Key Takeaways
- Industry leaders are investing billions of dollars annually in IoT research and development to create standardized protocols that enable seamless device communication across platforms.
- The convergence of artificial intelligence with IoT ecosystems is accelerating predictive maintenance capabilities and reducing operational downtime by up to 50% in manufacturing sectors.
- Enterprise-driven IoT infrastructure is establishing security frameworks that address critical vulnerabilities and protect sensitive data across interconnected networks worldwide.
- Smart manufacturing initiatives led by major corporations are transforming traditional production lines into intelligent automated systems that optimize resource utilization continuously.
- Collaborative efforts between technology giants and regulatory bodies are shaping compliance standards that balance innovation with consumer protection requirements effectively.
- The transportation sector is experiencing revolutionary changes through connected vehicle technologies and intelligent traffic management systems deployed by leading automotive manufacturers.
- Energy companies are leveraging IoT solutions to build sustainable smart grid infrastructures that reduce carbon emissions while improving distribution efficiency significantly.
- Interoperability challenges are being addressed through industry consortia that develop universal communication standards enabling diverse devices to work together harmoniously.
- Digital identity management and device authentication protocols established by leading enterprises are becoming foundational elements of secure IoT network architectures.
- The future of IoT technology will be characterized by edge computing expansion, 5G integration, and autonomous decision making capabilities driven by machine learning algorithms.
Introduction: The Growing Influence of Industry Leaders in IoT
The Internet of Things has evolved from a futuristic concept into a transformative force reshaping industries across the globe. Today, industry leaders are not merely participants in this technological revolution but are actively architecting its trajectory through substantial investments, strategic partnerships, and groundbreaking innovations. From multinational technology corporations to specialized manufacturing giants, these pioneers are establishing the frameworks, protocols, and infrastructures that will define how billions of connected devices interact, communicate, and deliver value in the coming decades.
The influence of these industry titans extends far beyond product creation. They are shaping regulatory landscapes, establishing security benchmarks, and creating ecosystems that smaller organizations can leverage for their own digital transformation journeys. Understanding how these leaders operate and the directions they are pursuing provides invaluable insights for businesses seeking to navigate the complex IoT landscape successfully. This comprehensive exploration examines the multifaceted ways in which industry leaders are molding the future of IoT technology and what this means for enterprises, consumers, and society at large.[1]
Understanding the Core Concept of IoT Technology
The Internet of Things represents a vast network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect, exchange, and act upon data. These connected devices range from simple household appliances and wearable gadgets to sophisticated industrial machinery and critical infrastructure components. The fundamental principle underlying IoT is the ability to bridge the physical and digital worlds, creating intelligent systems that can monitor, analyze, and respond to real world conditions autonomously or with minimal human intervention.
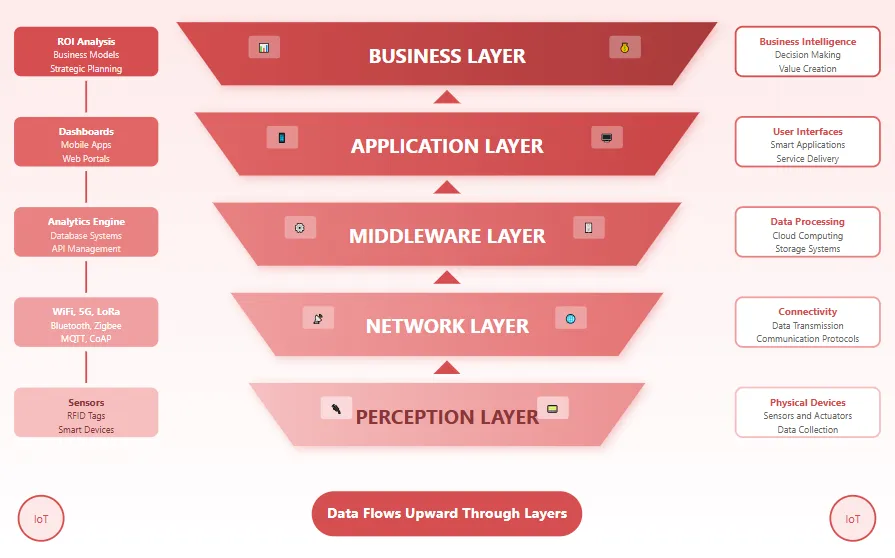
At its core, IoT architecture comprises several essential layers including perception, network, middleware, application, and business layers. The perception layer consists of sensors and actuators that gather environmental data. The network layer facilitates data transmission through various communication protocols. Middleware provides the computational infrastructure for data processing and storage. The application layer delivers user facing services, while the business layer focuses on generating actionable insights and value creation. Understanding this layered architecture is crucial for appreciating how industry leaders are influencing each component to advance the overall IoT ecosystem
Why Industry Leadership Matters in IoT Evolution
The trajectory of IoT technology is significantly influenced by organizations that possess the resources, expertise, and market position to drive meaningful change. Industry leadership in IoT matters because these entities establish the benchmarks against which all other solutions are measured. When a major technology corporation introduces a new connectivity standard or security protocol, it often becomes the de facto industry standard that competitors and partners must adopt to remain relevant. This phenomenon creates a cascading effect that accelerates innovation while simultaneously ensuring a degree of standardization essential for widespread interoperability.
Furthermore, industry leaders serve as validators for emerging technologies. Their adoption of particular IoT solutions signals market viability and encourages broader acceptance among enterprise customers and consumers alike. These organizations also bear the responsibility of addressing critical challenges such as data privacy concerns, cybersecurity threats, and environmental sustainability, setting precedents that shape regulatory frameworks and consumer expectations. The decisions made by industry leaders today will reverberate through the IoT landscape for years to come, making their strategic directions worthy of close examination by all stakeholders in the connected device ecosystem.
The Role of Innovation in Advancing IoT Ecosystems
Innovation serves as the lifeblood of IoT advancement, with industry leaders consistently pushing technological boundaries to unlock new possibilities. These organizations maintain dedicated research and innovation centers where engineers and scientists explore breakthrough technologies ranging from advanced sensor designs and low power communication protocols to sophisticated edge computing architectures and artificial intelligence integration. The investments made by leading companies in research and innovation often exceed the entire budgets of smaller competitors, creating significant competitive advantages and accelerating the pace of technological progress.
One notable area of innovation involves the miniaturization of sensors and processing units, enabling IoT capabilities to be embedded in increasingly smaller form factors. Industry leaders are also pioneering developments in energy harvesting technologies that allow devices to operate indefinitely without battery replacement, addressing a critical limitation in widespread IoT deployment. Additionally, innovations in communication protocols such as narrow band IoT and low power wide area networks are extending connectivity options for devices in remote or challenging environments where traditional networks cannot reach effectively.
How Large Enterprises Are Defining IoT Standards
The establishment of universal standards represents one of the most significant contributions industry leaders make to IoT evolution. Standards ensure that devices from different manufacturers can communicate seamlessly, data can be exchanged securely, and consumers can enjoy consistent experiences across various products and platforms. Major technology corporations actively participate in standards bodies and industry consortiums, dedicating substantial resources to developing specifications that address interoperability, security, and performance requirements across diverse IoT applications.
These standardization efforts cover multiple aspects of IoT technology including communication protocols, data formats, security frameworks, and device management procedures. Industry leaders often collaborate on these initiatives despite being competitors in the marketplace, recognizing that shared standards benefit the entire ecosystem by reducing fragmentation and accelerating adoption. The following table highlights key IoT standards and the organizations leading their establishment.
| Standard Name | Primary Focus | Leading Organizations | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matter | Smart Home Interoperability | Apple, Google, Amazon, Samsung | Consumer IoT Devices |
| OPC UA | Industrial Communication | Siemens, Bosch, Rockwell | Manufacturing Systems |
| OneM2M | Service Layer Platform | ETSI, TIA, CCSA | Cross Domain IoT |
| Thread | Mesh Networking Protocol | Google, Apple, Qualcomm | Home Automation |
| MQTT | Lightweight Messaging | IBM, OASIS | Telemetry Applications |
Industry Driven IoT Infrastructure and Architecture
The infrastructure supporting IoT deployments has matured significantly under the guidance of industry leaders who have invested heavily in creating robust, scalable, and secure foundations for connected device ecosystems. Cloud computing giants have established specialized IoT platforms that provide comprehensive services, including device provisioning, data ingestion, storage, analytics, and application integration. These platforms abstract away much of the complexity involved in managing millions of connected devices, enabling organizations of all sizes to implement IoT solutions without building infrastructure from scratch.
Edge computing architecture represents another area where industry leaders are making substantial contributions. By processing data closer to its source rather than transmitting everything to centralized cloud servers, edge architectures reduce latency, conserve bandwidth, and enhance privacy. Leading technology companies are developing purpose-built edge computing hardware and software solutions that bring intelligence to the network periphery, enabling real-time decision making for time-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring systems.
The Impact of Data Intelligence on IoT Growth
Data represents the ultimate value generator in IoT ecosystems, and industry leaders are pioneering sophisticated approaches to extract meaningful insights from the massive volumes of information generated by connected devices. Advanced analytics platforms leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend actions that would be impossible for human analysts to discern manually. These capabilities transform raw sensor readings into actionable business intelligence that drives operational improvements, enhances customer experiences, and creates entirely new revenue opportunities.
The integration of AI with IoT, often referred to as AIoT, represents a particularly transformative development championed by industry leaders. Machine learning models trained on historical IoT data can predict equipment failures before they occur, optimize energy consumption patterns based on usage predictions, and personalize services based on individual behavior patterns. Leading organizations are also developing federated learning approaches that enable AI models to be trained across distributed IoT devices without centralizing sensitive data, addressing privacy concerns while still benefiting from collective intelligence.
Real World Example: Predictive Maintenance
A leading manufacturing corporation implemented IoT sensors across its production facilities, combined with AI driven analytics. The system monitors equipment vibration, temperature, and operational parameters in real time, predicting potential failures 72 hours in advance. This implementation reduced unplanned downtime by 45% and maintenance costs by 30% within the first year of deployment.
Security and Trust: How Leaders Are Strengthening IoT Networks
Security remains one of the most critical challenges in IoT adoption, and industry leaders are at the forefront of developing comprehensive solutions to protect connected device ecosystems. The expanded attack surface created by billions of interconnected devices presents unprecedented security challenges that require multi layered defense strategies. Leading organizations are implementing security by design principles that embed protection mechanisms at every level of IoT architecture from hardware trusted execution environments to encrypted communication channels and secure cloud platforms.
Zero trust security models are gaining prominence in IoT deployments guided by industry leader implementations. These frameworks assume no device or user should be automatically trusted, requiring continuous verification regardless of network location. Advanced threat detection systems employing behavioral analytics can identify anomalous device activities that might indicate compromise, enabling rapid response to emerging threats. Industry leaders are also establishing certification programs and security assessment frameworks that help organizations evaluate the protection capabilities of IoT solutions before deployment.
Essential IoT Security Parameters
Device Authentication
Verifying device identity before network access
Data Encryption
Protecting information in transit and at rest
Firmware Updates
Secure over the air patching capabilities
Access Control
Granular permission management systems
The Rise of Scalable and Interoperable IoT Systems
Scalability and interoperability represent foundational requirements for IoT ecosystems that aspire to connect billions of devices across diverse applications and environments. Industry leaders are addressing these challenges through modular architectures that can expand seamlessly as deployment requirements grow. Cloud native designs leveraging containerization and microservices enable IoT platforms to scale horizontally across distributed infrastructure, accommodating sudden increases in connected device populations without performance degradation.
Interoperability efforts led by industry consortiums are breaking down silos between proprietary systems that historically prevented devices from different manufacturers working together effectively. Open APIs and standardized data models facilitate integration across platforms, enabling organizations to select best of breed solutions without being locked into single vendor ecosystems. These developments are particularly significant for enterprise IoT deployments where organizations need to connect legacy systems with modern connected devices while maintaining flexibility for future technology evolution.
Industry Leaders and the Expansion of Smart Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector has emerged as one of the most transformative domains for IoT technology adoption, with industry leaders driving the Industry 4.0 revolution. Smart factories equipped with interconnected sensors, automated machinery, and intelligent control systems are redefining production capabilities. Leading manufacturers are implementing digital twin technologies that create virtual replicas of physical production systems, enabling simulation, optimization, and predictive analysis without disrupting actual operations.
Collaborative robots working alongside human operators represent another innovation pioneered by industry leaders in manufacturing IoT. These intelligent machines use sensors and AI to perform tasks safely in shared workspaces, enhancing productivity while maintaining workplace safety. Supply chain visibility has also improved dramatically through IoT implementations that track materials, components, and finished goods throughout their journey from suppliers to customers, enabling just in time inventory management and rapid response to disruptions.
Smart Manufacturing IoT Implementation Lifecycle
Transforming Mobility and Transportation Through IoT
The transportation industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation driven by IoT technologies championed by leading automotive manufacturers and technology companies. Connected vehicles equipped with hundreds of sensors generate vast amounts of data about vehicle performance, driver behavior, traffic conditions, and environmental factors. This information enables advanced safety features such as collision avoidance systems, adaptive cruise control, and lane departure warnings that are saving lives on roads worldwide.
Fleet management solutions leveraging IoT provide logistics companies with unprecedented visibility into their operations. Real time tracking enables route optimization, fuel efficiency improvements, and proactive maintenance scheduling that reduces costs while improving service reliability. Autonomous vehicle development represents the ultimate expression of IoT in transportation, with industry leaders investing billions in research and development to create self driving systems that promise to revolutionize mobility for future generations.
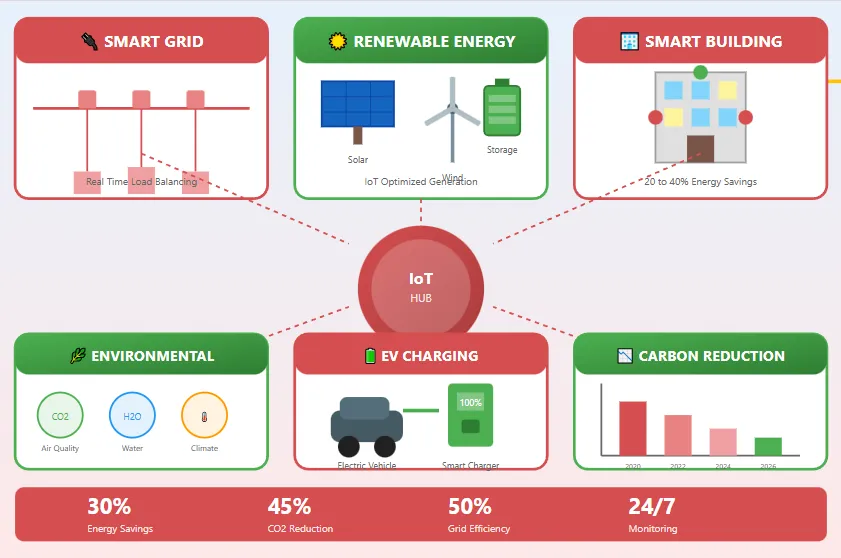
The Role of IoT in Energy and Sustainability Initiatives
Energy sector transformation through IoT represents one of the most impactful applications of connected device technology, with industry leaders driving sustainability initiatives that address global climate challenges. Smart grid implementations enable utility companies to balance electricity supply and demand in real time, integrating renewable energy sources more effectively while reducing waste and improving reliability. Advanced metering infrastructure provides consumers with detailed insights into their energy consumption patterns, empowering informed decisions that reduce both costs and environmental impact.
Building management systems incorporating IoT sensors and controls optimize heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy patterns and environmental conditions. These implementations typically achieve energy savings of 20% to 40% in commercial buildings. Industry leaders in the energy sector are also developing IoT solutions for monitoring and maintaining renewable energy installations including solar farms and wind turbines, maximizing generation efficiency while minimizing maintenance costs through predictive analytics.
Digital Identity and Device Authentication in IoT
Establishing trustworthy digital identities for IoT devices has become a critical focus area for industry leaders concerned with security and accountability in connected ecosystems. Every device requires a unique, verifiable identity that enables authentication, authorization, and audit trail maintenance throughout its operational lifecycle. Public key infrastructure adapted for IoT environments provides cryptographic foundations for device identity management, though resource constraints in many IoT devices require innovative lightweight implementations.
Hardware security modules and trusted platform modules embedded in IoT devices provide tamper resistant storage for cryptographic keys and certificates that form the basis of device identity. Industry leaders are also exploring blockchain-based approaches to decentralized identity management that could eliminate single points of failure while enabling verifiable credentials across organizational boundaries. These identity frameworks are essential for scenarios requiring high assurance such as medical devices, critical infrastructure, and financial applications where the consequences of identity spoofing could be severe.
Collaboration Between Enterprises and IoT Ecosystems
The complexity of IoT deployments increasingly requires collaboration between multiple organizations contributing specialized expertise to comprehensive solutions. Industry leaders are fostering ecosystem partnerships that bring together device manufacturers, connectivity providers, platform operators, application developers, and system integrators. These collaborative models enable end to end solutions that would be difficult for any single organization to deliver independently while creating opportunities for innovation at each layer of the technology stack.
Partner programs established by major technology companies provide smaller organizations with access to resources, training, and go-to-market support that accelerate their IoT initiatives. Co development agreements enable joint innovation efforts that combine the scale and resources of industry leaders with the agility and specialized domain knowledge of smaller partners. These collaborative approaches are proving essential for addressing vertical market requirements in sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and retail where deep industry expertise must combine with sophisticated IoT capabilities.
Regulatory Influence and Compliance Shaped by Industry Leaders
Industry leaders play significant roles in shaping the regulatory frameworks that govern IoT deployments across different jurisdictions. Through participation in standards bodies, government advisory committees, and public policy discussions, these organizations influence the development of regulations that balance innovation enablement with consumer protection and security requirements. Their technical expertise helps regulators understand the practical implications of proposed rules, often resulting in more effective and implementable compliance requirements.
Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California has become a significant consideration for IoT deployments that collect and process personal information. Industry leaders have developed privacy enhancing technologies and data governance frameworks that help organizations meet regulatory requirements while still extracting value from IoT data. The following comparison table outlines major regulatory frameworks affecting IoT implementations globally.
| Regulation | Region | Key Requirements | IoT Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | European Union | Data protection, consent, right to erasure | Privacy by design mandatory |
| CCPA | California, USA | Consumer rights, data disclosure | Transparency requirements |
| Cyber Resilience Act | European Union | Security standards, vulnerability handling | Mandatory security updates |
| NIST Framework | United States | Cybersecurity best practices | Reference architecture guidance |
| PSTI Act | United Kingdom | Default passwords banned, disclosure | Consumer device security |
Real World Use Cases Driving IoT Adoption
Compelling use cases developed and deployed by industry leaders serve as powerful demonstrations of IoT value that accelerate broader market adoption. In healthcare, remote patient monitoring systems enable continuous tracking of vital signs for individuals with chronic conditions, reducing hospital readmissions while improving quality of life. Agricultural IoT solutions combining soil sensors, weather data, and satellite imagery optimize irrigation and fertilization, increasing crop yields while reducing resource consumption and environmental impact.
Retail environments are being transformed through IoT implementations that enhance customer experiences while improving operational efficiency. Smart shelves automatically track inventory levels and trigger replenishment orders. Connected fitting rooms provide personalized recommendations based on items customers try on. Supply chain visibility from warehouse to store shelf ensures products are available when and where customers want them. These use cases demonstrate the tangible business value that IoT delivers across diverse industry sectors.
Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring, connected medical devices, hospital asset tracking, medication adherence systems
Agriculture
Precision farming, livestock monitoring, automated irrigation, drone based crop analysis
Retail
Smart inventory management, customer analytics, connected point of sale, personalized shopping experiences
Smart Cities
Intelligent traffic management, public safety systems, waste management optimization, environmental monitoring
Challenges Industry Leaders Face in IoT Advancement
Despite their substantial resources and capabilities, industry leaders face significant challenges in advancing IoT technology. The sheer diversity of devices, protocols, and use cases creates complexity that defies simple solutions. Legacy system integration remains problematic as organizations seek to connect decades-old industrial equipment with modern IoT platforms. Talent shortages in specialized areas such as embedded systems engineering, data science, and cybersecurity constrain the pace of innovation even for well funded initiatives.
Monetization models for IoT investments continue to evolve as organizations seek sustainable approaches to funding ongoing platform operations and innovation. The transition from product sales to service based revenue requires fundamental changes in organizational structure and customer relationships. Additionally, managing the environmental impact of billions of connected devices including electronic waste and energy consumption presents sustainability challenges that industry leaders must address responsibly to maintain public trust and regulatory compliance.
Thesis: The successful advancement of IoT technology requires industry leaders to address technical, economic, and sustainability challenges simultaneously while fostering ecosystem collaboration that enables innovation at scale without compromising security or consumer trust.
The Future Outlook: What’s Next for IoT Technology
The future of IoT technology promises even more transformative developments as industry leaders continue pushing technological boundaries. The proliferation of 5G networks will enable IoT applications requiring ultra low latency and massive device density that were previously impractical. Satellite-based IoT connectivity will extend coverage to remote locations globally, enabling applications in maritime, agriculture, and resource extraction industries that lack terrestrial network infrastructure.
Artificial intelligence integration will deepen, with more sophisticated machine learning models running directly on IoT devices rather than relying on cloud processing. This evolution toward truly intelligent edge devices will enable autonomous decision-making in real-time applications while enhancing privacy through local data processing. Quantum computing developments may eventually enable cryptographic protections far stronger than current approaches while potentially threatening existing security implementations, requiring proactive preparation by industry leaders.
Digital twin technology will expand beyond manufacturing into areas such as urban planning, healthcare, and environmental management, creating virtual replicas of complex systems that enable simulation and optimization. The convergence of IoT with augmented reality and virtual reality will create immersive interfaces for monitoring and controlling connected devices. As these technologies mature, the boundary between physical and digital worlds will continue blurring, creating new possibilities limited only by imagination and the willingness of industry leaders to invest in realizing them.
Ready to Transform Your Business with IoT Solutions?
Partner with experts who understand the complexities of IoT implementation and can guide your digital transformation journey.
Why Choose Nadcab Labs for Your IoT Journey
With over 8 years of dedicated experience in IoT technology and connected systems, Nadcab Labs has established itself as a trusted authority in delivering cutting-edge IoT solutions across diverse industry verticals. Our team of seasoned engineers and technology specialists has successfully implemented hundreds of IoT projects ranging from smart manufacturing systems and connected vehicle platforms to comprehensive smart city infrastructures and healthcare monitoring networks.
At Nadcab Labs, we combine deep technical expertise with practical industry knowledge to create IoT solutions that deliver measurable business value. Our comprehensive approach encompasses strategy consulting, architecture design, device integration, platform development, security implementation, and ongoing support services. We understand the nuances of working with industry leaders and have developed methodologies that ensure successful outcomes regardless of project scale or complexity.
Our commitment to excellence has earned us recognition as a preferred IoT partner for enterprises seeking to leverage connected technologies for competitive advantage. Whether you are beginning your IoT journey with a pilot project or scaling existing implementations across global operations, Nadcab Labs provides the expertise, resources, and commitment necessary to transform your vision into reality. Partner with us to experience the difference that genuine technical authority and unwavering dedication to client success can make in your digital transformation initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
IoT refers to general consumer connected devices like smart home gadgets, wearables, and appliances. IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) focuses specifically on industrial applications such as manufacturing plants, oil refineries, and logistics operations. IIoT typically requires higher reliability, security standards, and real time data processing capabilities compared to standard IoT implementations used in everyday consumer products.
IoT implementation costs vary significantly based on scale, complexity, and industry requirements. Small scale projects may start from $10,000 to $50,000, while enterprise level deployments can range from $100,000 to several million dollars. Costs include hardware sensors, connectivity infrastructure, cloud services, software platforms, integration work, and ongoing maintenance fees that businesses must budget for long term success.
Python leads IoT programming due to its simplicity and extensive libraries for data processing. C and C++ are preferred for embedded systems requiring low level hardware control. JavaScript powers many IoT dashboards and web interfaces. Other popular choices include Java for enterprise applications, Rust for security critical systems, and Go for scalable backend services handling IoT data streams.
Simple IoT pilot projects can be deployed within 2 to 4 months. Medium complexity implementations typically require 6 to 12 months including planning, development, testing, and rollout phases. Large scale enterprise IoT deployments may take 18 to 24 months or longer depending on integration requirements, regulatory compliance needs, and organizational change management processes involved.
Yes, many IoT systems incorporate edge computing capabilities allowing devices to process data locally without continuous internet access. These devices store information temporarily and sync when connectivity resumes. Mesh networks enable device to device communication independently. However, cloud dependent features and remote monitoring require stable internet connections for full functionality and real time analytics.
AWS IoT Core dominates enterprise deployments with comprehensive cloud integration. Microsoft Azure IoT Hub offers strong hybrid cloud capabilities. Google Cloud IoT provides excellent analytics and machine learning integration. Other notable platforms include IBM Watson IoT, Cisco IoT Cloud Connect, and open source options like ThingsBoard and Home Assistant for various scale requirements and specific use cases.
IoT devices use various communication protocols based on requirements. WiFi handles high bandwidth short range connections. Bluetooth and Zigbee serve low power short range applications. LoRaWAN and NB IoT enable long range low power communications. Cellular networks (4G/5G) provide mobile connectivity. MQTT and CoAP protocols facilitate lightweight messaging between devices and cloud platforms efficiently.
Edge computing processes data closer to where it originates rather than sending everything to centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency for time sensitive applications, decreases bandwidth costs, improves reliability during connectivity issues, and enhances privacy by keeping sensitive data local. Edge computing is essential for autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real time monitoring systems.
Evaluate vendors based on industry experience, technical expertise, platform compatibility, and support capabilities. Review case studies and client references from similar projects. Assess security certifications, compliance standards, and data privacy practices. Consider scalability options, integration flexibility, and long-term roadmap alignment. Request proof of concept demonstrations before committing to significant investments.
Consumer IoT devices typically last 3 to 5 years before requiring replacement due to battery degradation or software obsolescence. Industrial IoT sensors designed for harsh environments can operate 10 to 15 years with proper maintenance. Lifespan depends on power source, environmental conditions, usage intensity, and manufacturer quality standards. Regular firmware updates extend functional life significantly.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






