Key Takeaways
- Crypto MLM projects without real products or utility almost always fail within 12 to 24 months
- Ponzi-like reward structures that depend heavily on recruitment rather than sales are legally and financially unsustainable
- Ignoring AML and KYC regulations has led to shutdowns and legal action against numerous crypto MLM platforms
- Poor tokenomics, including unlimited supply and lack of vesting periods, destroy investor trust quickly
- Centralized control and anonymous teams are major red flags that often precede exit scams
- Sustainable crypto MLM projects require transparent operations, audited smart contracts, and compliance-first approaches
- Building trust through ethical marketing and realistic return promises is essential for long-term success
Introduction: The Rise and Fall of Crypto MLM Projects
The cryptocurrency boom of the past decade created a perfect storm for network marketing businesses. Combine the promise of decentralized wealth with multi-level marketing structures, and you get a business model that attracted millions of participants worldwide. Unfortunately, the vast majority of these projects ended in disaster.
Between 2017 and 2023, hundreds of crypto MLM projects launched with big promises. Most collapsed within months. Some turned out to be outright scams. Others simply could not sustain their business models once the initial excitement faded. The total losses for participants run into billions of dollars globally.
But here is the thing. Not every crypto MLM project is destined to fail. The technology itself is not the problem. The failures happened because of specific, avoidable mistakes. Understanding what went wrong with these projects gives us a roadmap for building something better.
This article breaks down the biggest lessons from failed crypto MLM projects. Whether you are an entrepreneur planning to launch a network marketing platform, an investor evaluating opportunities, or simply someone curious about this space, these insights will help you separate legitimate projects from disasters waiting to happen.
What Is a Crypto MLM Project?
A crypto MLM project combines blockchain technology with multi-level marketing business structures. Participants typically earn rewards in cryptocurrency for both personal sales and the sales made by people they recruit into the network. If you want to understand MLM meaning, types, benefits and global regulations, it helps to first grasp how traditional network marketing works before adding the crypto layer.
Traditional MLM companies sell physical products like supplements, cosmetics, or household goods. Distributors earn commissions on their sales and a percentage of sales made by their downline (people they recruited). The crypto version replaces physical products with digital tokens, trading platforms, or blockchain-based services.
Common Crypto MLM Business Models
| Model Type | How It Works | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Token Investment | Buy tokens at launch price, recruit others to buy, earn bonuses | Very High |
| Trading Pools | Pool funds for crypto trading, share profits based on recruitment tier | High |
| Mining Operations | Invest in mining hardware or cloud mining, earn based on network size | Medium to High |
| NFT Marketplace | Buy and sell NFTs with commission structures for referrals | Medium |
| DeFi Products | Decentralized finance services with MLM referral bonuses | Variable |
The key difference between traditional and crypto MLM lies in the speed and scale. Cryptocurrency transactions happen instantly across borders. There are no shipping delays or inventory management issues. This speed made crypto MLM projects grow explosively. It also made them collapse just as fast when problems emerged.
Why So Many Crypto MLM Projects Failed
According to data from blockchain analytics firms, over 80% of crypto MLM projects launched between 2017 and 2022 either shut down or became inactive within two years. The reasons fall into several categories, but they all connect to fundamental flaws in how these projects were designed and operated.
The most common failure points include lack of real products, unsustainable reward structures, regulatory violations, poor tokenomics, lack of transparency, centralized control, and weak technology. Each of these problems alone can sink a project. Most failed crypto MLMs had multiple issues happening simultaneously.
Let us examine each lesson in detail.
Lesson 1: No Real Product Means No Long-Term Survival
The single biggest predictor of crypto MLM failure is the absence of a genuine product or service. Many projects launched with nothing more than a token and promises of future value. Participants were essentially paying for the right to recruit others, which is the textbook definition of a pyramid scheme.
Take the example of BitConnect, which collapsed in 2018. The project promised returns of up to 40% per month through a “trading bot.” There was no verifiable product. The bot was never independently audited. When regulators issued cease and desist orders, the whole thing fell apart within weeks. Investors lost an estimated 2 billion dollars.
Compare this to legitimate blockchain businesses that happen to use MLM distribution models. Companies selling actual software, verified trading tools, or real utility tokens can sustain themselves because the product generates independent value. The MLM structure becomes a marketing channel rather than the entire business model.
The Test:
Would anyone buy this product or service if there was no referral bonus attached? If the answer is no, the project is built on sand.
Lesson 2: Ponzi-Like Structures Always Collapse
A Ponzi scheme pays existing investors using money from new investors rather than from legitimate profits. In crypto MLM projects, this manifests as reward structures where recruitment bonuses far exceed what the underlying business actually generates.
The math is simple and brutal. If each participant needs to recruit three people to break even, and those three need to recruit three more, the network needs to grow exponentially forever. After just 13 levels, you would need more participants than there are people on Earth. Every pyramid structure eventually runs out of new recruits, and when it does, it collapses.
The Pyramid Math Problem
| Level | New Recruits Needed | Total Participants |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 243 | 364 |
| 10 | 59,049 | 88,573 |
| 13 | 1.59 million | 2.39 million |
| 20 | 3.48 billion | 5.23 billion |
Warning signs of Ponzi behavior include guaranteed returns regardless of market conditions, pressure to recruit above all else, complicated payout structures designed to obscure where money actually comes from, and difficulty withdrawing funds when large numbers of participants request payouts simultaneously.
Lesson 3: Ignoring Regulations Leads to Shutdowns
Cryptocurrency operates in a regulatory grey area in many countries. Some crypto MLM operators took this as permission to ignore regulations entirely. This was a catastrophic mistake.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements exist for good reasons. They prevent criminal organizations from using financial systems to launder money. They create accountability and paper trails. When crypto MLM projects skip these requirements, they attract regulatory attention for all the wrong reasons.
OneCoin is perhaps the most notorious example. Operating without proper licensing or compliance procedures, the project attracted billions in investments before regulators across multiple countries shut it down. Its founder was convicted of fraud and money laundering. Participants who thought they were investing in the next Bitcoin lost everything.
The lesson is clear. Operating in regulatory grey areas might seem like a competitive advantage initially, but it creates existential risk for the entire project. Legitimate projects build compliance into their foundation from day one.
Lesson 4: Poor Tokenomics Destroy Trust
Tokenomics refers to the economic design of a cryptocurrency token. It includes total supply, distribution method, inflation rate, and mechanisms that control buying and selling pressure. Bad tokenomics can destroy even projects with good intentions.
Common tokenomics failures in crypto MLM projects include unlimited token supply that dilutes value over time, no vesting periods that allow founders and early investors to dump tokens immediately, concentrating large percentages of tokens in few wallets, and no real utility driving demand for the token.
When founders hold 30% or more of total supply without lock-up periods, participants are essentially hoping the founders will not sell and crash the price. That is not investing. That is gambling on human behavior.
Comparison: Failed vs Sustainable Tokenomics
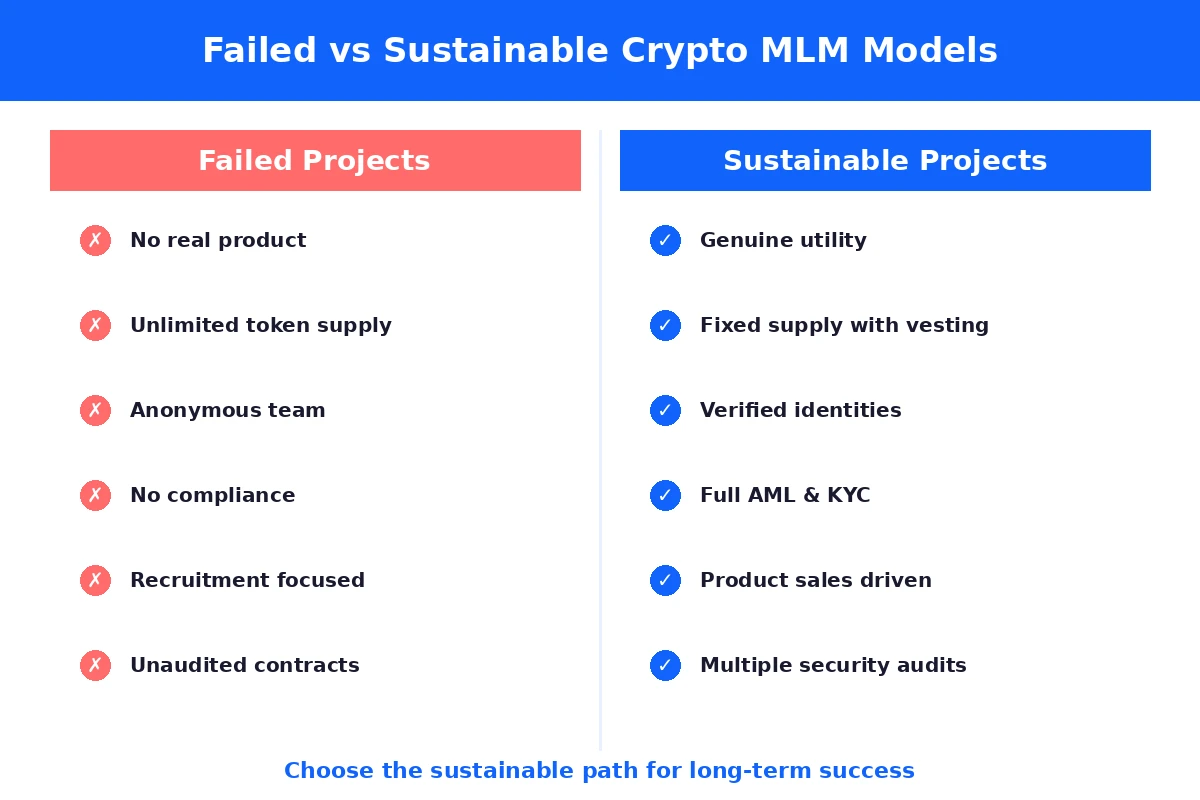
| Factor | Failed Projects | Sustainable Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Token Supply | Unlimited or excessive | Fixed or deflationary |
| Vesting Period | None or very short | 12 to 48 months with gradual release |
| Team Allocation | 30% or more | 10 to 15% with long lock-ups |
| Utility | Speculation only | Required for platform services |
| Burn Mechanism | Absent | Transaction fees burned or redistributed |
Lesson 5: Lack of Transparency Kills Credibility
Anonymous teams became popular in crypto because early Bitcoin developers valued privacy. Some crypto MLM operators exploited this culture to hide their identities while running questionable operations. When things went wrong, participants had no one to hold accountable.
Transparency failures go beyond anonymous founders. They include missing or plagiarized whitepapers, no third-party audits of smart contracts or business practices, exaggerated or false partnership claims, fabricated trading volume or user statistics, and marketing that promises specific returns without basis.
Legitimate crypto projects maintain transparency through verified team identities, regular financial reporting, independent audits, and honest marketing that acknowledges risks alongside opportunities. Understanding what MLM business is and its types helps distinguish between legitimate network marketing and operations designed to deceive.
Build Your Crypto MLM Platform the Right Way
Avoid the mistakes that sank hundreds of projects. Get transparent, compliant, and sustainable blockchain MLM solutions built by experts with 8+ years of experience.
Lesson 6: Centralized Control Increases Risk
One of the core promises of blockchain technology is decentralization. Ironically, most failed crypto MLM projects were highly centralized. A small group of people controlled the smart contracts, held the private keys, and could modify the rules at will.
This centralization enabled several types of abuse. Admin wallet manipulation allowed operators to mint tokens for themselves or freeze participant accounts. Frozen withdrawals prevented people from accessing their funds during critical moments. Exit scams happened when operators simply disappeared with the treasury.
The PlusToken scam demonstrated this risk on a massive scale. Operators controlled all aspects of the platform and eventually ran off with an estimated 2 billion dollars worth of cryptocurrency. Participants had no recourse because the entire system depended on trusting a few anonymous individuals.
Decentralized governance, multi-signature wallets, and time-locked smart contracts can reduce these risks. But implementing true decentralization requires technical expertise and a genuine commitment to giving participants control.
Lesson 7: Weak Technology and Security Failures
Building a crypto MLM platform requires serious technical capabilities. Smart contracts must be secure. The platform must handle thousands of concurrent users. Security protocols must protect participant funds and data. Many failed projects cut corners on technology and paid the price.
Smart contract bugs have resulted in millions of dollars in losses. Some bugs allowed hackers to drain funds. Others locked tokens permanently. A few enabled operators to manipulate balances without detection. These failures were preventable with proper auditing and testing.
Infrastructure failures caused different problems. Platforms that could not scale crashed during high-traffic periods. This prevented withdrawals exactly when people most wanted their money, fueling panic and distrust. Inadequate security led to data breaches that exposed participant information.
Professional cryptocurrency MLM software development addresses these issues through rigorous testing, third-party security audits, scalable architecture, and ongoing maintenance. Nadcab Labs has spent over 8 years developing blockchain solutions that prioritize security and reliability, understanding that technical shortcuts create business-ending vulnerabilities.
Common Red Flags in Failed Crypto MLMs

Looking at patterns across hundreds of failed projects reveals consistent warning signs. Learning to spot these red flags can save you from participating in doomed ventures.
| Red Flag | Why It Matters | What to Look For Instead |
|---|---|---|
| Guaranteed high returns | No legitimate investment can guarantee returns | Realistic projections with risk disclosures |
| Recruitment focus over sales | Indicates pyramid structure | Product sales driving most revenue |
| Anonymous team | No accountability when problems arise | Verified identities and professional backgrounds |
| No compliance framework | Regulatory action can shut down operations | Licensed operations with AML and KYC procedures |
| Aggressive influencer marketing | Paid promoters rarely disclose risks | Organic growth through product quality |
| Withdrawal restrictions | Sign of liquidity problems | Clear, unrestricted withdrawal policies |
| Unaudited smart contracts | Security vulnerabilities and potential manipulation | Multiple independent audits from reputable firms |
The Lifecycle of a Failed Crypto MLM Project
Failed crypto MLM projects tend to follow a predictable pattern. Understanding this lifecycle helps identify where a project stands and whether collapse is imminent.
Stage 1: Launch Hype (Months 1 to 3)
Aggressive marketing creates excitement. Early participants see quick returns as new money flows in. Testimonials spread on social media. Everything seems legitimate.
Stage 2: Growth Phase (Months 3 to 12)
Network expands rapidly. Token price rises due to buying pressure. Participants reinvest earnings. The project appears successful. Red flags are dismissed as FUD (fear, uncertainty, doubt).
Stage 3: Plateau (Months 12 to 18)
Recruitment slows. Token price stagnates or drops. Withdrawal requests increase. Platform begins implementing restrictions. Leaders start quietly exiting positions.
Stage 4: Collapse (Months 18 to 24)
Withdrawals freeze partially or completely. Token price crashes. Communication from leadership becomes sparse. Regulatory action or exit scams occur. Participants realize losses.
Stage 5: Aftermath
Legal proceedings may follow. Participants attempt recovery through lawsuits or law enforcement. Founders may face criminal charges. Most participants never recover their investments.
What Future Crypto MLM Projects Can Learn
The failures of past projects provide a clear blueprint for building sustainable crypto MLM ventures. The key is learning from mistakes rather than repeating them.
Sustainable compensation models ensure that rewards come from actual value creation rather than endless recruitment. This means capping recruitment bonuses, emphasizing product sales commissions, and designing structures that remain profitable even with zero network growth.
Regulatory-friendly architecture treats compliance as a feature rather than an obstacle. This includes proper licensing, KYC and AML procedures, transparent financial reporting, and legal structures that protect both the business and participants.
Transparent operations build the trust that failed projects destroyed. This means verified team identities, regular audits, honest marketing, and open communication about both successes and challenges.
Long-term utility focus ensures the project has value beyond speculation. Products or services that people actually want, regardless of investment returns, create sustainable demand for the token and the network.
Best Practices to Build a Sustainable Crypto MLM
Drawing from both the failures and the few successes in this space, here are the essential practices for building a crypto MLM that lasts.
| Category | Best Practice | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Real product with independent value | Product should sell without referral incentives |
| Compensation | Sustainable reward structure | Commissions tied to actual revenue, not recruitment |
| Compliance | Full regulatory alignment | Proper licensing, AML, KYC, and legal structure |
| Tokenomics | Sound economic design | Fixed supply, vesting periods, utility-driven demand |
| Technology | Security-first development | Audited contracts, scalable infrastructure, ongoing maintenance |
| Transparency | Open operations | Verified team, regular reporting, honest marketing |
| Governance | Decentralized control | Multi-sig wallets, community voting, time-locked contracts |
Nadcab Labs brings over 8 years of blockchain development experience to building these systems correctly. The company has seen firsthand what happens when projects cut corners on compliance, security, or economic design. That experience informs an approach that prioritizes long-term sustainability over short-term gains.
Conclusion: Turning Failures into Smarter Crypto MLM Models
The history of crypto MLM projects is largely a history of failures. But those failures teach us exactly what not to do. Projects that ignore these lessons will join the list of cautionary tales. Projects that learn from them have a chance to build something genuinely valuable.
The core message is straightforward. Build real products that people want. Design compensation structures that work without constant growth. Comply with regulations from day one. Create transparent operations that earn trust. Invest in security and technology. Give participants meaningful control over their investments.
Compliance is not just about avoiding legal problems. It is a competitive advantage. In a space filled with scams and failures, legitimate operations stand out. Trust becomes a differentiator that attracts both participants and partners.
The future of crypto MLM depends on whether new projects learn from the mistakes of their predecessors. The technology offers real benefits for network marketing businesses. Instant global transactions, programmable rewards, transparent tracking, and reduced friction are genuine advantages. But realizing those benefits requires building on solid foundations.
For entrepreneurs considering this space, the path forward is clear. Do not try to reinvent the wheel. Do not assume you can avoid the problems that sank hundreds of projects before you. Instead, invest in the expertise, compliance infrastructure, and technology that sustainable projects require. The upfront investment pays for itself many times over compared to the cost of failure.
The crypto MLM space will continue evolving. Regulations will tighten. Technology will improve. Participants will become more sophisticated. Projects that adapt to these changes while maintaining ethical operations will thrive. Those that cling to the failed models of the past will continue failing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Most crypto MLM projects fail due to unsustainable business models that rely heavily on recruitment rather than real product value. Many projects promise high returns without a viable revenue source, making them vulnerable to collapse once new member inflow slows. Poor tokenomics, lack of transparency, regulatory violations, and weak technical infrastructure further accelerate failure. Without long-term utility and compliance, these projects struggle to survive market pressure.
No, not all crypto MLM projects are scams, but a large number fail because they unintentionally adopt Ponzi-like structures. Legitimate projects focus on real products or services, ethical compensation plans, and regulatory compliance. Scam projects, on the other hand, emphasize guaranteed returns and aggressive recruitment. The key difference lies in transparency, sustainability, and value creation beyond member onboarding.
Common mistakes include unrealistic reward promises, poorly designed tokenomics, ignoring legal compliance, and lack of transparency. Many projects failed to implement AML and KYC procedures, leading to regulatory crackdowns. Others suffered from centralized control, where founders could manipulate funds or halt withdrawals. These mistakes eroded user trust and ultimately caused project collapse.
Investors face risks such as financial loss, frozen funds, regulatory action, and exposure to fraudulent schemes. Market volatility can quickly devalue tokens, while poorly secured platforms are vulnerable to hacks. Additionally, investors may unknowingly participate in illegal structures, putting them at legal risk. Understanding these risks is essential before engaging with any crypto MLM opportunity.
Red flags include guaranteed or fixed returns, referral income outweighing product value, lack of verifiable team information, and absence of regulatory compliance. Projects that avoid audits, discourage questions, or rely heavily on influencer hype should be approached with caution. A transparent whitepaper, clear token utility, and compliant onboarding process are signs of a healthier project.
Future projects must prioritize sustainability over hype by building real utility, ethical compensation models, and strong compliance frameworks. Transparent operations, audited smart contracts, and balanced tokenomics are critical. Learning from past failures helps developers design platforms that protect users, comply with regulations, and build long-term trust in the crypto ecosystem.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







