Key Takeaways
- Decentralization in Web3 eliminates single points of failure and central authorities, creating trustless systems where users maintain full control over their data and digital assets
- Peer-to-peer network structures and distributed ledger technology form the foundation of decentralized Web3 architecture, enabling direct participant interaction without intermediaries
- Smart contracts serve as decentralized logic engines that execute automatically, transparently, and immutably, replacing traditional backend systems in dApp architecture
- Decentralized governance through DAOs and token-based voting empowers community-driven protocol decisions with transparent, verifiable outcomes
- Security in decentralized networks benefits from cryptographic protection and distributed validation, making attacks prohibitively expensive and easily detectable
- Layer 2 scaling solutions and modular blockchain architecture address throughput limitations while preserving decentralization guarantees [1]
- Censorship resistance and permissionless access ensure global, borderless participation regardless of geographic or political constraints
- Technical challenges including complex infrastructure, debugging difficulties, and user onboarding barriers require specialized expertise and innovative solutions
Introduction to Decentralization in Web3
The emergence of Web3 represents a fundamental shift in how digital systems are designed, operated, and governed. At the heart of this transformation lies decentralization in Web3, a principle that redistributes power from centralized entities to network participants. This architectural philosophy challenges decades of internet infrastructure built around centralized servers, databases, and authorities, proposing instead a model where trust emerges from mathematical proofs and distributed consensus.
Understanding decentralization’s impact on Web3 requires examining not just the technical mechanisms but also the philosophical underpinnings that drive this movement. The transition from Web2’s centralized platforms to Web3’s distributed networks affects every aspect of application building, from system architecture to user experience design.
Understanding the Core Idea of Decentralization
Decentralization as a concept extends beyond mere technical architecture to encompass a complete reimagining of digital trust and authority.
What Decentralization Means in Blockchain?
In blockchain decentralization, control over the network distributes across numerous independent nodes rather than concentrating in a single organization or server farm. Each node maintains a complete copy of the ledger and participates in validating transactions, ensuring no single party can unilaterally alter records or censor participants. This distributed architecture creates systems where trust derives from transparent rules and mathematical verification rather than institutional reputation.
Blockchain decentralization operates on multiple dimensions including geographic distribution of nodes, diversity of node operators, and decentralization of governance and decision-making processes. True decentralization requires attention to all these dimensions, as centralization in any layer can undermine the system’s integrity and resilience.
Evolution From Web2 to Web3
The evolution from Web2 to Web3 represents a paradigm shift from read-write platforms controlled by corporations to read-write-own networks governed by participants. Web2 platforms like social media sites and cloud services concentrate user data and platform control in the hands of companies that can change rules, access data, or terminate accounts unilaterally. Web3 architecture instead embeds user rights directly into protocol code, creating systems where participants maintain sovereignty over their digital presence.
This transition addresses fundamental issues with Web2’s centralized model including data privacy violations, platform censorship, value extraction from users, and single points of failure that can affect millions of users simultaneously when systems experience outages or security breaches.
Why Decentralization Is Fundamental to Web3?
Decentralization isn’t merely a technical preference in Web3 but rather the foundational principle that enables all other benefits these systems provide.
Trustless and Permissionless Systems
Trustless systems eliminate the need to trust any single party by ensuring all operations are verifiable and all rules are enforced automatically through code. Users can verify transaction validity independently without relying on attestations from authorities. Permissionless access means anyone can participate in the network as a user, validator, or builder without requiring approval from gatekeepers.
These properties combine to create open financial and social infrastructure accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location, identity, or relationship with existing institutions.
Eliminating Central Authorities
By eliminating central authorities, decentralized Web3 systems remove points where power can be abused, rules can be changed arbitrarily, or access can be restricted unfairly. Protocol rules apply equally to all participants, and changes require community consensus rather than unilateral decisions. This creates more predictable, fair systems where participants can trust the rules rather than trusting rule-makers.
What Is Decentralization in Web3 Development?
Decentralized Web3 development encompasses specific technical approaches and architectural patterns that distinguish it from traditional software building.
Decentralized Web3 Architecture Explained
Web3 architecture fundamentally differs from traditional client-server models by distributing processing, storage, and validation across networks of participants.
Peer-to-Peer Network Structure
Peer-to-peer networks form the communication layer of Web3 systems, enabling direct information exchange between participants without central routing. In these decentralized networks, each node acts as both client and server, capable of requesting and providing data to other nodes. This architecture ensures the network remains functional even when significant portions go offline, providing exceptional fault tolerance.
P2P networks in Web3 handle not just transaction propagation but also state synchronization, block distribution, and discovery of new peers. Protocols like libp2p provide standardized implementations that Web3 projects can leverage to build robust networking layers.
Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledger technology provides the data layer for Web3 systems, maintaining synchronized state across all network participants. Unlike traditional databases where a single authority controls writes, distributed ledgers allow any authorized participant to propose state changes that become permanent once validated through consensus. This creates an append-only, tamper-evident record that all participants can trust.
| Component | Function | Decentralization Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| P2P Network Layer | Node communication and data propagation | No central servers to target or censor |
| Distributed Ledger | State storage and synchronization | Tamper-evident, replicated data |
| Consensus Protocol | Transaction validation and ordering | No trusted validators required |
| Smart Contract Layer | Programmable business logic | Automated, transparent rule execution |
| Client Interface | User interaction with protocols | Multiple access points, no lock-in |
Role of Blockchain in Web3 Decentralization
Blockchain technology provides the foundation upon which Web3 decentralization is built, combining cryptography, game theory, and distributed systems.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms enable decentralized networks to agree on the state of the ledger without requiring a central coordinator. Proof of Work achieves this through computational competition, while Proof of Stake uses economic incentives to align validator behavior with network health. These mechanisms ensure that even in adversarial environments with potentially malicious participants, the network can maintain accurate, consistent state.
The choice of consensus mechanism profoundly impacts a blockchain’s decentralization properties, affecting factors like validator accessibility, energy consumption, and resistance to various attack vectors.
Smart Contracts as Decentralized Logic
Smart contracts represent programmable rules that execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, serving as the decentralized logic layer for Web3 applications. Unlike traditional software where operators can modify behavior arbitrarily, smart contract logic is immutable once deployed, providing users certainty about how applications will behave. This deterministic execution across all nodes ensures consistent outcomes regardless of which node processes a transaction.
Impact of Decentralization on Web3 Application Development
The impact of decentralization on Web3 fundamentally transforms how applications are designed, built, and maintained.
Decentralized Application (dApp) Development
Building decentralized applications requires fundamentally different approaches compared to traditional software.
How dApps Differ From Traditional Apps
Decentralized applications (dApps) differ from traditional applications primarily in their backend architecture, where centralized servers are replaced by blockchain networks and smart contracts. Users interact directly with on-chain logic through their wallets rather than authenticating through centralized identity providers. Data persists on the distributed ledger rather than in company-controlled databases, giving users true ownership of their information and assets.
This architectural shift means dApps can continue operating as long as the underlying blockchain exists, independent of any single company’s continued operation or interest in maintaining the application.
Backend-Free Application Models
Many dApps operate with minimal or no traditional backend infrastructure, relying entirely on smart contracts for business logic and blockchain for data storage. This backend-free model eliminates server costs, DevOps complexity, and central points of failure. Frontend interfaces can be hosted on decentralized storage networks like IPFS, creating truly unstoppable applications that no single entity can take offline.
Important: While backend-free models offer significant benefits, they require careful smart contract design and security auditing. Once deployed, contract logic cannot be easily modified, making thorough testing and formal verification essential before mainnet deployment.
Builder Control and Flexibility
Decentralization provides builders with new freedoms while also imposing different constraints than traditional building environments.
Open-Source Practices
Web3 decentralization embraces open-source practices where code is publicly auditable, forkable, and improvable by anyone. This transparency builds trust as users can verify exactly what logic governs their interactions. Open-source building also accelerates innovation through code reuse, composability between protocols, and community contributions that improve security and functionality.
Reduced Platform Dependency
Builders on decentralized networks enjoy reduced dependency on any single platform, hosting provider, or payment processor. Applications built on public blockchains cannot be deplatformed by decisions of private companies. This independence allows builders to create applications that might be controversial or compete with established interests without fear of arbitrary removal.
Security and Trust Benefits of Decentralization

Decentralization provides inherent security benefits that complement traditional security measures.
Enhanced Security in Web3 Systems
The distributed nature of Web3 systems creates security properties impossible to achieve in centralized architectures.
No Single Point of Failure
Decentralized networks eliminate single points of failure by distributing operations across many independent nodes. An attacker cannot bring down the network by targeting a single server or data center. Even if a significant portion of nodes are compromised or go offline, the remaining nodes can continue operating, maintaining network availability and data integrity.
Cryptographic Security Models
Web3 systems employ cryptographic security models where user assets and data are protected by mathematical guarantees rather than trust in custodians. Private keys provide strong authentication that cannot be reset or overridden by administrators. Digital signatures ensure transaction authenticity and integrity, while hash functions provide tamper detection. These cryptographic foundations make security guarantees verifiable and independent of institutional trust.
Trustless Interactions in Web3
Trustless interactions represent one of decentralization’s most transformative contributions to digital systems.
Transparent Transactions
All transactions on public blockchains are transparent and verifiable by anyone, creating unprecedented accountability in digital systems. Users can audit the complete history of any address, verify fund flows, and confirm that protocols operate as advertised. This transparency discourages fraud and enables community monitoring of system health.
Immutable Smart Contracts
Smart contract immutability ensures that the rules governing user interactions cannot be changed after deployment without explicit upgrade mechanisms approved by governance. Users can rely on contracts behaving consistently over time, providing a foundation for long-term agreements and financial instruments that would be impractical if counterparties could unilaterally change terms.
Role of Decentralization in Web3 Governance
Decentralization enables novel governance models that distribute decision-making power to stakeholders.
Decentralized Governance Models
Web3 introduces governance mechanisms that operate without central authorities making decisions.
DAO-Based Decision Making
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) enable collective decision-making where token holders vote on proposals affecting protocol parameters, treasury allocation, and strategic direction. DAOs operate transparently with all proposals, votes, and outcomes recorded on-chain for anyone to verify. This model aligns governance power with economic stake, incentivizing decisions that benefit long-term protocol health.
Token-Based Voting Systems
Token-based voting systems quantify governance participation through token holdings, with various mechanisms to balance plutocratic tendencies with broader participation. Techniques like quadratic voting, time-weighted voting, and delegation systems help create more nuanced governance that considers both stake size and community breadth. These systems continue evolving as the ecosystem experiments with different approaches to decentralized decision-making.
Community-Driven Work
Decentralization enables communities to direct protocol evolution rather than relying on corporate roadmaps.
User Participation in Protocol Growth
Users in decentralized protocols participate actively in growth through governance, testing, feedback, and even code contributions. This creates tight feedback loops between users and protocol improvements, ensuring that changes reflect actual community needs. Active participation also builds stronger communities with deeper investment in protocol success.
Incentive-Aligned Ecosystems
Tokenomics design aligns incentives across different ecosystem participants including users, validators, builders, and investors. Well-designed incentive structures ensure that individually rational behavior contributes to collective benefit, creating self-sustaining ecosystems that grow through participant contributions rather than corporate subsidy.
| Aspect | Centralized Governance | Decentralized Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Authority | Corporate leadership, board of directors | Token holders and community members |
| Transparency | Limited, often opaque processes | Full on-chain visibility of all decisions |
| Speed | Fast executive decisions | Deliberative, voting periods required |
| Accountability | To shareholders and regulators | To all token holders equally |
| Participation | Limited to management team | Open to all stakeholders |
Impact of Decentralization on Web3 Scalability
Scalability represents one of the most significant challenges in maintaining decentralization while achieving mainstream performance requirements.
Scalability Challenges in Decentralized Networks
The distributed nature of decentralized networks introduces inherent scalability constraints that require innovative solutions.
Network Congestion Issues
Decentralized networks can experience congestion when transaction demand exceeds processing capacity, leading to increased fees and delayed confirmations. Unlike centralized systems that can add servers to handle load, decentralized networks must balance throughput increases against maintaining accessibility for node operators. This tension creates challenging design tradeoffs that the ecosystem continues working to resolve.
Throughput Limitations
Maintaining decentralization requires that regular participants can validate all transactions, which limits how much data the network can process. Higher throughput typically requires more powerful hardware, potentially centralizing validation to well-resourced operators. The blockchain trilemma describes this tension between decentralization, security, and scalability that constrains design choices.
Scalability Solutions in Web3
The Web3 ecosystem has developed various approaches to scale while preserving decentralization benefits.
Layer 2 Scaling Technologies
Layer 2 solutions process transactions off the main chain while inheriting its security guarantees through cryptographic proofs or fraud detection mechanisms. Rollups, state channels, and sidechains each offer different tradeoffs between throughput, cost, and security assumptions. These technologies enable applications to achieve thousands of transactions per second while maintaining connection to highly decentralized base layers.
Modular Blockchain Architecture
Modular blockchain architecture separates concerns like execution, data availability, and consensus into specialized layers that can be optimized independently. This approach allows each layer to achieve high performance in its specific function while maintaining overall system decentralization. Projects building blockchain solutions and decentralized applications increasingly adopt modular designs to balance performance with decentralization requirements.
How Decentralization Improves Transparency and Censorship Resistance?
Transparency and censorship resistance emerge naturally from decentralized architecture, providing crucial properties for open systems.
Transparency in Decentralized Web3 Platforms
Decentralized systems enable unprecedented transparency in digital operations.
Publicly Verifiable Transactions
Every transaction on a public blockchain is visible to anyone, creating a complete, auditable history of all system activity. This transparency enables users to verify claims independently, track fund flows, and confirm that protocols operate honestly. Public verifiability builds trust through observation rather than requiring faith in attestations from authorities.
Open Protocol Design
Decentralized protocols publish their logic openly, allowing anyone to review, audit, and understand system behavior. This openness contrasts sharply with proprietary systems where users must trust that software behaves as described. Open protocols also enable competition and innovation as anyone can build interfaces, extensions, or competing implementations.
Censorship Resistance in Web3
Censorship resistance represents one of decentralization’s most powerful properties for ensuring open access to digital systems.
Permissionless Access
Permissionless access means anyone can use Web3 protocols without requiring approval from gatekeepers. Users generate their own accounts through cryptographic key generation, eliminating identity verification requirements that can exclude marginalized populations. This open access creates truly global systems available to anyone regardless of their relationship with existing institutions.
Global and Borderless Networks
Decentralized networks operate globally without respect to political boundaries, providing consistent services regardless of user location. Nodes distributed worldwide ensure that local restrictions cannot prevent access to the network as long as users can reach any participating node. This borderless nature makes Web3 particularly valuable for users in regions with restrictive internet policies.
Challenges of Decentralization in Web3 Development
Despite its benefits, decentralization introduces significant challenges that builders and users must navigate.
Technical Challenges for Builders
Building decentralized systems requires specialized knowledge and approaches that differ substantially from traditional software work.
Complex Infrastructure Requirements
Decentralized Web3 building requires understanding multiple complex technologies including blockchain networks, cryptographic primitives, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract languages. Teams must manage node infrastructure, handle wallet integrations, and optimize for on-chain gas costs. This complexity raises the barrier to entry and increases project costs compared to traditional web building.
Debugging and Maintenance Issues
Debugging decentralized applications presents unique challenges because transactions are irreversible and network conditions are difficult to reproduce exactly. Smart contract bugs can result in permanent fund losses, creating extreme pressure for correctness that exceeds typical software requirements. Maintenance becomes complicated by immutability, requiring carefully designed upgrade patterns or migration strategies.
Selecting the Right Decentralization Model: Key Criteria
When evaluating decentralization approaches for your project, consider these essential factors:
- Security Requirements: Assess the value at risk and choose decentralization levels that provide appropriate protection
- Performance Needs: Balance throughput requirements against decentralization tradeoffs using Layer 2 or modular approaches
- Governance Model: Determine how decisions will be made and who should have voting power
- Regulatory Environment: Consider how different decentralization choices affect compliance requirements
- User Experience: Evaluate the friction introduced by decentralization and plan mitigation strategies
- Upgrade Capability: Design for evolution while maintaining user trust in system stability
User Adoption Challenges
Decentralized systems present adoption barriers that can slow mainstream uptake.
Usability and Onboarding Barriers
Using decentralized applications requires understanding concepts like wallets, private keys, gas fees, and transaction confirmation that are unfamiliar to mainstream users. The irreversibility of blockchain transactions creates anxiety for users accustomed to reversible actions and customer support. Improving usability while maintaining decentralization benefits remains an active area of innovation.
Education and Awareness Gaps
Many potential users lack understanding of why decentralization matters or how it benefits them, making it difficult to justify the additional friction these systems currently impose. Education efforts must communicate complex technical concepts in accessible terms while avoiding both oversimplification and information overload. Building this understanding takes time and sustained effort across the ecosystem.
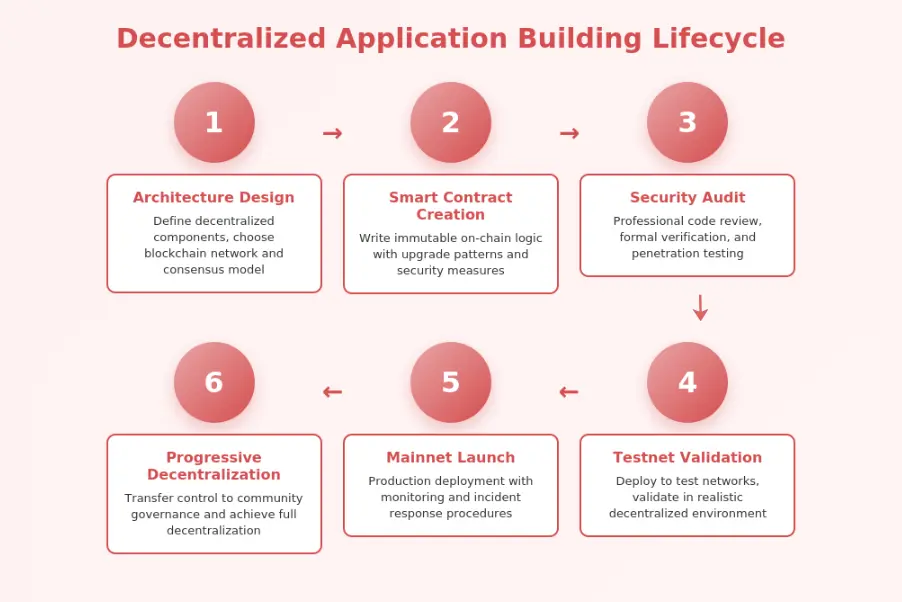
| Phase | Stage | Activities | Decentralization Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Architecture Design | Define system components and interactions | Choose blockchain, consensus, and governance model |
| 2 | Smart Contract Creation | Write and test on-chain logic | Design for immutability and upgradeability |
| 3 | Security Audit | Professional review and testing | Verify decentralization assumptions hold |
| 4 | Testnet Deployment | Deploy to test networks | Validate in realistic decentralized environment |
| 5 | Mainnet Launch | Production deployment | Transition control to community governance |
| 6 | Progressive Decentralization | Gradual power distribution | Achieve full decentralization over time |
Future of Decentralization in Web3 Development
Decentralization continues evolving as the Web3 ecosystem matures and addresses current limitations.
Evolving Decentralized Web3 Infrastructure
Infrastructure improvements will make decentralized systems more accessible and capable.
Integration of Advanced Consensus Models
Next-generation consensus mechanisms promise to improve scalability, reduce energy consumption, and enhance security while maintaining or improving decentralization. Research into mechanisms like proof of stake variants, directed acyclic graphs, and committee-based approaches continues yielding improvements. These advances will enable decentralized networks to compete with centralized alternatives on performance metrics.
Improved Tooling for Builders
Better tooling will lower barriers to building decentralized applications, enabling more creators to participate in Web3 innovation. Improved testing frameworks, debugging tools, and abstraction layers will make complex blockchain interactions more accessible. This tooling maturation follows patterns seen in earlier technology transitions where improved tooling drove mainstream adoption.
Decentralization as a Driver of Web3 Innovation
Decentralization will continue enabling new models impossible in centralized systems.
Building Trustless Digital Economies
Trustless digital economies enabled by decentralization will expand to encompass more economic activity, from finance to creative work to identity management. These systems will provide alternatives to centralized intermediaries that extract value and impose restrictions. The vision of programmable, open, fair economic infrastructure drives continued innovation in decentralized systems.
Long-Term Impact on Internet Architecture
Decentralization may eventually reshape fundamental internet infrastructure, replacing centralized services with distributed alternatives. Decentralized storage, computing, and identity systems could become standard components of internet architecture. This transformation would create a more resilient, open, and user-empowering internet aligned with the original vision of distributed, peer-to-peer computing.
Conclusion
Decentralization’s impact on Web3 encompasses every dimension of how digital systems are built, operated, and governed.
How Decentralization Shapes the Future of Web3 Development?
The transformation driven by decentralization represents a fundamental shift in digital infrastructure philosophy.
Scale Web3 Solutions with Decentralization
Discover how decentralization transforms Web3 applications, enhances security, and drives scalable, innovative blockchain solutions for the next-generation digital ecosystem.
Key Takeaways for Builders and Businesses
Decentralization in Web3 offers transformative benefits including elimination of single points of failure, trustless operation, censorship resistance, and community governance. These advantages come with tradeoffs in complexity, scalability, and user experience that require thoughtful navigation. Success in decentralized systems requires understanding both the technical mechanisms and the philosophical principles that guide design decisions.
For businesses evaluating Web3 opportunities, decentralization represents both competitive advantage and technical challenge. Organizations that master decentralized architecture can create products with unique properties impossible in centralized systems. The investment in understanding decentralization pays dividends through access to growing Web3 markets and alignment with user demands for sovereignty and transparency.
Final Thoughts on Decentralized Innovation
Web3 decentralization represents more than a technical architecture choice; it embodies a vision of digital systems that serve users rather than extracting from them. As blockchain-based building matures and tooling improves, the friction associated with decentralization will decrease while its benefits remain. The future of Web3 infrastructure points toward decentralization as the default foundation, creating an internet where trust emerges from transparent rules rather than institutional authority.
The journey toward this decentralized future requires continued innovation, education, and commitment from builders, users, and communities. Those who understand and embrace decentralization’s implications position themselves to lead in the emerging Web3 economy. The impact of decentralization on Web3 will only deepen as these systems mature, making now the ideal time to build understanding and capability in this transformative technology paradigm.
Frequently Asked Questions
Decentralization in Web3 refers to the distribution of control, data, and decision-making power across a network of participants rather than relying on a single central authority. This architectural approach ensures that no single entity can control or manipulate the system, creating more resilient and trustworthy digital ecosystems. In Web3, decentralization is achieved through blockchain technology, peer-to-peer networks, and consensus mechanisms that enable transparent and tamper-resistant operations.
Peer-to-peer networks form the communication backbone of Web3 by allowing nodes to directly exchange information without routing through central servers. This architecture ensures that the network remains operational even if some nodes go offline, providing high availability and fault tolerance. P2P networks also distribute the computational and storage burden across participants, making the system more scalable and resistant to targeted attacks.
Decentralization fundamentally changes how applications are architected by replacing traditional backend servers with blockchain networks and smart contracts. Builders must design applications that interact with distributed nodes rather than centralized databases, requiring different approaches to data storage, user authentication, and state management. This shift introduces new considerations around gas costs, transaction finality, and network consensus while eliminating single points of failure.
Decentralization is the foundational principle that gives blockchain its core properties of immutability, censorship resistance, and trustless operation. Without decentralization, a blockchain would simply be a distributed database controlled by a single entity, vulnerable to manipulation and censorship. The distributed nature ensures that transactions are validated by multiple independent parties, making the system highly resistant to attacks and manipulation.
Builders working with decentralized systems must navigate complex infrastructure requirements including node management, wallet integration, and smart contract deployment across multiple networks. Debugging and testing become more challenging because transactions are irreversible and the distributed nature makes it difficult to reproduce exact network conditions. Additionally, achieving good user experience while maintaining decentralization principles requires creative solutions for issues like transaction speed and gas fee management.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






