Key Takeaways – DeFi Protocols Explained
- System Architecture: DeFi protocols function as complete financial systems that combine smart contracts, automation, governance, and economic logic.
- Secure Contract Design: Core contracts must stay minimal, modular, and invariant-driven to reduce attack surfaces and prevent systemic failures.
- State & Risk Management: Clear separation of global parameters, pool states, and user positions is essential for protocol safety and stability.
- Reliable Oracle Infrastructure: Accurate pricing depends on secure oracles with freshness checks, deviation limits, and fallback mechanisms.
- Automation & Keepers: Liquidations, rebalancing, and maintenance rely on permissionless, incentivized keeper networks.
- Governance & Safety Controls: DAOs, timelocks, caps, and emergency pause mechanisms protect protocols during upgrades and market stress.
Sending money, earning interest, or taking a loan should not require banks, paperwork, or long waiting times. Yet, in traditional finance, users still face delays, hidden fees, and restricted access.
This is where Decentralized Finance (DeFi) changes the system. Instead of depending on banks, DeFi allows users to access financial services directly through blockchain technology by using only a digital wallet and an internet connection.
At the core of this system are DeFi protocols. These protocols are based on smart contract systems that automatically manage trading, lending, borrowing, and rewards without any intermediaries.
From our experience working on blockchain and DeFi solutions at Nadcab Labs, we’ve seen how well-designed decentralized finance protocols help businesses and users build trust, transparency, and global financial access.
In this guide, we’ll clearly explain what DeFi protocols are, how they work, their types, real-world use cases, benefits, and risks in simple and easy language.
What are DeFi Protocols?
DeFi protocols are the systems that make decentralized finace work. In very simple words, a DeFi protocol is a set of rules written as computer code and stored on a blockchain. These rules decide how money can be traded, lent, borrowed, or managed without using banks or any middlemen.
Unlike traditional finance, where banks control everything, DeFi protocols work automatically through smart contracts. Once they are live on the blockchain, they follow the rules on their own. There is no manual approval and no human interference.
In real DeFi platforms like Aave or Uniswap, these protocols do all the work in the background. They calculate interest, complete trades, and move funds safely between users. This gives people full control over their money while keeping the system transparent and secure.
How DeFi Protocols Work?
To understand how DeFi protocols work, it helps to see how different components come together behind the scenes. While decentralized finance may sound complex, the process itself is simple and logical. Each step plays a key role in running financial services without banks or intermediaries.
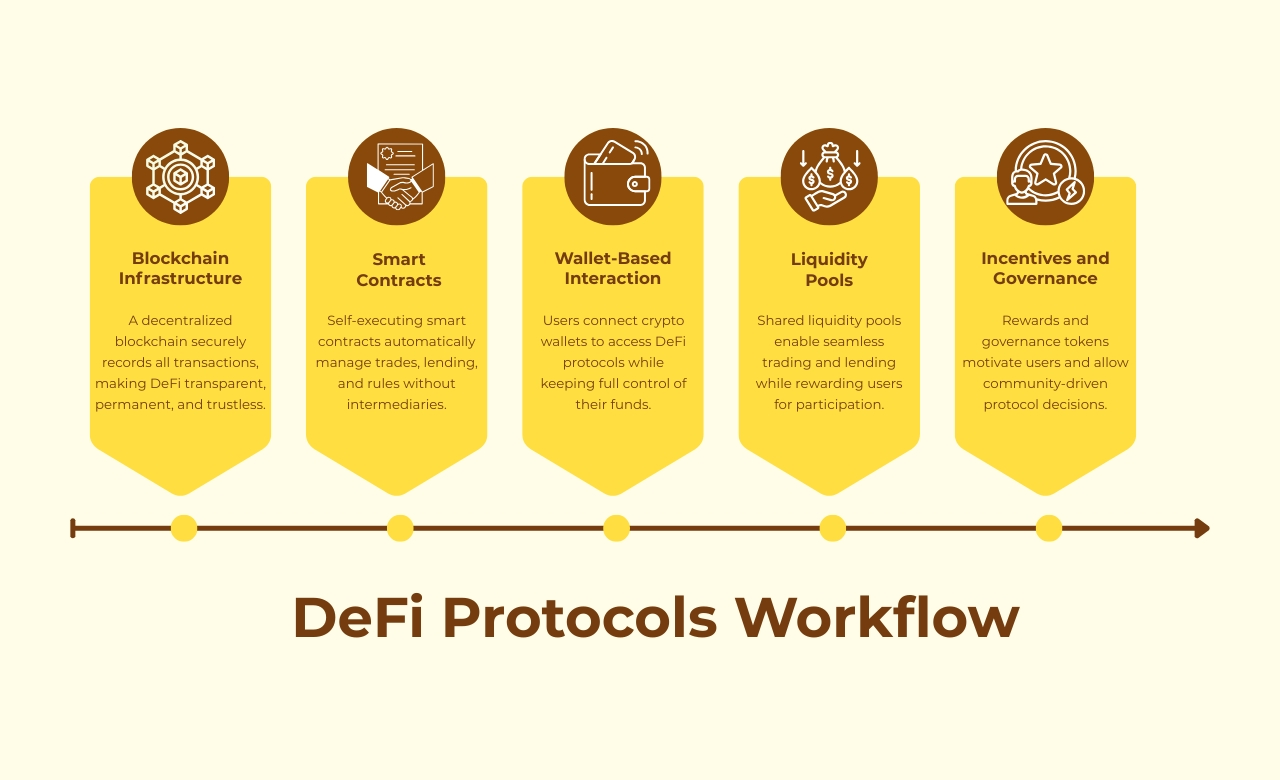
Step 1: Blockchain Infrastructure
DeFi protocols are built on blockchain networks such as Ethereum. The blockchain acts as a shared digital record where every transaction is stored securely and cannot be changed. Because the blockchain is decentralized, no single company or authority controls it. This creates a trustless blockchain environment where users do not have to rely on banks or third parties.
The blockchain ensures that all actions within a DeFi protocol are permanent, transparent, and verifiable by anyone.
Step 2: Digital Contracts
Smart contracts are the heart of decentralized finance protocols. They are self-executing programs written into the blockchain that automatically follow predefined rules. For example, a smart contract can decide how interest is calculated, when funds are released, or how trades are completed.
Once a smart contract is deployed, it runs exactly as programmed. There is no manual approval and no middleman involved. This automation reduces human error and makes decentralized finance systems faster and more reliable.
Step 3: Wallet-Based Interaction
In decentralized finance, users do not create traditional accounts. Instead, they connect their crypto wallets to interact with DeFi protocols. The wallet acts as both an identity and a tool to approve transactions.
When a user wants to use a DeFi application, they simply connect their wallet and confirm actions like swapping tokens or lending assets. The protocol never takes custody of the funds, which keeps the system non-custodial and secure.
Step 4: Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are shared pools of digital assets provided by users. These pools allow DeFi protocols to support activities such as trading, lending, and borrowing without relying on traditional buyers and sellers.
Users who add their assets to liquidity pools help keep the protocol running smoothly. In return, they earn rewards such as fees or incentives. Liquidity pools are essential because they ensure that DeFi platforms remain active and functional at all times.
Step 5: Incentives and Governance
To encourage participation, many DeFi protocols offer incentives. Users may receive rewards for providing liquidity, staking assets, or actively using the platform. These incentives help grow and stabilize decentralized finance ecosystems.
Some DeFi protocols also include governance systems. Governance tokens allow users to vote on decisions like protocol upgrades or rule changes. This makes DeFi community-driven, where users help shape the future of the protocol instead of relying on a central authority.
When combined, blockchain infrastructure, smart contracts, wallets, liquidity pools, and governance create a fully decentralized financial system. DeFi protocols use these components to offer open, transparent, and automated financial services without traditional intermediaries.
This step-by-step process is what makes DeFi protocols the backbone of decentralized finance platforms and applications worldwide.
Binance Academy[1] explains that DeFi protocols use smart contracts on blockchain networks to automate lending, trading, and other financial activities without centralized control.
How DeFi Protocols Are Different from Apps or Platforms?
Many people think DeFi protocols and DeFi apps are the same, but they are actually different.
A DeFi protocol is the core system that works in the background. It manages the rules, security, and financial logic using smart contracts. A DeFi app or platform is the user interface that people see and interact with.
You can think of the protocol as the engine of a car, while the app is the dashboard. Even if the dashboard design changes or the app goes offline, the engine can still run.
In the same way, even if a DeFi app changes its layout or stops working temporarily, the DeFi protocol can continue running on the blockchain. This is why DeFi protocols are more important and long-lasting than individual platforms.
Core Features of DeFi Protocols
DeFi protocols follow a few key principles that make them different from traditional finance:
- Permissionless
Anyone can use decentralized finance protocols. There is no need to sign up, submit documents, or get approval. If you have a wallet and internet access, you can participate in decentralized finance. - Non-Custodial
Users keep full control of their funds. DeFi protocols do not hold your money. Transactions happen directly from your wallet, reducing the risk of centralized control or misuse. - Transparent
All transactions and rules are visible on the blockchain. Anyone can verify how a DeFi protocol works, which builds trust and accountability.
Because of these features, decentralized finance protocols have become the foundation of modern decentralized finance platforms and applications. They enable open, secure, and automated financial systems that work the same way for everyone, anywhere in the world.
Core Components of the DeFi Ecosystem
DeFi protocols may sound complex, but they are built on a few core components that make decentralized finance work smoothly. Understanding these components helps you see why DeFi platforms are powerful, secure, and flexible.
1. Digital Contracts
Smart contracts are the backbone of every DeFi protocol. They are self-executing programs on the blockchain that automatically enforce rules and manage transactions. For example:
- Lending protocols calculate interest automatically.
- Trading platforms swap tokens based on predefined rules.
Because smart contracts run exactly as programmed, there is no need for banks or middlemen. This automation ensures transparency, efficiency, and trustless operation, which is why smart contracts are at the heart of all DeFi applications.
2. Oracles
Oracles act as bridges between the blockchain and the real world. They provide smart contracts with accurate external data such as:
- Cryptocurrency prices
- Exchange rates
- Market events
Without Oracles smart contract, DeFi protocols cannot make informed decisions, as Oracles smart contract provides reliable information to operate correctly and prevent errors caused by inaccurate data.
3. Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Traditional trading relies on buyers and sellers matching orders. DeFi uses Automated Market Makers (AMMs) instead. AMMs use mathematical formulas to price assets in liquidity pools, allowing users to trade directly from their wallets without order books.
This system makes decentralized exchanges (DEXs) efficient and always active. Users can trade anytime, and liquidity providers earn rewards for supporting these pools.
4. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Many DeFi protocols are governed by DAOs. A DAO is a community-driven organization where users collectively make decisions about protocol upgrades, rules, or fund allocation. Governance is typically handled through voting with governance tokens.
DAOs give power to the community instead of central authorities, reinforcing the decentralized nature of finance and increasing trust in the system.
5. Composability (“Money Legos”)
One of the most exciting aspects of DeFi is composability, often called “money legos.” This means different DeFi protocols can be combined to create new financial products. For example:
- You can borrow from one protocol, lend on another, and stake in a third, all at the same time.
- Developers can build new applications by stacking multiple protocols together.
Composability allows DeFi platforms to innovate rapidly and create complex financial systems that are flexible, transparent, and fully programmable.
Smart contracts, oracles, AMMs, DAOs, and composability form the core of the DeFi ecosystem. They work together to make decentralized finance secure, automated, and innovative. By understanding these components, users and businesses can better navigate DeFi platforms and make informed decisions.
Types of DeFi Protocols
DeFi protocols are diverse, each serving a unique financial function. Understanding the different types helps you see how decentralized finance recreates traditional systems while offering new possibilities. Here are the main categories.

1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs use Automated Market Makers (AMMs) to price assets and provide liquidity.
Example: Uniswap and SushiSwap are popular DEX protocols. Users can swap tokens, provide liquidity, and earn fees without giving up custody of their funds.
Key benefits:
- Permissionless trading
- Non-custodial transactions
- Reduced reliance on intermediaries
2. Lending and Borrowing Protocols
DeFi lending protocols let users lend assets to earn interest or borrow by providing collateral. Interest rates adjust dynamically based on supply and demand.
Example: Aave and Compound allow users to deposit assets into lending pools or borrow against collateral.
Key benefits:
- Passive income through lending
- Access to liquidity without selling assets
- Transparent interest calculations
3. Stablecoin Protocols
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value, often pegged to fiat currencies like USD. They reduce volatility and provide a reliable medium for trading, lending, or payments within DeFi ecosystems.
Example: DAI, USDC, and USDT are widely used stablecoins.
Key benefits:
- Price stability for trading and lending
- Easy integration with other DeFi protocols
- Reliable unit of account for users
4. Yield Farming & Liquidity Incentives
Yield farming allows users to earn additional rewards by providing liquidity or participating in multiple protocols simultaneously. It’s a way to maximize returns on crypto assets.
Example: Users can stake tokens in a liquidity pool on Uniswap and earn trading fees along with protocol tokens as rewards.
Key benefits:
- Incentivizes liquidity provision
- Encourages ecosystem growth
- High potential returns (with associated risks)
5. Derivatives & Synthetic Asset Protocols
Derivatives and synthetic assets let users trade or gain exposure to real-world or crypto assets without holding them directly. These protocols create on-chain representations of assets like stocks, commodities, or indexes.
Example: Synthetix allows users to trade synthetic assets representing currencies, commodities, or other financial instruments.
Key benefits:
- Access to a wide range of assets
- Hedging and speculation opportunities
- Fully decentralized trading
6. Insurance & Risk Management Protocols
DeFi insurance protocols help users protect their assets against smart contract failures, hacks, or other risks in the ecosystem. These protocols offer coverage for potential losses.
Example: Nexus Mutual provides insurance for smart contract exploits and protocol risks.
Key benefits:
- Risk mitigation for DeFi participants
- Increases trust in decentralized finance
- Supports safer ecosystem adoption
Smart contracts, oracles, AMMs, DAOs, and composability together form the core of the DeFi ecosystem. These components power decentralized finance by making it automated, transparent, and community-driven. Understanding them helps users and businesses confidently explore and use DeFi platforms.
Real-World Use Cases of DeFi Protocols
DeFi protocols are not just theoretical ideas, they are actively being used in real-world financial systems. Here are some of the most important use cases that show how decentralized finance is changing the way people manage money.
1. Trading Without Intermediaries
One of the first and most common uses of DeFi protocols is trading cryptocurrencies directly from wallets. Using decentralized exchanges (DEXs), users can swap tokens without giving control of their funds to a centralized platform.
Example: Platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap allow instant token swaps with low fees. Trades are executed automatically using smart contracts.
Key benefits:
- No middlemen involved
- Lower fees compared to traditional exchanges
- Full control of funds remains with users
2. Lending & Borrowing
DeFi lending protocols let users lend their crypto assets to earn interest or borrow funds by putting up collateral. Everything is automated and transparent through smart contracts.
Example: Aave and Compound allow users to earn passive income by lending assets, while borrowers can access liquidity without selling their holdings.
Key benefits:
- Earn interest without traditional banks
- Borrow quickly without complex approval processes
- Transparent and trustless transactions
3. Passive Income Mechanisms
DeFi protocols provide opportunities for earning passive income through staking, yield farming, or liquidity provision. Users can deposit tokens into protocols and earn rewards, fees, or additional tokens automatically.
Example: Users can stake stablecoins on a platform like Curve Finance and receive rewards in the platform’s native token.
Key benefits:
- Generate returns on idle assets
- Incentivizes participation in the ecosystem
- Flexible and user-controlled
4. Cross-Border Payments
Traditional cross-border payments are often slow and expensive due to banks and intermediaries. DeFi protocols allow instant, low-cost international transfers directly between wallets.
Example: Using stablecoins like USDC or DAI, users can send funds anywhere in the world without delays or excessive fees.
Key benefits:
- Fast and affordable
- Open to anyone with an internet connection
- Transparent and secure transactions
5. Financial Inclusion
DeFi opens access to financial services for people who are underbanked or excluded from traditional systems. Anyone with a digital wallet can participate in lending, borrowing, trading, or savings.
Example: People in regions without local banking infrastructure can still earn interest, borrow funds, or trade crypto using DeFi protocols.
Key benefits:
- Democratizes access to finance
- Empowers global users
- Reduces reliance on centralized institutions
DeFi protocols are more than just technology—they are practical tools that allow trading, lending, borrowing, earning passive income, making cross-border payments, and promoting financial inclusion. These real-world applications show why DeFi is not just a trend but a transformative shift in global finance.
Benefits of DeFi Protocols
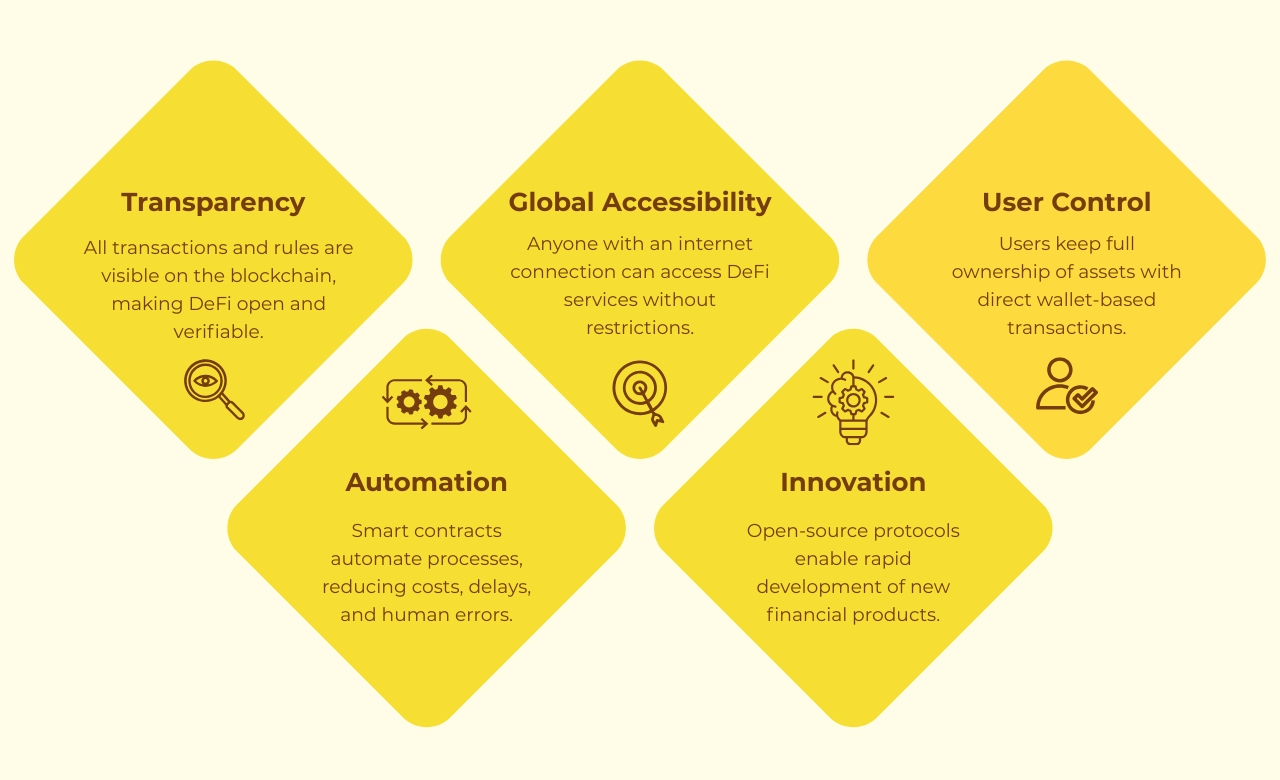
DeFi protocols are not just innovative, they provide real, practical advantages over traditional financial systems. Here are the key benefits that make decentralized finance powerful and attractive for users worldwide.
1. Transparency
One of the main advantages of DeFi protocols is complete transparency. All transactions, rules, and operations are recorded on the blockchain, which anyone can verify. Users can check how the protocol works, where funds are going, and how interest or rewards are calculated.
Key benefit: Users can trust the system without relying on banks or intermediaries.
2. Global Accessibility
DeFi protocols are open to anyone with an internet connection. There are no location restrictions, approval processes, or account requirements. People from anywhere in the world can participate in lending, borrowing, trading, or staking.
Key benefit: Financial services become inclusive and accessible for everyone, even in underbanked regions.
3. User Control of Funds
Unlike traditional finance, DeFi is non-custodial. Users keep full control of their assets in their wallets, and transactions are executed only with their approval. This eliminates the risk of centralized platforms misusing or freezing funds.
Key benefit: Users maintain autonomy and ownership of their money at all times.
4. Efficiency & Automation
DeFi protocols use smart contracts to automate financial operations. Processes like lending, trading, and interest calculation happen automatically without human intervention. This reduces costs, saves time, and eliminates errors.
Key benefit: Faster, cheaper, and more efficient financial services compared to traditional systems.
5. Open Innovation
DeFi protocols are open-source, meaning developers can study, modify, and build upon existing protocols. This creates a culture of innovation where new financial products and services can be launched quickly and collaboratively.
Key benefit: Encourages rapid ecosystem growth and continuous improvement, benefiting users and businesses alike.
The combination of transparency, global accessibility, user control, efficiency, and open innovation is what makes DeFi protocols powerful. They are not only reshaping finance but also creating a more inclusive, automated, and trustworthy financial ecosystem for everyone.
Risks and Limitations of DeFi Protocols
While DeFi protocols offer many advantages, they also come with risks and limitations that every user and business should understand. Awareness of these risks is essential to use decentralized finance safely and responsibly.
1. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
DeFi protocols rely on smart contracts to automate transactions. If there is a bug or flaw in the code, it can be exploited by hackers, leading to potential loss of funds.
Example: Several DeFi platforms have suffered attacks due to vulnerabilities in their smart contracts.
Key takeaway: Users should prefer audited protocols and platforms with a strong security track record.
2. Market Volatility
Cryptocurrencies are known for their price fluctuations, which can impact lending, borrowing, and trading in DeFi platforms. Sudden drops in asset prices can trigger liquidations or reduce the value of collateralized positions.
Key takeaway: Users must understand the risks of volatility before participating in DeFi lending, borrowing, or yield farming.
3. User Responsibility
DeFi is non-custodial, which means users have full control of their funds. While this is a benefit, it also places responsibility on users to manage private keys and wallets safely. Losing access to a wallet or sharing credentials can lead to irreversible loss of funds.
Key takeaway: Strong security practices and careful management of wallets are critical.
4. Regulatory Uncertainty
DeFi protocols operate in a largely unregulated environment. Laws and regulations vary by country and are evolving rapidly. Regulatory changes may affect how protocols operate or how users can access DeFi platforms.
Key takeaway: Users and businesses should stay informed about legal requirements in their region before participating in decentralized finance.
DeFi protocols are powerful, but they are not risk-free. Understanding smart contract risks, market volatility, user responsibility, and regulatory uncertainty is essential for anyone using decentralized finance. By being aware and cautious, users can enjoy the benefits of DeFi while minimizing potential losses.
Organizations like Nadcab Labs focus on secure and compliant approaches to DeFi, helping businesses adopt decentralized finance responsibly.
DeFi Protocols vs Traditional Finance
Decentralized finance operates very differently from traditional financial systems. Understanding these differences helps users see why DeFi is reshaping global finance.
| Feature | Traditional Finance | DeFi Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Centralized, controlled by banks or financial institutions | Decentralized, run by protocols on blockchain |
| Control & Custody | Users trust banks or intermediaries with their funds | Users retain full control; funds stay in wallets (non-custodial) |
| Accessibility | Restricted; requires approval, documentation, and accounts | Permissionless; anyone with a digital wallet can participate |
| Transparency | Limited, internal operations are not visible | Fully transparent; all transactions and rules are on the blockchain |
| Risk Profile | Regulated and insured but subject to centralized failures | Less regulated; smart contract bugs, volatility, and regulatory uncertainty exist |
Security, Audits, and Trust in DeFi
Security is a major concern in decentralized finance. Since DeFi protocols are automated and non-custodial, users need to trust the code itself. Ensuring safety and building credibility is critical for widespread adoption.
Importance of Audits
Audits are independent reviews of a protocol’s smart contract code. They help detect bugs or vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. Platforms that undergo regular audits are considered more reliable and trustworthy.
Role of Open-Source Review
Most DeFi protocols are open-source, meaning anyone can inspect the code. Open-source review allows the community and developers to identify potential issues, improving transparency and security.
Risk Mitigation Practices
- Using audited and reputable protocols
- Diversifying assets across multiple protocols
- Avoiding unverified new projects
User Best Practices
- Always secure private keys and wallets
- Double-check transaction addresses and amounts
- Stay updated on platform updates or protocol changes
By combining strong audits, open-source review, and user awareness, DeFi platforms can operate safely, giving confidence to both users and businesses. Companies like Nadcab Labs emphasize secure and compliant approaches to decentralized finance, ensuring reliability in their services.
Role of DeFi Protocols in Web3
DeFi protocols are not just financial tools, they are key building blocks of Web3, the next-generation internet.
Integration with dApps, Wallets, and NFTs
DeFi protocols power decentralized applications (dApps), wallets, and NFT marketplaces. Users can trade, stake, or borrow assets directly through these integrated platforms.
Interoperability
Protocols are often compatible with multiple blockchains, allowing assets to move across networks. This interoperability ensures a seamless experience for users and developers.
Protocol Composability
DeFi protocols can be stacked like “money legos,” creating new applications by combining existing protocols. For example, a user could borrow funds from one protocol, provide liquidity in another, and stake rewards in a third, all seamlessly.
By supporting Web3 ecosystems, DeFi protocols expand the possibilities of decentralized applications, enabling open finance, gaming, and NFT innovations.
How Businesses and Enterprises Approach DeFi
For businesses, adopting DeFi requires strategic planning and careful implementation.
Strategic Adoption
Enterprises analyze which decentralized finance services align with their goals, such as payments, lending, or treasury management.
Risk-Aware Implementation
Businesses prioritize security, compliance, and smart contract audits to mitigate risks while experimenting with DeFi solutions.
Long-Term Sustainability
Successful adoption involves building flexible systems, integrating with existing finance infrastructure, and staying updated with regulatory changes.
Companies like Nadcab Labs help businesses leverage DeFi safely, offering solutions that combine innovation with compliance.
Build Secure DeFi Protocols with Experts
From smart contract development to full DeFi platforms, Nadcab Labs helps you design secure, scalable, and compliant decentralized finance solutions tailored to your business goals.
Future of DeFi Protocols
The future of DeFi looks promising, with several trends shaping the next generation of decentralized finance.
Scalability Improvements
Blockchain networks are continuously improving speed and reducing transaction costs, making DeFi protocols more efficient and user-friendly.
Regulatory Evolution
Governments worldwide are exploring regulations to protect users without stifling innovation. Clear legal frameworks will increase confidence in DeFi.
Institutional Adoption
More businesses and financial institutions are exploring DeFi services for trading, lending, and asset management, increasing credibility and liquidity in the ecosystem.
Real-World Asset Integration
Future protocols may link blockchain with real-world assets like stocks, bonds, or property, expanding the use cases and bridging traditional and decentralized finance.
Final Words
DeFi protocols are redefining the future of finance. They provide transparent, permissionless, and automated financial systems that are accessible globally. From trading, lending, and borrowing to passive income, cross-border payments, and financial inclusion, DeFi protocols power a wide range of real-world applications.
By understanding their benefits, risks, and core components, users and businesses can participate responsibly. With continuous innovation, secure practices, and strategic adoption, DeFi protocols form the foundation of the decentralized finance ecosystem and the broader Web3 movement.
Decentralized finance is more than a trend, it is a new financial infrastructure. With proper awareness, audits, and trusted platforms, anyone can safely participate and benefit from the opportunities DeFi offers.
Frequently Asked Questions
DeFi protocols handle price volatility by using real-time price data from oracles and requiring collateral to secure loans. If asset prices fall sharply, the protocol may automatically liquidate collateral to protect lenders and maintain system stability.
Once deployed, most DeFi protocols are controlled by smart contracts and governed by the community through governance tokens. No single company controls the protocol, and decisions are made collectively by token holders.
Yes, DeFi protocols can change rules if they include governance mechanisms. Changes are proposed and voted on by the community, and updates are implemented only if approved through decentralized governance.
DeFi protocols require overcollateralization to protect against price volatility and default risk. Since there is no credit scoring or identity verification, extra collateral ensures loans remain secure even during market fluctuations.
DeFi protocols interact with each other through composability, often called “money legos.” Smart contracts can connect seamlessly, allowing users to combine lending, trading, staking, and other services across multiple protocols.
If liquidity runs low, users may experience higher fees, slower transactions, or limited borrowing and trading options. Many protocols use incentives or dynamic interest rates to attract more liquidity and restore balance.
Yes, some DeFi protocols operate without governance tokens by using fixed rules written into smart contracts. However, governance tokens offer flexibility by allowing communities to upgrade or improve the protocol over time.
Security depends on factors such as smart contract audits, open-source code review, reliable oracles, strong governance, and a proven track record. Protocols with multiple audits and active communities are generally more secure.
If a front-end platform shuts down, the protocol often continues to exist on the blockchain. Users can still access their funds directly through smart contracts using wallets or alternative interfaces.
DeFi protocols remain trustless by relying on blockchain technology and smart contracts that execute rules automatically. Transparency, cryptographic security, and decentralized consensus replace the need for banks or intermediaries.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







