Key Takeaways – DeFi Debt Redemption
- DeFi debt redemption is a stability mechanism that allows debt to be exchanged for collateral within decentralized protocols
- Smart contracts automate the redemption process, ensuring transparency and trustless execution
- Debt redemption helps prevent bad debt and supports overall protocol health
- Redemption differs from liquidation by offering a proactive, non-forced risk management approach
- Accurate oracle pricing is essential for fair and efficient debt redemption
- Market volatility can significantly impact redemption outcomes and execution risk
- Redemption mechanisms play a key role in maintaining stablecoin price pegs
- Governance decisions directly influence redemption rules, limits, and fees
Decentralized Finance has fundamentally revolutionized traditional financial systems by introducing programmable, transparent, and autonomous debt management mechanisms that operate without intermediaries. At the heart of this transformation lies debt redemption, a critical operational primitive that ensures protocol solvency, maintains asset peg stability, and safeguards user capital across lending markets and stablecoin platforms.
Why Debt Redemption Matters
Through our eight years at Nadcab Labs working with various DeFi protocols, we’ve observed that debt redemption is far more than simple loan repayment. It represents a sophisticated ecosystem of smart contracts, oracle integrations, and economic incentive structures that enable users to settle debt obligations without intermediaries, creating the foundation for truly decentralized financial markets.
The complexity of debt redemption has grown substantially since the early days of DeFi. What began as straightforward repayment functions has evolved into multi-faceted systems incorporating partial redemptions, dynamic fee structures, cross-protocol composability, and sophisticated risk management frameworks. Modern protocols must account for gas optimization, MEV protection, oracle reliability, and market volatility, all while maintaining user-friendly interfaces that don’t overwhelm participants with technical complexity.
Understanding debt redemption is essential for anyone participating in DeFi lending markets, whether as a borrower seeking to manage positions effectively, a protocol designer implementing new debt systems, or an investor evaluating protocol risk profiles. The design quality of redemption mechanisms often determines protocol resilience during market stress, influences capital efficiency, and directly impacts user experience.
Understanding Debt Mechanisms in DeFi Protocols
Overcollateralization
DeFi eliminates credit checks through overcollateralization, borrowers lock collateral exceeding debt by 150-200%, ensuring protocol solvency without institutional trust.
Smart Contract Automation
Automated systems encode lending logic, calculate interest in real-time, and continuously monitor position health through blockchain-based execution.
Dynamic Interest Rates
Utilization-based models create natural equilibrium by adjusting rates based on capital availability, making borrowing responsive to market conditions.
At Nadcab Labs, we’ve architected debt systems for numerous protocols, and the foundation always centers on smart contracts encoding lending logic, collateral management rules, interest calculations, and debt servicing requirements. When users deposit collateral, the smart contract records this position on-chain, calculates maximum borrowing capacity based on collateralization requirements, and continuously monitors position health through real-time price feeds from oracles.
The debt itself typically manifests as a token balance or internal accounting entry within the protocol’s state. Interest accrues algorithmically, often using compound interest calculations updated at each block or through periodic rate updates. Many protocols implement utilization-based interest rate models where rates increase as more of the available capital pool is borrowed, creating natural market equilibrium.
What Is Debt Redemption in Decentralized Finance?
Debt redemption in DeFi encompasses the processes, mechanisms, and smart contract functions enabling settlement and closure of outstanding debt obligations. It’s the sophisticated choreography of code, economics, and user interaction that makes decentralized lending truly trustless and efficient.
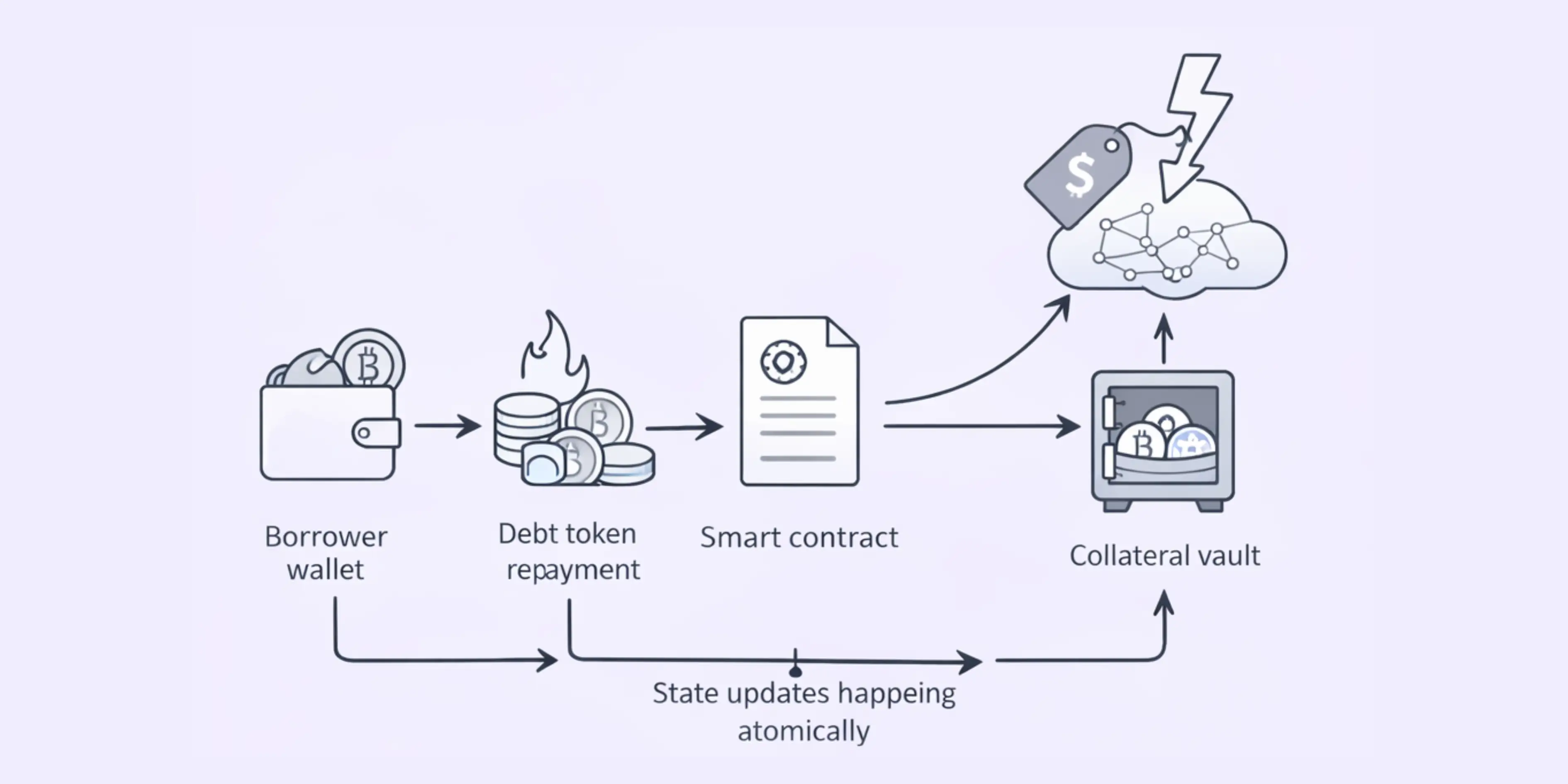
In typical lending protocols we’ve developed, debt redemption follows a straightforward model where borrowers return borrowed assets plus accrued interest. The smart contract calculates the exact amount owed including accumulated interest, verifies sufficient repayment, processes token transfers, and updates protocol state to reflect the closed position. This requires atomic precision, any error could compromise protocol integrity or user funds.
Types of Redemption Mechanisms
Standard Borrower-Initiated Redemption
Users voluntarily repay debt and reclaim collateral at their convenience, maintaining full control over timing and amount. This model prioritizes user autonomy and flexibility.
Direct Redemption Against Collateral
Any stablecoin holder can redeem tokens for underlying collateral at face value, creating powerful arbitrage opportunities that maintain peg stability automatically.
Stability Pool Redemption
Shared risk pools automatically absorb debt from liquidated positions, rewarding depositors with discounted collateral while maintaining system solvency.
Protocol-Level Automated Redemption
Smart contracts trigger redemptions automatically when specific conditions are met, enabling emergency procedures and stability operations without human intervention.
Why Debt Redemption Is Critical for DeFi Stability
Debt redemption mechanisms serve as fundamental stability infrastructure within Decentralized Finance protocols, directly influencing their ability to maintain economic guarantees, preserve asset pegs, and withstand extreme market volatility. From our extensive experience, we’ve seen firsthand how protocols lacking robust redemption systems struggle during market stress, while those with well-designed redemption pathways maintain stability even during significant downturns.
The psychological and confidence-building aspects of redemption mechanisms extend beyond direct economic functions. Through our client consultations at Nadcab Labs, we consistently emphasize that users must trust they can exit positions under various scenarios, including high congestion, extreme volatility, or protocol stress. Well-designed redemption systems functioning reliably even under adverse conditions provide this assurance, reducing user anxiety and supporting continued protocol engagement.
Key Components Involved in DeFi Debt Redemption
Implementing effective debt redemption requires coordination of multiple technical and economic components, each serving specific functions within the broader redemption architecture. Our protocol development methodology emphasizes understanding how these components interact to create secure, efficient, and economically sound debt resolution systems.
| Component | Primary Function | Critical Requirements | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Smart Contracts
|
Execute redemption logic and state updates | Security, atomicity, gas efficiency | High |
|
Collateral Management
|
Track and release locked assets | Accurate accounting, secure transfers | Medium-High |
|
Price Oracles
|
Provide market valuation data | Timeliness, manipulation resistance | Medium |
|
Interest Systems
|
Calculate total debt obligation | Precision, consistent methodology | Medium |
|
Access Controls
|
Manage redemption permissions | Security, operational efficiency | Low-Medium |
How Smart Contracts Enable Automated Debt Redemption
The Power of Trustless Automation
Eliminating intermediaries through deterministic code execution
Smart contracts revolutionize debt redemption by eliminating human intermediaries and enabling fully automated, trustless settlement of debt obligations. Traditional debt redemption requires coordination between multiple parties, document processing, payment verification, and collateral release all managed through manual processes prone to delays and errors. Smart contracts consolidate these functions into deterministic code executing automatically when conditions are met.
The fundamental architecture of redemption smart contracts centers on state management and conditional logic. In our development work , we maintain detailed records of every debt position including principal amount, accrued interest, collateral deposits, collateralization ratios, and position metadata. When a redemption function is called, the contract evaluates whether the caller has authority, calculates exact debt including all accrued interest up to the current block, verifies provided assets are sufficient, and executes atomic state updates simultaneously processing debt repayment, collateral release, and position closure.
Gas Optimization
Efficient contracts minimize storage operations, batch processes, and optimize data structures, reducing redemption costs by 50% or more compared to naive implementations.
Security Mechanisms
Reentrancy guards, checks-effects-interactions patterns, and input validation protect against attacks while maintaining atomic execution integrity.
Modular Design
Proxy patterns and modular architectures enable upgrades and bug fixes while maintaining continuity for existing user positions.
Collateralized Debt Positions (CDPs) and Redemption Logic
Collateralized Debt Positions represent the fundamental structure through which users create and manage debt in DeFi protocols, particularly within stablecoin systems. A CDP encapsulates all information related to a single debt position: collateral assets locked, debt amount issued, accrued stability fees or interest, collateralization ratio, and position health status.
| CDP Redemption Phase | Contract Operations | User Requirements | Gas Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Phase 1
Initiation
|
Verify ownership, calculate total debt with fees | Approve debt token transfer, call function | Low |
|
Phase 2
Debt Settlement
|
Transfer and burn debt tokens, update state | Provide sufficient tokens to cover obligation | Medium |
|
Phase 3
Collateral Release
|
Calculate collateral amount, transfer to user | Receive collateral in wallet | Medium-High |
|
Phase 4
Position Closure
|
Mark CDP as closed or update for partial | Position removed or adjusted | Low |
Role of Oracles in Accurate Debt Valuation
The Critical Bridge Between Blockchain and Reality
Price oracles serve as critical infrastructure for DeFi debt redemption by providing the external market data necessary to value collateral assets, calculate collateralization ratios, determine redemption amounts, and trigger automated protocol responses to changing market conditions.
We typically integrate oracle solutions involving off-chain components that observe prices from exchanges or aggregated sources, cryptographically sign this price data, and submit it to on-chain oracle contracts that smart contracts can query. This architecture must be robust against manipulation, failures, and attacks while maintaining timely updates.
Chainlink Networks
Decentralized oracle networks aggregate prices from multiple sources and node operators, requiring consensus before updates.
TWAP Mechanisms
Time-weighted average prices from DEXs provide manipulation-resistant feeds by averaging over extended periods.
Economic Security
Staking mechanisms and liquidity depth ensure manipulation costs exceed potential exploit profits.
Fallback Systems
Multiple oracle sources with median calculations and circuit breakers protect against failures.
Types of Debt Redemption Models in DeFi
DeFi protocols implement various redemption models, each with distinct characteristics, tradeoffs, and suitability for different protocol architectures and economic goals. Through our work we are developing and consulting on multiple DeFi protocols, we’ve gained deep insights into how these models perform under various market conditions.
Redemption vs Liquidation: Key Differences Explained
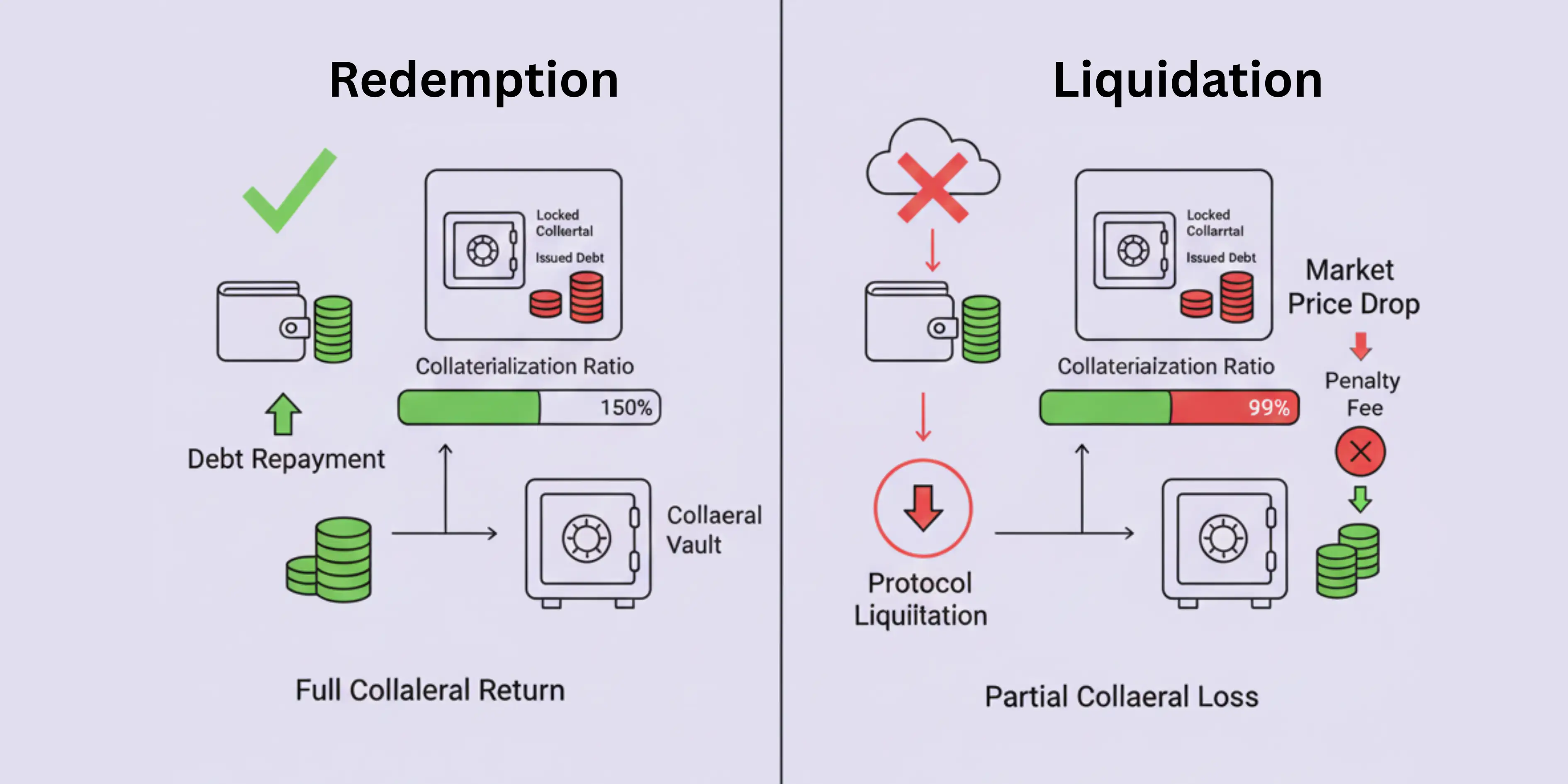
Redemption and liquidation both involve closing or reducing debt positions and releasing collateral, but they differ fundamentally in their initiation triggers, execution mechanisms, economic implications, and roles within DeFi architectures.
| Comparison Factor | Redemption |
Liquidation |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation |
Voluntary, user-controlled action
|
Automatic, protocol-triggered event
|
| Trigger Condition |
User decision under normal operations
|
Collateralization falls below threshold
|
| Economic Impact |
Minimal costs (interest, small fees)
|
Significant penalties (typically 5-15%)
|
| User Control |
Full control over timing and amount
|
No control, forced closure
|
| Protocol Purpose |
Enable capital flows, lifecycle management
|
Protect solvency, manage systemic risk
|
Designing Robust Debt Management
From a protocol perspective, redemption and liquidation serve complementary but distinct purposes. Well-designed protocols implement both robust redemption pathways for normal operations and efficient liquidation systems for risk management, recognizing that each addresses different scenarios and risk profiles in the debt lifecycle.
Risks Associated with DeFi Debt Redemption
Despite their critical importance to protocol stability and user experience, debt redemption mechanisms introduce various risks that can impact both individual users and overall protocol health. Based on our extensive security auditing experience at Nadcab Labs, understanding and mitigating these risks is essential for protocol viability.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Bugs in redemption contracts could enable fund theft or accounting manipulation. Reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and access control failures pose severe threats requiring comprehensive audits.
Economic Attacks
Front-running and sandwich attacks exploit transaction ordering, while manipulated redemption mechanics can extract value from protocols or other users through adversarial strategies.
Oracle Manipulation
Flash loan attacks and price manipulation can cause incorrect redemption valuations, leading to unfair outcomes and potential protocol losses if oracles lack sufficient resistance.
Liquidity Crises
Redemption rushes during panic can congest networks and spike gas prices, potentially trapping users who cannot afford redemption transactions or exit before losses mount.
Impact of Market Volatility on Debt Redemption
When Markets Move: The Ultimate Stress Test
Market volatility profoundly affects debt redemption dynamics, user behavior, and protocol stability in ways that extend far beyond simple price movements. During volatile periods, the relationship between collateral values, debt obligations, redemption incentives, and system capacity becomes stressed, often revealing weaknesses in redemption mechanism design.
Through our protocol monitoring observed that rapid collateral price declines trigger cascading effects: deteriorating collateralization ratios, users rushing to add collateral or redeem debt, network congestion, gas price spikes, and in worst cases, users with smaller positions finding themselves economically trapped when redemption costs exceed position values.
User Experience Challenges in Debt Redemption Processes
Despite the technical sophistication of DeFi debt redemption mechanisms, user experience often represents a critical barrier to effective redemption and optimal position management. Through our user interface development work, we’ve identified numerous friction points that affect redemption effectiveness and user satisfaction.
Common User Pain Points
Calculation Complexity
Interest accrues continuously, making exact redemption amounts difficult to calculate. Transactions may fail if amounts are even slightly insufficient.
Token Approvals
Multi-step processes require separate approval transactions, adding gas costs and complexity that confuses less experienced users.
Gas Cost Uncertainty
Variable gas prices and unpredictable transaction costs can make redemption economically irrational, especially for smaller positions.
Information Gaps
Users often don’t understand redemption options, fee structures, or optimal timing, leading to suboptimal decisions and unnecessary costs.
Security Considerations and Smart Contract Risks
The Non-Negotiable Foundation
At Nadcab Labs, our security auditing practice emphasizes that vulnerabilities in redemption contracts can lead to catastrophic fund losses and protocol insolvency. Comprehensive security practices are absolutely essential for production systems.
Reentrancy Attacks
Malicious contracts can recursively call redemption functions, potentially draining protocol funds. Defense requires reentrancy guards and checks-effects-interactions patterns.
Arithmetic Errors
Complex calculations involving collateral values, debt amounts, and fees can produce overflow, underflow, or precision loss leading to incorrect settlements.
Access Control Flaws
Inadequate permission verification could allow unauthorized redemptions or parameter manipulation, potentially enabling fund theft or protocol disruption.
Popular DeFi Protocols Implementing Debt Redemption
Examining how established DeFi protocols implement debt redemption provides valuable insights into design patterns, tradeoffs, and real-world performance. Through our consulting work at Nadcab Labs, we’ve analyzed multiple implementations to understand their strengths and limitations.
Regulatory and Compliance Implications
The regulatory landscape surrounding DeFi debt redemption remains in flux as regulators worldwide grapple with applying existing frameworks to decentralized protocols. Our compliance consulting practice helps navigate this uncertain environment across multiple regulatory domains.
Securities Law
Debt tokens may constitute securities under frameworks like the Howey Test, requiring registration, disclosure, and investor protection compliance.
Banking Regulation
Protocols accepting deposits and issuing debt may be viewed as unlicensed banks, requiring money transmitter licenses in some jurisdictions.
AML/KYC Requirements
Permissionless redemption challenges traditional identity verification requirements, with regulators increasingly pressuring DeFi to implement controls.
Consumer Protection
Requirements may mandate clear disclosures about redemption processes, risks, fees, and outcomes to protect users engaging with debt products.
Future Trends in DeFi Debt Redemption Mechanisms
The Next Evolution of Debt Redemption
Through our research at Nadcab Labs, we’re actively exploring emerging trends that promise to transform redemption mechanisms, offering improvements in efficiency, security, and user experience across the DeFi ecosystem.
Cross-Chain Redemption
Multi-chain coordination enabling atomic redemption operations spanning multiple blockchains, dramatically improving capital efficiency and flexibility.
AI-Powered Optimization
Machine learning analyzing market conditions, gas prices, and user preferences to recommend optimal redemption timing and automated execution strategies.
Zero-Knowledge Privacy
Privacy-preserving redemption where users close positions without revealing details, balancing transparency needs with privacy protection.
The Role of Defi Debt Redemption in Long Term Growth
Debt redemption mechanisms represent foundational infrastructure that enables DeFi to function as a credible alternative to traditional financial systems. Without robust, reliable, and economically sound redemption pathways, users cannot confidently enter debt positions knowing they can exit when needed, and protocols cannot maintain the stability necessary for long-term operation.
Through our eight years at Nadcab Labs, we’ve witnessed the maturation of redemption mechanisms from simple repayment functions into sophisticated systems handling multiple scenarios and market conditions. This evolution reflects DeFi’s broader transformation from experimental technology toward production-grade financial infrastructure capable of supporting real economic activity at scale.
The diversity of redemption approaches demonstrates that no single model optimizes for all objectives simultaneously. Trade-offs between user control and protocol stability, capital efficiency and security, simplicity and sophisticated functionality require careful consideration of specific goals and user needs. The continuing experimentation with novel redemption designs will yield improved mechanisms that better balance these competing priorities.
Technical implementation quality directly determines whether redemption mechanisms achieve their design goals or create vulnerabilities threatening protocol viability. Our security auditing experience has taught us that comprehensive security practices, defensive programming, extensive testing, professional audits, and ongoing monitoring, are absolutely essential for production systems. The DeFi community’s growing emphasis on security reflects hard lessons learned from redemption failures and exploits.
User experience improvements remain critical for broader adoption. Current processes often require technical sophistication that excludes less experienced users. Simplifying redemption through better interfaces, helper functions, intent-based systems, and automated position management would dramatically improve accessibility, but simplification must not compromise security or user understanding of risks.
Ultimately, debt redemption mechanisms serve as a critical pillar supporting DeFi’s value proposition of providing open, permissionless, and transparent financial services. The protocols that successfully implement redemption mechanisms balancing security, efficiency, stability, and usability while adapting to evolving regulatory landscapes will define the next generation of decentralized financial infrastructure, infrastructure capable of supporting the debt markets that will power DeFi’s expansion into mainstream financial services.
Looking forward, debt redemption will continue evolving as DeFi expands to new use cases, blockchains, and user populations. Cross-chain redemption, privacy-preserving protocols, AI-assisted position management, and institutional infrastructure all promise to extend capabilities and improve effectiveness. The integration of redemption mechanisms with broader financial primitives will create increasingly sophisticated debt markets capable of supporting diverse financial needs.
Expert Insights from Nadcab Labs
With over 8 years of pioneering experience in DeFi protocol development and smart contract architecture, Nadcab Labs brings you unparalleled insights into debt redemption mechanisms. Our team has architected, audited, and optimized redemption systems that process billions in transactions across multiple blockchain ecosystems. This comprehensive guide distills our hands-on expertise into actionable knowledge for developers, investors, and DeFi enthusiasts.
FAQs: DeFi Debt Redemption
In most DeFi protocols, debt redemption is permissionless. Borrowers, lenders, and third-party participants can initiate redemption, helping correct system imbalances and maintain protocol stability through open-market incentives.
Debt redemption is usually optional and driven by economic incentives rather than obligation. However, protocol rules, governance decisions, or risk conditions may indirectly encourage users to redeem debt to stabilize the system.
DeFi debt redemption may include protocol-level redemption fees, blockchain gas fees, and indirect costs such as slippage. These fees vary across networks and protocols and influence the overall efficiency of the redemption process.
Some users profit from debt redemption during market inefficiencies or stablecoin de-pegging events. However, profitability depends on execution speed, competition, gas costs, and accurate assessment of collateral value.
Yes, debt redemption often helps stabilize stablecoin prices by reducing excess circulating supply. By exchanging debt for collateral, the mechanism supports price parity during periods of market volatility.
Debt redemption can fail due to insufficient liquidity, oracle price updates, network congestion, or smart contract conditions changing mid-transaction. Such failures highlight the importance of timing and system awareness.
When debt is not redeemed, risk accumulates within the protocol. This can lead to increased liquidations, weakened peg stability, or governance intervention to adjust parameters and restore balance.
Protocols may delay or cap redemptions to protect liquidity, prevent exploitation, and reduce systemic risk during volatile markets or potential bank-run scenarios that could threaten overall protocol health.
DeFi governance can modify redemption parameters such as fees, limits, collateral thresholds, and timing. These adjustments allow protocols to respond dynamically to changing market conditions and risk exposure.
Debt redemption becomes riskier during extreme market crashes due to rapid collateral devaluation and oracle lag. Safety largely depends on collateral quality, oracle reliability, and protocol risk management design.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







