Understanding transaction costs is essential in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for anyone aiming to maximize returns and reduce expenses. Whether operating within a crypto coin and token ecosystem or interacting with decentralized applications, gas fees play a critical role in overall blockchain usability.
Among the innovative solutions that emerged to tackle high transaction fees, gas tokens represent a fascinating chapter in Ethereum’s history and blockchain optimization. This comprehensive guide explores what gas tokens are, how they work, and their role in the broader landscape of crypto token solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Gas Tokens Defined: Gas tokens were specialized crypto tokens that allowed users to store gas when fees were low and release it when fees were high, effectively locking in lower transaction costs.
- Minting and Burning: Users minted gas tokens by deploying minimal smart contracts during low-fee periods and burned them during high-fee periods to trigger gas refunds that offset transaction costs.
- Popular Solutions: GasToken2 (GST2) and CHI Gastoken were the most widely used Ethereum gas tokens, popular among traders, DeFi users, and smart contract developers.
- London Hard Fork Impact: EIP-3529, implemented in the London Hard Fork, eliminated the gas refund mechanism that made traditional gas tokens economically viable, rendering them obsolete.
- Modern Alternatives: Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon now offer dramatically reduced gas fees by processing transactions off the main Ethereum chain.
- EIP-1559 Benefits: The reformed fee structure introduced base fees that burn ETH, making gas prices more predictable while creating deflationary pressure on the network.
- Gas Optimization Strategies: Transaction timing, batching multiple operations, and using gas-efficient protocols remain effective methods to reduce blockchain transaction costs.
- Future Improvements: Ethereum’s roadmap includes increased gas limits, ZK-EVM integration, and state structure updates aimed at further reducing fees and improving scalability.
- Cross-Chain Solutions: Alternative networks like Solana, Polygon, and BSC offer different gas models with significantly lower transaction costs for users seeking cheaper alternatives.
What Are Gas Tokens?
To understand what gas tokens are, we first need to grasp the concept of gas fees in blockchain networks. In the cryptocurrency ecosystem, particularly on Ethereum, every transaction requires computational resources to be processed and validated. These computational costs are measured in “gas,” and users pay crypto gas fee tokens to compensate network validators (previously miners) for their work.
A blockchain gas token is a specialized type of crypto token designed to help users save on transaction fees by leveraging specific mechanisms within the Ethereum protocol. Think of gas tokens as a way to “store” gas when network fees are low and “release” it when fees are high, effectively allowing users to lock in lower gas prices for future use.
The most well-known examples of Ethereum gas tokens include GasToken2 (GST2) and CHI (Chi Gastoken), which were revolutionary crypto token solutions that enabled significant cost savings for frequent Ethereum users and decentralized application (dApp) developers.
How Gas Tokens Work
Understanding how gas tokens work requires diving into the technical mechanisms of the Ethereum blockchain. The genius behind gas tokens crypto lies in exploiting two features of the Ethereum protocol that provided gas refunds:
The Gas Refund Mechanism
Historically, Ethereum’s protocol included gas refund mechanisms designed to incentivize good blockchain housekeeping. Users could receive partial refunds on their transaction fees by:
- Clearing storage within smart contracts
- Destroying contracts using the SELFDESTRUCT operation
The contract destruction method, which refunded 24,000 gas units, proved more efficient and became the foundation for gas token implementations.
Minting and Burning Process
The lifecycle of gas tokens crypto involves two key operations:
Minting (Creation):
- Users “mint” gas tokens when network gas prices are low
- The minting process deploys minimal smart contracts to the blockchain
- Each deployed contract can later be destroyed for a gas refund
- This requires paying gas fees upfront, but at a lower price point
Burning (Destruction):
- Users “burn” or “free” gas tokens when gas prices are high
- Burning destroys the previously created contracts
- The destruction triggers a gas refund that offsets transaction costs
- The savings come from the difference in gas prices between minting and burning
This meant that even though gas tokens consumed more total gas units, they saved users actual ETH when the gas price differential was favorable – typically requiring a ratio of 3:4 between low and high gas prices.
Popular Gas Token Solutions
GasToken2 (GST2)
GST2 was one of the pioneering crypto token solutions for gas optimization. It created extremely simple “dummy” contracts with minimal bytecode:
if (msg.sender != GST2) { throw; }
selfdestruct(msg.sender)
This simple logic ensured that only the GST2 contract could destroy these child contracts and claim the refund, preventing unauthorized access to stored gas.
CHI Gastoken
CHI, developed by the 1inch team, operated on similar principles but with enhanced efficiency. Both Ethereum gas tokens worked by:
- Creating contracts during low-fee periods
- Storing them until network congestion increased fees
- Destroying them to offset high transaction costs
Users could buy and hold these gas tokens during periods of lower network activity and redeem them during peak periods to pay for gas at a lower effective cost. This made them popular among:
- High-frequency traders
- DeFi protocol users
- Smart contract developers
- Automated trading bots
The London Hard Fork: End of an Era
The story of traditional gas tokens took a dramatic turn with Ethereum London Hard Fork[1] on August 5, 2021. This upgrade implemented several Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), most notably EIP-3529, which fundamentally changed the gas refund mechanism.
EIP-3529 Impact
EIP-3529 significantly reduced gas refunds to prevent exploitation and optimize network resources. This change:
- Eliminated the economic viability of traditional gas tokens like GST2 and CHI
- Removed the SELFDESTRUCT gas refund mechanism
- Made these crypto tokens largely obsolete for their original purpose
The Ethereum community recognized that while gas refunds were designed to incentivize good practices, they were being “gamed” by gas token systems, creating inefficiencies in the network. As one source noted, “gas tokens such as GST2 and CHI, used by developers to secure lower prices when deploying smart contracts, will become obsolete” with the London upgrade.
Modern Gas Optimization Strategies
While traditional gas tokens crypto are no longer effective post-London Hard Fork, the need for gas optimization remains critical. Here are contemporary crypto token solutions and strategies:
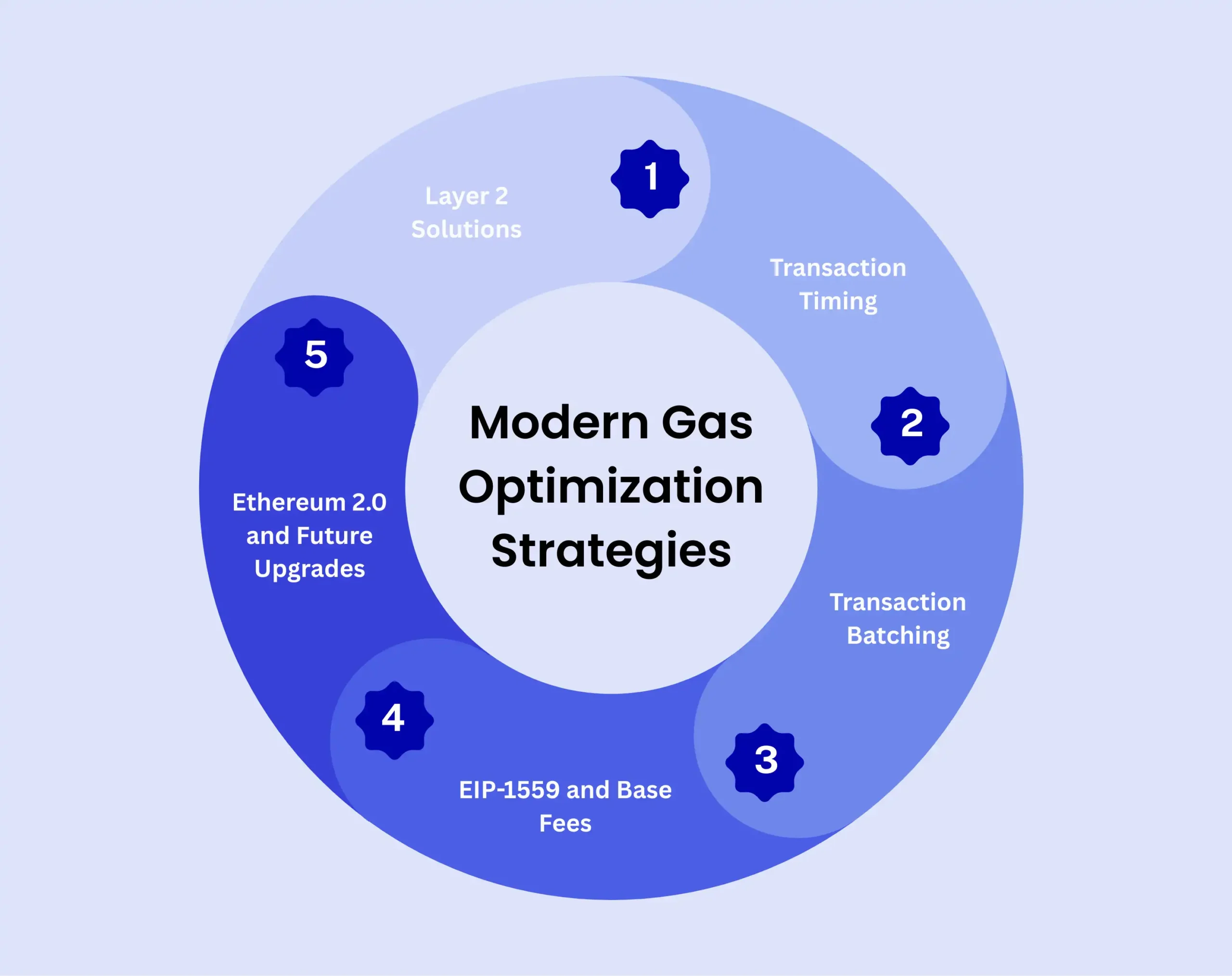
1. Layer 2 Solutions
L2[2] networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon offer dramatically reduced gas fees by processing transactions off the main Ethereum chain while maintaining security through the main network.
2. Transaction Timing
Users can monitor gas prices and schedule transactions during off-peak hours when network congestion is lower. Tools like ETH Gas Station provide real-time gas price tracking.
3. Transaction Batching
Combining multiple operations into a single transaction reduces overall gas costs by executing multiple actions within one transaction context.
4. EIP-1559 and Base Fees
The London Hard Fork also introduced EIP-1559[3], which reformed the fee structure with a base fee that burns ETH, making gas prices more predictable and the network deflationary.
5. Ethereum 2.0 and Future Upgrades
Ethereum’s ongoing transition to Proof of Stake and future scalability improvements aim to reduce gas fees through increased throughput and efficiency. Vitalik Buterin recently indicated that Ethereum is making significant progress on the blockchain trilemma, with plans for gas limit increases between 2026 and 2028.
Alternative Networks and Their Gas Models
Different blockchain networks have developed various approaches to transaction fees:
Binance Smart Chain (BSC):
- Uses BNB as the gas token
- Generally lower fees than Ethereum mainnet
Polygon:
- Uses MATIC for gas fees
- Significantly cheaper transactions
Arbitrum:
- Uses ETH for gas but at fraction of mainnet costs
- Configurable to use other ERC-20 tokens
Solana:
- Uses SOL for transaction fees
- Extremely low costs but different architecture
The Evolution of Crypto Token Solutions
The rise and fall of gas tokens illustrates the dynamic nature of blockchain technology. While GST2 and CHI served their purpose during a specific period, the Ethereum network evolved to address the underlying issues more comprehensively.
Lessons from Gas Tokens
- Innovation within constraints: Gas tokens demonstrated how users could creatively work within protocol rules to optimize costs
- Protocol evolution: Ethereum’s willingness to eliminate exploitable mechanisms shows commitment to long-term network health
- User-driven solutions: The cryptocurrency community continuously develops tools to address pain points
Modern Token Economics
Today’s successful crypto tokens focus on:
- Real utility and use cases
- Sustainable tokenomics
- Revenue-sharing mechanisms
- Governance rights
- Staking rewards
According to recent trends, tokens that survive and thrive in 2026 will have “cash flow and/or revenue sharing and/or fee capture mechanisms” built into their design.
Practical Considerations for Users
If You’re New to Crypto:
Understanding crypto gas fee tokens is essential for managing your transaction costs effectively. Always:
- Check current gas prices before transacting
- Use gas price estimation tools
- Consider alternative networks for smaller transactions
- Factor gas costs into your trading strategy
For Developers:
Gas optimization in smart contract development remains crucial:
- Write efficient code to minimize computational costs
- Batch operations where possible
- Consider Layer 2 deployment
- Use optimization tools and best practices
For Active Traders:
Managing gas tokens and fees impacts profitability:
- Monitor network congestion patterns
- Use DEX aggregators that optimize gas usage
- Consider gas-efficient protocols
- Evaluate whether Layer 2 solutions meet your needs
The Future of Gas Fees and Blockchain Optimization
As we move through 2026 and beyond, the landscape of blockchain gas tokens and fee optimization continues to evolve:
Upcoming Ethereum Improvements
- Increased gas limits: Planned expansions to 75M-80M gas limit
- ZK-EVM integration: Zero-knowledge rollups for enhanced scalability
- State structure updates: Improvements to how Ethereum stores data
- Gas repricing: Adjustments to operation costs for better efficiency
Cross-Chain Innovation
New solutions are emerging that address gas fees across multiple chains:
- Universal gas payment systems
- Cross-chain fee optimization
- Gasless transaction protocols
- Meta-transaction services
Sustainability Focus
Modern crypto token solutions increasingly emphasize:
- Energy efficiency
- Environmental sustainability
- Economic sustainability
- Long-term viability
Conclusion
Gas tokens represent an important milestone in Ethereum’s journey toward scalable and efficient blockchain infrastructure. While solutions like GST2 and CHI are no longer viable after the London Hard Fork, they showcased how creative engineering and economic incentives could temporarily alleviate high transaction costs. Their rise and fall also highlighted Ethereum’s ability to adapt, removing exploitable mechanisms in favor of more sustainable, protocol-level improvements such as EIP-1559 and Layer 2 scaling.
Today, gas optimization has shifted from token-based workarounds to holistic network upgrades and smarter user strategies. With Layer 2 solutions, improved fee predictability, and ongoing scalability enhancements, the future of blockchain transactions is becoming more efficient and accessible. The legacy of gas tokens lives on as a lesson in innovation, reminding users and developers alike that blockchain technology evolves rapidly, and successful solutions must evolve with it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Gas tokens are specialized crypto tokens that were designed to reduce Ethereum transaction fees by taking advantage of gas refund mechanisms. Users could mint them when gas prices were low and burn them later to offset higher gas costs.
Gas tokens worked by storing gas through smart contract deployment and later releasing it via contract destruction. The gas refunds received during destruction helped lower the effective cost of transactions during periods of high network congestion.
The most widely used Ethereum gas tokens were GasToken2 (GST2) and CHI (Chi Gastoken). These tokens were commonly used by DeFi traders, developers, and automated bots to optimize transaction costs.
Gas tokens became obsolete after Ethereum’s London Hard Fork in August 2021. The introduction of EIP-3529 significantly reduced gas refunds, removing the economic incentive that gas tokens relied on.
Modern gas optimization relies on Layer 2 solutions, efficient smart contract design, transaction batching, better fee predictability through EIP-1559, and using alternative blockchains with lower fees.
While gas token contracts still exist on-chain, they no longer provide meaningful gas savings and are not recommended for use. Most wallets and DeFi platforms have moved away from supporting them.
Most blockchains do not use gas tokens like Ethereum once did. Instead, they use native tokens (such as BNB, SOL, or MATIC) for transaction fees and rely on network design to keep costs low.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.