Key Takeaways
- On-chain MLM logic runs entirely on smart contracts, offering full transparency and automated payouts without any middleman involvement.
- Off-chain MLM logic uses centralized servers and APIs, delivering faster speeds, lower costs, and greater flexibility for complex business rules.
- Gas fees and blockchain scalability limits remain the biggest drawbacks of on-chain systems, while trust and centralization risks affect off-chain setups.
- A hybrid model that combines both on-chain and off-chain elements often provides the most balanced and practical approach for real-world MLM platforms.
- Choosing between on-chain and off-chain MLM logic depends on your specific priorities: transparency vs. speed, cost vs. security, and trust vs. flexibility.
- Nadcab Labs, with 8+ years in blockchain development, recommends evaluating your user base size, budget, and regulatory needs before picking an architecture.
Introduction to MLM Logic in Blockchain Systems
Multi-level marketing has been around for decades. But the technology behind it has changed a lot in recent years. When blockchain entered the picture, MLM businesses got access to tools like smart contracts, decentralized ledgers, and trustless payment systems. These tools opened the door to a new debate: should your MLM logic run on-chain, off-chain, or somewhere in between?
If you are planning to launch a cryptocurrency MLM software platform or you already run one, understanding how these two approaches work is critical. The choice between on-chain and off-chain MLM logic affects everything from cost to speed, from security to scalability. And making the wrong call can lead to problems that are expensive to fix later.
This article breaks down both models in plain terms. We will look at how each one works, what they are good at, where they fall short, and when you should use one over the other. We will also touch on hybrid setups that combine the strengths of both worlds. At Nadcab Labs, we have spent more than 8 years building blockchain solutions, including MLM platforms, so we are drawing from hands-on experience throughout this guide.
Before we go further, it helps to understand what MLM means, its types, and how it is regulated globally, since the logic layer you choose must align with the compensation plan and the legal requirements of your target market.
What is On-Chain MLM Logic?
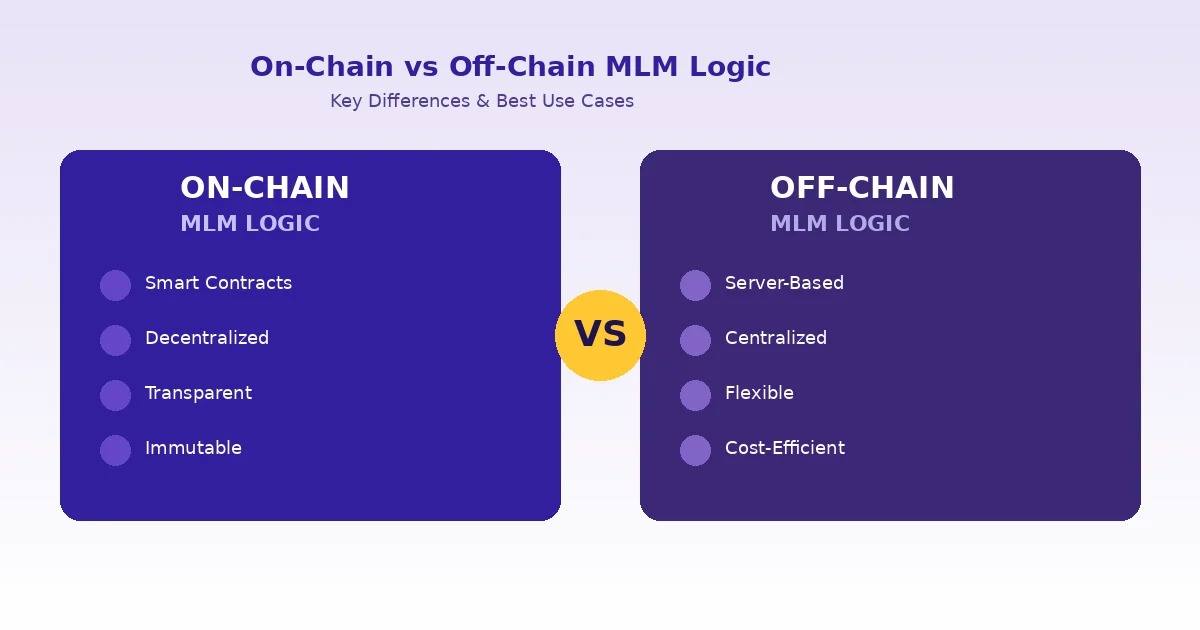
On-chain MLM logic means that the entire business logic of your MLM system lives on a blockchain. The rules for commissions, referral tracking, rank upgrades, bonuses, and payouts are all written into smart contracts. Nothing is stored on a private server. Everything runs on a distributed ledger that anyone can verify.
Think of it like a vending machine. You put in the right amount, press a button, and you get your product. No cashier needed. Smart contracts work the same way for MLM. When a user refers someone and that person makes a purchase or investment, the contract automatically calculates the commission and sends it to the right wallet. There is no human approval step. No backend team processing payments.
Platforms built on Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Tron, and Polygon are common choices for on-chain MLM systems. The contracts are deployed once, and they execute the same way every time. This makes them predictable and tamper-proof, which is a big selling point for users who want proof that the system is fair.
According to Wikipedia’s overview of smart contracts, these self-executing programs enforce the terms of an agreement directly in code, removing the need for intermediaries. That definition captures exactly what on-chain MLM logic aims to do.
How On-Chain MLM Logic Works in Smart Contracts
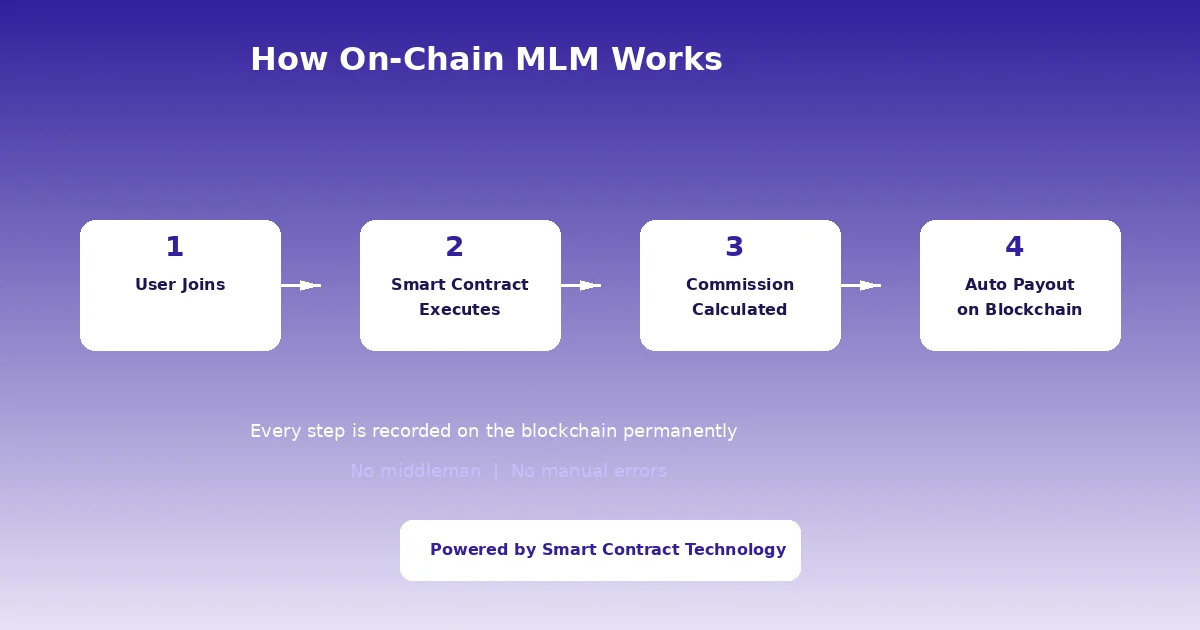
Let us walk through a typical on-chain MLM process step by step.
First, a user connects their crypto wallet to the platform and registers. The smart contract records this user on the blockchain, linking them to their referrer. This forms the genealogy tree, which is the backbone of any MLM structure.
When the new user makes a purchase or deposits funds, the smart contract kicks in. It reads the compensation plan rules that are coded into it. Based on those rules, it calculates who gets what. For example, if the plan says that a direct referrer gets 10% and the second level gets 5%, the contract sends those amounts instantly to the respective wallets.
Every single transaction, from registration to payout, is recorded on the blockchain. This means there is a permanent, public record of every action. No one can go back and change it. No one can claim they did not receive a payment if the blockchain says they did.
The lifecycle of an on-chain MLM transaction looks like this:
Step 1: User connects wallet and registers via the smart contract.
Step 2: Registration is recorded on-chain with referrer mapping.
Step 3: User deposits or purchases through the contract.
Step 4: Smart contract auto-calculates commissions based on coded rules.
Step 5: Payouts are sent directly to upline wallets in real time.
Step 6: All actions are permanently logged on the blockchain.
At Nadcab Labs, we have deployed on-chain MLM systems across Ethereum and BNB Chain for clients who prioritize maximum transparency. Our smart contracts go through rigorous smart contract testing for blockchain security before going live, because even a small bug in an on-chain system can be very costly once the contract is deployed.
Core Features of On-Chain MLM Systems
On-chain MLM platforms share several defining characteristics that separate them from traditional software-based systems.
The most obvious feature is immutability. Once a smart contract is deployed, the rules cannot be changed unless the contract was designed with an upgrade mechanism. This gives participants confidence that the rules will not be altered after they join.
Automated execution is another hallmark. There is no manual processing. No waiting for admin approval. Commissions go out the moment the triggering event happens. This removes human error and delays from the equation.
Public verifiability is perhaps the most attractive feature for users. Anyone can look at the blockchain explorer, read the contract code (if it is verified), and see exactly how money flows. This level of openness builds trust in ways that traditional MLM platforms cannot easily match.
Token integration is also straightforward. Because everything lives on the blockchain, on-chain systems can easily work with native cryptocurrencies and custom tokens. This is particularly useful for MLM platforms that have their own token economy.
Advantages of On-Chain MLM Logic
Complete Transparency. Every transaction is visible on a public ledger. Participants do not have to trust the company behind the platform because they can verify everything themselves. This is especially valuable in an industry where trust has historically been a major issue.
Automation Without Middlemen. Smart contracts handle all the heavy lifting. From calculating commissions to sending payouts, everything happens automatically. This cuts down on operational costs for the business owner and ensures faster payouts for participants.
Tamper-Proof Records. Once data is written to the blockchain, it cannot be edited or deleted. This protects both the company and its members from disputes about payments, rankings, or referral counts.
Global Accessibility. Anyone with a crypto wallet and internet access can participate, regardless of where they live. There are no bank account requirements, no wire transfer delays, and no currency conversion hassles.
Understanding how crypto MLM systems work at a technical level can help you see why these advantages matter so much in practice.
Limitations of On-Chain MLM Logic
Gas Costs. Every action on the blockchain costs gas. On Ethereum, these fees can spike during busy periods. If your MLM system processes thousands of small transactions daily, gas fees can eat into profits significantly.
Scalability Constraints. Blockchains have limited throughput. Ethereum handles roughly 15 to 30 transactions per second. If your platform has thousands of active users making transactions at the same time, bottlenecks are inevitable.
Complexity of Updates. Changing the rules of an already-deployed smart contract is not simple. You either need to build upgradeable proxy patterns from the start or deploy an entirely new contract and migrate users. Both options involve risk and cost.
Limited Business Logic. Smart contracts are not ideal for complex calculations or workflows that involve conditional logic, external data, or frequent changes. The more complex the compensation plan, the harder and more expensive it becomes to code it entirely on-chain.
What is Off-Chain MLM Logic?
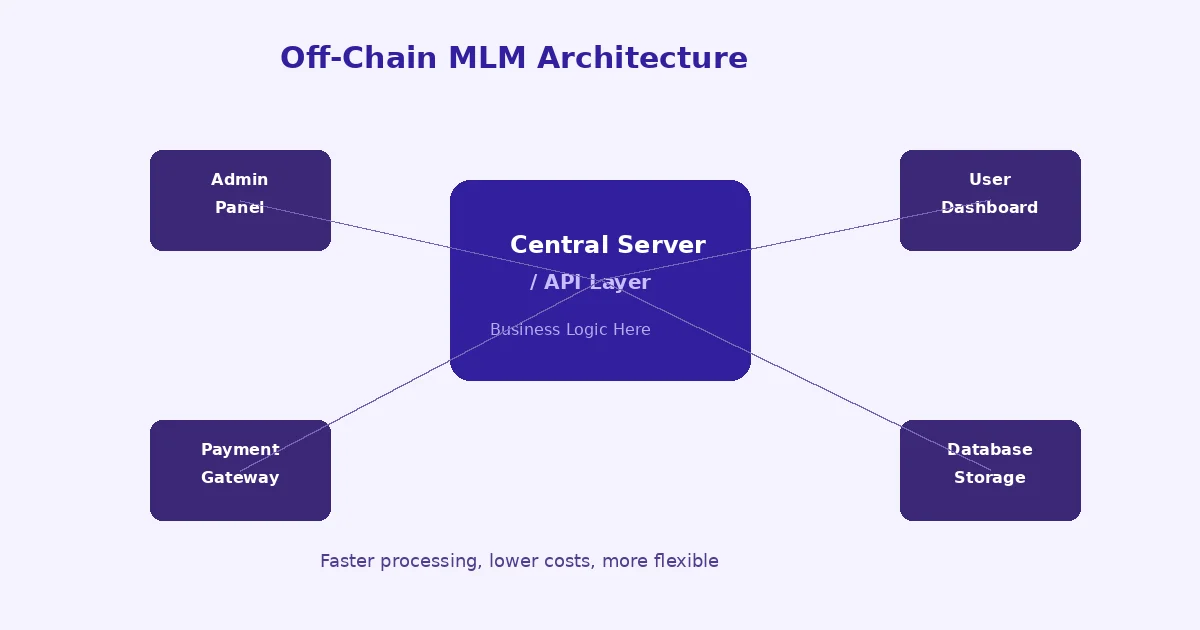
Off-chain MLM logic runs on centralized servers, just like traditional web applications. The MLM business rules, commission calculations, user management, and reporting all happen on a backend server. The blockchain might still be involved for certain tasks like payments, but the core logic sits off the blockchain.
Think of it as a regular software application with optional blockchain features. The admin panel, the user dashboard, the referral tracking, and the bonus calculations all run on a server controlled by the company. Data is stored in a traditional database like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
This is the model most cryptocurrency MLM plans have historically used, and it remains popular because it offers greater control and flexibility. The company can update commission rules, add new bonus structures, or change the user interface without touching any smart contracts.
How Off-Chain MLM Logic Works with Servers or APIs
In an off-chain MLM system, users interact with a web or mobile application. When a user signs up, the application saves their data to a centralized database. Their referral link, personal information, and position in the genealogy tree are all managed server-side.
When a transaction happens, such as a purchase or a deposit, the backend server processes it. The server runs the commission calculation algorithms, updates balances in the database, and queues payouts. Depending on the platform, payouts might happen in cryptocurrency (sent through an API call to the blockchain) or through traditional payment methods.
The key difference here is that the server acts as the brain of the operation. It makes all the decisions. It holds all the data. And it can be updated, patched, or modified at any time by the development team.
Off-chain systems often use APIs to connect with external services. Payment gateways, KYC providers, email notification services, and analytics tools all plug in through API integrations. This is much harder to do in a purely on-chain setup.
Core Features of Off-Chain MLM Systems
Off-chain MLM platforms have their own set of distinctive features that make them suitable for many real-world scenarios.
Centralized data management is the most defining characteristic. All user data, transaction records, and business logic live on servers that the company controls. This allows for faster queries, complex reporting, and easier data manipulation.
Flexible business rules are another big advantage. Want to change the commission structure next month? Just update the server code. No need to redeploy a smart contract or worry about migration headaches. The ability to iterate quickly is crucial for businesses that are still refining their compensation plans.
Rich user interfaces are much easier to build when the backend is off-chain. You can create detailed dashboards with real-time analytics, interactive genealogy trees, and notifications without worrying about gas fees for every data read.
Integration with existing systems is seamless. Off-chain platforms can connect to CRM tools, email services, payment processors, and accounting software using standard APIs. Building a mobile app for your MLM platform is also much more straightforward when the backend is a conventional server.
Advantages of Off-Chain MLM Logic
Speed. Off-chain systems process transactions instantly. There is no waiting for block confirmations. A commission calculation that might take 30 seconds on-chain can happen in milliseconds on a server.
Cost Efficiency. There are no gas fees. The only costs are server hosting and maintenance, which are predictable and typically much lower than cumulative blockchain transaction fees, especially at scale.
Flexibility. Business rules can be updated quickly. New features can be added. Bugs can be fixed. The development cycle is much faster compared to smart contract development, where every update needs careful auditing.
Scalability. Servers can be scaled horizontally or vertically. Adding more users or handling more transactions is a matter of adding server capacity. There is no hard throughput cap like you find on most blockchains.
User Experience. Off-chain platforms can offer richer, more polished user interfaces. Complex dashboards, real-time notifications, and detailed reports are all much easier to implement when you are not constrained by blockchain limitations.
Limitations of Off-Chain MLM Logic
Centralization Risks. When one entity controls all the data and logic, there is a single point of failure. If the server goes down, the entire platform stops. If the company acts dishonestly, users have limited recourse.
Trust Issues. Users have to trust that the company is running the system fairly. They cannot independently verify commission calculations, payout records, or user counts. This lack of transparency can be a dealbreaker for crypto-savvy audiences.
Data Manipulation. Since the database is controlled by the company, records can be changed. This opens the door to potential fraud, whether by the company itself or by hackers who breach the system.
Security Vulnerabilities. Centralized servers are targets for cyberattacks. DDoS attacks, SQL injection, and data breaches are all risks that do not apply to on-chain systems in the same way. Proper security practices and decentralized identifiers can help mitigate some of these risks, but they add to the development complexity.
Build Your MLM Platform With the Right Architecture
Whether you need on-chain transparency, off-chain flexibility, or a hybrid model, Nadcab Labs has the expertise to deliver. Over 8 years of blockchain development backing every project.
Key Differences Between On-Chain and Off-Chain MLM Logic
Understanding the differences between these two approaches comes down to a handful of core factors. The table below puts them side by side so you can see where each model stands.
| Parameter | On-Chain MLM Logic | Off-Chain MLM Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Blockchain (public ledger) | Centralized database |
| Execution | Smart contracts | Server-side code |
| Transparency | Fully transparent and verifiable | Depends on company disclosure |
| Transaction Speed | Depends on network (seconds to minutes) | Near instant (milliseconds) |
| Cost Per Transaction | Gas fees (variable, can be high) | Minimal server costs |
| Scalability | Limited by blockchain capacity | Highly scalable with more servers |
| Updatability | Difficult (requires redeployment) | Easy (server-side updates) |
| Trust Model | Trustless (code is law) | Trust-based (trust the operator) |
| Security | Very high (blockchain security) | Moderate (depends on server security) |
| User Experience | Basic (wallet-based interaction) | Rich (full dashboard features) |
Performance, Cost, Security, and Scalability Comparison
Let us get into the specifics of how these two approaches stack up across the metrics that matter most to MLM business owners.
| Metric | On-Chain | Off-Chain | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | 3 to 60 seconds | Under 100 milliseconds | Off-Chain |
| Cost at 10K Transactions/Day | $500 to $5,000+ in gas | $50 to $200 in server costs | Off-Chain |
| Security Against Tampering | Extremely high | Moderate to high | On-Chain |
| Scalability Ceiling | 15 to 4,000 TPS (chain dependent) | 100,000+ TPS (with scaling) | Off-Chain |
| Audit Transparency | Public, real-time | Internal reports only | On-Chain |
| Downtime Risk | Near zero (blockchain uptime) | Possible (server outages) | On-Chain |
As the comparison shows, neither approach is universally better. Off-chain wins on speed, cost, and scalability. On-chain wins on security, transparency, and reliability. The right choice depends entirely on your priorities and your target audience.
At Nadcab Labs, we often advise clients to run performance benchmarks specific to their expected user base before committing to an architecture. A platform expecting 500 users has very different needs than one targeting 50,000. Our team, with over 8 years of experience in blockchain infrastructure, helps clients model these scenarios before a single line of code is written.
When to Use On-Chain vs Off-Chain MLM Logic
Picking the right model is not about which one is technically superior. It is about which one fits your business situation.
Choose On-Chain When:
Your target audience is crypto-native and expects full transparency. Your compensation plan is relatively straightforward. You want to minimize the trust factor between your company and its participants. You are building on a low-fee chain like BNB Smart Chain or Polygon. Your platform handles moderate transaction volumes.
Choose Off-Chain When:
You need complex compensation structures with multiple bonus types. Speed and user experience are top priorities. You expect high transaction volumes that would be too costly on-chain. You want to iterate quickly on features and business rules. You need to integrate with third-party services like KYC, CRM, or analytics tools.
Example Scenario: A startup launching a simple binary MLM plan for a crypto community of 2,000 people might do perfectly fine with a fully on-chain system on Polygon. The low gas fees, high transparency, and automated payouts make it a good match. But a large MLM company with 100,000 members, a complex unilevel plan with 15 payout levels, team bonuses, rank qualifications, and real-time leaderboards would struggle to put all of that on-chain. The off-chain model, potentially with on-chain settlement for payouts, would make much more sense.
Comparing infrastructure choices is a bit like weighing Azure Functions vs AWS Lambda for serverless computing. There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Context matters.
Hybrid MLM Logic: Combining On-Chain and Off-Chain Models
In practice, the best MLM platforms do not pick one model exclusively. They combine both. This is the hybrid approach, and it is what we at Nadcab Labs recommend most often.
In a hybrid setup, the computationally heavy and frequently changing parts of the system run off-chain. This includes things like the user dashboard, genealogy tree management, reporting, analytics, notifications, and complex commission calculations. These operations need speed and flexibility.
The critical, trust-sensitive parts of the system run on-chain. This includes financial settlements, commission payouts, key identity records, and audit trails. These are the operations where transparency and immutability matter most.
The hybrid engine acts as a bridge between the two layers. It routes each task to the appropriate layer automatically. User activity and data processing happen off-chain. Final payouts and verifiable records get settled on-chain.
Here is a simple way to think about what goes where in a hybrid model:
| Function | Recommended Layer | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| User Registration | Off-Chain | Needs speed and data flexibility |
| Commission Calculation | Off-Chain | Complex logic, frequent updates |
| Fund Transfers | On-Chain | Needs transparency and security |
| Genealogy Tree Display | Off-Chain | Needs fast rendering |
| Payout Settlement | On-Chain | Permanent record, user trust |
| Rank Qualification | Off-Chain | Complex multi-criteria logic |
| Audit Trail | On-Chain | Immutable record keeping |
| Notifications and Alerts | Off-Chain | Real-time delivery needed |
This layered approach gives you the best of both worlds. Your users get fast, polished interfaces. Your financial transactions get the security and transparency of the blockchain. And your development team gets the flexibility to iterate without being locked into rigid smart contracts for every feature.
If you are exploring a cryptocurrency MLM software solution that uses a hybrid approach, Nadcab Labs has built dozens of such platforms and can help you decide exactly which components belong on-chain and which belong off-chain.
Real-World Use Cases for Each Approach
To make this more concrete, let us look at some real-world scenarios where each approach shines.
Use Case 1: DeFi Referral Program (On-Chain)
A decentralized finance protocol wants to reward users who bring in new liquidity providers. The referral logic is simple: 3% of the new user’s first deposit goes to the referrer. Since the entire protocol runs on Ethereum, it makes sense to keep the referral logic on-chain too. The smart contract handles everything. The DeFi community trusts it because the code is open source and audited. Gas costs are acceptable because deposits are large and infrequent.
Use Case 2: Health Supplement MLM (Off-Chain)
A health supplement company runs a traditional MLM with 50,000 members across 12 countries. Their compensation plan includes direct sales commissions, team volume bonuses, leadership pools, car bonuses, and travel incentives. The plan has 20+ conditions for rank qualifications. This level of complexity requires an off-chain system. The company uses a server-based platform with crypto payout options, giving members the choice between bank transfers and stablecoin payments.
Use Case 3: Crypto Investment Community (Hybrid)
A crypto investment community wants to build a platform where members earn commissions by referring new investors. They want the investment deposits and commission payouts to be fully on-chain for transparency. But they also need a rich dashboard with portfolio tracking, leaderboards, and a communication system. The hybrid model works perfectly here. The frontend and admin logic run off-chain, while all financial transactions settle on the blockchain.
Future Trends in Blockchain-Based MLM Architectures
The landscape of blockchain MLM is evolving quickly, and several trends are worth watching.
Layer 2 Solutions Are Changing the Game. Networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync are drastically reducing gas costs and increasing throughput. This makes on-chain MLM logic much more practical than it was even two years ago. As Layer 2 adoption grows, more businesses will be able to put complex logic on-chain without worrying about cost or speed.
Account Abstraction Is Improving User Experience. One of the biggest barriers to on-chain MLM has been the user experience. Requiring users to manage wallets, sign transactions, and pay gas is friction that turns people away. Account abstraction standards are simplifying this by letting users interact with the blockchain without needing deep crypto knowledge.
Cross-Chain MLM Platforms Are Emerging. With more blockchains than ever, MLM platforms are starting to operate across multiple chains. A user on Ethereum can refer someone on BNB Chain, and the system handles the cross-chain settlement. This is still early, but it is a direction that Nadcab Labs is actively researching and building toward.
AI and Blockchain Convergence. Some forward-thinking MLM platforms are starting to use AI for predictive analytics, fraud detection, and personalized compensation recommendations, while relying on blockchain for the execution and settlement layer. This convergence of AI and blockchain is something we expect to see a lot more of in the next few years.
Regulatory Pressure Is Driving Transparency. Governments around the world are increasing scrutiny of MLM businesses, particularly those involving crypto. This pressure is pushing more platforms toward on-chain or hybrid models because the transparent, auditable nature of blockchain records makes regulatory compliance easier to demonstrate.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right MLM Logic Strategy
There is no perfect answer to whether your MLM platform should use on-chain or off-chain logic. It depends on your compensation plan complexity, your target audience, your budget, your scalability requirements, and how much transparency your users demand.
On-chain logic gives you unmatched transparency, trust, and automation. But it comes with higher costs, less flexibility, and scalability limits. Off-chain logic gives you speed, cost savings, and the freedom to build complex features quickly. But it requires your users to trust you, and it introduces centralization risks.
For most real-world MLM businesses, the hybrid approach hits the sweet spot. Keep the trust-critical operations on-chain and the performance-critical operations off-chain. This gives your users the confidence they need while giving your business the flexibility it requires to grow.
At Nadcab Labs, we have been in the blockchain development space for over 8 years. We have built MLM platforms of every type, from fully on-chain systems to complex hybrid architectures serving tens of thousands of users. If you are trying to figure out the right architecture for your MLM business, our team can help you map it out based on your specific needs, not generic advice.
The bottom line is this: pick the architecture that serves your users and your business goals. Do not choose on-chain just because it sounds impressive, and do not default to off-chain just because it is easier. Make a deliberate, informed decision, and build on a foundation that can grow with you.
Frequently Asked Questions
On-chain MLM logic stores all business rules and commission calculations inside smart contracts on a blockchain. Every transaction is public and cannot be altered. Off-chain MLM logic runs on centralized servers where the company controls the business rules, data storage, and processing. The main difference boils down to transparency and control. On-chain is trustless and public, while off-chain gives the operator more flexibility but requires users to trust the company running the platform.
On-chain MLM logic benefits from blockchain’s inherent security features, including cryptographic protection, decentralization, and immutability. Once deployed, the code cannot be tampered with by any single party. Off-chain systems rely on server security practices such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls. While off-chain systems can be made very secure, they face risks from server breaches, DDoS attacks, and insider threats that do not apply in the same way to on-chain platforms.
Every action in an on-chain system requires a blockchain transaction, and each transaction costs gas. For MLM platforms that process many small commission payouts daily, these fees add up quickly. On Ethereum, gas fees can spike unpredictably during periods of high network activity. This makes on-chain MLM less cost-effective for high-volume platforms. However, using lower-cost chains like Polygon, BNB Smart Chain, or Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum can significantly reduce these costs.
Switching from off-chain to on-chain after launch is technically possible but involves significant effort. You would need to develop and audit smart contracts, migrate user data and genealogy structures to the blockchain, and potentially redesign parts of your compensation plan to work within smart contract limitations. It is much easier and cheaper to plan your architecture before launch. A hybrid model is often the safest starting point because it lets you move more logic on-chain over time without a complete rebuild.
A hybrid MLM model combines on-chain and off-chain components. The off-chain layer handles tasks that need speed and flexibility like dashboards, commission calculations, and reporting. The on-chain layer handles tasks that need trust and transparency like fund transfers, payout settlements, and audit trails. Experts recommend this because it avoids the drawbacks of going fully on-chain (high costs, limited flexibility) or fully off-chain (trust issues, centralization risk) while keeping the advantages of both approaches.
The best blockchain depends on your priorities. BNB Smart Chain offers low fees and fast transactions, making it popular for MLM platforms targeting cost-conscious users. Ethereum provides the highest security and largest developer ecosystem but has higher gas fees. Polygon offers a good balance of low cost and Ethereum compatibility. Tron is popular in certain Asian markets. Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism are gaining traction for their low fees and Ethereum-level security. Your blockchain choice should align with your budget, audience, and transaction volume.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.