide proof of ownership for unique digital items. Unlike cryptocurrencies where each unit is identical, each NFT is distinct and can represent ownership of specific digital art, collectibles, virtual real estate, music, or any other unique digital asset.
NFTs have expanded the concept of digital ownership beyond financial assets into creative and cultural domains. Artists can create scarce digital editions of their work. Musicians can offer exclusive experiences to token holders. Game items can be truly owned by players and traded across platforms.
The technology continues evolving, with “soulbound” tokens exploring non-transferable credentials, and dynamic NFTs that can change based on external conditions. These innovations extend what ownership can mean in digital contexts.
Understanding Trust in Web3
Trustless systems in Web3 represent one of the most revolutionary aspects of blockchain technology. Rather than requiring trust in institutions, individuals, or intermediaries, these systems allow participants to verify everything themselves.
Trustless Systems Explained
The term “trustless” does not mean that trust is absent from Web3 systems. Instead, it means that participants do not need to trust each other or any central authority. They can trust the system itself because its operation is transparent, deterministic, and cryptographically secured.
In a trustless system, smart contracts execute exactly as written. No human intervention can change the outcome once conditions are met. If you send payment to a smart contract that will release funds upon delivery confirmation, the funds will release automatically when the condition is satisfied, without either party needing to trust the other’s honesty.
This shifts trust from people and institutions to mathematics and code. Users can audit smart contracts, verify the blockchain’s state, and confirm that rules are being followed. This verifiability creates a foundation for trustless interactions between strangers worldwide.
How Cryptography Builds Trust in Web3
Cryptography provides the mathematical foundation for trust in Web3 systems. Public-key cryptography enables secure ownership through private keys that cannot be forged. Digital signatures prove that transactions were authorized by rightful owners. Hash functions ensure data integrity, making any tampering immediately detectable.
These cryptographic tools create certainty without requiring trust. When you receive cryptocurrency, you can mathematically verify that the transaction is valid, that the sender had the funds, and that the network has confirmed the transfer. No intermediary’s assurance is needed because the mathematics is irrefutable.
Consensus mechanisms extend this cryptographic trust to network-wide agreement. Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and other consensus algorithms ensure that thousands of independent nodes agree on the blockchain’s state without trusting each other. The economic incentives embedded in these mechanisms make honest behavior profitable and dishonest behavior costly.
Smart Contracts and Automated Trust
Smart contracts serve as the primary mechanism for implementing trustless systems in Web3. These self-executing programs enforce agreements automatically, removing the need for manual trust verification.
Role of Smart Contracts in Web3
Smart contracts are programs stored on the blockchain that execute when predetermined conditions are met. They can handle complex logic, manage assets, and coordinate interactions between multiple parties without any central authority overseeing the process.
In practice, smart contracts power virtually every Web3 application. Decentralized exchanges use smart contracts to enable token swaps without custodians. Lending protocols use smart contracts to manage collateral and interest calculations. NFT marketplaces use smart contracts to handle sales and royalty distributions.
The immutable nature of deployed smart contracts creates both benefits and challenges. Once deployed, the code cannot be changed, providing certainty about how the contract will behave. However, bugs in smart contract code can be exploited, and there is no way to patch vulnerabilities without creating entirely new contracts.
Eliminating Manual Trust Dependencies
Traditional agreements rely on trust that parties will fulfill their obligations, legal systems to enforce compliance, and intermediaries to facilitate execution. Smart contracts eliminate these dependencies by making non-compliance technically impossible.
Consider a simple escrow arrangement. In traditional systems, both buyer and seller must trust the escrow agent. With smart contracts, the escrow logic is encoded in transparent, verifiable code. Funds automatically release when conditions are met, and neither party can manipulate the outcome.
This automation extends to complex arrangements like insurance payouts, derivatives settlement, and supply chain management. Oracles, which bring real-world data onto the blockchain, enable smart contracts to respond to external events, triggering automatic execution based on verified information from the physical world.
Web3 vs Web2: Principles Comparison
The Web3 vs Web2 trust model represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how digital systems operate and how users interact with technology. Understanding these differences clarifies why Web3 principles matter and what changes they bring.
Centralized Trust in Web2
Web2 operates on a model of institutional trust. Users trust that Google will not read their emails maliciously, that Facebook will protect their personal data, that banks will process transactions honestly, and that cloud providers will maintain data availability. This trust is placed in organizations and their employees, policies, and systems.
When this institutional trust is violated, whether through data breaches, policy changes, or service terminations, users have limited recourse. They can switch to competitors (who operate on the same model) or accept the situation. The fundamental power asymmetry between platforms and users remains constant.
This model has enabled tremendous innovation and convenience. Centralized platforms can iterate quickly, provide customer support, and create seamless user experiences. However, these benefits come at the cost of user autonomy and the concentration of power in a small number of companies.
Decentralized Trust Model in Web3
Web3 replaces institutional trust with cryptographic verification. Rather than trusting that a company will behave honestly, users can verify every transaction and interaction. Trust is placed in mathematics and open-source code rather than corporate policies and human administrators.
This decentralized trust model distributes power among network participants. Protocol changes require community consensus. No single entity can unilaterally alter the rules. Users maintain custody of their own assets and data, eliminating the risk of platform-level actions affecting their holdings.
The trade-offs include increased personal responsibility, steeper learning curves, and currently limited recourse when users make mistakes. Web3 is still maturing, and the user experience often lags behind polished Web2 applications.
| Feature | Web2 Trust Model | Web3 Trust Model |
|---|---|---|
| Trust Basis | Institutional reputation | Cryptographic proof |
| Data Control | Platforms control user data | Users control their data |
| Transaction Verification | Trust intermediary records | Verify on public blockchain |
| Account Recovery | Customer support can help | No recovery if keys lost |
| Rule Changes | Platform decides unilaterally | Community governance |
| User Experience | Polished, beginner-friendly | Still maturing |
Governance and Community Trust
Web3 governance models represent a new approach to collective decision-making in digital systems. Rather than corporate boards making decisions behind closed doors, governance power is distributed among community members who have stake in the protocol’s success.
Decentralized Governance Models
Decentralized governance distributes decision-making power among token holders or network participants. Different protocols implement governance in various ways, from simple token voting to complex delegation systems with multiple layers of representation.
Common governance decisions include protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, treasury allocations, and partnership approvals. The transparency of blockchain-based governance means all votes and proposals are publicly visible, allowing community members to hold each other accountable.
Effective governance requires balancing multiple concerns: ensuring informed decision-making, preventing plutocratic control by large token holders, maintaining efficiency, and creating inclusive participation opportunities. The Web3 ecosystem continues experimenting with different governance mechanisms to address these challenges.
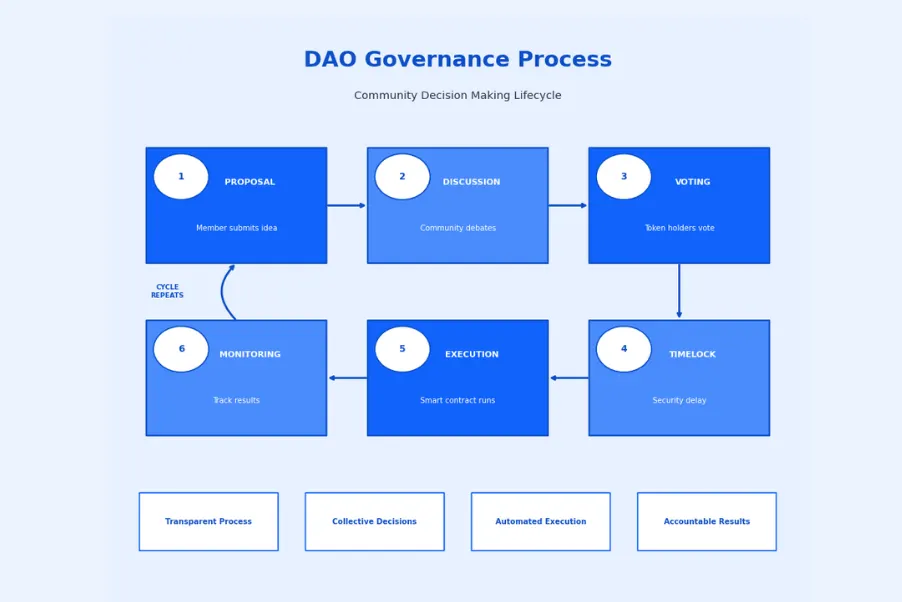
DAOs and Collective Decision-Making
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent the organizational structure native to Web3. These entities operate through smart contracts and collective governance rather than traditional corporate hierarchies. Members coordinate around shared goals, with rules encoded in transparent, immutable code.
DAOs manage billions of dollars in treasury assets, make investment decisions, fund public goods, and coordinate complex operations across global communities. They demonstrate that organizations can function effectively without centralized management, though challenges around decision-making speed and accountability remain.
The evolution of DAOs continues as communities experiment with sub-DAOs, working groups, delegation systems, and hybrid models that combine on-chain governance with off-chain coordination. These experiments are helping define what organizational structures work best in decentralized contexts.
| Stage | Description | Key Activities | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Proposal Creation | Community member drafts proposal | Research, drafting, forum discussion | 1-2 weeks |
| 2. Temperature Check | Initial community sentiment gauge | Snapshot voting, feedback collection | 3-5 days |
| 3. Formal Proposal | Refined proposal submitted on-chain | Technical review, security assessment | 1 week |
| 4. Voting Period | Token holders cast votes | Campaigning, delegation, voting | 5-7 days |
| 5. Timelock | Security delay before execution | Final review, emergency veto if needed | 2-3 days |
| 6. Execution | Approved changes implemented | Smart contract execution, monitoring | Immediate |
Real-World Applications of Web3 Principles
Web3 principles have moved beyond theoretical concepts into practical applications affecting millions of users. Understanding these applications illustrates how decentralization, ownership, and trust function in real-world contexts.
Decentralization in DeFi Platforms
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms demonstrate Web3 principles in action within financial services. These protocols enable lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest without traditional financial intermediaries. Users maintain custody of their assets throughout transactions, interacting directly with smart contracts.
Leading DeFi protocols manage billions in assets through code rather than corporate structures. Automated market makers enable token swaps without order books. Lending protocols algorithmically set interest rates based on supply and demand. Yield optimization protocols automatically move funds to maximize returns.
The transparency of DeFi allows anyone to audit protocols, verify collateralization ratios, and understand exactly how their funds are being used. This represents a stark contrast to traditional finance, where complex instruments and opaque practices contributed to the 2008 financial crisis.
Ownership and Trust in NFTs and Gaming
Gaming and digital collectibles showcase the Web3 ownership model in action. Players can truly own in-game items as NFTs, trading them freely across marketplaces without needing game publisher permission. This creates secondary economies where player skill and time investment can generate real value.
NFT art markets have enabled creators to sell directly to collectors, with smart contracts ensuring automatic royalty payments on secondary sales. This addresses a long-standing problem in traditional art markets, where artists rarely benefit when their works appreciate and change hands.
The gaming industry continues exploring blockchain integration, with some titles building entirely on-chain and others implementing selective NFT features. The evolution of these models will likely influence how digital ownership functions across entertainment broadly.
Identity and Trust in Web3 Applications
Web3 identity and ownership solutions are emerging to address how users authenticate and maintain reputations across decentralized applications. Rather than creating separate accounts for each service, users connect their wallets, which carry their transaction history, token holdings, and past interactions.
Decentralized identity protocols allow users to prove credentials without revealing underlying data. You can prove you are over 18 without sharing your birthdate, or demonstrate professional qualifications without exposing personal details. This privacy-preserving verification has applications across finance, healthcare, education, and government services.
Reputation systems built on blockchain create persistent, portable identity across applications. Your track record in one protocol can influence your access and terms in others. This creates accountability incentives while allowing users to maintain privacy about their specific identities.
Business Value of Web3 Principles
Enterprises increasingly recognize that understanding Web3 fundamentals offers competitive advantages. The core concepts of Web3 enable new business models, customer relationships, and operational efficiencies that traditional approaches cannot replicate.
Building User Trust in Web3 Platforms
Transparency inherent in blockchain technology can strengthen user trust. When customers can verify that a company is operating as claimed, whether in supply chain management, financial services, or data handling, trust develops more quickly and deeply than through marketing claims alone.
Companies building on Web3 principles can differentiate themselves through verifiable commitments. Smart contracts can encode promises about how user data will be handled, how revenues will be shared, or how governance decisions will be made. These coded commitments are more credible than policy documents that can be changed at will.
Early adopters of Web3 principles often cultivate highly engaged communities. Token holders have direct stakes in platform success, creating alignment between company and user interests rarely achieved in traditional business models.
Why Businesses Are Adopting Web3 Models
Cost reduction motivates many enterprise Web3 explorations. Eliminating intermediaries from payment processing, supply chain coordination, and contract execution can significantly reduce operational expenses. While blockchain transactions have their own costs, they often compare favorably to traditional intermediary fees for specific use cases.
New revenue models become possible through tokenization. Fractional ownership of assets, programmable loyalty points, and community-driven value creation open opportunities unavailable in traditional structures. Companies can align customer incentives with business success through token mechanisms.
Regulatory clarity is improving in many jurisdictions, reducing the uncertainty that previously deterred enterprise adoption. Companies now have clearer frameworks for implementing blockchain solutions while maintaining compliance.
Challenges in Implementing Web3 Principles
While Web3 principles offer significant potential, implementing them involves real challenges that must be understood and addressed. Honest assessment of these challenges is essential for making informed decisions about Web3 adoption.
Scalability and Usability Concerns
Blockchain scalability remains a significant technical challenge. Processing thousands of transactions per second while maintaining decentralization requires innovations in consensus mechanisms, layer-2 solutions, and network architecture. Progress is being made, but Web3 still cannot match the throughput of centralized systems for all applications.
User experience in Web3 applications often lags behind Web2 equivalents. Wallet management, gas fee estimation, transaction signing, and error handling create friction that deters mainstream adoption. Significant work is underway to abstract these complexities, but the gap between Web3 and Web2 usability persists.
Security risks multiply when users bear full responsibility for their own assets. Phishing attacks, smart contract vulnerabilities, and simple user errors can result in irreversible losses. The lack of customer support and recovery mechanisms creates real barriers for non-technical users.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Regulatory uncertainty affects Web3 adoption across jurisdictions. Different countries take varying approaches to cryptocurrency, tokens, and blockchain applications. Businesses must navigate complex and evolving legal landscapes that may affect their operations and user access.
Compliance requirements for financial services, data protection, and consumer protection do not disappear in Web3 contexts. Projects must determine how decentralized systems can meet requirements designed for centralized operators. This creates tensions between regulatory expectations and Web3 principles.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements present particular challenges for privacy-focused protocols. Balancing regulatory compliance with user privacy remains an active area of innovation and debate within the Web3 community.
Future of Web3 Principles
The key principles of Web3 continue evolving as technology matures and adoption expands. Understanding likely trajectories helps organizations and individuals prepare for upcoming changes.
Evolution of Decentralization and Ownership
Decentralization is becoming more nuanced. Pure decentralization maximalism is giving way to pragmatic approaches that optimize for specific outcomes. Different applications may require different degrees of decentralization, and hybrid models combining centralized efficiency with decentralized trust are emerging.
The Web3 ownership model is expanding into new domains. Real-world asset tokenization is bringing physical property onto blockchain rails. Intellectual property, carbon credits, and other traditionally illiquid assets are becoming tradable through tokenization. These expansions test and extend our understanding of digital ownership.
Interoperability between different blockchains is improving, enabling ownership to flow more freely across networks. Cross-chain bridges, shared security models, and standardized token formats are creating more unified Web3 experiences.
Trust as the Foundation of Web3 Adoption
Trustless systems in Web3 are becoming more accessible as user interfaces improve and abstraction layers hide technical complexity. Users will increasingly benefit from cryptographic guarantees without needing to understand the underlying mechanisms.
Institutional adoption is validating Web3 trust models. When major financial institutions, governments, and corporations implement blockchain solutions, they signal confidence in these systems’ security and reliability. This mainstream validation encourages broader adoption.
The ultimate vision of Web3 involves seamless integration of trustless principles into everyday digital experiences. Users may not know or care that they are interacting with blockchain technology, just as most internet users today do not think about TCP/IP protocols. Trust will simply work differently, embedded invisibly in the systems people use.
Web3 Trust and Ownership
Understand how decentralization and ownership redefine trust in the Web3 ecosystem.
Why Decentralization, Ownership, and Trust Define Web3
The key principles of Web3, specifically decentralization, ownership, and trust, collectively define a new paradigm for digital interaction. Decentralization distributes power and eliminates single points of control. The Web3 ownership model gives users true sovereignty over their digital assets and data. Trustless systems replace institutional faith with cryptographic verification.
These principles matter because they address fundamental issues with how digital systems currently operate. Concentration of power in a few technology companies, lack of user control over personal data, and dependence on intermediaries create vulnerabilities that Web3 principles are designed to resolve.
Understanding Web3 fundamentals prepares individuals and organizations for a changing digital landscape. Whether as participants building on these principles, users benefiting from their implementation, or observers understanding their implications, familiarity with the core concepts of Web3 will prove valuable as this paradigm shift continues unfolding.
The journey toward a more decentralized, user-owned, and trustworthy internet is ongoing. Challenges remain significant, but progress continues across technology, adoption, and regulation. The Web3 vs Web2 trust model represents not just a technical evolution but a philosophical shift in how we relate to digital systems and each other within them.
Frequently Asked Questions
The key principles of Web3 revolve around decentralization, user ownership, and trustless systems. Unlike traditional internet models, Web3 eliminates central authorities by distributing control across networks of participants. These principles ensure that users maintain sovereignty over their data, assets, and digital identities while interacting with applications that operate transparently without requiring blind trust in intermediaries.
Decentralization in Web3 functions by distributing data and decision-making power across multiple nodes in a blockchain network rather than storing everything on centralized servers. Each participant in the network maintains a copy of the shared ledger, and consensus mechanisms validate transactions without needing a central authority. This architecture prevents single points of failure and makes censorship extremely difficult.
The Web3 vs Web2 trust model represents a fundamental paradigm shift. In Web2, users must trust centralized platforms like banks, social media companies, and cloud providers to handle their data honestly and securely. Web3 replaces this institutional trust with cryptographic proof and transparent code execution, allowing users to verify every transaction and smart contract operation independently.
Web3 fundamentals for beginners include understanding wallet setup, gas fees, blockchain transactions, and the importance of private key security. Beginners should learn how to connect wallets to decentralized applications, recognize common scams, and understand the irreversibility of blockchain transactions. Starting with small amounts and learning on test networks before handling significant assets is highly recommended for newcomers.
Businesses are adopting Web3 principles because they offer new ways to build customer trust, create innovative revenue models, and reduce dependence on intermediaries. The transparency of blockchain operations can enhance brand credibility, while tokenization enables new forms of customer loyalty programs and community engagement. Additionally, decentralized systems can reduce operational costs associated with traditional payment processors and data management.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






