Key Takeaways
- A Crypto Derivatives Exchange enables traders to speculate on cryptocurrency price movements through futures, options, and perpetual contracts without owning the underlying asset directly.
- Perpetual contracts crypto have become the dominant instrument in the crypto derivatives market 2026, accounting for over 70% of all derivatives trading volume globally.
- Crypto futures trading and crypto options trading serve fundamentally different purposes: futures are used for directional bets and hedging, while options provide asymmetric risk profiles with capped downside.
- Leverage in crypto derivatives trading amplifies both gains and losses, making robust risk management, liquidation protection, and margin monitoring critical for every participant.
- The crypto derivatives market 2026 is characterized by growing institutional participation, clearer regulatory frameworks, and the rise of decentralized derivatives protocols.
- Building a crypto derivatives platform requires a high-performance matching engine, robust risk engine, liquidation mechanism, funding rate system, and integrated KYC/AML compliance.
- AI-powered trading tools, automated hedging strategies, and cross-margin innovations are reshaping crypto derivatives trading strategies in 2026.
- White-label crypto derivatives exchange solutions offer a faster go-to-market path, while custom builds provide maximum flexibility for differentiated product offerings.
What is a Crypto Derivatives Exchange?
A Crypto Derivatives Exchange is a trading platform specifically designed for buying and selling financial instruments whose value is derived from underlying cryptocurrency assets. Unlike spot exchanges where traders exchange actual tokens, a derivatives exchange allows participants to trade contracts that represent the future or conditional value of those assets. These platforms are the backbone of sophisticated trading in the digital asset space, enabling strategies that range from simple speculation to complex institutional hedging.
The explosive growth of crypto derivatives trading over the past several years has been remarkable. In 2026, derivatives volume consistently exceeds spot trading volume by a factor of five to ten on most major platforms. This growth reflects the maturation of the crypto market and the increasing participation of professional traders, market makers, and institutional investors who require the tools that derivatives provide: leverage, hedging, and advanced risk management.
Definition of Cryptocurrency Derivatives
Cryptocurrency derivatives are financial contracts that derive their value from the price performance of an underlying crypto asset such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other digital tokens. The most common forms include futures contracts, perpetual contracts, and options. These instruments allow traders to take positions on price direction (long or short), hedge existing portfolio exposure, and access leverage to amplify their market participation without requiring full upfront capital.
What makes cryptocurrency derivatives particularly powerful is their flexibility. A trader in any major financial market can use a futures contract to bet on Bitcoin reaching $150,000 by year-end, use put options to protect a large Ethereum holding against a price crash, or use perpetual contracts to run an intraday trading strategy with 20x leverage. Each instrument serves a specific purpose in a trader’s toolkit, and understanding the nuances of each is essential for anyone participating in the crypto derivatives market 2026.
How a Crypto Derivatives Exchange Works
A Crypto Derivatives Exchange operates as a sophisticated marketplace that matches buyers and sellers of derivative contracts, manages margin and collateral, calculates real-time risk, and enforces liquidation rules. The exchange sits at the center of every trade, acting as the counterparty to both sides to eliminate credit risk between individual traders. This central counterparty model is what gives traders confidence that their positions will be honored regardless of the other party’s financial situation.
Role of the Order Book and Matching Engine
The order book is the real-time record of all open buy and sell orders on the exchange, organized by price level. The matching engine is the core technology that pairs compatible orders and executes trades. In a crypto derivatives platform, the matching engine must handle not just order matching but also the complex calculations associated with margin requirements, leverage positions, and funding rate adjustments. A high-performance matching engine can process millions of orders per second, which is critical during volatile market conditions when order flow spikes dramatically.
Mark Price vs Index Price Explained
Mark price and index price are two critical reference prices in crypto derivatives trading. The index price is an aggregate of spot prices from multiple exchanges, providing a manipulation-resistant reference for the underlying asset’s true market value. The mark price is a calculated price used by the exchange to evaluate positions and trigger liquidations. It is typically derived from the index price plus a decaying funding basis.
The distinction matters because using last-traded price for liquidation calculations would expose traders to manipulation attacks. A malicious actor could briefly crash the price on a single exchange to trigger mass liquidations. By using the mark price, which is anchored to a multi-exchange index, the crypto derivatives exchange protects traders from artificial price wicks and ensures that liquidations only occur when genuine market movements warrant them.
Liquidation Mechanism in Crypto Derivatives
The liquidation mechanism is the exchange’s automated system for closing positions that have lost too much value relative to their margin. When a trader’s unrealized losses bring their margin balance below the maintenance margin level, the risk engine triggers liquidation. The position is closed at the mark price, and any remaining margin after covering the loss is returned to the trader. If the loss exceeds the margin, the exchange’s insurance fund covers the difference to prevent socialized losses among other traders.
Risk Warning: Leverage in crypto derivatives trading amplifies both potential gains and potential losses. A 100x leveraged position can be liquidated by a 1% adverse price movement. Always understand the margin requirements and liquidation thresholds before opening any leveraged position on a crypto derivatives platform.
Types of Crypto Derivatives Explained

Crypto Futures Trading
Crypto futures trading involves contracts where two parties agree to buy or sell a cryptocurrency at a predetermined price on a specified future date. Futures are the oldest and most established form of derivatives, tracing their origins to agricultural commodities markets centuries ago. In crypto, futures have become the primary tool for directional speculation and institutional hedging.
The crypto futures market offers two distinct product types: traditional (fixed-expiry) futures and perpetual contracts. Both allow traders to go long or short with leverage, but they differ in their settlement mechanics and how they maintain price alignment with the underlying asset.
Traditional Futures vs Perpetual Contracts Crypto
Traditional futures have a fixed expiration date (typically weekly, monthly, or quarterly) and settle at the index price on expiry. Perpetual contracts crypto have no expiration date and use a funding rate mechanism instead of time-based settlement to keep their price aligned with spot. This fundamental difference makes perpetuals more flexible for short-term trading, while traditional futures are preferred for longer-term hedging and basis trading strategies.
Perpetual Futures vs Traditional Futures
Perpetual vs Traditional Futures Comparison
| Feature | Perpetual Contracts | Traditional Futures |
|---|---|---|
| Expiration | No expiry date | Fixed expiry (weekly, monthly, quarterly) |
| Price Anchoring | Funding rate mechanism | Convergence at expiry |
| Settlement | Continuous (funding every 8 hours) | At expiration date |
| Holding Period | Indefinite | Until expiry or early exit |
| Basis Risk | Minimal (funding keeps price aligned) | Can diverge before expiry |
| Best For | Intraday and swing trading | Calendar spreads, basis trading, hedging |
| Market Share (2026) | ~75% of derivatives volume | ~15% of derivatives volume |
Crypto Options Trading
Crypto options trading provides traders with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a cryptocurrency at a specified price (strike price) before or at a specified date (expiry). Options are the most versatile derivative instrument, offering asymmetric risk profiles where the buyer’s maximum loss is limited to the premium paid while profit potential remains theoretically unlimited. This characteristic makes options invaluable for hedging and income generation strategies.
Call Options vs Put Options
A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. Traders buy calls when they expect the price to rise. A put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. Traders buy puts when they expect the price to fall or want to hedge an existing long position. The seller (writer) of an option collects the premium but assumes the obligation to fulfill the contract if exercised. Understanding these dynamics is foundational to crypto options trading.
Options Expiry and Strike Price Mechanics
Strike price is the predetermined price at which the option can be exercised. Options are classified as in-the-money (ITM), at-the-money (ATM), or out-of-the-money (OTM) depending on their strike relative to the current spot price. Expiry is the date after which the option becomes worthless if not exercised. Time decay (theta) works against option buyers, with the option losing value as expiry approaches. These mechanics are crucial for anyone participating in crypto derivatives trading through options.
Margin Trading in Crypto Explained
Cross Margin vs Isolated Margin
Cross margin uses the trader’s entire account balance as collateral for all open positions. If one position is losing, margin from profitable positions or idle balance can prevent liquidation. Isolated margin dedicates a specific amount of margin to each individual position, limiting the maximum loss to that isolated amount. Cross margin is more capital-efficient but exposes the entire account to risk. Isolated margin provides clearer risk boundaries but may result in faster liquidation of individual positions.
How Leverage Works in Crypto Derivatives
Leverage allows traders to control positions larger than their deposited capital. On a crypto derivatives platform, leverage ratios typically range from 2x to 125x depending on the asset and the platform. The initial margin requirement determines how much capital is needed to open a position, while the maintenance margin is the minimum balance required to keep it open. Higher leverage means lower initial margin but also a smaller margin for error before liquidation occurs.
How Crypto Derivatives Trading Works
Funding Rate Mechanism in Perpetual Contracts
The funding rate is the mechanism that keeps perpetual contract prices tethered to the spot market. Unlike traditional futures that naturally converge to spot at expiry, perpetual contracts crypto require an active balancing mechanism. The funding rate is calculated based on the premium or discount of the perpetual price relative to the index price and a fixed interest rate component.
When the perpetual price trades above the index (indicating bullish sentiment), the funding rate is positive, and long positions pay short positions. When the perpetual price trades below the index (bearish sentiment), shorts pay longs. These payments occur at regular intervals, typically every 8 hours, and serve as a continuous incentive for traders to take positions that bring the perpetual price back in line with spot. Funding rates are a critical consideration in crypto derivatives trading, especially for positions held over multiple funding periods.
Leverage Trading Engine Architecture
A leverage trading engine is a specialized system that manages all aspects of leveraged position management on a crypto derivatives exchange. It handles margin calculations, position updates, P&L tracking, funding rate application, and liquidation triggers in real time. The engine must process these calculations with sub-millisecond latency to ensure accurate risk management during fast-moving markets.
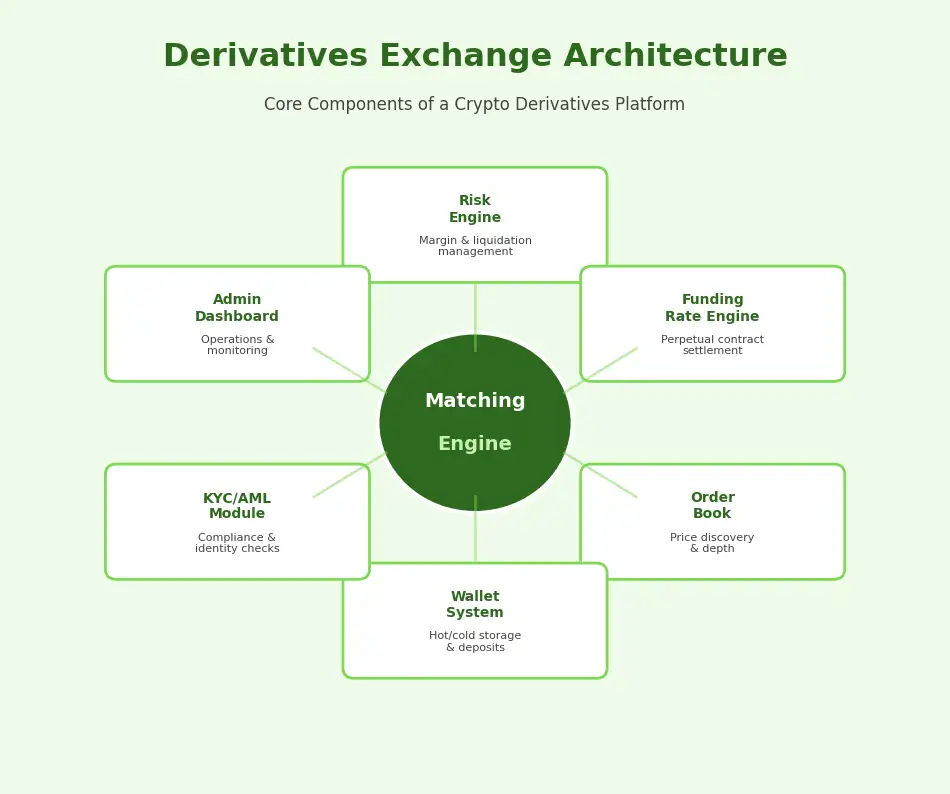
The architecture typically includes a matching engine for order execution, a risk engine for margin and liquidation management, a settlement engine for funding rate and P&L calculations, and an insurance fund module for handling bankrupt positions. Each component must be designed for high availability and fault tolerance, as any downtime can result in significant financial losses for both the platform and its users.
Risk Management in Crypto Derivatives Trading
Risk Engine Architecture
The risk engine is the guardian of the entire crypto derivatives platform. It continuously monitors every open position, calculating unrealized P&L, margin ratios, and liquidation prices in real time. Advanced risk engines incorporate portfolio-level margining, where correlated positions across different instruments can offset each other, reducing overall margin requirements for sophisticated traders.
Liquidation Protection Strategies
Modern crypto derivatives exchanges implement several liquidation protection mechanisms. Partial liquidation closes only a portion of a position to bring the margin ratio above the maintenance level. Auto-deleveraging (ADL) reduces the positions of the most profitable traders when the insurance fund is insufficient to cover bankrupt positions. And graduated margin tiers require higher margin ratios for larger positions, preventing a single large trader’s liquidation from destabilizing the market.
Crypto Derivatives Trading Lifecycle
| Phase | Action | Key Components | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Account Setup | KYC verification and margin account creation | Identity verification, compliance check | Trading access granted |
| 2. Margin Deposit | Transfer collateral to derivatives wallet | Wallet system, deposit verification | Available margin balance |
| 3. Order Placement | Select instrument, leverage, direction, and size | Order book, matching engine | Order submitted to matching engine |
| 4. Position Opening | Order matched, position created with margin locked | Risk engine, margin system | Active leveraged position |
| 5. Position Management | Monitor P&L, adjust margin, manage risk | Mark price, funding rate, liquidation engine | Ongoing position tracking |
| 6. Settlement / Close | Close position manually, at expiry, or via liquidation | Settlement engine, insurance fund | P&L realized, margin released |
Crypto Derivatives Trading Strategies 2026
Hedging Strategies for Institutional Crypto Derivatives Trading
Institutional crypto derivatives trading relies heavily on hedging strategies to manage portfolio risk. The most common approach is delta hedging, where a portfolio’s exposure to price movements is neutralized by taking offsetting positions in futures or perpetual contracts. For example, a fund holding 500 BTC in cold storage can short 500 BTC worth of futures contracts to protect against a price decline, locking in the current value regardless of market direction.
Options-based hedging provides another layer of sophistication. Protective puts allow institutions to set a floor price for their holdings while maintaining upside exposure. Collar strategies combine buying puts with selling calls to reduce the cost of hedging. These strategies are becoming standard practice as institutional capital flows into the crypto derivatives market 2026 at an accelerating pace.
Arbitrage Opportunities in the Crypto Derivatives Market
The crypto derivatives market offers several arbitrage opportunities that professional traders actively exploit. Basis arbitrage captures the spread between spot prices and futures prices. Funding rate arbitrage involves taking opposite positions on spot and perpetual markets to collect funding payments. Cross-exchange arbitrage exploits price differences for the same contract across different platforms. These strategies require low-latency execution and are typically automated through algorithmic trading systems built on robust derivatives exchange infrastructure.
AI-Powered Crypto Trading Platforms and Automation
AI and machine learning are transforming crypto derivatives trading in 2026. AI-powered systems analyze vast datasets to identify trading signals, optimize execution timing, manage portfolio risk in real time, and adapt strategies to changing market conditions. From automated market making to predictive liquidation alerts, artificial intelligence is embedded across the trading stack of modern cryptocurrency derivatives platforms.
For retail traders, AI-assisted tools lower the barrier to sophisticated strategies like options Greeks management and volatility surface analysis. For institutions, AI enables high-frequency strategies and portfolio-level risk optimization that would be impossible to manage manually. The integration of AI into a crypto derivatives platform is no longer a differentiator; it is becoming a baseline expectation.
Risk Management Best Practices for Traders
Effective risk management in crypto derivatives trading starts with position sizing. Never risk more than a small percentage of total capital on any single trade. Use stop-loss orders to define maximum loss per trade. Choose isolated margin for positions where you want to cap your exposure. Monitor funding rates for perpetual positions held overnight. And diversify across instruments and timeframes to avoid concentration risk. These practices apply whether you are trading on a centralized or decentralized crypto derivatives exchange.
Principle: In crypto derivatives trading, the quality of your risk management determines your long-term survival. Profitable strategies with poor risk management will eventually fail. Average strategies with excellent risk management can produce consistent results over time.
Crypto Derivatives Market Trends 2026
Institutional Crypto Derivatives Trading Growth
The crypto derivatives market 2026 is defined by institutional growth. Pension funds, asset managers, proprietary trading firms, and corporate treasuries are allocating capital to crypto derivatives as part of their broader digital asset strategies. This institutional influx has driven several market changes: deeper liquidity, tighter spreads, more sophisticated products like structured derivatives and variance swaps, and higher compliance standards across the industry.
Institutional participation has also increased demand for prime brokerage services, portfolio margining, and cross-collateralization across derivative products. Crypto derivatives exchanges that cater to institutional clients must offer segregated custody, sub-accounts, API-driven execution, and comprehensive reporting. These requirements are shaping the feature roadmaps of every serious crypto derivatives platform in the market.
Regulatory Framework for Crypto Derivatives
Regulatory clarity for cryptocurrency derivatives has improved significantly by 2026. Major financial regulators have established licensing frameworks for crypto derivatives exchanges, position reporting requirements, leverage limits, and customer protection standards. These regulations vary by jurisdiction but share common themes: investor protection, market integrity, and systemic risk management.
Are Crypto Derivatives Legal in 2026?
Yes, crypto derivatives are legal in most major financial markets in 2026, subject to proper licensing and compliance. Regulated exchanges operate under established frameworks, and institutional participants are comfortable trading cryptocurrency derivatives within these regulated environments. However, restrictions on leverage levels, available assets, and retail access vary by jurisdiction. Traders should always verify the regulatory status of their chosen crypto derivatives exchange in their specific jurisdiction.
Rise of Decentralized Derivatives Exchange (DEX Derivatives)
Decentralized derivatives exchanges have experienced explosive growth in the crypto derivatives market 2026. Platforms built on blockchain smart contracts offer transparent settlement, self-custodial trading, and permissionless access. The value proposition is compelling: no counterparty risk from the exchange itself, verifiable liquidation mechanics, and censorship-resistant access.
On-Chain Derivatives Protocols
On-chain derivatives protocols like dYdX, GMX, Hyperliquid, and Synthetix have pioneered different approaches to decentralized crypto derivatives trading. Order book-based models (dYdX) replicate the centralized exchange experience on-chain. AMM-based models (GMX) use liquidity pools instead of order books. Synthetic models (Synthetix) create derivatives through collateralized debt positions. Each approach offers different trade-offs in terms of latency, liquidity, and capital efficiency, reflecting the diversity of innovation in this space.
How to Build a Crypto Derivatives Exchange in 2026
Building a crypto derivatives exchange is one of the most technically demanding projects in the digital asset industry. The platform must handle high-throughput order matching, real-time risk calculations, complex margin management, and regulatory compliance simultaneously. Teams looking to build crypto exchanges with derivatives capability need both deep financial engineering expertise and robust systems architecture.
Crypto Derivatives Exchange Creation Process
Matching Engine and Trading Engine Setup
The matching engine is the heart of every crypto derivatives exchange. It must support multiple order types (limit, market, stop, trailing stop, post-only), handle high concurrency during peak trading, and integrate seamlessly with the risk engine for pre-trade margin checks. The trading engine layer on top manages instrument definitions, contract specifications, funding rate calculations, and settlement procedures. Partnering with an experienced derivatives exchange solutions provider is critical for getting this core infrastructure right.
KYC and Compliance for Derivatives Exchange
Compliance is non-negotiable for any crypto derivatives platform operating in regulated markets. This includes KYC (Know Your Customer) verification at onboarding, ongoing AML (Anti-Money Laundering) transaction monitoring, suspicious activity reporting, position reporting to regulators, and adherence to leverage limits. The compliance infrastructure must be built into the platform from the ground up, not bolted on as an afterthought.
Liquidity Integration and Market Making
Liquidity is the lifeblood of any crypto derivatives exchange. Without sufficient liquidity, spreads widen, slippage increases, and traders leave. Liquidity integration involves connecting with external market makers, implementing market making incentive programs, aggregating liquidity from multiple sources, and potentially running proprietary market making operations. The liquidity strategy must be planned before launch and actively managed afterward.
White Label Crypto Derivatives Exchange Solutions
White-label solutions provide a pre-built crypto derivatives platform that can be customized with the operator’s branding, configuration, and specific feature requirements. This approach dramatically reduces time-to-market and upfront investment compared to custom builds. High-quality white-label solutions include the matching engine, risk engine, wallet system, admin dashboard, trading interface, and API layer. For operators looking for a proven crypto derivatives platform solution, white-label options offer a compelling balance of speed, cost, and functionality.
Crypto Derivatives Trading Platform Cost Factors
Exchange Build Cost Factors
| Component | Custom Build | White Label |
|---|---|---|
| Matching Engine | $50K – $150K | Included |
| Risk Engine | $30K – $80K | Included |
| Trading UI/UX | $20K – $60K | Included (customizable) |
| Compliance/KYC | $15K – $40K | Partially included |
| Liquidity Integration | $10K – $30K | Available as add-on |
| Timeline | 6-12 months | 4-8 weeks |
| Total Estimated Range | $150K – $500K+ | $30K – $100K |
Derivatives Exchange Model Selection Criteria
Choosing between a custom-built and white-label crypto derivatives exchange requires evaluating several critical factors. The right decision depends on your budget, timeline, differentiation strategy, regulatory requirements, and long-term technology roadmap. Here is a framework for making this decision.
Custom vs White-Label Selection Framework
| Criteria | Choose Custom When | Choose White Label When |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | $200K+ available for infrastructure | Budget-conscious, under $100K |
| Timeline | 6-12 months acceptable | Need to launch in 4-8 weeks |
| Differentiation | Unique features are core to business | Standard features sufficient |
| Tech Team | In-house blockchain engineering team | Limited technical resources |
| Scale Target | Building for millions of users | Starting with niche market |
Working with a proven crypto derivatives exchange engineering partner helps navigate these decisions and avoid costly mistakes regardless of which path you choose.
Launch Your Crypto Derivatives Exchange with Expert Development
Launch a secure and scalable crypto derivatives exchange with expert development, advanced trading engine integration, and full compliance support for 2026 markets.
Launch Your Exchange Now
Key Features of Cryptocurrency Derivatives Exchange Software
A production-ready crypto derivatives exchange must include several essential features to meet the expectations of professional traders and regulators in 2026. The matching engine must support sub-millisecond order processing with deterministic matching logic. The risk engine must handle real-time margin calculations, multi-tier liquidation, and portfolio margining. The funding rate engine must calculate and settle perpetual contract funding accurately across all open positions.
Beyond the core trading infrastructure, the platform needs multi-asset collateral support, cross-margin and isolated margin options, comprehensive API access for algorithmic traders, advanced charting with TradingView integration, mobile and web trading interfaces, admin dashboard for operations management, and a robust wallet system with hot and cold storage. Security features including multi-signature wallets, two-factor authentication, withdrawal whitelisting, and DDoS protection are non-negotiable. The best derivatives exchange software solutions deliver all of these capabilities in an integrated, scalable package.
Frequently Asked Questions
A crypto derivatives exchange is a trading platform where users buy and sell financial contracts whose value is derived from underlying cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Unlike spot exchanges where you trade actual tokens, a crypto derivatives exchange lets traders speculate on future price movements through instruments like futures, options, and perpetual contracts. These platforms support leverage, enabling traders to control larger positions with smaller capital.
The main types of cryptocurrency derivatives include futures contracts (both traditional and perpetual), options contracts (calls and puts), and margin trading products. Crypto futures trading allows traders to agree on buying or selling an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. Crypto options trading gives traders the right but not the obligation to buy or sell at a set price. Perpetual contracts crypto are futures without an expiry date, settled through a funding rate mechanism.
Leverage in crypto derivatives trading allows traders to open positions larger than their actual capital by borrowing funds from the exchange. For example, 10x leverage means a trader can control a $10,000 position with just $1,000 of margin. While leverage amplifies potential profits, it equally amplifies losses. If the market moves against a leveraged position beyond the maintenance margin, the position is automatically liquidated to prevent further losses.
A perpetual contract is a type of futures contract that has no expiration date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. Perpetual contracts crypto use a funding rate mechanism to keep the contract price aligned with the spot market price. When the contract trades above spot, long positions pay short positions, and vice versa. This self-balancing mechanism has made perpetual contracts the most traded derivative instrument in the crypto derivatives market 2026.
The legality of crypto derivatives varies by jurisdiction. Many major financial markets have established regulatory frameworks that permit crypto derivatives trading under licensed conditions. Regulated exchanges must comply with KYC/AML requirements, position limits, and reporting obligations. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with clearer guidelines emerging across global financial hubs in 2026.
Crypto futures obligate both parties to execute the trade at a specified price and date, while crypto options give the buyer the right but not the obligation to execute. Futures carry unlimited profit and loss potential in both directions, while options buyers have capped losses (limited to the premium paid) with unlimited profit potential. Options are generally used for hedging, while futures are popular for directional speculation.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







