Key Takeaways
- Cryptocurrency exchanges primarily generate revenue through transaction fees and trading fees, which scale directly with trading volume and can represent 60-80% of total income for established platforms.
- Token listing fees provide substantial one-time revenue ranging from $50,000 to several million dollars per listing, while simultaneously driving additional trading volume and enhancing platform credibility in the blockchain technology ecosystem.
- Subscription services offering advanced trading tools and analytics create recurring revenue streams that remain stable during market volatility, with premium tiers priced between $30 to $500 monthly depending on features.
- Crypto lending programs generate interest income by facilitating loans between users, with exchanges earning spreads between borrower interest rates (8-15%) and lender returns (5-12%), creating a profitable financial services division.
- Revenue diversification across NFT marketplaces, margin trading, affiliate programs, and educational resources ensures long-term sustainability and reduces dependency on volatile cryptocurrency trading volumes.
- Strategic partnerships with payment processors, institutional investors, and blockchain projects create mutually beneficial revenue opportunities while expanding service offerings and strengthening market position in the global economy.
- User experience optimization and platform transparency directly impact profitability by improving retention rates, with studies showing that superior UX can increase trading frequency by 40-60% and reduce customer acquisition costs significantly.
- Emerging monetization models including DeFi integration, institutional custody services, and AI-powered trading tools represent the future of crypto exchange revenue as the industry matures and regulatory frameworks solidify.
The cryptocurrency industry has evolved from a niche technology experiment into a multi-trillion dollar global economy, with cryptocurrency exchanges serving as the critical infrastructure enabling digital asset trading worldwide. Understanding how these platforms generate revenue is essential for investors, entrepreneurs, and anyone looking to build crypto exchange platforms or evaluate the financial sustainability of existing exchanges. With over 8 years of experience developing and analyzing cryptocurrency exchanges, we have witnessed firsthand the evolution of monetization strategies from simple transaction fees to sophisticated multi-revenue ecosystems.
This comprehensive guide examines every major revenue stream utilized by cryptocurrency exchanges, from primary income sources like trading fees and commissions to emerging opportunities in NFT marketplaces, lending programs, and educational resources. We will explore how successful exchanges balance user acquisition with profitability, maintain transparency while maximizing revenue, and adapt their monetization strategies to changing market conditions and regulatory landscapes. Whether you are a blockchain entrepreneur, investor, or cryptocurrency enthusiast, this analysis provides actionable insights into the business models powering the digital asset revolution.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges and Their Role in the Global Economy
Cryptocurrency exchanges have become indispensable participants in the global economy, facilitating trillions of dollars in digital asset transactions annually. These platforms serve as the gateway between traditional finance and the blockchain technology ecosystem, enabling millions of users worldwide to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies with unprecedented accessibility. The rise of cryptocurrency exchanges has democratized access to digital assets, allowing individuals in developed and developing nations alike to participate in a borderless financial system that operates 24/7 without traditional banking intermediaries.
The economic impact of cryptocurrency exchanges extends beyond simple trading facilitation. These platforms drive innovation in financial services, create employment opportunities in the technology sector, and contribute to the development of blockchain infrastructure globally. Major exchanges process billions of dollars in trading volume daily, generating substantial tax revenue for governments while providing liquidity that stabilizes cryptocurrency markets. As institutional adoption accelerates, cryptocurrency exchanges increasingly bridge the gap between traditional financial institutions and decentralized finance, positioning themselves as critical infrastructure in the evolving digital economy.
Evolution of Cryptocurrency Exchanges
The evolution of cryptocurrency exchanges reflects the broader maturation of the digital asset industry. Early exchanges operated with minimal regulation, basic user interfaces, and limited security measures, focusing primarily on Bitcoin trading. These pioneering platforms charged simple transaction fees and operated on rudimentary technology infrastructure. As the industry grew, exchanges expanded their offerings to include hundreds of digital assets, introduced sophisticated trading tools like margin trading and futures contracts, and developed complex fee structures that reward high-volume traders while maintaining profitability.
Modern cryptocurrency exchanges bear little resemblance to their predecessors. Today’s platforms incorporate institutional-grade security protocols, advanced trading engines capable of processing millions of transactions per second, comprehensive customer support systems, and regulatory compliance frameworks. The evolution has also brought diversification in exchange types, from centralized platforms offering maximum liquidity and user experience to decentralized exchanges providing enhanced privacy and control over assets. This progression has been accompanied by increasingly sophisticated monetization strategies, with leading exchanges now operating as comprehensive financial services platforms rather than simple trading venues.
Digital Assets and Cross-Border Trading
Cryptocurrency exchanges have revolutionized cross-border trading by eliminating traditional barriers associated with international money transfers. Digital assets enable instantaneous value transfer across borders without requiring intermediary banks, currency conversion through multiple institutions, or compliance with varying international banking regulations. This capability has proven particularly valuable for remittances, international commerce, and individuals seeking to preserve wealth in unstable economic environments. Exchanges facilitate this global movement of digital assets while generating revenue through currency conversion fees, withdrawal charges, and premium services for international users.
The infrastructure supporting cross-border digital asset trading represents a significant competitive advantage for cryptocurrency exchanges. Platforms that offer diverse fiat currency on-ramps, support for regional payment methods, and localized customer service can capture larger market shares in international markets. These exchanges often partner with local payment processors and financial institutions to streamline the conversion between traditional currencies and cryptocurrencies, creating additional revenue opportunities through strategic partnerships while improving user experience for global customers seeking seamless access to digital asset markets.
Financial Inclusion Through Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Financial inclusion represents one of the most significant social contributions of cryptocurrency exchanges. Approximately 1.7 billion adults globally lack access to traditional banking services, yet many possess mobile phones capable of accessing cryptocurrency exchanges. These platforms enable unbanked populations to participate in the global economy, save and invest in digital assets, and access financial services previously unavailable to them. Exchanges serving these markets often adopt mobile-first strategies, support low minimum deposits, and provide educational resources to help new users navigate the cryptocurrency ecosystem safely and effectively.
The financial inclusion mission also creates unique monetization opportunities for cryptocurrency exchanges. Platforms targeting underserved markets can generate revenue through micro-transactions, remittance services with lower fees than traditional providers, and partnerships with local merchants enabling cryptocurrency payments. While individual transaction values may be smaller in these markets, the sheer volume of potential users and the loyalty generated by providing essential financial services create sustainable long-term revenue streams. Successful exchanges balance profitability with social responsibility, ensuring their fee structures remain accessible while maintaining operational sustainability.
Transparency and Trust in Blockchain Technology
Transparency stands as a foundational principle of blockchain technology, and leading cryptocurrency exchanges leverage this attribute to build user trust and differentiate themselves in competitive markets. Transparent exchanges publish proof of reserves, undergo regular third-party audits, maintain public order books, and clearly communicate their fee structures and operational policies. This openness reduces information asymmetry between exchanges and users, enabling informed decision-making and fostering confidence in platform security and financial stability. Transparency also serves as a powerful marketing tool, as users increasingly prefer exchanges that demonstrate accountability and operational integrity.
The commitment to transparency extends beyond technical implementations to encompass corporate governance, regulatory compliance, and community engagement. Exchanges that publish regular financial reports, maintain responsive customer support channels, and actively participate in industry self-regulation initiatives build stronger reputations that translate into user loyalty and higher trading volumes. While transparency requires investment in auditing, reporting infrastructure, and communication systems, the resulting trust premium enables exchanges to maintain competitive fee structures, attract institutional clients, and weather market volatility more effectively than opaque competitors.
Crypto Exchange Monetization: How Crypto Exchanges Generate Revenue
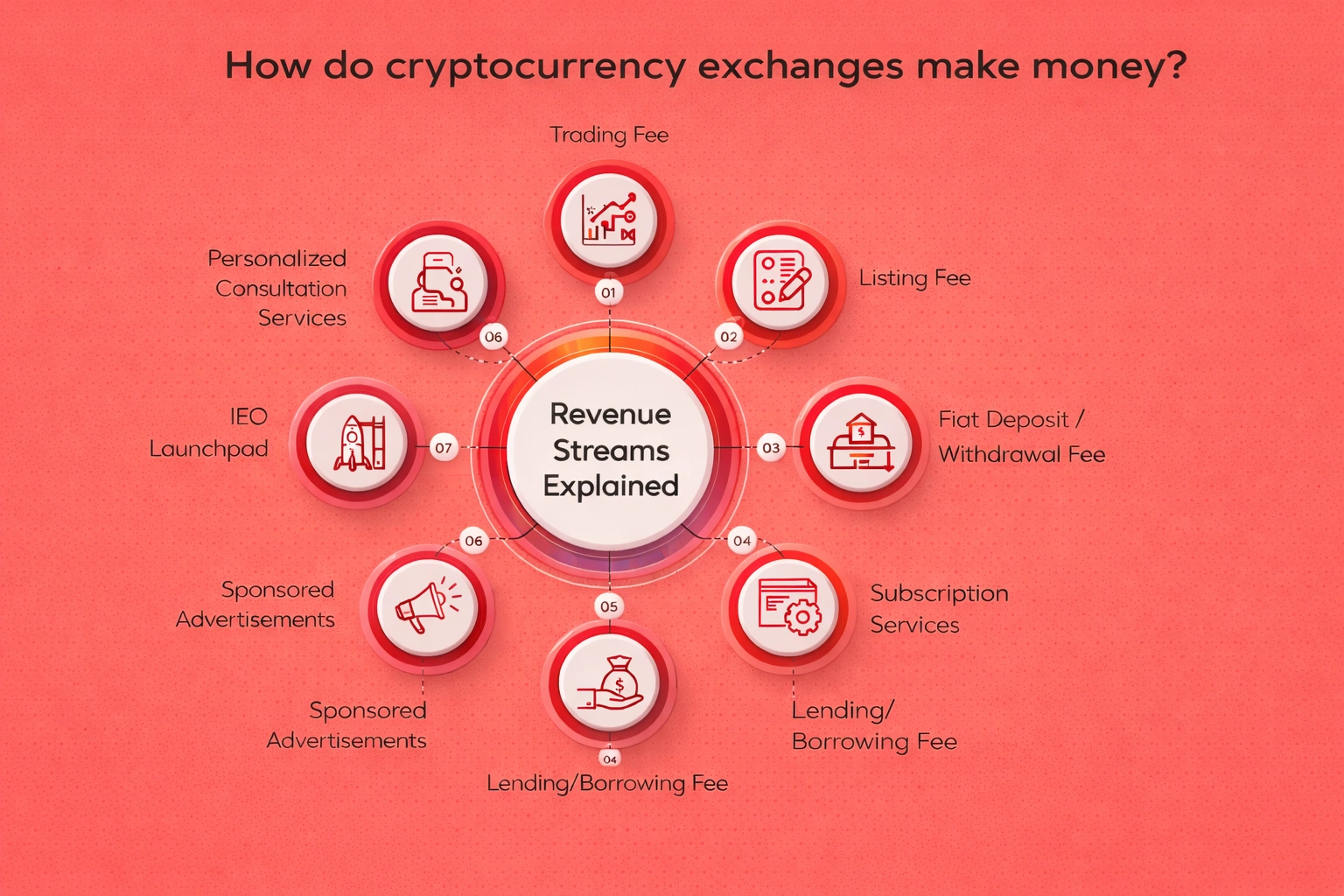
Crypto exchange monetization encompasses a diverse ecosystem of revenue streams designed to create sustainable, profitable businesses while delivering value to users. Understanding these monetization mechanisms is crucial for anyone evaluating exchange platforms, whether as a trader assessing fee structures, an investor analyzing business models, or an entrepreneur planning to enter the market. Successful cryptocurrency exchanges typically combine multiple revenue sources, creating a balanced portfolio that remains profitable across varying market conditions and regulatory environments.
Overview of Crypto Exchange Revenue Models
The revenue architecture of cryptocurrency exchanges has evolved into a sophisticated framework balancing immediate transaction-based income with long-term subscription and service-based revenue. The foundation rests on trading fees and commissions, which directly correlate with platform trading volume and typically account for 60-80% of total revenue for established exchanges. Beyond this core income, exchanges have developed complementary revenue streams including token listing fees that can generate millions per listing, subscription services providing recurring monthly income, and lending programs creating interest-based revenue similar to traditional banks.
Secondary revenue models complement primary income sources by targeting specific user segments and market opportunities. These include margin trading services that charge premium fees and interest on leveraged positions, NFT marketplaces capturing the growing digital collectibles market, affiliate programs that reduce customer acquisition costs while expanding user base, and educational resources that enhance user capabilities while generating additional income. The most successful exchanges continuously experiment with new revenue models, adapting to market trends and user needs while maintaining focus on core trading services that drive the majority of profitability.
| Revenue Model | Revenue Contribution | Stability Level | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Fees | 60-80% | Medium (volume-dependent) | Low |
| Token Listing Fees | 5-15% | High (one-time payments) | Medium |
| Subscription Services | 3-8% | Very High (recurring) | Medium |
| Lending Programs | 5-12% | Medium-High | High |
| Margin Trading | 4-10% | Medium | High |
| NFT Marketplaces | 2-6% | Low-Medium | Medium |
| Affiliate Programs | 1-5% | Medium | Low |
| Advertising Revenue | 1-3% | Medium | Low |
Primary vs Secondary Revenue Generation Strategies
Primary revenue generation strategies form the backbone of crypto exchange profitability, representing core services that users expect and regularly utilize. These include transaction fees on spot trading, token listing fees, subscription services for premium features, crypto lending programs, and integrated NFT marketplaces. Primary strategies typically require substantial initial development investment but scale efficiently as user base grows. They directly align with the exchange’s core value proposition of facilitating digital asset trading and provide predictable revenue streams that financial planners can model with reasonable accuracy. Exchanges must excel at primary revenue generation to achieve profitability and compete effectively in crowded markets.
Secondary revenue strategies complement primary income by exploiting market opportunities, reducing customer acquisition costs, and maximizing lifetime value of existing users. These encompass arbitrage trading support services, margin trading for advanced users, affiliate and referral programs, strategic partnerships generating revenue sharing, and knowledge sharing through educational resources and online courses. While individually smaller revenue contributors, secondary strategies collectively represent 20-40% of total income for mature exchanges. They also serve strategic purposes beyond direct revenue, such as improving user retention, enhancing brand reputation, and creating competitive moats that differentiate exchanges in commodity-like markets where primary fee structures converge.
Importance of Revenue Diversification for Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Revenue diversification has transitioned from optional strategy to essential survival mechanism for cryptocurrency exchanges operating in volatile markets. Exchanges dependent solely on trading fees experience severe revenue fluctuations during bear markets when trading volume contracts by 70-90%. The 2022 cryptocurrency market downturn demonstrated this vulnerability, with some exchanges losing 80% of revenue while diversified competitors maintained 50-60% of peak income through subscription services, lending programs, and other stable revenue streams. Diversification also provides strategic flexibility, enabling exchanges to cross-subsidize user acquisition, invest in technology improvements, and weather regulatory challenges without compromising financial stability.
The path to effective diversification requires careful analysis of user needs, competitive positioning, and operational capabilities. Exchanges should prioritize revenue streams that complement existing services, leverage current technology infrastructure, and align with brand identity and user demographics. For instance, exchanges serving professional traders might emphasize margin trading and advanced analytics subscriptions, while platforms targeting retail users could focus on educational resources and simplified lending programs. Diversification efforts should be measured against implementation costs, regulatory requirements, and potential cannibalization of existing revenue. Successful exchanges regularly review their revenue portfolio, discontinuing underperforming initiatives while scaling successful experiments into major profit centers.
Primary Revenue Generation Strategies for Crypto Exchanges
Transaction Fees and Trading Fees
Transaction fees and trading fees represent the lifeblood of cryptocurrency exchange economics, generating the majority of revenue for virtually all platforms regardless of size or market focus. These fees are charged on every trade executed on the platform, typically calculated as a percentage of the transaction value. The elegance of this model lies in its scalability: as trading volume increases, revenue grows proportionally without requiring additional customer service, marketing, or operational overhead beyond infrastructure scaling. Leading exchanges process billions of dollars in daily trading volume, with even modest fee rates of 0.1-0.5% generating substantial income that funds platform development, security enhancements, and competitive expansion.
The structure of trading fees has evolved to balance competitiveness with profitability. Most exchanges employ tiered fee schedules that reward high-volume traders with progressively lower rates, creating incentives for users to consolidate trading activity on a single platform. This volume-based pricing simultaneously maximizes revenue from retail traders who pay higher rates while remaining attractive to institutional traders and market makers whose activity provides essential liquidity. The fee optimization challenge requires continuous market analysis, as exchanges must price competitively against rivals while avoiding destructive fee wars that erode industry profitability. Exchanges increasingly differentiate through value-added services rather than competing solely on fees.
Commissions and Fee Structures
Commission structures on cryptocurrency exchanges typically distinguish between maker and taker fees, recognizing the different roles these traders play in market dynamics. Makers provide liquidity by placing limit orders that rest on the order book, while takers remove liquidity by executing market orders against existing positions. Most exchanges charge takers higher fees (0.1-0.3%) than makers (0.05-0.2%), incentivizing liquidity provision that benefits all market participants. This tiered approach ensures healthy order books with tight bid-ask spreads while generating predictable revenue across varying market conditions. Advanced fee structures may include additional tiers based on 30-day trading volume, native token holdings, or VIP status.
The granular design of fee structures reflects sophisticated revenue optimization strategies informed by data analytics and competitive intelligence. Exchanges continuously analyze how fee changes impact trading volume, user retention, and overall profitability. Small adjustments of 0.01-0.02% in fee rates can significantly influence trader behavior, potentially driving users to competitors or increasing platform loyalty. Some exchanges have experimented with zero-fee trading for specific trading pairs or promotional periods, gambling that increased volume and user acquisition will offset foregone fee revenue. These strategies work best when combined with secondary monetization through other services, as transaction fee revenue alone may prove insufficient to sustain operations at unsustainably low rates.
Trading Volume and Revenue Impact
Trading volume serves as the fundamental driver of crypto exchange revenue, with direct mathematical correlation between daily volume and income generation. A platform processing $1 billion in daily trading volume at average fees of 0.15% generates $1.5 million in daily transaction fee revenue, translating to approximately $547 million annually from trading fees alone. This relationship explains why exchanges invest heavily in market making incentives, liquidity mining programs, and trading competitions designed to boost volume. However, volume quality matters as much as quantity, as sustainable organic volume from genuine traders proves more valuable than artificially inflated volume from wash trading or bot activity that provides no real liquidity or revenue stability.
Market conditions dramatically influence trading volume and consequent revenue generation. Bull markets typically see 3-5x volume increases as new participants enter cryptocurrency markets and existing traders increase activity frequency. Conversely, bear markets can reduce volume by 70-80%, forcing exchanges to rely on diversified revenue streams for survival. Smart exchanges prepare for cyclical volatility by building revenue reserves during bull markets, optimizing operational efficiency to reduce break-even volume requirements, and developing counter-cyclical services like lending programs that may see increased demand during market downturns. Understanding and planning for volume volatility separates sustainable exchanges from those that fail during inevitable market corrections.
Subscription Services and Premium Features
Subscription services represent a growing revenue stream for cryptocurrency exchanges seeking stable, recurring income independent of trading volume fluctuations. These premium tiers typically offer advanced trading tools, enhanced API access, priority customer support, detailed market analytics, and reduced trading fees. Monthly subscription prices range from $30 for basic premium features to $500+ for institutional-grade services, with annual subscriptions often discounted 15-25% to encourage long-term commitment. The subscription model creates predictable revenue that financial planners value highly, as monthly recurring revenue (MRR) compounds over time and exhibits lower volatility than transaction-based income tied to cryptocurrency market cycles.
The value proposition of premium subscriptions must justify the monthly cost through tangible benefits that improve trading outcomes or save time. Professional traders readily pay for advanced charting tools, automated trading bots, portfolio management features, and premium research reports if these tools enhance profitability beyond subscription costs. Exchanges must continuously innovate premium offerings to maintain subscriber interest and prevent churn, which typically runs 5-10% monthly for financial software services. Successful subscription programs segment users effectively, offering entry-level plans for active retail traders, mid-tier plans for semi-professional traders, and enterprise solutions for institutional clients. Each tier should provide clear value differentiation while encouraging upgrades to higher-priced plans.
Advanced Trading Tools and Analytics
Advanced trading tools and analytics form the cornerstone of premium subscription offerings, providing serious traders with capabilities unavailable on free tiers. These typically include professional-grade charting packages with 100+ technical indicators, real-time market depth analysis, algorithmic trading interfaces, backtesting environments, and custom alert systems. Institutional features may include order flow analytics, market microstructure data, cross-exchange arbitrage scanners, and API access with higher rate limits enabling automated trading strategies. The development of these tools requires significant investment in engineering talent and data infrastructure, but creates strong competitive differentiation and justifies premium pricing for users whose trading sophistication demands advanced capabilities.
Analytics services extend beyond real-time trading tools to encompass comprehensive market intelligence, research reports, and predictive modeling. Premium subscribers might receive daily market analysis from professional traders, weekly sector reports on emerging cryptocurrency trends, sentiment analysis derived from social media and news sources, and portfolio optimization recommendations based on modern portfolio theory. These value-added services position exchanges as comprehensive trading platforms rather than simple transaction facilitators, strengthening user loyalty and justifying recurring subscription fees. The most successful analytics offerings combine proprietary data accessible only through the exchange with expert interpretation that helps traders make informed decisions in complex, fast-moving cryptocurrency markets.
Subscription-Based Revenue Models
Subscription-based revenue models create financial stability through predictable monthly recurring revenue that smooths the volatility inherent in transaction fee income. A cryptocurrency exchange with 10,000 premium subscribers paying an average of $50 monthly generates $500,000 in guaranteed monthly revenue regardless of trading volume fluctuations. This baseline income supports fixed operational costs including salaries, infrastructure, compliance, and customer support while providing financial runway during market downturns. Subscription revenue also enhances business valuation, as investors and acquirers apply higher revenue multiples to recurring income compared to volatile transaction-based revenue when determining exchange worth.
The economics of subscription models require careful balance between pricing, feature differentiation, and customer acquisition costs. If a premium subscription costs $100 monthly and average customer lifetime is 18 months, each subscriber generates $1,800 in lifetime value. If customer acquisition cost through marketing and onboarding exceeds $500, the unit economics become challenging. Successful exchanges optimize this equation by improving retention through continuous feature enhancement, reducing acquisition costs through referral programs and organic growth, and increasing average revenue per user (ARPU) through upselling and cross-selling complementary services. The subscription business within crypto exchanges often operates with gross margins exceeding 80%, as marginal costs of serving additional subscribers remain minimal once infrastructure is established.
Token Listing and Listing Fees
Token listing represents one of the most lucrative revenue streams for established cryptocurrency exchanges, with listing fees ranging from $50,000 for smaller platforms to well over $1 million for tier-one exchanges. These fees compensate exchanges for the substantial due diligence required to evaluate new tokens, technical integration work to support trading, liquidity requirements to ensure functional markets, and reputational risk associated with listing potentially fraudulent or low-quality projects. The listing process typically takes 4-12 weeks and involves security audits, team background checks, tokenomics analysis, regulatory compliance review, and community sentiment evaluation. For major exchanges, token listings also drive significant secondary revenue through trading fees generated by new trading pairs.
The strategic value of selective listing extends beyond immediate fee revenue to encompass platform reputation, user satisfaction, and long-term competitiveness. Exchanges that maintain high listing standards build trust with users and attract quality projects, creating a virtuous cycle where successful token listings generate trading volume while unsuccessful listings damage platform credibility. Leading exchanges increasingly compete on discovery of promising early-stage projects, offering incubator programs, token launch platforms, and strategic advisory services that position them as partners to blockchain projects rather than mere listing venues. This consultative approach creates deeper relationships, potential equity participation, and ongoing revenue opportunities beyond one-time listing fees.
Token Listing Criteria and Due Diligence
Token listing criteria have matured considerably as the cryptocurrency industry evolved from the wild west of 2017 into a more regulated environment. Modern exchanges evaluate projects across multiple dimensions including team credentials and track record, technical architecture and smart contract security, regulatory compliance status, community size and engagement, tokenomics and distribution fairness, use case viability, and market demand indicators. This comprehensive due diligence protects exchanges from regulatory action, reduces risk of listing scam projects that damage reputation, and ensures listed tokens meet minimum quality standards. The process increasingly resembles traditional exchange listing requirements, with formal applications, financial disclosures, and ongoing reporting obligations.
Due diligence procedures incorporate third-party security audits, legal opinion letters, proof of team identity, and sometimes financial audits of project treasuries. Exchanges may require projects to maintain minimum liquidity commitments, often $100,000 to $1 million in trading pairs to ensure functional markets. Some platforms mandate market making agreements or require projects to purchase native exchange tokens as part of listing arrangements. The thoroughness of due diligence correlates directly with exchange reputation and regulatory standing. Platforms operating in jurisdictions with strong securities regulations must apply particularly rigorous standards to avoid listing tokens that regulators might deem unregistered securities, potentially exposing the exchange to significant legal liability.
Revenue Potential of Token Listings
The revenue potential of token listings extends well beyond initial listing fees through trading volume generation, market making services, and ongoing relationship revenue. A successful token listing on a major exchange might generate $500,000 in listing fees plus $2-5 million annually in trading fee revenue if the token achieves reasonable trading volume. Exchanges often structure deals to include revenue sharing on trading fees, additional payments for promotional marketing, and participation in token sales or equity rounds. The most valuable listings involve projects with strong communities, genuine utility, and growth potential that will drive sustained trading activity rather than one-time speculative frenzies.
Market dynamics significantly influence listing fee potential, with bull markets enabling exchanges to command premium fees while bear markets force competitive pricing to maintain deal flow. Some exchanges have moved away from fixed listing fees toward performance-based models where projects pay lower upfront fees but commit to revenue sharing or token grants based on trading performance. This alignment of incentives ensures exchanges benefit from successful projects while reducing barriers for promising but capital-constrained teams. The listing business also creates data advantages, as exchanges gain early insight into emerging blockchain trends, enabling strategic investments and partnership opportunities that multiply the value of listing relationships beyond direct fee revenue.
Crypto Lending and Lending Programs
Crypto lending programs have emerged as significant revenue generators for cryptocurrency exchanges, operating similarly to traditional banking by intermediating between savers seeking yield and borrowers requiring capital. Exchanges facilitate these transactions through automated lending platforms where users deposit cryptocurrency to earn interest (typically 3-8% annually) while borrowers pay higher rates (8-15% annually) to access leveraged trading or other capital needs. The exchange captures the interest rate spread, often 2-5%, while providing technology infrastructure, counterparty risk management, and liquidation services that protect lenders. Annual lending volume on major exchanges can exceed $10 billion, generating tens of millions in interest income.
The risk-reward profile of lending programs requires sophisticated financial management to prevent catastrophic losses from borrower defaults. Exchanges implement over-collateralization requirements, typically demanding 120-150% collateral value relative to loan amount, and automatically liquidate positions when collateral ratios fall below safety thresholds. Advanced platforms employ dynamic interest rates that adjust based on utilization, increasing borrowing costs when capital supply tightens to attract more lenders while reducing rates when capital exceeds demand. These algorithmic mechanisms create efficient markets that optimize capital deployment while protecting the exchange’s financial stability and lender funds from market volatility and borrower default risk.
Interest Rates and Lending Mechanisms
Interest rates in cryptocurrency lending programs fluctuate based on supply and demand dynamics for specific assets, with popular trading currencies like Bitcoin and stablecoins typically offering lower yields (3-6%) due to abundant supply, while more volatile altcoins may yield 10-15% or higher to compensate lenders for increased risk. Exchanges employ various mechanisms to determine rates, including algorithm-based systems that adjust rates in real-time based on utilization ratios, fixed-rate programs where exchanges guarantee specific yields for defined periods, and peer-to-peer marketplaces where lenders and borrowers negotiate terms directly. The most sophisticated platforms combine these approaches, offering users flexibility while maintaining exchange control over risk parameters.
Lending mechanisms must balance capital efficiency with safety, a challenge amplified by cryptocurrency volatility. Most programs operate on a pooled model where all lenders supply a collective pool from which borrowers draw, with interest distributed proportionally to lender contributions. This pooling smooths individual risk and enables instant liquidity for lenders to withdraw funds, although exchanges may implement minimum lending periods or withdrawal fees during high-demand periods. Collateral management systems monitor positions continuously, triggering automatic liquidations when market movements threaten lender protection. The technical complexity of these systems requires significant engineering investment but creates competitive advantages through superior capital efficiency and risk management that attract both lenders and borrowers.
Lending Programs as Financial Services
Lending programs position cryptocurrency exchanges as comprehensive financial services providers rather than simple trading platforms, creating stickier user relationships and increasing platform switching costs. Users who maintain both trading and lending positions on a single exchange benefit from consolidated asset management, simplified tax reporting, and seamless capital deployment between trading and lending activities. This integration creates powerful network effects where users concentrate assets on preferred platforms, increasing lifetime value and reducing churn. Exchanges market lending services as passive income opportunities, appealing to long-term cryptocurrency holders seeking yield on otherwise idle assets while providing the exchange with stable, predictable interest income.
The regulatory landscape for crypto lending remains uncertain in many jurisdictions, with some regulators classifying these products as securities requiring registration and compliance with banking regulations. Leading exchanges work proactively with regulators to structure compliant lending programs, implementing KYC verification, accredited investor restrictions, and transparent disclosures about risks. This regulatory foresight creates competitive moats, as smaller exchanges may lack resources to navigate complex compliance requirements. Exchanges also differentiate through insurance programs protecting lender funds, reserve requirements ensuring liquidity, and transparent reporting of loan portfolio health. These trust-building measures justify premium positioning and enable exchanges to offer slightly lower yields while maintaining lender preference through enhanced safety and reliability.
NFT Marketplaces and Digital Asset Trading
NFT marketplaces integrated into cryptocurrency exchanges create synergistic revenue opportunities by leveraging existing user bases, payment infrastructure, and custody solutions. These marketplaces charge transaction fees typically ranging from 2-5% on NFT sales, generating revenue from a rapidly growing market segment that reached $25 billion in trading volume at its peak. Exchanges benefit from offering comprehensive digital asset services under one platform, enabling users to trade both fungible cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens without managing multiple accounts or navigating different interfaces. This convenience factor drives user engagement while providing exchanges with exposure to high-value NFT transactions that can generate substantial per-trade revenue exceeding typical cryptocurrency trading fees.
The strategic value of NFT integration extends beyond direct transaction fees to encompass user acquisition, brand positioning, and future market leadership. NFT enthusiasts often represent younger, tech-savvy demographics attractive to cryptocurrency exchanges seeking to expand beyond early adopter audiences. By supporting NFT trading, creation tools, and discovery features, exchanges position themselves as comprehensive digital asset platforms capable of adapting to evolving market trends. Some platforms have launched their own NFT collections, creating brand awareness and community engagement while generating both initial sales revenue and ongoing royalties. The NFT marketplace business also provides valuable data on emerging creators, trending collections, and user preferences that inform broader platform strategy and partnership opportunities.
NFT Marketplaces as Revenue Channels
NFT marketplaces function as high-margin revenue channels with fee structures typically exceeding cryptocurrency trading fees due to lower price elasticity in digital collectibles markets. A 2.5% fee on a $100,000 NFT sale generates $2,500 in revenue from a single transaction, far exceeding typical cryptocurrency trades. Additionally, many exchanges implement creator royalties automatically, capturing a percentage of secondary sales that provides ongoing revenue as NFTs change hands. The unit economics prove particularly attractive during NFT market booms when trading volume surges, with leading platforms processing hundreds of millions in daily NFT sales. However, NFT markets demonstrate significant volatility, with trading volume declining 70-90% during bear markets, necessitating conservative financial planning.
Differentiation in NFT marketplaces centers on user experience, curation quality, creator support, and technical capabilities. Leading platforms invest in recommendation algorithms, rarity analysis tools, authentication services, and creator incubation programs that attract both high-value collectors and influential artists. Some exchanges offer launchpad services for new NFT collections, charging fees for minting infrastructure, marketing support, and whitelist management. These value-added services create additional revenue streams while building relationships with successful creators whose future projects may launch exclusively on the platform. The social and community aspects of NFT trading also enable exchanges to host virtual events, collaborations, and experiences that strengthen brand loyalty beyond transactional relationships.
Digital Assets and Tokenized Value
Digital assets represent a paradigm shift in value storage and transfer, encompassing cryptocurrencies, NFTs, tokenized real-world assets, and emerging categories like decentralized identity credentials. Cryptocurrency exchanges positioned to support diverse digital asset classes benefit from multiple revenue streams as tokenization expands beyond art and collectibles into real estate, commodities, intellectual property, and financial instruments. The technology infrastructure supporting digital asset trading translates across asset types, enabling exchanges to add new categories relatively efficiently while capturing transaction fees from each market segment. This expansion strategy mirrors how traditional exchanges evolved from stock trading to bonds, commodities, derivatives, and other financial products.
The tokenized value proposition extends beyond speculative trading to encompass utility, governance, access rights, and fractional ownership of previously illiquid assets. Exchanges facilitating these use cases position themselves as critical infrastructure for the digital economy, generating revenue while enabling innovation across industries. Regulatory clarity around digital asset classification will significantly influence exchange strategy, as securities-classified tokens require compliance with registration, disclosure, and investor protection requirements. Forward-thinking exchanges invest in regulatory technology (RegTech) and maintain proactive dialogue with regulators to shape frameworks that enable compliant digital asset trading while protecting investors. This regulatory leadership creates first-mover advantages in emerging digital asset categories with substantial long-term revenue potential.
Advertising Revenue and Sponsored Advertisements
Advertising revenue provides cryptocurrency exchanges with a supplementary income stream that leverages their substantial user traffic and engaged audiences. Exchanges with millions of monthly active users represent valuable advertising inventory for cryptocurrency projects, blockchain services, trading tools, and even traditional financial products seeking crypto-savvy consumers. Sponsored advertisements appear in various formats including banner placements, featured token listings, promoted educational content, and email newsletter sponsorships. Premium advertising placements can command $10,000 to $100,000 monthly depending on positioning and exchange traffic, with programmatic advertising filling remnant inventory at lower rates to maximize revenue from available ad space.
The challenge of advertising monetization lies in balancing revenue generation with user experience and platform integrity. Excessive advertising creates visual clutter, slows page load times, and potentially exposes users to scam projects if vetting proves insufficient. Leading exchanges implement strict advertiser screening, clear disclosure of sponsored content, and user controls enabling ad-free experiences for premium subscribers. This careful balance maintains trust while monetizing attention from users who might otherwise encounter advertising on external platforms. Exchanges also benefit from first-party data about user behavior, trading preferences, and demographics that enables targeted advertising with higher conversion rates and premium pricing compared to generic display advertising networks.
Sponsored Advertisements on Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Sponsored advertisements on cryptocurrency exchanges typically focus on new token launches, DeFi protocols, trading competitions, and blockchain infrastructure services relevant to platform users. These campaigns often include performance-based pricing models where advertisers pay per click, per acquisition, or per trading volume generated rather than simple impression-based fees. This alignment of incentives ensures advertisers receive measurable value while exchanges benefit from sharing in successful campaign outcomes. Major token launches might spend $50,000 to $200,000 on exchange advertising to reach concentrated audiences of potential investors, with exchanges providing detailed analytics on campaign performance, user engagement, and conversion metrics that justify premium pricing.
The advertising product suite extends beyond static display ads to encompass native advertising formats that integrate seamlessly with platform user experience. These include sponsored market analysis articles, promoted trading pairs appearing prominently in interface navigation, featured placement in token discovery tools, and sponsorship of educational webinars or trading tutorials. Native advertising typically commands 3-5x higher pricing than standard display ads due to superior engagement rates and perceived credibility. Exchanges must maintain editorial independence and clearly distinguish sponsored content from organic platform content to preserve user trust. The most successful advertising programs create win-win-win outcomes where advertisers reach relevant audiences, users discover valuable products and services, and exchanges generate revenue while enhancing rather than degrading platform experience.
Advertising Revenue and User Acquisition Balance
Balancing advertising revenue with user acquisition and retention requires sophisticated analysis of lifetime value economics and user satisfaction metrics. If aggressive advertising drives 10% of users to competitor platforms, the lost trading fee revenue over customer lifetime may exceed advertising income, creating value destruction disguised as revenue growth. Smart exchanges monitor key performance indicators including ad load impact on page speed, user complaints about advertising quality, correlation between ad exposure and churn rates, and comparative satisfaction scores versus competitors. These metrics inform advertising policy decisions about maximum ad density, acceptable advertiser categories, and pricing floors that ensure advertising enhances rather than detracts from overall business performance.
User acquisition campaigns themselves represent a form of advertising expenditure that exchanges must optimize for return on investment. Performance marketing through Google, social media, affiliate networks, and content partnerships can cost $50 to $500 per acquired trader depending on geography and competition. Exchanges analyze customer acquisition costs (CAC) against lifetime value (LTV), targeting LTV:CAC ratios of 3:1 or higher to ensure profitable growth. The advertising inventory exchanges possess enables them to reduce external marketing spending by promoting their own products, running referral campaigns, and cross-selling services to existing users. This dual role as both advertising platform and advertiser creates strategic advantages, as exchanges can experiment with ad formats and messaging internally before offering similar products to external advertisers.
Secondary Revenue Generation Strategies for Crypto Exchanges
Arbitrage Trading and Market Opportunities
Arbitrage trading represents a sophisticated revenue opportunity for cryptocurrency exchanges willing to develop proprietary trading operations or provide services enabling user arbitrage activities. Price inefficiencies between exchanges create arbitrage opportunities where cryptocurrencies trade at different prices, enabling traders to buy on cheaper exchanges and sell on expensive ones for risk-free profit. Some exchanges operate internal arbitrage desks that capture these spreads, generating revenue while providing valuable market-making services that improve price discovery and reduce volatility. The technical requirements include real-time price monitoring across multiple exchanges, rapid execution capabilities, and sophisticated risk management systems that account for transfer times, withdrawal limits, and counterparty risk.
Exchanges can monetize arbitrage without direct participation by offering tools and services that enable sophisticated traders to execute arbitrage strategies efficiently. These services include unified API access to multiple exchanges, algorithmic trading infrastructure, low-latency data feeds, and analytics identifying profitable arbitrage opportunities. Premium subscriptions for arbitrage tools can command $200-$1,000 monthly from professional traders generating substantial profits through these strategies. Additionally, exchanges benefit indirectly from arbitrage activity through increased trading volume as arbitrageurs execute frequent trades to capture small profit margins. The presence of active arbitrage traders also improves market efficiency and liquidity, enhancing overall platform quality and attracting additional users.
Price Inefficiencies Across Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Price inefficiencies across cryptocurrency exchanges arise from market fragmentation, varying liquidity levels, regional demand differences, and information asymmetries. A Bitcoin might trade at $45,000 on one exchange while simultaneously trading at $45,150 on another, creating a $150 arbitrage opportunity. These discrepancies typically persist for seconds to minutes before arbitrageurs eliminate the spread, but in fragmented markets with hundreds of exchanges and thousands of trading pairs, new opportunities constantly emerge. The magnitude of arbitrage opportunities varies inversely with market maturity, with newer tokens and smaller exchanges exhibiting larger spreads while major cryptocurrencies on leading platforms maintain tight price alignment through constant arbitrage activity.
Exchanges contribute to or mitigate price inefficiencies through their technology infrastructure, liquidity programs, and market structure design. Platforms with slow execution speeds or high withdrawal fees create barriers that widen arbitrage spreads and reduce market efficiency. Conversely, exchanges offering instant settlement, low fees, and API access facilitate arbitrage activity that tightens spreads and improves price discovery. Some exchanges deliberately create inefficiencies by offering promotional trading pairs with subsidized fees or guaranteed liquidity, knowing that arbitrageurs will drive volume while slightly distorted prices exist. Understanding these dynamics enables exchanges to strategically manage their position in the arbitrage ecosystem, either as destination venues for execution or as origination points for price discovery.
Margin Trading and Advanced Financial Services
Margin trading services enable cryptocurrency exchanges to generate substantial revenue by allowing users to trade with borrowed capital, amplifying both potential profits and losses. Exchanges offer leverage ratios typically ranging from 2x to 100x, meaning traders can control positions worth 2 to 100 times their account balance. The exchange charges interest on borrowed funds, typically 0.01% to 0.1% daily (3.65% to 36.5% annually), creating significant interest income on total borrowed capital. Additionally, margin traders pay higher transaction fees on leveraged positions and exchanges charge liquidation fees when positions are automatically closed due to insufficient collateral. During bull markets, margin trading can represent 15-30% of total exchange revenue as traders seek to maximize exposure to rising prices.
The risk management requirements for margin trading are substantial, requiring sophisticated systems that monitor position values in real-time, automatically liquidate losing positions before they threaten exchange solvency, and maintain adequate capital reserves to cover extreme market movements. Exchanges must balance revenue potential against catastrophic risk, as failures in margin trading systems have bankrupted platforms when cascading liquidations during extreme volatility created losses exceeding user collateral. Leading exchanges implement circuit breakers that halt trading during unusual market conditions, position limits preventing excessive concentration in individual accounts, and insurance funds that cover losses when liquidations fail to protect the exchange. These safeguards enable sustainable margin trading operations that generate revenue while protecting platform integrity.
Margin Trading Risk and Reward Models
Margin trading risk and reward models fundamentally alter the dynamics of crypto exchange revenue generation by introducing leverage that amplifies both user activity and exchange income. A trader with $10,000 using 10x leverage controls a $100,000 position, generating 10x the transaction fees of an unleveraged trader executing the same dollar value of trades. However, the same leverage that amplifies fees also concentrates risk, as rapid market movements can wipe out leveraged positions and create bad debt if liquidations execute at worse prices than anticipated. Exchanges manage this through over-collateralization requirements, insurance funds built from profitable liquidations, and dynamic leverage adjustments that reduce available leverage during high volatility periods when risk escalates.
The reward model for margin trading extends beyond interest and transaction fees to encompass strategic benefits. Margin trading attracts professional and institutional traders who generate higher volumes and operate more sophisticated trading strategies. These users often become anchor clients who provide substantial revenue while demanding premium services that push exchanges to improve technology infrastructure and market depth. The presence of robust margin trading also creates competitive differentiation, as not all exchanges possess the technical capabilities or risk appetite to offer leveraged trading. However, regulatory scrutiny of margin trading has intensified, with some jurisdictions restricting or banning high leverage products due to retail investor protection concerns, forcing exchanges to balance revenue opportunity against regulatory compliance requirements.
Affiliate Programs and Referral Programs
Affiliate programs and referral programs represent highly efficient user acquisition channels for cryptocurrency exchanges, creating performance-based marketing where partners earn commission on trading activity they generate. Typical structures offer affiliates 20-50% of trading fees generated by referred users for 6-12 months or indefinitely, incentivizing sustained promotion. The economics prove compelling for both parties, as exchanges pay only for successful conversions while affiliates earn passive income from their audience or network. Major affiliates, including cryptocurrency influencers, educational platforms, and trading communities can earn $10,000 to $100,000+ monthly by directing thousands of traders to partner exchanges, creating stable income while exchanges acquire users at costs below traditional advertising channels.
The strategic value of affiliate programs extends beyond cost-effective acquisition to encompass credibility and targeted reach. When respected cryptocurrency educators or analysts recommend specific exchanges, their endorsement carries weight that paid advertising cannot replicate. Exchanges cultivate relationships with influential affiliates through tiered commission structures, exclusive promotions for affiliate audiences, dedicated support teams, and performance bonuses rewarding exceptional results. The most sophisticated programs provide affiliates with tracking dashboards, marketing materials, and analytics enabling optimization of promotional efforts. This partnership approach transforms affiliates from transactional vendors into brand advocates who genuinely believe in the exchange’s value proposition and recommend it authentically rather than purely for financial gain.
Incentive-Based User Acquisition Strategies
Incentive-based user acquisition strategies leverage both affiliate programs and direct-to-user referral bonuses to create viral growth loops. Exchanges offer existing users rewards for referring friends, typically providing both referrer and referee with trading fee discounts, bonus cryptocurrency deposits, or tiered rewards based on referred user activity levels. A common structure might offer $10 in Bitcoin to both parties when the new user completes their first trade, then additional bonuses if the referred user achieves specific trading volume thresholds. These programs cost exchanges only when new users generate meaningful activity, ensuring positive return on investment while motivating existing users to become voluntary marketers sharing personal referral links with their networks.
The effectiveness of incentive programs depends on careful calibration of reward amounts, qualification requirements, and fraud prevention mechanisms. If rewards are too generous, mercenary users create multiple accounts to exploit bonuses without genuine trading intent. If too restrictive, legitimate users lack motivation to participate in referral activities. Leading exchanges employ sophisticated fraud detection analyzing device fingerprints, IP addresses, trading patterns, and behavioral signals to identify fake accounts while rewarding genuine referrals generously. They also implement tiered qualification where initial small rewards require minimal activity but substantial bonuses demand significant trading volume, aligning incentives with user quality. Successful programs can reduce customer acquisition costs by 40-60% compared to paid advertising while generating higher-quality users with better retention due to social proof effects of joining platforms recommended by trusted contacts.
Strategic Partnerships and Industry Collaboration
Strategic partnerships enable cryptocurrency exchanges to expand service offerings, enter new markets, and create additional revenue streams through collaboration rather than internal development. Common partnerships include integrations with payment processors enabling fiat currency deposits, custody providers offering institutional-grade asset storage, tax software companies simplifying reporting obligations, and blockchain analytics firms providing compliance solutions. These partnerships generate revenue through revenue sharing agreements where exchanges receive percentage of fees generated through integrated services, referral fees for directing customers to partner platforms, or white-label licensing fees for partner-branded services. Strategic alliances also reduce development costs and time-to-market for new features that would require years of internal investment to build independently.
The evolution toward platform ecosystems reflects maturing cryptocurrency markets where users expect comprehensive service suites rather than fragmented experiences across multiple providers. Exchanges increasingly position themselves as operating systems for cryptocurrency users, curating best-in-class partnerships for wallet services, DeFi access, tax optimization, portfolio tracking, and other adjacent services. This aggregation strategy creates sticky user relationships where platform switching requires abandoning an entire ecosystem rather than just a trading venue. Partnership revenue may represent only 5-10% of total income initially but provides strategic optionality and reduces competitive vulnerability by embedding the exchange deeply into user workflows. The most valuable partnerships also provide data sharing opportunities enabling improved user insights, personalized recommendations, and cross-selling effectiveness.
Strategic Partnerships in the Global Economy
Strategic partnerships in the global economy extend cryptocurrency exchange reach into previously inaccessible markets and user segments. Collaborations with traditional financial institutions like banks and payment networks provide regulatory credibility and access to established customer bases skeptical of pure cryptocurrency platforms. Partnerships with e-commerce platforms enable cryptocurrency payment integration, driving transaction volume as digital assets move from speculative trading into everyday commerce. Geographic expansion partnerships with local exchanges, payment providers, and regulatory consultants accelerate international growth while navigating complex regional compliance requirements. These global partnerships create network effects where each collaboration enhances platform value for all users and attracts additional partnership opportunities.
The financial structure of global partnerships often involves equity investments, joint ventures, or acquisition agreements that align long-term interests beyond simple revenue sharing. An exchange might invest $5-10 million in a regional payment processor to secure preferential integration, exclusive market access, or strategic influence in emerging markets. These investments create portfolio diversification beyond core exchange operations while building relationships that generate sustained competitive advantages. Cross-border partnerships also facilitate regulatory arbitrage where exchanges leverage different jurisdictional frameworks to serve global users more effectively. However, partnership complexity increases operational overhead and coordination requirements, necessitating dedicated business development teams and partnership management infrastructure that justify investment through material revenue contribution and strategic value creation.
Knowledge Sharing and Educational Resources
Knowledge sharing and educational resources serve dual purposes for cryptocurrency exchanges, building user competence while creating additional revenue streams and competitive differentiation. Free educational content including trading guides, market analysis, and cryptocurrency fundamentals helps onboard new users while positioning the exchange as a trusted authority rather than purely transactional platform. This content marketing generates organic traffic through search engines, reduces customer support burden by answering common questions proactively, and improves trading outcomes by creating more informed users who trade more confidently and frequently. The investment in quality educational content typically returns multiples through improved user activation, higher trading volumes, and enhanced brand reputation.
Monetization of educational resources occurs through premium content offerings, certification programs, live training events, and consulting services targeting serious traders and institutions. These paid offerings might include advanced trading courses priced at $200-$2,000, one-on-one coaching sessions with professional traders at $500-$5,000, institutional training programs at $10,000-$100,000, and exclusive research subscriptions providing proprietary market insights. The educational business typically operates at high gross margins once content is created, as digital distribution costs remain minimal regardless of user numbers. Exchanges also benefit from the data generated by educational engagement, understanding which topics interest specific user segments and personalizing product recommendations accordingly to maximize lifetime value.
Online Courses and Learning Platforms
Online courses and learning platforms represent structured educational offerings that cryptocurrency exchanges develop to capture value from the substantial demand for cryptocurrency trading education. These range from beginner courses covering cryptocurrency basics and account security to advanced programs on technical analysis, algorithmic trading, and blockchain fundamentals. Course pricing typically ranges from $50 for introductory content to $500+ for comprehensive multi-module programs with certification. Exchanges partner with industry experts, successful traders, and blockchain developers to create authoritative content that delivers genuine value rather than promotional material disguised as education. The credibility of educational offerings directly impacts enrollment rates and course completion, with high-quality programs generating positive reviews and word-of-mouth marketing that drives organic enrollment growth.
Learning platforms increasingly incorporate gamification, community features, and practical trading simulations that enhance engagement and learning outcomes. Exchanges might offer paper trading environments where students practice strategies risk-free, competitions where learners compete for prizes while applying course concepts, and forums where students support each other’s learning journeys. These interactive elements improve course completion rates from typical 5-10% for passive video courses to 30-50% for engaging learning experiences. Higher completion rates translate to better student outcomes, more positive reviews, and increased willingness to recommend courses to others. The learning platform business also creates valuable user data about interests, skill levels, and learning preferences that inform broader product development and marketing strategies.
Educational Resources as Monetization Tools
Educational resources function as monetization tools through multiple mechanisms beyond direct course sales. Free educational content attracts organic search traffic that converts into platform signups, with users who discover exchanges through educational content demonstrating 20-40% higher lifetime value than those acquired through paid advertising due to higher trust and platform familiarity. Educational engagement also creates opportunities for upselling premium services, with learning platform users showing increased propensity to adopt advanced trading tools, subscribe to premium features, and participate in higher-margin services like margin trading. The education business serves as a profitable customer acquisition channel with superior economics compared to traditional marketing.
The strategic value of educational resources extends to community building and thought leadership that strengthens exchange positioning in competitive markets. Exchanges hosting regular webinars, publishing market research, and contributing to industry knowledge sharing establish themselves as expert authorities rather than commodity trading platforms. This reputation attracts institutional clients, media coverage, and partnership opportunities unavailable to exchanges focusing solely on execution services. Educational initiatives also create content libraries that provide enduring value, as evergreen material on blockchain fundamentals or trading psychology remains relevant for years and continues attracting users long after initial creation. The compound effect of educational investment accelerates over time as content libraries grow and organic reach expands through search rankings and social sharing.
Key Factors Influencing Crypto Exchange Profitability
User Experience and Platform Optimization
User experience directly impacts cryptocurrency exchange profitability through its influence on user acquisition costs, trading frequency, retention rates, and lifetime value. Exchanges with superior UX convert website visitors to registered users at 2-3x higher rates than competitors with clunky interfaces, immediately reducing customer acquisition costs. Once onboarded, users encountering intuitive navigation, responsive design, and frictionless trading workflows trade 40-60% more frequently than those struggling with complex interfaces. This increased activity directly translates to higher transaction fee revenue without additional marketing expenditure. User experience excellence also dramatically improves retention, with well-designed platforms maintaining 70-80% annual retention compared to 40-50% for poorly designed competitors, multiplying lifetime value and overall profitability.
Platform optimization encompasses technical performance, mobile responsiveness, and continuous improvement based on user feedback and behavioral analytics. Exchanges achieving 99.9%+ uptime and sub-100 millisecond latency attract high-frequency traders and institutional clients whose activity generates disproportionate revenue. Mobile optimization proves critical as 60-70% of cryptocurrency users access platforms via smartphones, with mobile-first design improving engagement metrics across all user segments. A/B testing of interface elements, onboarding flows, and feature placements enables data-driven optimization that incrementally improves conversion rates and trading activity. The cumulative impact of UX excellence can represent 20-30% revenue advantage over comparable exchanges with average user experience, making design quality a core competitive advantage rather than aesthetic consideration.
Blockchain Technology and Operational Transparency
Blockchain technology enables operational transparency that builds user trust and differentiates exchanges in markets where security concerns and platform failures have caused billions in user losses. Exchanges implementing proof of reserves through blockchain verification allow users to independently confirm that platform holdings match user balances, providing mathematical certainty that fractional reserve practices are not occurring. This transparency reduces user anxiety during market stress, preventing panic withdrawals that can threaten liquidity and operational stability. Transparent exchanges can maintain lower capital reserves as baseline trust reduces probability of bank runs, improving capital efficiency and return on equity. The technology investment in transparency systems typically generates positive return within 12-18 months through improved user retention and reduced risk of catastrophic trust failures.
Operational transparency extends beyond asset verification to encompass fee disclosure, order execution quality reporting, and security incident communication. Exchanges publishing real-time data on trading volume, liquidity depth, and fee revenue demonstrate confidence in their business model and provide users with information necessary for informed platform selection. This openness creates competitive pressure for industry improvement as less transparent competitors face difficult questions about what they might be hiding. The blockchain technology underlying cryptocurrency exchanges also enables automated compliance reporting, audit trail creation, and regulatory technology innovations that reduce operational overhead while demonstrating good faith cooperation with regulators. These factors combine to create a transparency premium where users willingly accept slightly higher fees or lower rewards from trustworthy exchanges versus opaque competitors offering marginally better economics but uncertain reliability.
Financial Inclusion and Currency Conversion Benefits
Financial inclusion initiatives create both social impact and commercial opportunity for cryptocurrency exchanges serving underbanked populations in developing economies. These markets often lack efficient banking infrastructure, forcing residents to pay exorbitant fees for basic financial services like remittances, savings, and currency conversion. Cryptocurrency exchanges providing mobile-accessible trading, low-minimum deposits, and competitive currency conversion rates tap into enormous unmet demand while generating sustainable revenue from high transaction volumes. The unit economics in emerging markets differ from developed economies, with lower average transaction values but much higher frequency and larger addressable populations. An exchange processing $10 million in monthly volume from 100,000 active users in emerging markets can generate equivalent or superior revenue to $50 million from 5,000 users in developed markets due to favorable cost structures and user engagement patterns.
Currency conversion represents a particularly lucrative service in markets with unstable local currencies, capital controls, or limited banking access. Exchanges facilitating conversion between local currencies and stable cryptocurrencies or major fiat currencies charge spreads of 1-3%, creating substantial revenue while providing genuine value to users seeking to protect savings from inflation or send money internationally. The financial inclusion mission also generates positive public relations, regulatory goodwill, and partnership opportunities with development organizations and governments seeking to expand financial access. Exchanges successfully balancing profitability with accessibility build loyal user communities that provide defensible competitive positions as markets mature and larger competitors attempt entry. The key lies in maintaining fee structures that remain profitable while significantly undercutting traditional financial services, creating compelling value propositions for underserved populations.
Future Trends in Crypto Exchange Monetization
Emerging Revenue Models in Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Emerging revenue models reflect the evolution of cryptocurrency exchanges beyond simple trading platforms into comprehensive financial services ecosystems. Decentralized exchange (DEX) aggregation services allow centralized exchanges to offer access to DEX liquidity while capturing fees on routed orders, combining centralized user experience with decentralized execution. Institutional custody and prime brokerage services target professional asset managers requiring secure storage, reporting, and multi-exchange execution, generating fees from asset under custody (AUM) in addition to trading commissions. Carbon credit trading and sustainability-linked products address growing environmental concerns while creating new revenue streams as exchanges facilitate markets for blockchain-based carbon offsets and renewable energy certificates. These innovations demonstrate how exchanges continuously identify adjacent markets and services where their infrastructure and user relationships create competitive advantages.
GameFi integration and metaverse asset trading represent frontier opportunities as gaming and virtual worlds increasingly incorporate blockchain technology and digital asset ownership. Exchanges supporting in-game item trading, virtual land transactions, and cross-game asset interoperability position themselves at the intersection of gaming, cryptocurrency, and social media, potentially tapping into gaming industry revenues exceeding $200 billion annually. Artificial intelligence integration enables automated trading assistants, sentiment analysis tools, and personalized recommendations offered through premium subscriptions or performance-based pricing. The revenue potential of these emerging models remains uncertain, but exchanges investing in experimentation and strategic positioning benefit from first-mover advantages as successful models achieve product-market fit and scale rapidly across competitive platforms seeking to avoid obsolescence.
Impact of Regulation on Revenue Strategies
Regulation profoundly shapes cryptocurrency exchange revenue strategies, with compliance requirements creating both constraints and opportunities. Jurisdictions implementing comprehensive licensing regimes for cryptocurrency exchanges typically mandate minimum capital requirements, operational standards, customer protection measures, and ongoing reporting obligations. These regulations increase operational costs by $1-5 million annually for medium-sized exchanges but also create barriers to entry that protect compliant platforms from unregulated competition. Exchanges investing proactively in regulatory compliance position themselves to capture institutional flows and serve regulated financial products like ETFs and pension funds that require licensed, compliant counterparties. The compliance investment generates return through access to higher-value market segments willing to pay premium fees for regulatory certainty.
Revenue model restrictions vary dramatically across jurisdictions, with some regions banning margin trading, limiting leverage ratios, restricting token listings, or prohibiting certain marketing practices. Exchanges operating globally must adapt revenue strategies to local regulations while maintaining platform consistency where possible. This complexity drives some platforms toward licensed operation in multiple jurisdictions to serve global users compliantly, while others exit regulated markets in favor of crypto-friendly jurisdictions with lighter regulatory oversight. The regulatory landscape will likely converge toward international standards over coming years, reducing arbitrage opportunities but creating clarity that enables long-term business planning. Exchanges developing strong regulatory relationships and contributing constructively to policy development gain influence over regulatory outcomes while building reputational assets valuable for partnerships, licensing, and institutional relationships.
Long-Term Sustainability of Crypto Exchange Revenue
Long-term sustainability of crypto exchange revenue depends on continuous adaptation to market evolution, regulatory changes, and competitive dynamics. Historical precedents from traditional exchange industries suggest fee compression as markets mature, with transaction costs declining by 80-90% over 20-30 year periods as competition intensifies and technology improves execution efficiency. Cryptocurrency exchanges should anticipate similar trends, planning for scenarios where trading fees decline from current 0.1-0.5% levels to 0.01-0.05% as market structure evolves. This trajectory necessitates continuous innovation in revenue diversification, operational efficiency, and value-added services that justify ongoing platform usage despite commoditization of basic trading functionality. Exchanges building strong brands, loyal communities, and comprehensive service suites position themselves to maintain pricing power longer than commodity platforms competing purely on execution price.
The sustainability equation also involves balancing growth investment with profitability extraction. Aggressive platforms reinvest 70-90% of revenue into technology development, marketing, and geographic expansion, sacrificing near-term profitability for market position and long-term dominance. Conservative approaches extract 30-50% profit margins, building financial reserves and shareholder returns but potentially ceding market share to growth-focused competitors. The optimal strategy depends on market maturity, competitive intensity, and available capital for growth investment. Exchanges in winner-take-most markets may require aggressive investment to achieve scale necessary for long-term profitability, while platforms serving niche markets or geographies can optimize for steady profitable operation. Understanding these strategic choices and their implications for revenue sustainability enables informed decision-making about resource allocation, competitive positioning, and the timeframe over which cryptocurrency exchanges must prove their business models viable in evolving digital asset markets. For those seeking to build their own cryptocurrency exchange, partnering with experienced developers is essential for long-term success.
Build a Revenue-Optimized Crypto Exchange
Build a secure, scalable, and revenue-diversified crypto exchange tailored to your business vision.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency exchanges have evolved from simple trading platforms into sophisticated financial services ecosystems generating revenue through diverse, complementary strategies. The foundation remains transaction fees and trading fees that scale with volume, but sustainable profitability increasingly depends on diversification across subscription services, token listings, lending programs, NFT marketplaces, and emerging revenue opportunities. Successful exchanges balance user acquisition costs with lifetime value optimization, maintain competitive fee structures while avoiding destructive price wars, and invest continuously in user experience, security, and regulatory compliance that justify premium positioning in crowded markets.
The future of crypto exchange monetization will be shaped by regulatory evolution, technological innovation, and competitive dynamics as the industry matures. Exchanges investing in transparency, financial inclusion, educational resources, and strategic partnerships position themselves to capture value as cryptocurrency transitions from speculative asset class to integral component of the global economy. Revenue diversification, operational excellence, and adaptive strategy will separate winners from losers as market consolidation accelerates and users concentrate activity on platforms delivering superior security, functionality, and trust. Understanding these monetization mechanisms and profitability drivers proves essential for anyone participating in the cryptocurrency ecosystem as investor, entrepreneur, or informed user navigating the digital asset revolution.
Revenue Model Lifecycle
| Stage | Primary Focus | Revenue Sources | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Launch (0-6 months) | User Acquisition | Transaction fees, referral programs | User growth, trading volume |
| Growth (6-18 months) | Market Expansion | Token listings, margin trading, subscriptions | Market share, revenue per user |
| Maturity (18-36 months) | Diversification | Lending, NFTs, partnerships, education | Profitability, retention rates |
| Scale (36+ months) | Ecosystem Building | All revenue streams, institutional services | Market dominance, lifetime value |
Frequently Asked Questions
Cryptocurrency exchanges generate revenue through multiple streams including transaction fees charged on every trade, listing fees for new tokens, subscription services for premium features, and margin trading commissions. Additionally, they earn from lending programs where they charge interest rates on borrowed crypto assets, advertising revenue from sponsored advertisements, and various financial services. The primary monetization comes from trading volume and transaction fees which can range from 0.1% to 1% per trade depending on the exchange and user tier.
The main revenue models include trading fees and commissions which represent the largest income source, subscription-based premium services offering advanced analytics and tools, token listing fees ranging from $50,000 to millions of dollars, and lending programs that generate interest income. Secondary models encompass NFT marketplaces, affiliate programs, referral programs, margin trading services, and strategic partnerships. Most successful cryptocurrency exchanges employ a diversified approach combining multiple revenue streams to ensure sustainability in the competitive global economy.
Transaction fees vary significantly across cryptocurrency exchanges, typically ranging from 0.04% to 0.50% per trade for maker and taker fees. Premium exchanges may charge higher fees but offer better security and user experience, while newer platforms often provide competitive rates to attract users. Volume-based fee structures reward high-frequency traders with reduced commissions, sometimes dropping below 0.02% for institutional traders. These transaction fees multiply with trading volume, making them the most substantial revenue source for most platforms.
Token listing is the process where cryptocurrency exchanges evaluate and add new digital assets to their trading platform. Exchanges charge listing fees that can range from $50,000 for smaller platforms to over $1 million for top-tier exchanges. This involves thorough due diligence, security audits, and compliance checks. The profitability is substantial as exchanges can list dozens of tokens annually, and successful listings often drive trading volume which generates additional transaction fees and enhances the platform’s reputation in blockchain technology circles.
Crypto lending programs allow users to lend their digital assets to borrowers in exchange for interest payments. Exchanges act as intermediaries, charging interest rates typically between 5% to 15% annually, while paying lenders a portion of these earnings. The exchange profits from the interest rate spread between what borrowers pay and what lenders receive. These lending programs have become significant financial services, contributing to revenue diversification while providing users with passive income opportunities and improving overall platform engagement.
NFT marketplaces integrated into cryptocurrency exchanges provide an additional revenue channel by charging transaction fees on NFT sales, typically 2% to 5% per transaction. As digital assets gain popularity, exchanges benefit from increased user acquisition and trading activity. NFT marketplaces also create cross-selling opportunities, encouraging users to trade both cryptocurrencies and NFTs on the same platform. This integration enhances user experience and positions exchanges as comprehensive digital asset platforms in the evolving global economy.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







