Key Takeaways
- What is DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is a blockchain-based, member-governed entity running via smart contracts with no central authority.
- Its value proposition lies in decentralization, transparency, global participation, alignment of incentives and innovative governance.
- Key mechanics include token-based membership, proposal submission, community voting, smart-contract execution, treasury management.
- DAOs have diversified into many types: protocol governance, investment, grants, social/creator DAOs.
- Benefits are significant, but so are the challenges: technical/contract risk, governance centralization, legal/regulatory ambiguity, operational complexity.
- If you’re considering participation or launching one, you’ll need to focus on mission, tokenomics, governance design, community building, legal structure and smart contract audit.
- The future of DAOs is promising: wider use-cases, improved tooling, evolving regulation, hybrid organizational models.
- For a project like yours (blockchain strategy, token launch, DeFi), understanding and integrating DAO structures can provide competitive advantage and long-term trust.
At Nadcab Labs, our journey into decentralized governance began years ago while developing blockchain ecosystems and smart contract frameworks for various Web3 clients. Through hands-on experience in designing DAO based governance models, we’ve seen how decentralized structures empower communities, enhance transparency, and reduce centralized risk. Having contributed to multiple DeFi and DAO deployment projects, we understand not only the technical foundations but also the real-world challenges of running a DAO, from on-chain voting and treasury management to regulatory compliance.
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and Web3, new organizational models are emerging that challenge traditional corporate structures. One of the most prominent among them is the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). But what exactly is a DAO, how does it work, and why should you care? In this article, we’ll provide a complete foundational overview, drawing on real-world examples, hands-on insights, and expert commentary to help you understand how DAOs are reshaping governance, decision-making, and value creation in Web3.
What is DAO?
A DAO, short for Decentralized Autonomous Organization, is an organizational form that runs through rules encoded in smart contracts on a blockchain, rather than through a centralized leadership hierarchy.
Key characteristics of a DAO include:
- Decentralization: No single individual or small team has unilateral control; governance is distributed.
- Autonomy via code: The rules and decision-mechanisms are encoded in software (smart contracts) that execute on the blockchain.
- Token-based membership / governance: Members hold governance tokens (or stake) that give them rights to propose, vote on decisions, and participate in governance.
- Transparency and auditability: Because the underlying ledger and contracts are on a blockchain, operations are publicly visible and verifiable.
- Shared purpose / common goal: A DAO is formed around a mission, protocol, product or community objective.
Thus, a DAO is more than just a “crypto club” it’s a novel organizational model that combines blockchain technology, token economics and community governance.
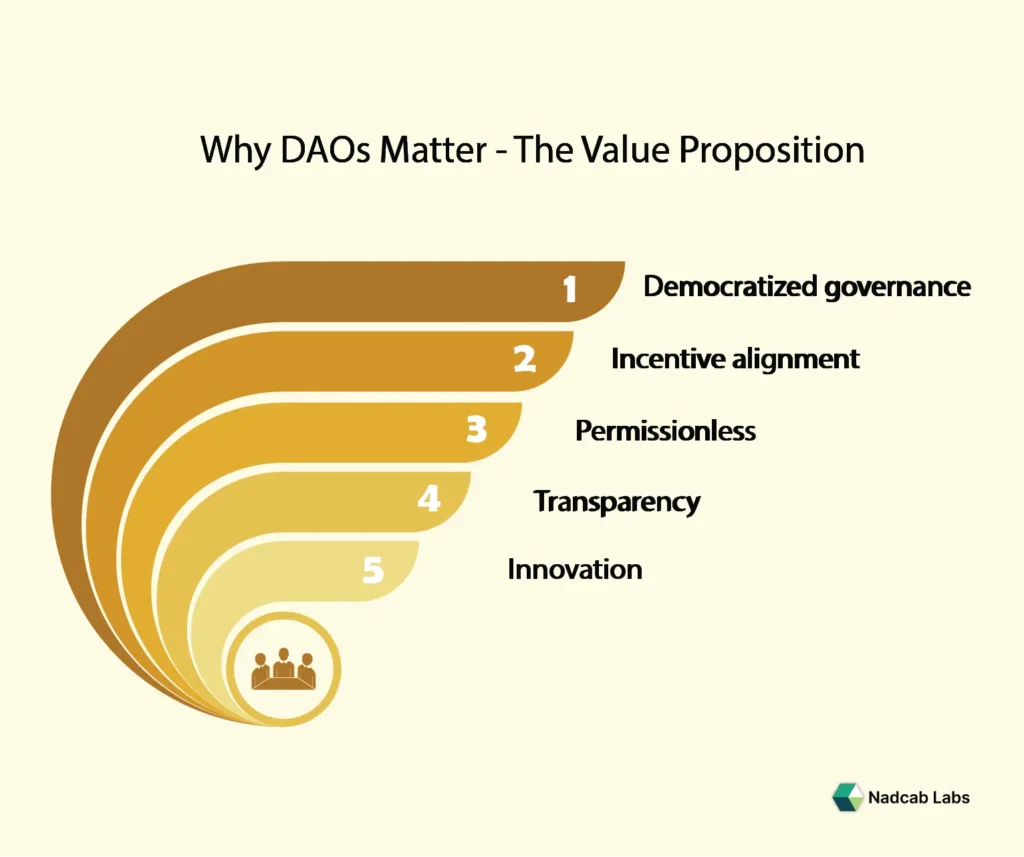
Why DAOs Matter
From a foundational expertise perspective, you want to understand why this model matters. Here are the main compelling reasons:
-
Democratized governance
Traditional companies have centralized leadership (boards, executives) making decisions behind closed doors. DAOs shift power to community stakeholders, anyone with voting rights can influence decision-making.
-
Incentive alignment
Because governance tokens often confer both voting power and economic interest, members are incentivized to act in the long-term interest of the organization, not just short-term profit.
-
Borderless and Permission less
DAOs can span geographies, enabling global participation without needing a physical headquarters. Smart contracts and tokens enable borderless membership.
-
Transparency & auditability
On-chain operations mean members (and outsiders) can view proposals, vote outcomes, treasury movements. That increases trust and reduces opaque decision-making.
-
Innovation in organizational structure
DAOs represent a shift in how organizations can be set up: fewer intermediaries, lower overhead, more community-driven, potentially more agile.
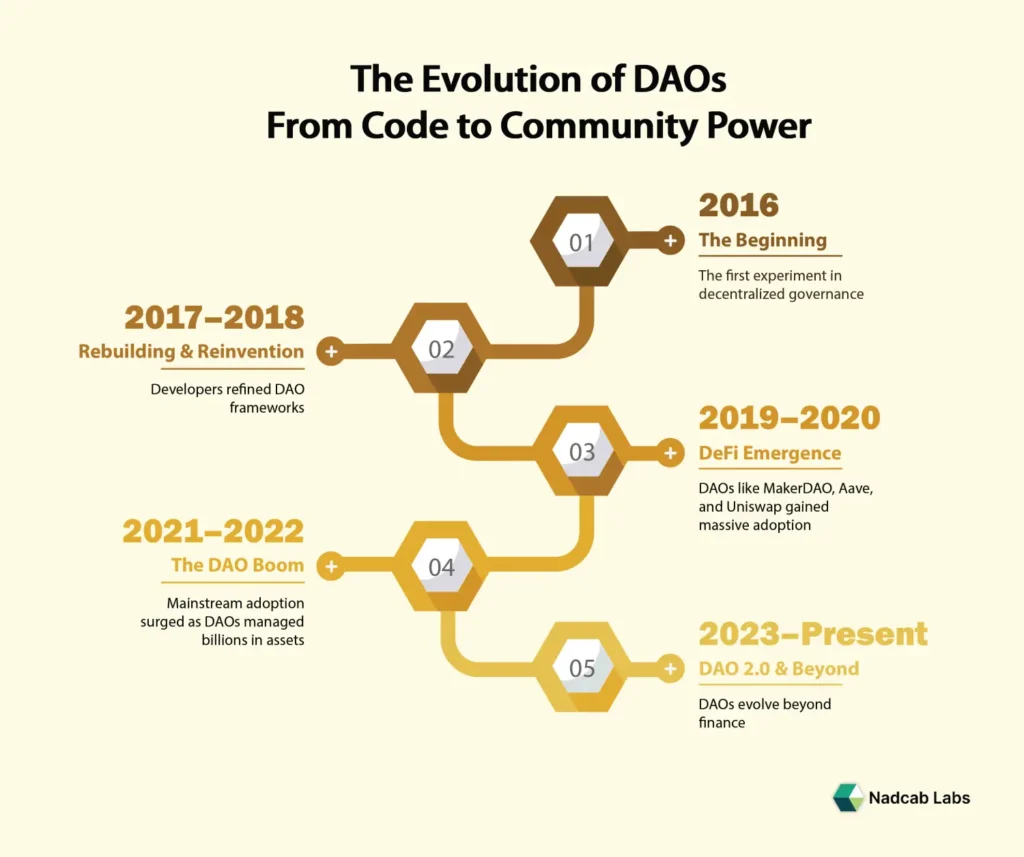
The Origins & Evolution of DAOs
Understanding history gives you authority and context.
-
Early beginnings
The idea of decentralized organizations on blockchain traces back to the launch of The DAO in 2016 (on the Ethereum network). It raised over US$150 million in Ether via a token-sale mechanism.
Unfortunately, The DAO was hacked, leading to the theft of millions of dollars worth of Ether, and triggering a controversial hard fork of Ethereum.
-
Growth and diversification
Since then, DAOs have proliferated across many uses: investment DAOs, social/community DAOs, protocol-governance DAOs, grant DAOs, even fan-club or creative DAOs.
-
Legal & regulatory recognition
Jurisdictions are starting to recognize DAO-friendly legal frameworks. For example, the U.S. state of Wyoming passed legislation recognizing decentralized autonomous organizations as legal entities.
As the ecosystem matures, we’re seeing improved tools, governance frameworks, and lessons learned from earlier failures.
How Does a DAO Work?
Here we dive into the operational mechanics, so your blog demonstrates real foundational expertise.
1. Formation and charter
- A group of founders or community members decide to create the DAO, define a mission, and write the initial governance rules (often in a “constitution” or charter).
- Smart contracts are deployed on a blockchain that implement the rules, membership criteria, proposal & voting logic, treasury rules.
- Governance tokens may be issued (via sale, airdrop, contribution), giving token-holders membership and voting rights.
2. Membership & tokenomics
- Holding a governance token often gives rights to create proposals, vote, delegate voting power, share in treasury or rewards.
- Sometimes membership is tied to off-chain criteria (e.g., community contribution requirement) plus token-ownership.
3. Proposal submission & discussion
- A community member drafts a proposal: for example, spending from treasury, changing governance rules, collaborating with another project, launching new product, or acquiring assets.
- The proposal is broadcast to the DAO community (via forums/discussion channels) for review, debate, amendments. This is the “off-chain” communication part (e.g., Discord, Telegram, governance forum).
- As one DAO researcher puts it: “a DAO works best when smart contract code and legal formation align with community governance.”
4. Voting & execution
- Members vote by staking their governance tokens or using delegated voting rights; votes may be weighted by holdings.
- Once the voting period ends and if the proposal meets the required threshold (e.g., quorum + majority), the smart contract executes the outcome automatically (or triggers the off-chain action).
- The treasury changes, rules update, or actions taken as per the code.
5. Treasury & funds management
- The DAO’s treasury is a smart contract address or set of addresses where funds are held (tokens, crypto assets) and can only be spent via approved proposals and smart contract logic.
- Members have visibility on assets and spendings.
6. Legal & operational oversight
- While the code automates a lot, many DAOs still engage legal structures (e.g., legal wrapper, contracts) and off-chain service providers (for audits, payroll, compliance).
- Governance forums, transparency reports, audits help build trust.
Also Read: Decentralized Autonomous Organization Guide for 2025
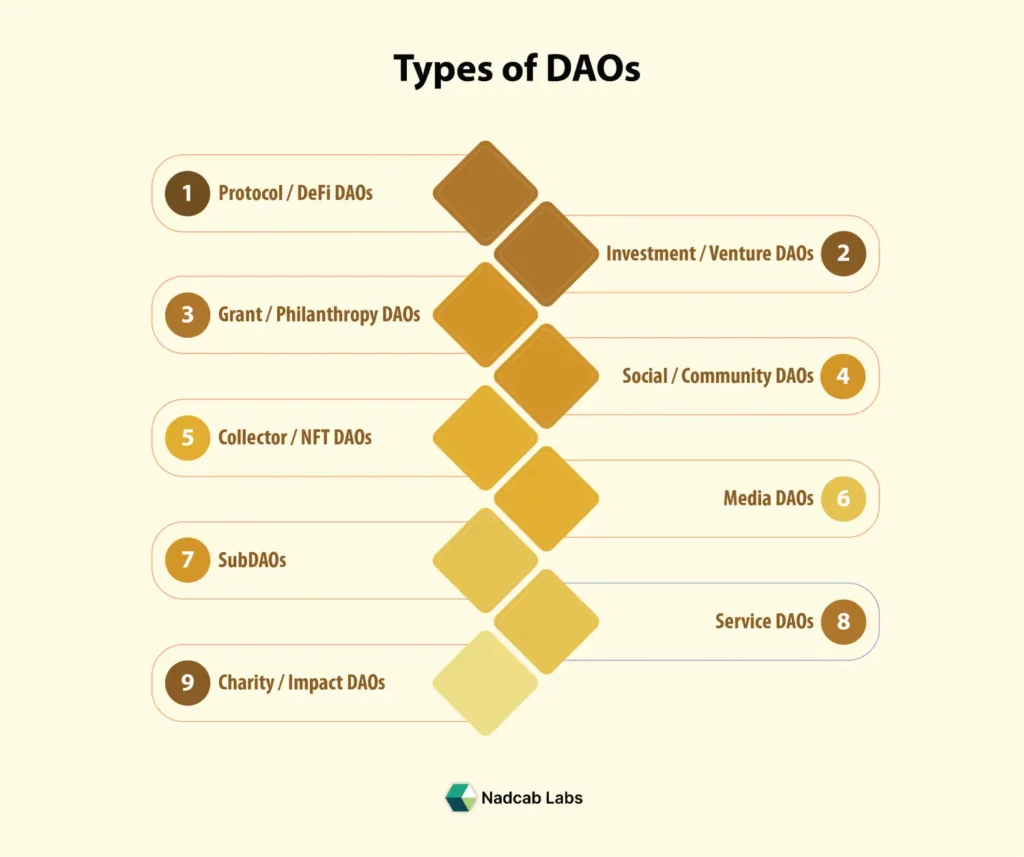
Types of DAOs
DAOs come in various forms based on their purpose and governance model. Understanding these categories shows how decentralized organizations function across different industries. Here are the main types of DAOs shaping the Web3 ecosystem today.
1. Protocol / DeFi DAOs
These DAOs govern decentralized finance protocols, allowing token holders to vote on updates, fee structures, and system improvements.
Examples: MakerDAO, Uniswap DAO, Aave DAO, Compound DAO
- Investment / Venture DAOs
Members pool capital to invest collectively in early-stage blockchain projects, NFTs, or startups.
Examples: MetaCartel Ventures, BitDAO, The LAO, Flamingo DAO
- Grant / Philanthropy DAOs
These DAOs distribute funds to support developers, researchers, or social causes decided by community votes.
Examples: Gitcoin DAO, Moloch DAO, KlimaDAO, Big Green DAO
- Social / Community DAOs
Focused on building communities of creators, artists, or builders with shared goals, events, and discussions.
Examples: Friends With Benefits (FWB), Seed Club, Cabin DAO, Bankless DAO
- Collector / NFT DAOs
Groups formed to purchase, curate, and manage valuable digital collectibles or NFTs collectively.
Examples: PleasrDAO, Flamingo DAO, Jenny DAO, ConstitutionDAO
- Media DAOs
Operate decentralized media or content platforms where contributors govern editorial and funding decisions.
Examples: Forefront DAO, Bankless DAO, Mirror DAO, Global Coin Research DAO
- Service DAOs
Networks of professionals offering blockchain, marketing, or development services to clients in a decentralized way.
Examples: RaidGuild, DxDAO, Opolis, DAOhaus
- SubDAOs
Smaller autonomous groups within larger DAOs focusing on specific projects, governance tasks, or product lines.
Examples: Aave Grants DAO (under Aave DAO), Maker Growth DAO, Index Coop SubDAOs
- Charity / Impact DAOs
Built for social good, climate action, and humanitarian efforts through transparent, on-chain governance.
Examples: Clean Carbon DAO, Angel Protocol, Endaoment, Giveth DAO
Real World Examples
Providing credible examples enhances authority.
Example 1 Uniswap
The decentralized exchange protocol Uniswap is governed by a DAO model, where token-holders vote on protocol upgrades, treasury usage and other governance decisions.
Example 2 MakerDAO
MakerDAO governs the Maker Protocol, which backs the DAI stablecoin. Token-holders vote on risk parameters, collateral types, and treasury management.
Example 3 ConstitutionDAO
A fascinating case: The group raised over US$40 million to bid for a rare copy of the U.S. Constitution but ultimately failed. Their DAO experiment highlighted both the power and challenges of DAOs.
Including such examples grounds your blog in real practice and boosts trustworthiness.
Benefits & Opportunities
Here’s a breakdown of what makes DAOs appealing (with the lens of foundational expertise).
- Greater member-engagement: Members feel ownership, more active participation in decisions.
- Transparency = trust: On-chain records allow auditing and community verification.
- Reduced overhead: Fewer intermediaries, potentially lower administrative cost.
- Global talent & participation: No geographic barriers for membership or contribution.
- Innovation & experimentation: DAOs allow new organizational models, new token-based incentives, community-driven products.
- Aligning incentives: Token economics ties governance and economic value together, aligning interests of participants.
Risks, Challenges & Limitations
To truly establish trustworthiness and authority, you also need to discuss the flipside.
Technical risks
- Smart contracts are code and code has bugs. The early DAO exploit showed how vulnerabilities can be catastrophic.
- Forks, security breaches, governance attacks.
Governance risks
- Token-weighted voting may lead to centralization of power (whales controlling votes).
- Voter apathy: if members don’t participate, decisions may be made by a small subset.
- Proposal spam or low-quality proposals can clog governance.
Legal & regulatory uncertainty
- Many jurisdictions haven’t clearly defined the legal status of DAOs: Are they partnerships? Corporations? Unincorporated associations?
- Token tokens may be considered securities (with regulatory implications) depending on jurisdiction.
Operational and human challenges
- Even though code executes, many off-chain actions (real-world tasks) still require humans: audits, legal, compliance, services.
- Aligning token incentives with long-term health vs short-term speculation.
- Scaling governance: As membership grows, coordination becomes harder.
Decision making speed & effectiveness
- Some studies show DAOs may be slower than traditional management when urgent decisions are required.
By acknowledging these challenges, your blog will present a balanced, trustworthy view, and build credibility.
How to Participate in or Launch a DAO
Since your audience may include those interested in launching or participating in a DAO, this section builds experience-based value.
Joining a DAO
Steps:
- Identify a DAO whose mission aligns with your interests.
- Acquire the governance token (if required).
- Join community channels (Discord, Telegram, forum) to engage in discussion and proposal drafting.
- Review the charter/governance rules.
- Participate by voting, submitting proposals, delegating votes or contributing to tasks.
- Monitor treasury/disbursements to ensure transparency and accountability.
Launching a DAO – Key considerations
If you’re launching a DAO (e.g., for a new Web3 project, community, protocol), consider these foundational steps:
- Define mission, purpose, value proposition: What problem is the DAO solving?
- Choose the blockchain and smart contract framework: e.g., Ethereum, BSC, Solana.
- Design tokenomics: How many governance tokens, distribution model, voting weight, delegation rights.
- Build governance framework: Charter, bylaws, proposal process, voting thresholds, quorum rules.
- Deploy smart contracts that implement the rules (membership rules, proposal/voting logic, treasury management).
- Engage the community: Pre-launch marketing, onboarding participants, education.
- Ensure legal/compliance oversight: Consider regulatory/regional laws (e.g., Wyoming legal entity recognition).
- Audit code, set up transparency mechanisms: Audit smart contracts, publish governance docs, open-source code.
- Launch treasury and proposal mechanism: Fund the DAO, open proposal submissions, begin governance.
- Iterate: Collect feedback, refine rules, adjust tokenomics/governance as the community grows.
Providing this blueprint demonstrates expertise and adds actionable value.
The Future of DAOs & Implications for Web3
A strong blog looks ahead, shows you’re an authority.
Mainstream adoption & hybrid models
We may see hybrid organizational forms: DAOs merging with legal entities, or traditional companies integrating DAO-style governance for communities. Legal frameworks are evolving to recognize DAOs.
Expanded use-cases beyond finance
While many DAOs exist in DeFi or investment spaces, we’ll likely see them in: public goods funding, philanthropy, media and content, gaming/NFT ecosystems, real-world asset management.
Improved tooling & governance frameworks
Tools for DAO governance (voting platforms, delegation services, treasury dashboards, proposal analytics) will become more mature. Academic research is identifying gaps (e.g., 60%+ of proposals lacked consistent description in one study).
Shift in organizational philosophy
DAOs challenge assumptions about hierarchy, control, transparency, and value creation. They may redefine how communities self-organize, how value is managed and how decisions are made.
Regulatory maturation
As regulators engage with DAOs, we’ll see clearer rules around token classification, liability of token-holders, legal status of DAOs and global coordination.
This forward-looking perspective reinforces your blog as up-to-date and credible.
Build Trustless Communities with DAO Solutions
Partner with Nadcab Labs to design, develop, and deploy a secure, transparent, and efficient DAO framework.
Why This Matters for You
Since you’re involved in blockchain strategy (as with your roles at Nadcab Labs), helping with token launches, DeFi, etc., here are some tailored insights:
- If you’re advising token launches, consider whether a DAO governance layer adds value, especially for community-driven projects.
- When building DeFi platforms (lending, staking, crowded liquidity) a DAO governance model can help decentralize control and create stakeholder buy-in.
- Incorporating DAO-aware architecture in your smart contract ecosystem from the start can future-proof your design, especially if you intend to migrate governance to the community.
- Educating your audience (investors, users, partners) about DAOs helps build trust and positions you as thought-leaders in the space.
By tying the concept of DAOs back to your strategic domain, you provide deeper relevance and authority.
Final Thoughts
In a world where decentralization is becoming more than just a buzzword, DAOs represent a real shift in how organizations can be structured, how values can be governed, and how communities can self organize. Whether you’re an investor, expert, community builder, or strategist, understanding DAOs will equip you to navigate the Web3 economy more confidently.
Drawing from real-world experience, professionals at Nadcab Labs have seen how DAOs empower communities to take ownership of decision-making, foster transparency, and eliminate centralized control. By mastering not just what a DAO is, but how it works and why it matters, you position yourself at the forefront of this paradigm shift building both credibility and capability in the evolving decentralized world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Legal recognition of DAOs is still evolving. However, Wyoming (USA) became the first jurisdiction to recognize DAOs as Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) in 2021. This allows them to operate legally, hold assets, and enter contracts. Other countries like Switzerland, Singapore, and the UAE are also exploring DAO-friendly regulations. Clearer laws are expected as governments adapt to the rise of decentralized governance.
While DAOs offer transparency and community-driven control, they also face several challenges such as smart contract bugs that can lead to massive fund losses, low voter participation resulting in poor governance decisions, and regulatory uncertainty due to unclear legal frameworks. Additionally, centralized voting power often allows wealthier token holders to dominate decision-making. Addressing these challenges through thorough smart contract audits, fair governance mechanisms, and clear legal compliance is essential for creating sustainable and trustworthy DAOs.
One of the best-known examples is MakerDAO, the organization behind the DAI stablecoin. MakerDAO enables token holders to manage monetary policies through on-chain governance. Other notable examples include Uniswap DAO, which governs the Uniswap DEX protocol, and ConstitutionDAO, which famously raised over $40 million to purchase a copy of the U.S. Constitution.
Each of these DAOs demonstrates unique use cases—from finance and investment to social collaboration and crowdfunding.
DAOs can be classified into various types based on their purpose and structure. Protocol or DeFi DAOs manage decentralized finance platforms, ensuring transparent and automated operations. Investment or Venture DAOs pool collective funds for investment opportunities. Grant or Philanthropy DAOs support open-source projects and social causes. Social or Community DAOs focus on building engaged communities around shared interests. Collector or NFT DAOs enable members to collectively own and manage NFTs. Lastly, Service DAOs function as decentralized organizations offering work, talent, and project-based services.
Joining a DAO usually involves acquiring its governance token and connecting your crypto wallet (like MetaMask) to the DAO’s platform. You can then participate by voting on proposals, joining discussions, or contributing to community tasks. Many DAOs, such as Bankless DAO or Aave DAO, actively encourage newcomers to contribute in marketing, design, or technical roles.
Engaging regularly helps you build reputation and influence in decentralized communities.
DAOs are set to become core governance structures in Web3—transforming how communities fund projects, manage assets, and make collective decisions. As tools like AI governance models, cross-chain voting, and on-chain legal frameworks mature, DAOs will integrate more deeply into DeFi, NFTs, and metaverse economies. Industry experts predict DAOs will evolve from experimental organizations into mainstream, compliant, and fully autonomous enterprises shaping the digital economy.
A DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is a blockchain-based organization that operates without centralized leadership. Rules and decisions are encoded in smart contracts, which automatically execute once conditions are met. DAO members use governance tokens to vote on proposals, fund initiatives, and make changes collectively.
Unlike traditional corporations managed by boards, DAOs rely on community consensus, ensuring transparency, security, and equal participation. This decentralized model minimizes human bias and fosters trust among members.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.