Key Takeaways
- Gas price in smart contract represents the cost per computational unit paid to network validators for processing blockchain transactions and executing contract code.
- Transaction fees equal gas units consumed multiplied by gas price, making code optimization essential for reducing costs across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian operations.
- Network congestion directly impacts gas price in smart contract, with peak periods seeing costs increase by 10x or more compared to low-activity windows.
- EIP-1559 introduced base fee plus priority fee model, improving gas price predictability while burning a portion of fees to manage network economics.
- Layer 2 solutions including Arbitrum, Optimism, and Polygon offer dramatically reduced gas price in smart contract execution compared to Ethereum mainnet.
- Failed transactions still consume gas, making proper gas limit estimation and price setting critical for avoiding unnecessary costs in production systems.
- DeFi protocols require careful gas price management to ensure transactions execute profitably, especially during arbitrage and liquidation operations.
- Enterprise blockchain implementations should implement gas price monitoring and automated adjustment systems for optimal transaction cost management.
Understanding Gas Price in Smart Contract Transactions
Gas price in smart contract represents the fundamental economic mechanism enabling blockchain networks to function securely and efficiently. With over eight years of experience building enterprise blockchain solutions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets, our agency has witnessed countless projects succeed or fail based on their gas price management strategies. Every operation on Ethereum and EVM-compatible networks requires computational resources, and gas price determines the cost users pay for these resources. Understanding this concept is essential for anyone building, deploying, or interacting with smart contracts, as improper gas management can lead to failed transactions, stuck funds, or unnecessarily high operational costs.
How Gas Price Determines the Cost of Smart Contract Execution
Gas price in smart contract directly determines your total transaction costs through a simple multiplication: total cost equals gas units consumed times gas price per unit. Each operation in the Ethereum Virtual Machine has a fixed gas cost, from simple transfers (21,000 gas) to complex contract interactions (potentially millions of gas). The gas price you set, measured in gwei (one-billionth of ETH), acts as your bid in a competitive market where validators prioritize higher-paying transactions for inclusion in blocks.
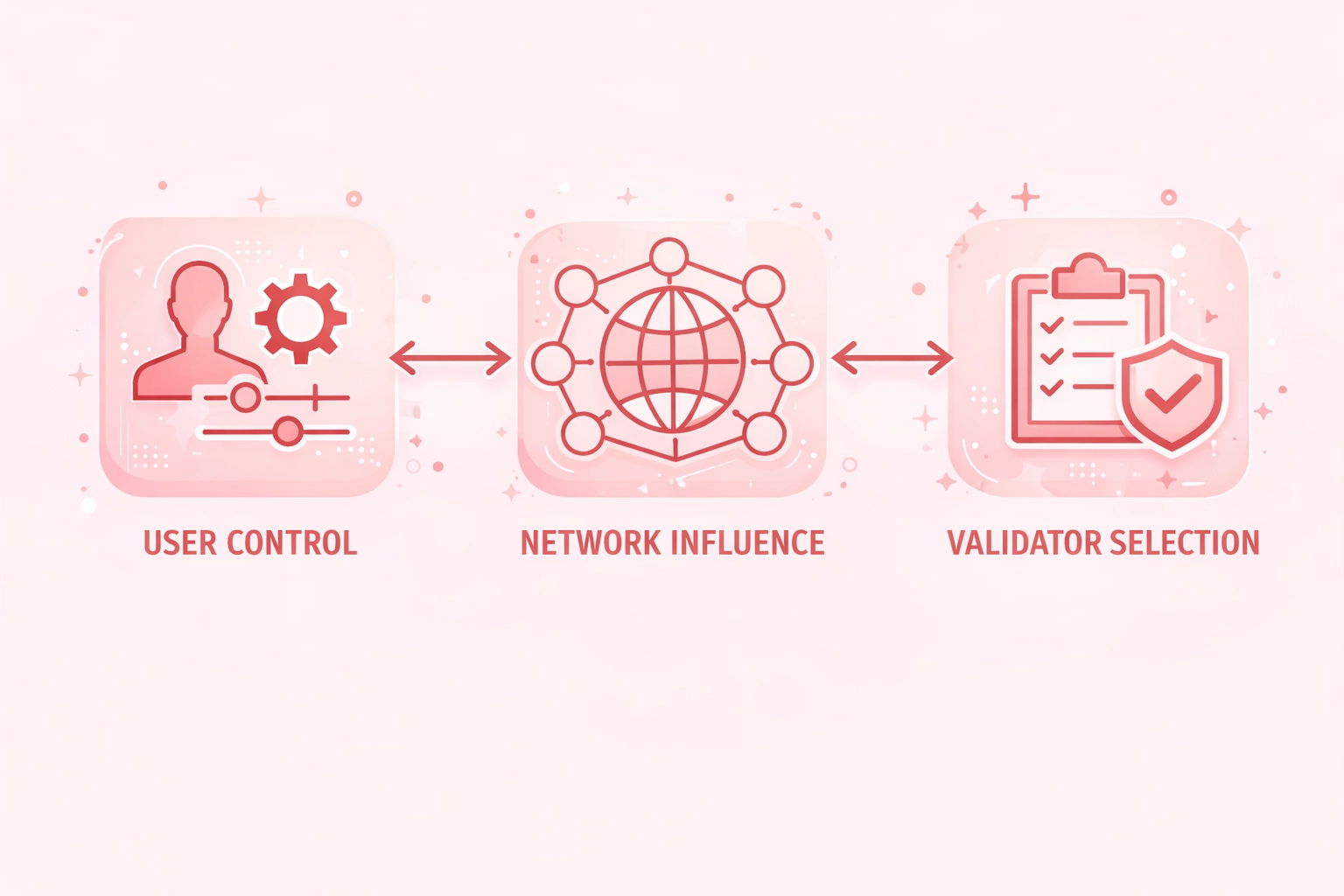
Who Sets the Gas Price in a Smart Contract?
User Control
- Transaction initiators set gas price
- Wallet suggestions guide decisions
- Manual override available
- Priority levels selectable
Network Influence
- Base fee set by protocol
- Demand affects pricing
- Block space limited
- Market dynamics apply
Validator Selection
- Validators choose transactions
- Higher prices prioritized
- Block ordering determined
- MEV considerations apply
Gas Price Dynamics in Public Blockchains
| Network | Avg Gas Price | Transaction Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Ethereum Mainnet | 20-100+ gwei | 12-15 seconds |
| Polygon | 30-100 gwei (MATIC) | 2 seconds |
| Arbitrum | 0.1-0.5 gwei | 250ms |
| Optimism | 0.001-0.01 gwei | 2 seconds |
| BSC | 3-5 gwei | 3 seconds |
Master Gas Price in Smart Contract Management
Our blockchain experts optimize gas price strategies for your smart contracts, reducing transaction costs while ensuring reliable execution on any network.
How Gas Price Affects Smart Contract Deployment Costs
Contract deployment represents one of the most gas-intensive operations, with gas price in smart contract deployment directly impacting project launch costs. A typical ERC-20 token contract consumes 1-2 million gas units, while complex DeFi protocols may require 5-10 million gas. At 50 gwei gas price, deploying a standard contract costs approximately 0.05-0.1 ETH. Enterprise projects across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada must budget carefully for deployment windows with favorable gas conditions.
Cost Example: Deploying Uniswap V3 contracts cost over $1 million in gas fees during high-congestion periods.
Gas Price Behavior During High Network Demand
| Event Type | Gas Price Impact | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| NFT Mint Launch | 500-2000+ gwei spike | 30-60 minutes |
| Market Crash | 200-500 gwei sustained | 2-6 hours |
| Token Airdrop | 100-300 gwei | 1-3 hours |
| DeFi Exploit | 300-1000 gwei | 1-4 hours |
| Network Congestion | 50-150 gwei | Variable |
Fixed vs Dynamic Gas Price Models Explained
Understanding the difference between fixed and dynamic gas price in smart contract systems is crucial for proper transaction management. Legacy transactions used fixed gas prices where users bid a single value. EIP-1559 introduced dynamic pricing with base fees that adjust automatically plus optional priority fees. The base fee increases when blocks are over 50% full and decreases when under, creating more predictable gas price in smart contract transactions.
Single Gas Price Bid
Base Fee + Priority Fee
Separate Blob Market
Smart Contract Functions and Their Gas Price Sensitivity
Different smart contract functions have varying gas price sensitivity based on their complexity and time-criticality. View functions consume no gas price in smart contract as they only read state. Write functions require gas proportional to storage changes and computation. Time-sensitive operations like liquidations and arbitrage require premium gas prices to ensure execution before market conditions change. Understanding function gas profiles helps optimize transaction timing and pricing strategies.
Gas Price Transaction Lifecycle
Transaction Creation
User initiates transaction with specified gas limit and gas price parameters in their wallet.
Mempool Submission
Transaction enters the mempool where it awaits validator selection based on gas price.
Priority Ordering
Validators sort transactions by effective gas price to maximize block revenue extraction.
Block Inclusion
Transaction selected for block if gas price meets current base fee requirements.
Gas Consumption
EVM executes transaction, consuming gas for each operation until completion or limit reached.
Fee Calculation
Final fee calculated as gas used times effective gas price, with base fee burned.
Refund Processing
Unused gas refunded to sender, storage clearing may provide additional gas rebates.
Confirmation
Transaction finalized after sufficient block confirmations, state changes become permanent.
How Wallets Automatically Suggest Gas Prices
Modern wallets like MetaMask analyze recent blocks to suggest appropriate gas price in smart contract transactions. They typically offer three tiers: slow (lower price, longer wait), average (balanced), and fast (premium price, quick confirmation). These suggestions query gas estimation APIs and consider current mempool conditions. Enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada often implement custom gas price oracles for more precise estimations tailored to their specific transaction requirements.[1]
Gas Price Handling in Failed Smart Contract Transactions
Out of Gas
- All gas consumed, no refund
- State changes reverted
- Transaction marked failed
- Full gas fee still charged
Revert Errors
- Partial gas consumed
- Remaining gas refunded
- Error message returned
- State unchanged
Stuck Transactions
- Gas price too low
- Pending indefinitely
- Can be replaced
- Cancel with higher gas
Security Implications of Incorrect Gas Price Settings
| Risk Type | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Front-Running | Attackers copy and outbid transactions | Use private mempools, MEV protection |
| Sandwich Attacks | Attackers wrap your trade | Set slippage limits, use DEX aggregators |
| Transaction Delay | Time-sensitive operations fail | Use appropriate priority fees |
| Griefing | Attackers spam to raise fees | Design gas-resilient contracts |
Gas Price Considerations for DeFi Smart Contracts
DeFi protocols face unique gas price in smart contract challenges due to the time-sensitive nature of financial operations. Liquidation bots must pay premium gas prices to execute before positions become underwater. Arbitrage opportunities often have narrow profit windows requiring aggressive gas pricing. Yield farmers across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets must calculate whether gas costs justify reward claims. Many protocols now implement gas-aware logic to prevent unprofitable transactions from executing.
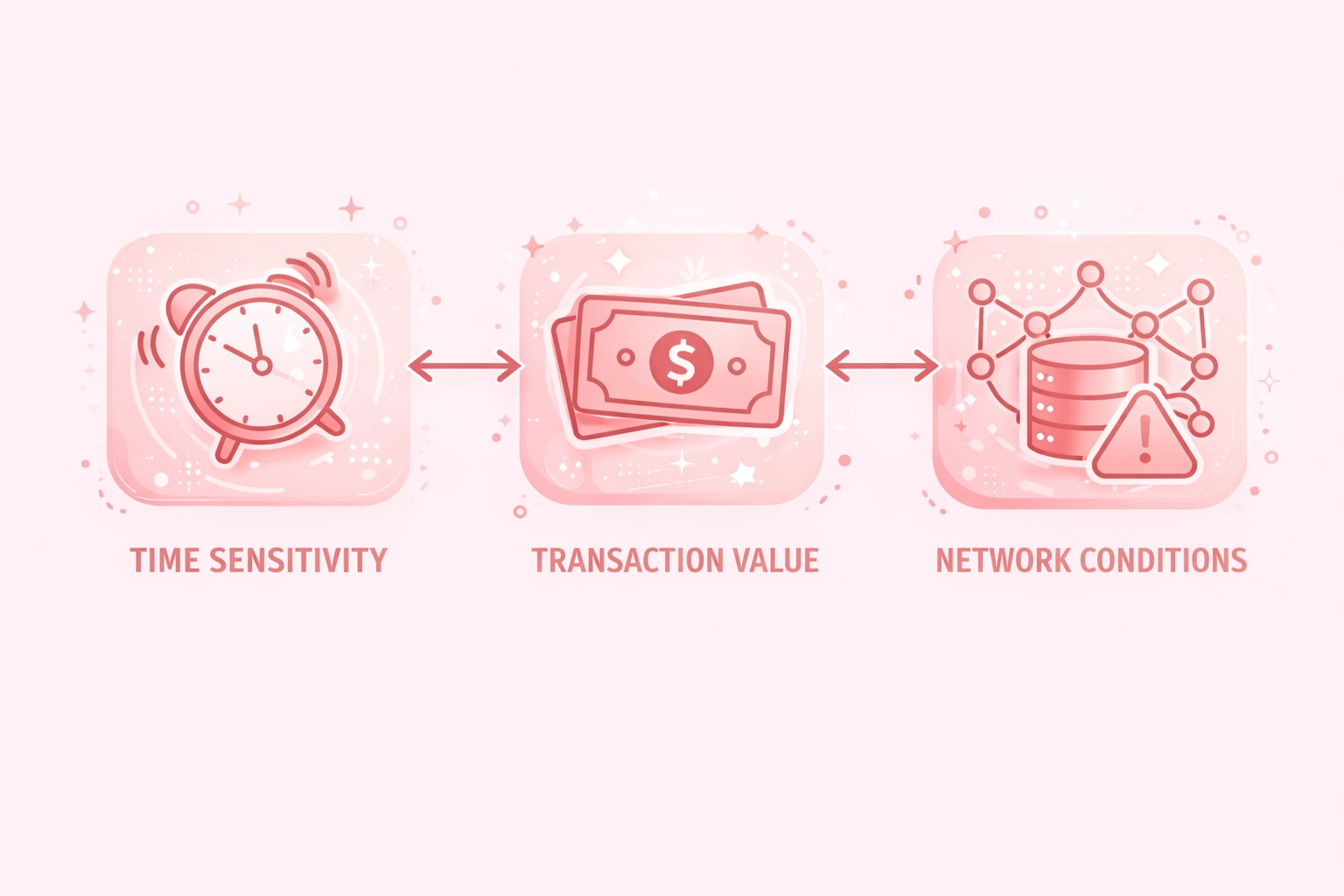
Gas Price Strategy Selection Criteria
Time Sensitivity
- Urgent: Use fast/aggressive
- Standard: Use average
- Flexible: Use slow/economy
- Batch: Wait for low periods
Transaction Value
- High value: Pay premium
- Medium: Balance cost/speed
- Low: Minimize gas costs
- Micro: Consider L2 solutions
Network Conditions
- Monitor base fee trends
- Check mempool congestion
- Consider time of day
- Watch for events/launches
Best Practices for Managing Gas Price in Production Contracts
| Practice | Description | Priority |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Estimation | Use eth_estimateGas with buffer for safety margin | Critical |
| Price Monitoring | Implement real-time gas price oracle integration | Critical |
| Retry Logic | Implement automatic transaction replacement on stuck | High |
| Batching | Combine multiple operations into single transaction | High |
| L2 Migration | Move high-frequency operations to layer 2 networks | High |
Gas Price Management Standards
Standard 1: Always estimate gas before submission and add 10-20% buffer for complex transactions.
Standard 2: Implement gas price monitoring with automated alerts for unusual network conditions.
Standard 3: Use EIP-1559 transaction types for more predictable fee estimation and execution.
Standard 4: Consider Layer 2 solutions for high-frequency, low-value transaction patterns.
Standard 5: Implement transaction replacement mechanisms for stuck or underpriced transactions.
Standard 6: Schedule non-urgent transactions for historically low-gas periods (weekends, off-hours).
Gas Price Evolution with Layer 2 and Rollup Solutions
Layer 2 solutions are fundamentally transforming gas price in smart contract economics. Optimistic rollups (Arbitrum, Optimism) and ZK rollups (zkSync, StarkNet) process transactions off-chain while posting compressed data to Ethereum mainnet. This architecture reduces gas costs by 10-100x compared to mainnet execution. Enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada are increasingly deploying smart contracts on L2 networks to achieve mainnet security guarantees at a fraction of the gas cost.
With eight years of experience building blockchain solutions, our agency has helped numerous clients migrate to L2 networks for dramatic cost savings. The future of gas price in smart contract lies in multi-layer architectures where high-value, security-critical operations remain on mainnet while routine transactions execute on cost-efficient L2 solutions. Understanding these dynamics is essential for building economically sustainable blockchain applications.
Optimize Your Smart Contract Gas Costs
Partner with our experienced blockchain team to implement efficient gas price strategies and reduce your operational costs significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Gas price in smart contract determines how much you pay per computational unit when executing transactions on blockchain networks. Higher gas prices incentivize miners to prioritize your transaction, ensuring faster confirmation. Understanding gas price helps users and businesses across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada optimize transaction costs.
Gas price in smart contract is measured in gwei (one-billionth of ETH). Total transaction cost equals gas units consumed multiplied by gas price. Network congestion, transaction complexity, and user-set priority levels all influence the final gas price applied to smart contract operations.
Setting gas price in smart contract too low causes transactions to remain pending indefinitely or eventually fail. Miners prioritize higher-paying transactions during network congestion. Users may need to cancel stuck transactions or resubmit with increased gas prices to achieve confirmation.
Gas price in smart contract fluctuates based on real-time network demand, making precise prediction challenging. However, tools like ETH Gas Station and blockchain explorers provide estimates based on current conditions. Historical patterns help anticipate peak periods for planning transaction timing.
EIP-1559 introduced base fee and priority fee mechanisms for gas price in smart contract transactions on Ethereum. Base fees adjust automatically based on network congestion while users set priority fees for faster processing. This model improves fee predictability compared to legacy auction systems.
Gas price in smart contract varies across networks due to different consensus mechanisms, block sizes, and network congestion levels. Ethereum typically has higher gas prices than layer 2 solutions or alternative chains like Polygon, BSC, or Arbitrum offering lower transaction costs.
Businesses reduce gas price in smart contract by timing transactions during low-congestion periods, optimizing contract code, batching multiple operations, and utilizing layer 2 solutions. Strategic gas management significantly reduces operational costs for enterprises deploying blockchain solutions.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







