Key Takeaways
- Crypto exchanges reduce cross-border transaction costs by 60-80% compared to traditional banking channels, with fees typically ranging from 1-3% versus 5-10% for conventional wire transfers.
- International cryptocurrency transfers settle in minutes to hours rather than 3-5 business days, enabling real-time global commerce and faster remittance delivery.
- Blockchain-based financial transfers eliminate intermediary banks and provide transparent, immutable transaction records that enhance security and reduce fraud risk.
- Cryptocurrency exchange platforms provide 24/7 accessibility for borderless payments, removing traditional banking hour restrictions and weekend delays from international money transfers.
- Digital wallets integrated with crypto exchanges enable seamless global digital asset transfers with enhanced user control and security through private key management.
- Small businesses can now access global markets through low-fee crypto remittances and fast crypto transactions across borders, democratizing international trade opportunities.
- Smart contracts automate cross-border payment solutions using crypto, reducing manual processing errors and enabling programmable financial agreements across jurisdictions.
- Regulatory compliance frameworks are evolving globally to support secure international cryptocurrency transfers while maintaining AML and KYC standards.
- Tokenized cross-border assets represent the future of international trade finance, enabling fractional ownership and instant settlement of trade instruments.
- FinTech innovations in crypto liquidity provision ensure sufficient market depth for large-scale cross-border cryptocurrency payments without significant price slippage.
The global financial landscape is experiencing a fundamental transformation as cryptocurrency exchanges emerge as powerful catalysts for cross-border financial transactions. With over 8 years of experience in blockchain technology implementation and digital asset infrastructure development, we have witnessed firsthand how crypto exchanges revolutionize international money transfer systems. Traditional cross-border payments have long been plagued by excessive fees, extended settlement times, and limited accessibility, creating barriers for individuals and businesses seeking to participate in the global economy.
Cryptocurrency exchange platforms now process billions of dollars in international crypto transactions daily, demonstrating the viability and scalability of blockchain-based financial transfers. These platforms serve as crucial gateways between traditional fiat currencies and digital assets, enabling borderless payments that transcend geographic boundaries and eliminate inefficiencies inherent in legacy banking infrastructure. The rise of secure international cryptocurrency transfers represents not merely a technological advancement but a paradigm shift in how value moves across borders in our increasingly interconnected world.
This comprehensive analysis explores how crypto exchanges improve cross-border financial transactions through technological innovation, cost reduction, enhanced security protocols, and expanded accessibility. We examine the mechanisms enabling fast crypto transactions across borders, the economic implications of low-fee crypto remittances, and the future trajectory of global digital asset transfers. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses, financial institutions, and individuals seeking to leverage cross-border cryptocurrency payments effectively while navigating the evolving regulatory landscape and technological capabilities of modern cryptocurrency exchange platforms.
The Evolution of Cross-Border Financial Transactions
Cross-border financial transactions have evolved dramatically from the early days of physical currency exchange and telegraphic transfers to today’s sophisticated digital payment networks. Traditional international money transfer systems developed through correspondent banking relationships, where financial institutions maintained accounts with foreign banks to facilitate cross-border payments. This infrastructure, while functional, introduced multiple intermediaries, each adding fees and processing delays to the transaction chain. The SWIFT network, established in 1973, standardized messaging protocols but did not fundamentally alter the multi-bank relay structure underlying international transfers.
The digital age brought incremental improvements through electronic funds transfers and online banking platforms, yet the fundamental architecture remained largely unchanged. Cross-border payments continued to rely on correspondent banking networks with limited transparency, high costs, and settlement times measured in days rather than hours. This legacy infrastructure proved particularly burdensome for individuals sending remittances to family members abroad and small businesses attempting to expand into international markets. The inefficiencies created economic friction that hindered global commerce and financial inclusion, particularly affecting developing economies with limited banking infrastructure.
The emergence of blockchain technology for payments introduced a revolutionary alternative architecture for cross-border financial transactions. By enabling peer-to-peer value transfer without intermediary institutions, blockchain networks fundamentally reimagined how money could move internationally. Crypto exchanges leveraged this technology to create platforms where users could seamlessly convert between fiat currencies and digital assets, execute international transfers with unprecedented speed and low cost, and access global financial markets regardless of geographic location. This evolution represents a critical inflection point in financial history, where technology enables truly borderless payments and democratizes access to international financial services.
Traditional International Money Transfer Challenges
Traditional international money transfer systems face numerous structural challenges that create significant friction for cross-border financial transactions. The correspondent banking model requires multiple intermediary banks to process a single international payment, with each institution charging fees ranging from $25 to $50 per transaction. These costs compound when currency conversion is required, as banks typically apply exchange rate markups of 3-5% above mid-market rates. For individuals sending remittances, these fees can consume 7-10% of the transfer amount, representing a substantial burden for workers supporting families across borders.
Settlement times represent another critical challenge, with traditional cross-border payments typically requiring 3-5 business days to complete. This delay stems from the sequential processing required as payments move through correspondent banking chains, combined with cut-off times, weekend closures, and time zone differences. Businesses conducting international trade face working capital constraints due to these extended settlement periods, while individuals sending urgent payments to family members abroad experience anxiety and uncertainty during the multi-day processing window. The lack of real-time tracking and limited transparency further compound these challenges, leaving senders unable to determine their payment’s status or expected arrival time.
| Challenge Category | Traditional Banking | Impact on Users |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Fees | $25-$50 + 3-5% FX markup | 5-10% total cost, significant burden for small transfers |
| Settlement Time | 3-5 business days | Working capital constraints, payment uncertainty |
| Accessibility | Limited to banking hours, weekday only | Delays for urgent transfers, inflexible scheduling |
| Transparency | Limited tracking, unclear fee structure | Uncertainty about delivery, hidden costs |
| Documentation | Extensive paperwork for compliance | Administrative burden, potential rejection |
| Currency Conversion | Opaque rates, multiple conversions | Value erosion through poor exchange rates |
Regulatory compliance requirements add further complexity to traditional cross-border transactions. Financial institutions must navigate varying anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations across jurisdictions, often requiring extensive documentation from senders and recipients. These compliance procedures, while necessary for financial system integrity, create additional friction and potential points of failure where transactions may be delayed or rejected. Small businesses and individuals often lack the resources or expertise to navigate these requirements effectively, limiting their ability to participate in international commerce. The combined effect of these challenges has created a compelling case for alternative cross-border payment solutions that leverage technology to overcome traditional banking system limitations.
Rise of Blockchain Technology for Payments
Blockchain technology for payments emerged as a revolutionary solution to the inefficiencies plaguing traditional cross-border financial systems. The distributed ledger architecture enables peer-to-peer value transfer without requiring trusted intermediaries, fundamentally altering the economics and mechanics of international money transfer. Blockchain networks maintain transparent, immutable records of all transactions across a decentralized network of nodes, eliminating the need for correspondent banking relationships and central clearing houses. This architectural shift reduces transaction costs, accelerates settlement times, and increases transparency throughout the payment lifecycle.
The cryptographic security protocols underlying blockchain networks provide robust protection against fraud and unauthorized access, addressing critical security concerns in cross-border financial transactions. Each transaction is validated through consensus mechanisms that ensure network agreement before recording to the blockchain, creating a tamper-resistant audit trail. Public-private key cryptography enables secure authentication without exposing sensitive information, while smart contract capabilities enable programmable payment logic that executes automatically when predetermined conditions are met. These features combine to create a payment infrastructure with security characteristics superior to traditional banking systems in many respects.
The programmability inherent in blockchain platforms enables innovative financial applications beyond simple value transfer. Smart contracts can encode complex business logic, escrow arrangements, and conditional payments that execute automatically without manual intervention. This capability proves particularly valuable for international trade finance, where letters of credit, trade documentation, and payment releases can be automated through blockchain-based systems. The transparency of blockchain transactions also facilitates regulatory compliance by providing auditable records of all payment activity, potentially simplifying AML and KYC processes while maintaining privacy through pseudonymous addressing schemes.
Multiple blockchain networks have emerged with varying technical characteristics optimized for different use cases in cross-border payments. Bitcoin pioneered cryptocurrency transactions but has relatively slower confirmation times and higher fees during network congestion. Ethereum introduced smart contract capabilities but faces scalability challenges. Newer networks like Ripple, Stellar, and various layer-two solutions offer faster transaction speeds and lower costs specifically designed for payment applications. This diverse ecosystem of blockchain-based financial transfer options enables users and businesses to select networks that best match their specific requirements for speed, cost, security, and functionality in cross-border transactions.
Role of Crypto Exchanges in Global Transactions
Cryptocurrency exchange platforms serve as essential infrastructure for global digital asset transfers, functioning as gateways between traditional financial systems and blockchain networks. These platforms provide the critical interface where users can convert fiat currencies into cryptocurrencies for cross-border transfers and subsequently convert received digital assets back into local currencies. Without this fiat-to-crypto conversion capability, blockchain technology’s potential for cross-border payments would remain largely theoretical for most users. Exchanges aggregate liquidity from millions of users worldwide, creating deep markets that enable large-value transactions without significant price slippage.
The operational model of crypto exchanges combines technology infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and financial services expertise to facilitate seamless cross-border cryptocurrency payments. Exchanges maintain relationships with banking partners in multiple jurisdictions to support fiat currency deposits and withdrawals, while simultaneously operating blockchain nodes to process cryptocurrency transactions. This dual integration requires sophisticated technical architecture and extensive regulatory licensing, as exchanges must comply with financial services regulations in each country where they operate. The most successful exchanges have invested heavily in scalable technology platforms capable of processing millions of transactions daily while maintaining robust security and compliance controls.
For businesses and individuals seeking to build crypto exchanges or leverage existing platforms for international transactions, understanding the complete transaction lifecycle is essential. The process involves account creation with identity verification, deposit of fiat or cryptocurrency, exchange transactions, cross-border transfer execution, and withdrawal to recipient accounts. Each step requires careful attention to security, regulatory compliance, and user experience optimization. Professional cryptocurrency exchange developers can help organizations navigate the technical and regulatory complexities involved in establishing or integrating with cryptocurrency exchange platforms for cross-border payment solutions.
Cryptocurrency Exchange Platforms as Financial Gateways
Cryptocurrency exchange platforms function as critical financial gateways by bridging the gap between traditional banking systems and decentralized blockchain networks. This gateway role encompasses multiple essential functions including fiat currency on-ramps and off-ramps, liquidity provision, price discovery, and custody services. The on-ramp function enables users to deposit local currency through bank transfers, credit cards, or other payment methods and exchange it for cryptocurrency, while the off-ramp enables conversion of received cryptocurrency back to fiat currency for withdrawal. These bidirectional conversion capabilities are fundamental to enabling practical cross-border cryptocurrency payments for users without pre-existing digital asset holdings.
The liquidity provision role of exchanges cannot be overstated, as adequate market depth is essential for executing large cross-border transfers without adverse price impact. Major cryptocurrency exchange platforms aggregate order books from millions of users globally, creating liquid markets where buyers and sellers can transact at fair market prices. This liquidity enables businesses to execute substantial international payments without the price slippage that would occur in thin markets. Exchanges also provide price discovery mechanisms through continuous trading, establishing reference prices for various cryptocurrency pairs that facilitate transparent, market-based valuation for cross-border transactions.
Custody services provided by exchanges offer convenience and security for users managing digital assets for cross-border payments. While self-custody through personal wallets provides maximum control, exchange custody services appeal to users seeking simplified asset management with professional security infrastructure. Leading exchanges implement multi-signature wallets, cold storage for the majority of assets, insurance coverage, and regular security audits to protect user funds. The trade-off between convenience and control represents an important consideration for users and businesses developing cross-border payment workflows, with many opting for hybrid approaches that leverage both exchange custody and personal wallet solutions depending on transaction volume and security requirements.
Enabling Borderless Payments Through Exchanges
Borderless payments represent a fundamental value proposition of cryptocurrency exchanges, eliminating the geographic restrictions inherent in traditional banking systems. Unlike conventional financial institutions that operate within specific jurisdictional boundaries and require correspondent banking relationships for international transfers, cryptocurrency exchanges leverage blockchain networks that operate globally without regard to national borders. Users in any location can send cryptocurrency to recipients anywhere in the world through the same streamlined process, without the complexity of navigating different banking systems, time zones, or regulatory frameworks for each destination country.
The 24/7 operational model of cryptocurrency exchanges contrasts sharply with traditional banking hours that limit when cross-border payments can be initiated and processed. Blockchain networks and crypto exchanges operate continuously, enabling users to execute international transfers at any time, including weekends and holidays when conventional banking systems are closed. This constant availability proves particularly valuable for urgent payments, international business transactions across time zones, and individuals in different countries coordinating time-sensitive financial activities. The elimination of business-hour constraints represents a substantial improvement in accessibility and flexibility for cross-border financial transactions.
The uniform user experience across different countries and currencies simplifies the cross-border payment process significantly compared to traditional systems. Users follow the same procedures whether sending payments domestically or internationally, to nearby countries or distant continents. The cryptocurrency serves as a neutral intermediate asset that facilitates exchange between any pair of fiat currencies without requiring direct currency markets or specialized knowledge of international banking procedures. This simplification democratizes access to cross-border payments, enabling individuals and small businesses to participate in international commerce with the same ease as large multinational corporations with dedicated treasury departments.
Improving Liquidity for Cross-Border Trade
Crypto liquidity for cross-border trade represents a critical enabler of efficient international commerce, with cryptocurrency exchanges serving as the primary liquidity providers for global digital asset transfers. Liquidity refers to the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without causing significant price movement, and exchanges aggregate trading activity from millions of users to create deep, liquid markets. This liquidity pool enables businesses conducting international trade to convert large sums between fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies at fair market prices, ensuring that cross-border payments can be executed efficiently regardless of transaction size. Without adequate liquidity, even technologically superior payment systems would face practical limitations for commercial use.
The market-making activities of exchanges contribute substantially to liquidity provision for cross-border cryptocurrency payments. Professional market makers continuously place buy and sell orders at multiple price levels, ensuring that traders can always find counterparties for their transactions. This market-making activity narrows bid-ask spreads, reducing the implicit cost of converting between currencies for cross-border transfers. Major cryptocurrency exchanges employ sophisticated algorithms and maintain substantial capital reserves dedicated to market-making operations, creating the liquid markets necessary for businesses to integrate cryptocurrency payments into their international trade operations with confidence in execution quality.
The diversity of trading pairs available on major exchanges further enhances liquidity for cross-border trade by enabling direct exchange between various cryptocurrency and fiat currency combinations. Rather than requiring multiple conversion steps through intermediate currencies, users can often exchange directly between their local fiat currency and the cryptocurrency optimal for their cross-border transfer needs. This direct exchange capability reduces costs, accelerates transaction execution, and simplifies the user experience. As cryptocurrency exchange developers expand their fiat currency support and deepen liquidity across diverse trading pairs, the efficiency and accessibility of cross-border cryptocurrency payments continue improving for international trade applications.
Cross-Border Cryptocurrency Payments Explained
Cross-border cryptocurrency payments operate through a fundamentally different mechanism than traditional international money transfers, leveraging blockchain technology to enable direct value transfer between parties in different countries. The process begins when a sender converts their local fiat currency into cryptocurrency through an exchange platform, initiating a blockchain transaction that transfers the digital asset to the recipient’s wallet address. The recipient can then either retain the cryptocurrency or convert it back to their local fiat currency through their own exchange account. This process eliminates intermediary banks, reduces settlement times from days to minutes or hours, and dramatically lowers transaction costs compared to conventional cross-border payment methods.
The technical infrastructure supporting cross-border cryptocurrency payments consists of multiple interconnected components working in concert. Blockchain networks provide the underlying transaction processing and validation infrastructure, maintaining distributed ledgers that record all transfers permanently and transparently. Cryptocurrency exchanges offer the fiat-crypto conversion interfaces, order books, and liquidity pools necessary for practical usability. Digital wallets enable secure storage and management of cryptocurrency holdings. Together, these components create an ecosystem where value can move across international borders with unprecedented speed, low cost, and accessibility compared to legacy payment systems.
Understanding Crypto Remittances
Crypto remittances represent one of the most impactful applications of cross-border cryptocurrency payments, addressing the high costs and inefficiencies plaguing traditional remittance services. The World Bank estimates that global remittances exceed $700 billion annually, with migrants sending money to family members in their home countries. Traditional remittance services charge fees averaging 6-7% of the transfer amount, with some corridors experiencing double-digit percentage costs. These fees disproportionately burden lower-income workers sending relatively small amounts home, consuming substantial portions of their hard-earned wages. Crypto remittances offer a compelling alternative by reducing fees to 1-3% while accelerating delivery from days to hours.
The operational model for crypto remittances involves the sender purchasing cryptocurrency through an exchange in their host country, transferring the digital asset via blockchain to a recipient in another country, and the recipient converting the cryptocurrency to local fiat currency through a local exchange or cash-out service. This model eliminates the extensive intermediary chain involved in traditional remittances, where money transfer operators, correspondent banks, and local payout agents each extract fees from the transaction. The peer-to-peer nature of blockchain transfers reduces the number of parties involved and thus the cumulative fees charged, enabling more of the sender’s money to reach the intended recipient.
Secure International Cryptocurrency Transfers
Secure international cryptocurrency transfers rely on multiple layers of cryptographic and operational security measures implemented across the blockchain network and cryptocurrency exchange infrastructure. The fundamental security of blockchain transactions stems from public-key cryptography, where each user controls a private key that authorizes transactions from their wallet address. This cryptographic architecture ensures that only the legitimate owner can initiate transfers, as possession of the private key is mathematically required to create valid transaction signatures. The distributed nature of blockchain networks provides additional security through consensus mechanisms that require network-wide agreement before recording transactions, making unauthorized alterations practically impossible without controlling a majority of network computing power.
Cryptocurrency exchanges implement comprehensive security protocols to protect user assets and transaction integrity. Industry-leading practices include cold storage of the majority of user funds in offline wallets inaccessible to network attacks, multi-signature wallet configurations requiring multiple authorized parties to approve withdrawals, regular security audits by independent firms, and insurance coverage for digital assets held in custody. Two-factor authentication (2FA) requirements add an additional verification layer beyond passwords, while withdrawal whitelist features enable users to specify approved destination addresses. Advanced monitoring systems detect suspicious activity patterns and trigger automatic security responses to prevent unauthorized access or fraudulent transactions.
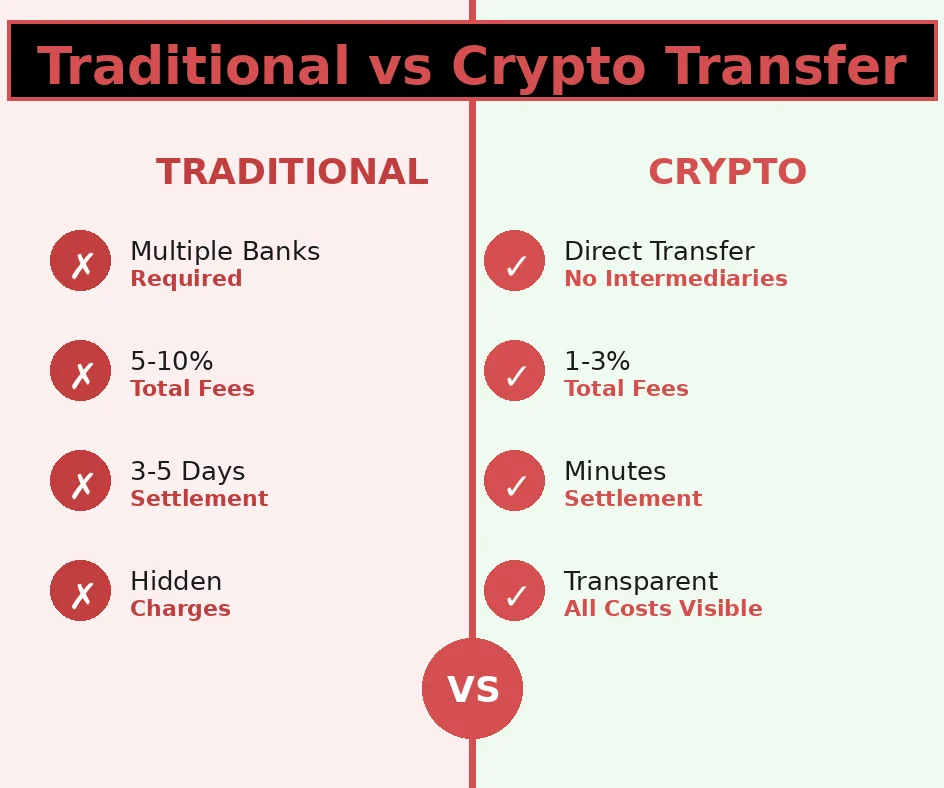
Cost-Efficiency and Speed in International Crypto Transactions
Cost-efficiency represents one of the most compelling advantages of international crypto transactions compared to traditional cross-border payment methods. Total costs for cryptocurrency-based international transfers typically range from 1-3% of the transaction amount, incorporating exchange trading fees, blockchain network fees, and fiat currency withdrawal charges. This contrasts dramatically with traditional international wire transfers charging $25-$50 in fixed fees plus 3-5% foreign exchange markups, resulting in total costs of 5-10% for typical transactions. The cost savings prove particularly significant for smaller transfers where fixed fees consume a larger percentage of the transferred amount, and for high-volume users conducting multiple international payments monthly.
The speed of fast crypto transactions across borders delivers substantial operational and financial benefits beyond the direct cost savings. Blockchain-based transfers typically settle within 10 minutes to 1 hour depending on the network and confirmation requirements, compared to 3-5 business days for traditional international wire transfers. This acceleration enables businesses to optimize working capital management, as funds arrive and become available much faster. Individuals benefit from reduced anxiety and uncertainty when sending urgent payments to family members or business partners abroad. The elimination of weekend and holiday delays further enhances the speed advantage, as cryptocurrency transactions process continuously regardless of business calendars in various countries.
Technological Innovations Driving Crypto Exchange Efficiency
Technological innovations continue advancing cryptocurrency exchange capabilities for cross-border financial transactions, with developments across blockchain protocols, smart contract platforms, security systems, and user interface design. These innovations address limitations in earlier implementations while expanding functionality to serve increasingly sophisticated use cases. Layer-two scaling solutions enable faster transaction processing and lower fees by conducting multiple transactions off-chain before settling final states to the main blockchain. Atomic swap technology allows direct peer-to-peer exchange between different cryptocurrencies without requiring trusted intermediaries. Improvements in consensus mechanisms reduce energy consumption and increase transaction throughput for blockchain networks supporting cross-border payments.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning enhances various aspects of cryptocurrency exchange operations. Fraud detection systems employ machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious transaction patterns and prevent unauthorized activity. Trading algorithms optimize execution quality for large cross-border payments by intelligently routing orders across multiple liquidity pools. Customer service chatbots powered by natural language processing provide instant support for users navigating cross-border transactions. Predictive analytics help exchanges anticipate liquidity needs and manage capital allocation efficiently. These AI-driven capabilities improve security, efficiency, and user experience for international cryptocurrency transfers.
Smart Contracts for Seamless Transfers
Smart contracts revolutionize cross-border financial transactions by enabling programmable, self-executing payment logic that operates automatically without manual intervention. These blockchain-based programs encode business rules, escrow conditions, and payment triggers directly into code that executes transparently on the blockchain network. For international trade, smart contracts can automate letter of credit processes, releasing payment automatically when shipping documentation meets specified conditions. For recurring cross-border payments like subscriptions or payroll, smart contracts execute scheduled transfers without requiring manual processing for each payment cycle. This automation reduces errors, accelerates transaction execution, and eliminates the administrative overhead associated with manual payment processing.
The transparency and immutability of smart contract execution provide significant trust and compliance benefits for cross-border transactions. All parties can inspect the smart contract code to verify its logic before committing funds, creating transparency impossible in traditional correspondent banking relationships where internal processing procedures remain opaque to customers. Once deployed, smart contracts execute deterministically based on their programmed logic, eliminating counterparty risk and the possibility of arbitrary rule changes mid-transaction. The permanent blockchain record of smart contract execution provides an auditable trail for regulatory compliance and dispute resolution, addressing key concerns in international business relationships where legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms vary across jurisdictions.
Integration of Digital Wallets
Digital wallets for global transfers serve as essential interfaces between users and blockchain networks, providing secure storage, transaction management, and user-friendly access to cryptocurrency holdings for cross-border payments. Modern wallet applications offer intuitive interfaces that abstract away complex technical details of blockchain transactions, making cryptocurrency accessible to mainstream users without requiring deep technical knowledge. Mobile wallet applications enable cross-border payments from smartphones, bringing cryptocurrency transaction capabilities to billions of users worldwide who may lack access to traditional banking infrastructure but possess mobile devices. The convenience and accessibility of digital wallets prove crucial for expanding cryptocurrency adoption for international transfers beyond early adopter communities.
The security architecture of digital wallets balances user control with practical usability considerations. Hardware wallets provide maximum security by storing private keys on dedicated devices isolated from internet connectivity, protecting against remote attacks while requiring physical device access for transaction authorization. Software wallets offer convenience through application-based access but require users to carefully protect their devices and backup phrases. Custodial wallets maintained by exchanges simplify key management by outsourcing security to the platform, though this reduces user control over private keys. Multi-signature wallets require multiple authorized parties to approve transactions, providing enhanced security for business accounts and large holdings used for cross-border payments.
Blockchain Security Protocols for Cross-Border Transactions
Blockchain security protocols provide the foundational infrastructure enabling secure international cryptocurrency transfers through multiple layers of cryptographic protection and distributed consensus mechanisms. Public-key cryptography forms the basis of transaction authorization, where each user controls a private key that mathematically corresponds to their public wallet address. Transaction signatures created with private keys prove ownership and authorize transfers, while public keys enable anyone to verify signature authenticity without accessing the private key itself. This asymmetric cryptography ensures that only legitimate owners can initiate transactions from their wallets, creating strong security without requiring trusted intermediaries to verify transaction authorization.
Consensus mechanisms ensure network-wide agreement on transaction validity and ordering, preventing double-spending attempts and maintaining the integrity of the distributed ledger. Proof-of-work consensus requires miners to solve computationally intensive puzzles to validate transaction blocks, making network attacks prohibitively expensive due to the computing power required to control a majority of network hashing power. Proof-of-stake consensus bases validation authority on cryptocurrency holdings staked as collateral, creating economic incentives aligned with network security. Byzantine fault tolerance algorithms enable networks to reach consensus even when some nodes behave maliciously, providing robustness against various attack scenarios in cross-border payment applications.
Economic and Business Impacts of Cross-Border Crypto Transactions
The economic and business impacts of cross-border crypto transactions extend far beyond simple payment cost reduction, fundamentally reshaping international commerce, remittance markets, and financial inclusion. The dramatic reduction in transaction costs and settlement times enables new business models previously economically unviable under traditional payment infrastructure. Small businesses can now serve international customers profitably despite lower transaction values that would be consumed by conventional payment fees. Digital service providers can receive micropayments from clients worldwide without prohibitive processing costs. The efficiency gains from blockchain-based financial transfers create economic value that flows to both businesses and consumers through reduced costs and expanded market access.
Global trade finance stands to benefit substantially from cryptocurrency adoption for cross-border payments. Traditional trade finance processes involve extensive documentation, multiple intermediary banks, and settlement periods extending weeks or months. Smart contract-based alternatives can automate letter of credit processing, automatically release payment upon delivery confirmation, and provide transparent audit trails throughout the transaction lifecycle. These improvements reduce working capital requirements for importers and exporters, accelerate cash conversion cycles, and lower the cost of trade finance. As tokenized cross-border assets enable fractional ownership and instant settlement of trade instruments, the efficiency and accessibility of international trade continue improving.
Enabling Small Businesses to Expand Globally
Small businesses historically faced significant barriers to international expansion due to payment processing costs, complexity, and minimum volume requirements imposed by traditional financial infrastructure. Cross-border payment solutions using crypto eliminate many of these barriers by providing affordable, accessible international payment capabilities without requiring extensive banking relationships or high transaction volumes. A small online retailer can now accept cryptocurrency payments from customers worldwide at costs competitive with domestic credit card processing, rather than paying premium fees for international card transactions. Freelancers and micro-businesses can receive payments from international clients without losing substantial portions to wire transfer fees and currency conversion markups.
The operational simplification enabled by cryptocurrency payments reduces administrative burden for small businesses conducting international trade. Rather than navigating different payment methods, banking procedures, and compliance requirements for each country, businesses can implement a standardized cryptocurrency payment process applicable globally. Invoice generation, payment processing, and reconciliation workflows become consistent regardless of customer location. Integration with accounting software automates transaction recording and tax reporting. This standardization and automation free small business resources from payment processing administration, enabling greater focus on core business activities and customer service.
Reducing Remittance Costs for Individuals
The impact of reduced remittance costs through cryptocurrency cannot be overstated, as remittances represent a critical income source for hundreds of millions of people in developing countries. The World Bank reports that remittances to low and middle-income countries exceeded $600 billion in 2023, with these funds directly supporting families and contributing significantly to local economies. Traditional remittance services charge fees averaging 6-7% globally, with some corridors experiencing costs exceeding 10%. These high fees disproportionately burden migrant workers, many earning modest incomes, who send money home to support family members in their countries of origin. Cryptocurrency remittances reducing costs to 1-3% represent savings of billions of dollars annually that can reach intended recipients rather than being consumed by intermediaries.
The practical impact of these savings extends beyond the immediate financial benefit to remittance recipients. Lower costs enable more frequent transfers, allowing families to receive funds more regularly rather than waiting for larger accumulated amounts to make transfer fees economically tolerable. This increased transfer frequency improves cash flow management for recipient families and provides more consistent financial support. The speed of cryptocurrency transfers also delivers significant practical advantages, with funds arriving within hours rather than days, enabling families to address urgent needs quickly. Emergency situations requiring rapid financial assistance become more manageable when transfers can execute nearly instantaneously rather than facing multi-day processing delays.
Enhancing Global FinTech Innovations
Cross-border cryptocurrency payments serve as catalysts for broader FinTech innovations by demonstrating the viability of blockchain technology for financial services and inspiring new applications beyond simple value transfer. The success of cryptocurrency exchanges in reducing costs and improving efficiency for international payments validates blockchain’s potential to address inefficiencies across the financial sector. This validation encourages investment, talent, and entrepreneurial energy into developing additional blockchain-based financial services. Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols built on blockchain networks now offer lending, borrowing, trading, and yield generation services accessible globally without traditional intermediaries, extending the benefits of blockchain technology beyond cross-border payments to comprehensive financial services.
The technological infrastructure developed to support cross-border cryptocurrency payments enables adjacent FinTech applications that leverage the same underlying blockchain networks and exchange platforms. Tokenization of real-world assets including real estate, commodities, and securities becomes practical using blockchain infrastructure originally developed for cryptocurrency transfers. Cross-border investment opportunities become more accessible as tokenized assets can be traded globally on cryptocurrency exchanges with settlement efficiency comparable to cryptocurrency transactions. As the crypto exchange market continues its growth trajectory, these innovations become increasingly mainstream and accessible to users worldwide.
Challenges and Considerations in Cross-Border Crypto Transactions
Despite substantial advantages, cross-border crypto transactions face meaningful challenges that users and businesses must understand and navigate. Regulatory uncertainty across jurisdictions creates compliance complexity, as cryptocurrency legal frameworks vary dramatically between countries ranging from outright bans to progressive regulatory clarity. Price volatility inherent in cryptocurrency markets introduces value risk during the transfer process, potentially resulting in recipients receiving different amounts than senders intended. Technical barriers including wallet setup complexity, private key management responsibility, and blockchain network congestion affect user experience and accessibility. Understanding these challenges enables informed decision-making about when and how to leverage cryptocurrency for international payments.
The nascent state of cryptocurrency infrastructure in some regions limits practical usability for cross-border payments to or from those areas. Local exchange availability varies significantly, with some countries hosting multiple well-capitalized exchanges while others have limited or no local options for fiat currency conversion. Banking relationships necessary for fiat on-ramps and off-ramps face challenges in jurisdictions where banks remain skeptical of cryptocurrency or face regulatory restrictions on serving crypto-related businesses. Internet connectivity and smartphone adoption, while expanding rapidly, remain limited in some developing regions where cryptocurrency remittances could otherwise provide substantial value. These infrastructure gaps will narrow over time but currently constrain cryptocurrency payment adoption in certain corridors.
Regulatory Compliance Across Countries
Regulatory compliance for cross-border cryptocurrency transactions requires navigating a complex patchwork of national laws, international standards, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Countries take vastly different approaches to cryptocurrency regulation, ranging from progressive frameworks with clear legal status and licensing requirements to outright bans on cryptocurrency transactions. This regulatory fragmentation creates compliance challenges for cryptocurrency exchanges operating internationally and users conducting cross-border payments across jurisdictions with conflicting rules. Exchanges must obtain licenses in each jurisdiction where they operate, implement appropriate AML and KYC procedures meeting local requirements, and ensure transaction monitoring satisfies varying regulatory standards across different countries.
Anti-money laundering and know-your-customer requirements form the cornerstone of cryptocurrency regulatory compliance globally. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) publishes international standards for cryptocurrency regulation that many countries adopt as the basis for their national frameworks. These standards require cryptocurrency exchanges and service providers to verify customer identities, monitor transactions for suspicious activity, maintain detailed records, and report certain transactions to authorities. The “travel rule” requires transmitting customer information along with cryptocurrency transfers above specified thresholds, creating technical challenges for implementing compliant cross-border cryptocurrency payment systems while preserving blockchain’s privacy characteristics.
Volatility and Risk Management
Cryptocurrency price volatility represents one of the most significant challenges for using digital assets in cross-border financial transactions, as value fluctuations during transfer processes can result in recipients receiving different amounts than senders intended. Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum frequently experience daily price movements of 5-10%, with occasional spikes reaching 20% or more during periods of market stress or excitement. This volatility creates uncertainty for users relying on cryptocurrency for international payments, particularly when transfers involve holding cryptocurrency for extended periods or when precise final amounts are critical for business transactions. Managing this volatility risk requires understanding available mitigation strategies and making informed choices about cryptocurrency selection and transaction timing.
Stablecoins provide a practical solution to volatility concerns by maintaining value pegs to fiat currencies through various backing mechanisms. Fiat-backed stablecoins like USDC and USDT maintain reserves of US dollars or dollar-equivalent assets to support their price stability, enabling transfers that preserve value throughout the transaction lifecycle. Algorithmic stablecoins attempt to maintain stable values through programmatic supply adjustments, though these have proven less reliable than asset-backed alternatives. Stablecoins enable users to capture the speed and cost benefits of blockchain-based transfers while avoiding the value risk associated with volatile cryptocurrencies, making them particularly suitable for business payments and remittances where predictable final amounts are essential.
Technological Barriers and Adoption Challenges
Technological barriers to widespread cryptocurrency adoption for cross-border payments include user experience complexity, infrastructure requirements, and scalability limitations. Wallet setup and management requires technical understanding beyond typical financial service applications, with users responsible for securing private keys, maintaining backup phrases, and understanding transaction fee dynamics. The irreversible nature of blockchain transactions means errors in recipient address entry result in permanent fund loss, creating higher stakes than traditional payment systems. Network congestion during periods of high activity can result in delayed transaction confirmation or elevated fees, complicating planning for time-sensitive international payments. These technical considerations create friction that inhibits mainstream adoption among less technically sophisticated users.
Overcoming adoption challenges requires continued progress across multiple dimensions including user interface design, educational resources, infrastructure development, and technical scalability improvements. Wallet applications with simplified interfaces abstract technical complexity while maintaining security, making cryptocurrency more accessible to mainstream users. Educational initiatives by exchanges, industry organizations, and community groups help users understand cryptocurrency basics and best practices. Infrastructure investments in blockchain scaling solutions, both on-chain improvements and layer-two protocols, increase transaction capacity while maintaining reasonable costs. As these efforts continue advancing, the technological barriers to cryptocurrency adoption for cross-border payments steadily diminish, enabling broader participation in blockchain-based international financial transactions.
Future Trends in Cross-Border Crypto Exchanges
The future evolution of cross-border crypto exchanges promises transformative developments in international financial infrastructure as technology matures and regulatory frameworks clarify. Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) represent establishment financial institutions’ embrace of blockchain technology, with dozens of countries actively developing or piloting digital currency initiatives. These government-backed digital currencies could integrate with cryptocurrency exchanges to create hybrid systems combining blockchain efficiency with regulatory oversight and fiat currency stability. Interoperability between CBDCs and cryptocurrencies might enable seamless conversion and cross-border transfers leveraging the strengths of both traditional and decentralized financial systems.
Artificial intelligence integration will enhance cryptocurrency exchange capabilities for cross-border transactions through improved fraud detection, optimized trade execution, and personalized user experiences. Machine learning algorithms will predict optimal transaction timing based on fee levels and network congestion patterns, automatically executing transfers when conditions are favorable. Natural language processing will enable conversational interfaces where users can initiate international payments through simple commands rather than navigating complex technical procedures. AI-powered compliance systems will streamline regulatory adherence while maintaining privacy, automatically generating required documentation and ensuring transaction legality across jurisdictions.
Tokenized Assets for International Trade
Tokenized cross-border assets represent the future of international trade finance, enabling digital representation of real-world assets on blockchain networks with the same transferability characteristics as cryptocurrency. Trade finance instruments including letters of credit, bills of lading, warehouse receipts, and invoice financing can be tokenized to enable instant transfer, fractional ownership, and automated processing through smart contracts. This tokenization transforms illiquid trade finance assets into tradeable digital securities that can be bought, sold, or used as collateral on cryptocurrency exchanges and DeFi platforms. The efficiency gains from tokenization could unlock trillions of dollars in currently illiquid trade finance assets, democratizing access to international trade financing and reducing costs for businesses engaged in cross-border commerce.
Supply chain tokenization enhances transparency and efficiency for international trade by creating digital representations of goods as they move through global supply networks. Each product or shipment receives a unique token that tracks its location, condition, ownership, and compliance documentation on the blockchain. Smart contracts automatically transfer token ownership as goods change hands, trigger payment releases upon delivery confirmation, and maintain immutable audit trails for regulatory compliance. This tokenized supply chain approach reduces documentation fraud, accelerates customs clearance, and enables better financing options as lenders can monitor collateral location and condition in real-time through blockchain records.
Expansion of Borderless Payment Networks
The expansion of borderless payment networks built on blockchain technology promises to further reduce friction in international financial transactions as infrastructure develops and adoption accelerates. Layer-two scaling solutions enable dramatically higher transaction throughput while maintaining the security characteristics of underlying blockchain networks, potentially processing thousands or millions of transactions per second at costs approaching negligible levels. State channel networks allow parties conducting frequent bilateral transactions to operate primarily off-chain with periodic settlement to the main blockchain, enabling instant, zero-fee transactions between regular trading partners across borders. These technical advances position blockchain networks to scale toward serving as global payment infrastructure capable of handling a substantial portion of international commerce.
Stablecoin adoption for borderless payments continues accelerating as these cryptocurrency variants address volatility concerns while maintaining blockchain efficiency advantages. Multiple central banks explore issuing CBDCs that could integrate with cryptocurrency exchange platforms to enable seamless cross-border transfers between digital fiat currencies. Payment stablecoins optimized specifically for transaction use cases rather than investment emerge with features including instant finality, predictable fees, and compliance features built into smart contracts. As stablecoin infrastructure matures and regulatory frameworks provide clarity, these digital currencies may become the primary medium for cross-border cryptocurrency payments, relegating volatile cryptocurrencies primarily to investment and store-of-value use cases.
Integration with Traditional Banking Systems
Integration between cryptocurrency exchanges and traditional banking systems represents a critical development for mainstream adoption of cross-border crypto payments. Banks increasingly recognize cryptocurrency as a significant innovation requiring engagement rather than opposition, with many major financial institutions now offering cryptocurrency custody services, facilitating client cryptocurrency purchases, and experimenting with blockchain technology for internal processes. This changing institutional attitude enables deeper integration between cryptocurrency and traditional financial infrastructure, creating hybrid systems that leverage blockchain efficiency while maintaining the regulatory oversight and fiat currency integration essential for widespread business and consumer adoption.
Real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems being developed by central banks increasingly consider interoperability with cryptocurrency networks and stablecoins. CBDC initiatives in numerous countries explicitly target cross-border payment improvement as a primary objective, with technical architectures designed to enable international transfers with settlement speeds and costs approaching those of cryptocurrency transactions. Some central banks explore allowing commercial banks and regulated cryptocurrency exchanges to participate in CBDC networks, creating direct bridges between traditional banking and blockchain-based payment systems. These developments could result in hybrid cross-border payment infrastructure combining benefits of both centralized regulatory oversight and decentralized blockchain efficiency.
Banking partnerships enable cryptocurrency exchanges to expand fiat currency support and geographic reach while providing traditional financial institutions with access to cryptocurrency markets and blockchain technology capabilities. These collaborative relationships benefit consumers through expanded payment options, reduced costs, and improved user experiences that seamlessly blend traditional and cryptocurrency payment methods. As integration deepens, the distinction between traditional cross-border banking and cryptocurrency-based international transfers may blur from a user perspective, with backend systems intelligently routing payments through optimal channels based on cost, speed, and regulatory requirements while presenting unified interfaces to end users.
Build Your Own Crypto Exchange for Seamless Cross-Border Payments
Launch a secure, high-speed crypto exchange with us and enable fast, low-cost cross-border transactions effortlessly.
Conclusion
Crypto exchanges have fundamentally transformed cross-border financial transactions by leveraging blockchain technology to eliminate inefficiencies inherent in traditional international payment systems. The combination of dramatically reduced costs, accelerated settlement times, enhanced security protocols, and expanded accessibility positions cryptocurrency-based cross-border payments as increasingly viable alternatives to conventional banking channels. Through secure international cryptocurrency transfers, low-fee crypto remittances, and fast crypto transactions across borders, exchanges enable individuals and businesses worldwide to participate more effectively in the global economy without the friction and expense historically associated with international money transfer.
The economic and social impacts extend beyond immediate cost savings to encompass financial inclusion, small business empowerment, and global commerce democratization. Millions of migrant workers benefit from reduced remittance costs that enable more money to reach their families in home countries. Small businesses gain access to international markets previously inaccessible due to prohibitive payment processing costs. Developing economies receive capital more efficiently through improved remittance channels and enhanced trade finance options. As Bitcoin and cryptocurrency investment vehicles continue maturing alongside payment infrastructure, the broader ecosystem supporting cross-border crypto transactions strengthens.
Looking forward, the trajectory points toward deeper integration between cryptocurrency exchanges and traditional financial systems, expansion of tokenized assets for international trade, and continued technological innovation addressing current limitations. Regulatory frameworks worldwide evolve toward providing clearer guidelines that balance innovation encouragement with consumer protection and financial system integrity. Infrastructure improvements through layer-two scaling solutions, cross-chain interoperability protocols, and user experience enhancements will further reduce barriers to cryptocurrency adoption for cross-border payments. Central bank digital currencies may integrate with cryptocurrency exchanges to create hybrid systems combining blockchain benefits with government backing and regulatory oversight.
For organizations considering entry into this space, whether through listing on major exchange platforms or developing proprietary solutions, the opportunity landscape continues expanding as adoption accelerates. With over 8 years of experience delivering blockchain-based solutions, our team has witnessed the remarkable transformation of cross-border payment capabilities enabled by cryptocurrency exchanges. The shift from days-long, expensive wire transfers to near-instantaneous, affordable blockchain transactions represents more than incremental improvement but rather a fundamental reimagining of how value moves globally.
The future of cross-border financial transactions lies in leveraging the complementary strengths of blockchain technology and traditional financial infrastructure. Cryptocurrency exchanges will continue serving as essential bridges between these worlds, enabling seamless value transfer that combines the speed and efficiency of digital currency cross-border payments with the stability and regulatory clarity of established financial systems. As technology matures, regulations clarify, and adoption broadens, the promise of truly frictionless international commerce moves steadily from aspiration toward reality, fundamentally reshaping global economic relationships and expanding financial opportunity for billions worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Crypto exchanges facilitate cross-border transactions by providing a decentralized platform where users can convert fiat currency into cryptocurrency, transfer digital assets across borders instantly, and convert back to local currency. This eliminates intermediary banks, reduces processing time from days to minutes, and significantly lowers transaction fees compared to traditional wire transfers or remittance services.
The main advantages include near-instantaneous settlement times regardless of geographic location, substantially lower transaction fees (often 1-3% compared to 5-10% for traditional methods), 24/7 availability without banking hour restrictions, enhanced security through blockchain encryption, and elimination of currency conversion complexities. Additionally, cryptocurrency transactions provide greater transparency and traceability through immutable blockchain records.
Yes, most crypto exchanges employ advanced security measures, including cryptographic protocols, two-factor authentication, and cold storage wallets, to secure funds. Additionally, blockchain ledgers provide transparency, allowing users to track payments in real time, which enhances trust in international transactions.
Modern crypto exchanges support multiple cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies. They integrate tools for seamless currency conversion, helping businesses settle international invoices quickly. Smart contracts can automate compliance checks and payment processes, reducing delays in global trade settlements.
For migrant workers and individuals sending funds home, crypto exchanges offer fast settlement and lower fees compared to banks or money transfer operators. Transactions that normally take days can now complete within minutes or even seconds, ensuring families receive more value instantly.
Cross-border cryptocurrency transactions typically complete within 10 minutes to 1 hour depending on the blockchain network and confirmation requirements. Bitcoin transactions usually take 10-60 minutes, while networks like Ripple or Stellar can process international transfers in 3-5 seconds. This represents a dramatic improvement over traditional international wire transfers that can take 3-5 business days to settle completely.
Absolutely, businesses increasingly leverage crypto exchanges for international trade to streamline cross-border payments, reduce transaction costs, and accelerate settlement times. Cryptocurrency exchange platforms enable businesses to pay suppliers, receive payments from international clients, and manage multi-currency transactions efficiently. Many exchanges now offer business accounts with higher transaction limits, API integrations, and compliance tools specifically designed for commercial use.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







