Key Takeaways
1. Block height is the sequential count of blocks on the Bitcoin blockchain, starting from zero at the Genesis Block, and it increases by one with every new block mined.
2. It serves as Bitcoin’s universal clock, allowing every participant on the network to agree on the exact state of the chain without relying on real world time zones.
3. Developers use block height to schedule and activate protocol upgrades like SegWit and Taproot, ensuring all nodes transition at the same point in the chain.
4. Bitcoin’s halving event, which cuts mining rewards in half, is triggered every 210,000 blocks based purely on block height.
5. Wallets and exchanges track block height to count transaction confirmations, which determine when a payment is considered final and secure.
6. Block height is different from a block hash: height is a sequential number, while a hash is a unique cryptographic fingerprint of the block’s data.
7. Miners depend on block height to calculate their reward, anticipate difficulty adjustments, and prepare for upcoming halvings.
8. Both soft forks and hard forks use block height as the activation trigger to coordinate rule changes across the global network.
9. Blockchain infrastructure providers such as Nadcab Labs use block height data for node deployment, protocol upgrades, and building enterprise grade solutions.
10. Block height will remain Bitcoin’s most reliable progress marker as the network evolves toward a fully fee based economy over the coming decades.
Bitcoin may seem complex from the outside, but at its core it runs on surprisingly simple principles. One of the most fundamental and yet often overlooked concepts is block height. Understanding how block height affects Bitcoin development unlocks a deeper appreciation of how the entire network operates, evolves, and stays secure.
Imagine a giant notebook where every new page gets the next number in sequence. Page one, page two, page three, and so on, forever. That is essentially what block height does for Bitcoin. It counts every block that has ever been added to the blockchain, starting from the very first one created on January 3, 2009. This number may seem basic, but it drives the most critical events in the Bitcoin world, from mining reward halvings to network wide software upgrades.
In this guide, we will break down every aspect of block height using simple language, real world examples, practical analogies, and visual illustrations so that beginners, developers, miners, and business leaders alike can fully grasp this essential concept.
▶ What Is Block Height in Bitcoin?
Block height refers to the position of a specific block within the Bitcoin blockchain. The very first block ever mined, called the Genesis Block, has a block height of zero. The next block is height one, the block after that is height two, and so on. It is a simple, sequential counter that never resets and never moves backward.
Think of it like the floors of a skyscraper. The ground floor is floor zero. Every new floor added on top increases the floor number by one. You can always tell how tall the building is by checking the number on the highest floor. Block height tells you exactly how many blocks have been stacked on the Bitcoin blockchain since its creation.
Another helpful way to picture it: imagine a book where each page gets the next number. If someone asks “what page are we on?” you immediately know your position in the story. Block height gives everyone on the Bitcoin network that same sense of position.
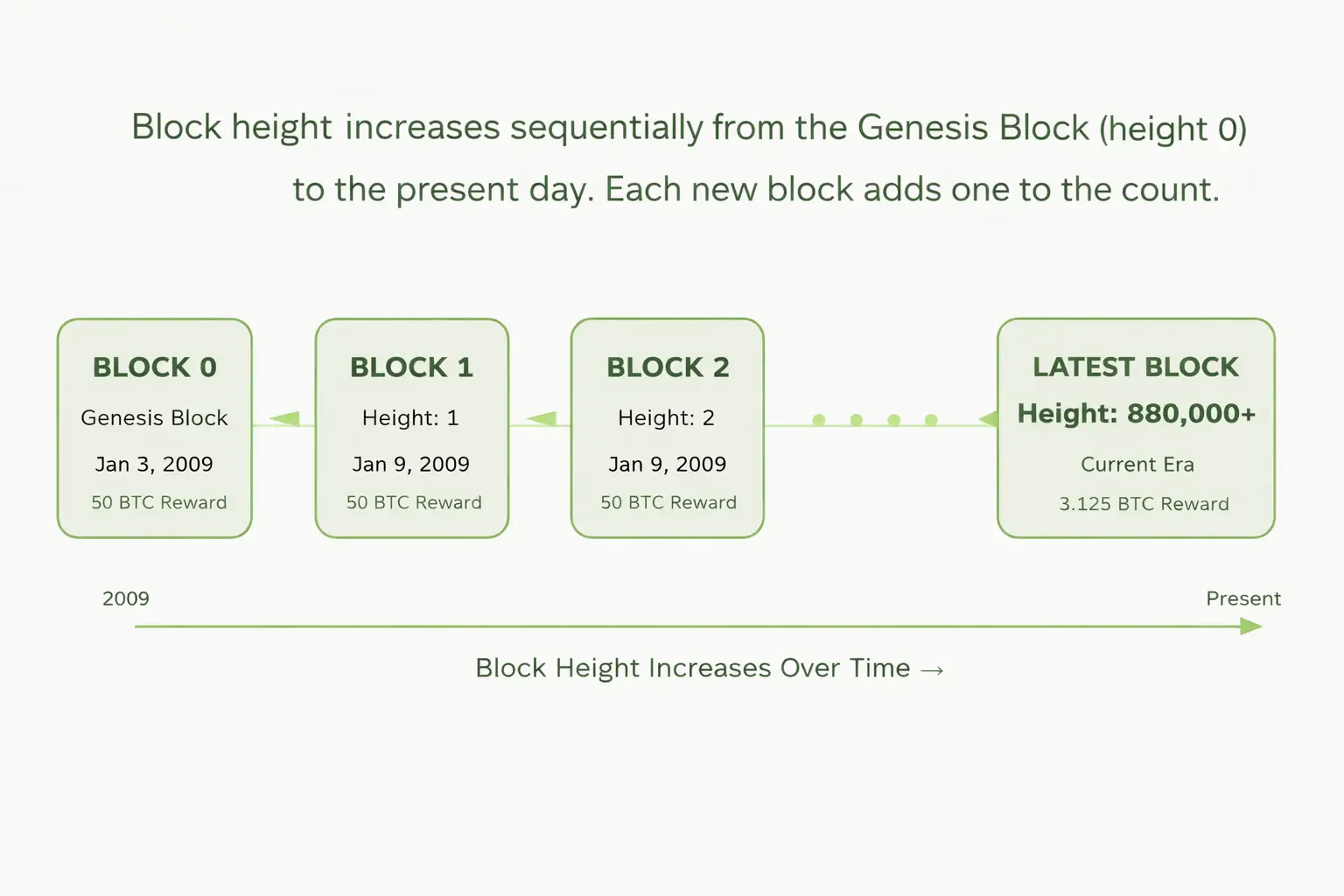
▶ How Block Height Increases Over Time
Block height grows by one every time a new block is successfully mined and added to the blockchain. On average, the Bitcoin network adds a new block approximately every 10 minutes. This timing is maintained by a mechanism called difficulty adjustment, which recalibrates the computational challenge miners face roughly every 2,016 blocks (about two weeks).
Here is a step by step walkthrough of how block height grows:
Step 1 ➜
Thousands of Bitcoin miners around the world compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle using their computing power.
Step 2 ➜
The first miner to solve the puzzle earns the right to propose the next block, which includes a batch of verified transactions from the network.
Step 3 ➜
Other nodes on the network validate this new block and confirm that it follows all the consensus rules.
Step 4 ➜
Once accepted, the block is permanently attached to the chain. Its block height equals the previous block’s height plus one.
Step 5 ➜
The winning miner receives a block reward (currently 3.125 BTC after the 2024 halving) along with transaction fees from the included transactions.
Step 6 ➜
The process starts again immediately for the next block, and the block height increments once more. This cycle has continued nonstop since 2009.
▶ Block Height vs. Block Hash: What Is the Difference?
These two terms are often confused by newcomers, but they serve very different purposes in the Bitcoin protocol.
Block height is the sequential number based on the block’s position. It answers the question: “Which block number is this in the chain?”
Block hash is a unique cryptographic fingerprint generated from the contents of a block. It answers: “What exact data does this block contain?” Even a tiny change would produce a completely different hash.
Here is an analogy: think of a library shelf. The block height is like the shelf number (Shelf 1, Shelf 2, Shelf 3), while the block hash is like the ISBN of a specific book on that shelf. Two editions could sit on the same shelf, but they always have different ISBNs. Similarly, during rare temporary forks, two blocks might briefly share the same height, but each will always have a unique hash.
Block Height vs. Block Hash Comparison
| Feature | Block Height | Block Hash |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sequential position number in the chain | Unique cryptographic fingerprint of block data |
| Format | Simple integer (e.g., 840000) | Long hexadecimal string (64 characters) |
| Uniqueness | May briefly be shared during temporary forks | Always unique to each block |
| Primary Use | Tracking position and scheduling events | Verifying data integrity and linking blocks |
| Human Readability | Easy to read and understand | Complex and not human friendly |
▶ Why Block Height Matters for Bitcoin Development
Block height is far more than just a number. It serves as one of the foundational reference points that the entire Bitcoin ecosystem relies upon. Here is why it is so important:
Universal Coordination
Every full node on the Bitcoin network tracks block height independently. When developers say “activate this change at block 840,000,” every node in the world knows exactly what that means and can act simultaneously.
Deterministic Event Scheduling
Unlike calendar dates which vary across time zones, block height is deterministic. An event tied to a block height happens when that block is mined, no matter where you are in the world.
Network Consensus
Block height helps nodes agree on the current state of the blockchain. If two nodes disagree on the block height, it signals a potential fork or synchronization issue that needs resolution.
▶ How Developers Use Block Height for Protocol Upgrades
One of the most critical ways block height affects Bitcoin development is through protocol upgrades. When the Bitcoin developer community agrees on a change to the network’s rules, they need a mechanism to tell every node around the world: “Start using the new rules now.” Block height provides this exact mechanism.
The famous Segregated Witness (SegWit) upgrade was activated using a combination of miner signaling and block height thresholds. More recently, the Taproot upgrade, which improved privacy and smart contract flexibility, was activated at block height 709,632 in November 2021.
This approach works because every Bitcoin node processes blocks sequentially. When a node reaches the designated block height, it automatically switches to the new consensus rules. There is no need for manual intervention, no coordination calls, and zero ambiguity.
Industry Insight: Blockchain infrastructure providers like Nadcab Labs play a key role in this process. When protocol upgrades are scheduled, enterprises need their nodes updated and tested well in advance. Nadcab Labs assists organizations with node deployment, upgrade testing, and ensuring compatibility with new consensus rules triggered by block height.
▶ How Block Height Triggers Bitcoin Halving
The Bitcoin halving is one of the most anticipated events in the cryptocurrency world, and it is triggered entirely by block height. Every 210,000 blocks, the reward that miners receive for adding a new block is cut in half. This rule is hardcoded into Bitcoin’s protocol and cannot be changed without consensus from the entire network.
To understand this with an analogy, imagine a gold mine that automatically reduces its output by 50% every four years. In the early days, miners pull out large quantities of gold. But as time goes on, the mine produces less and less, making each piece increasingly rare and valuable. Bitcoin’s halving works the same way: it is a built in scarcity mechanism.
Another way to picture it: imagine a company that issues new shares of stock. Every few years, the company decides to cut the number of new shares it issues in half. Over time, fewer new shares enter the market, which can drive up the value of existing shares if demand stays steady or grows.
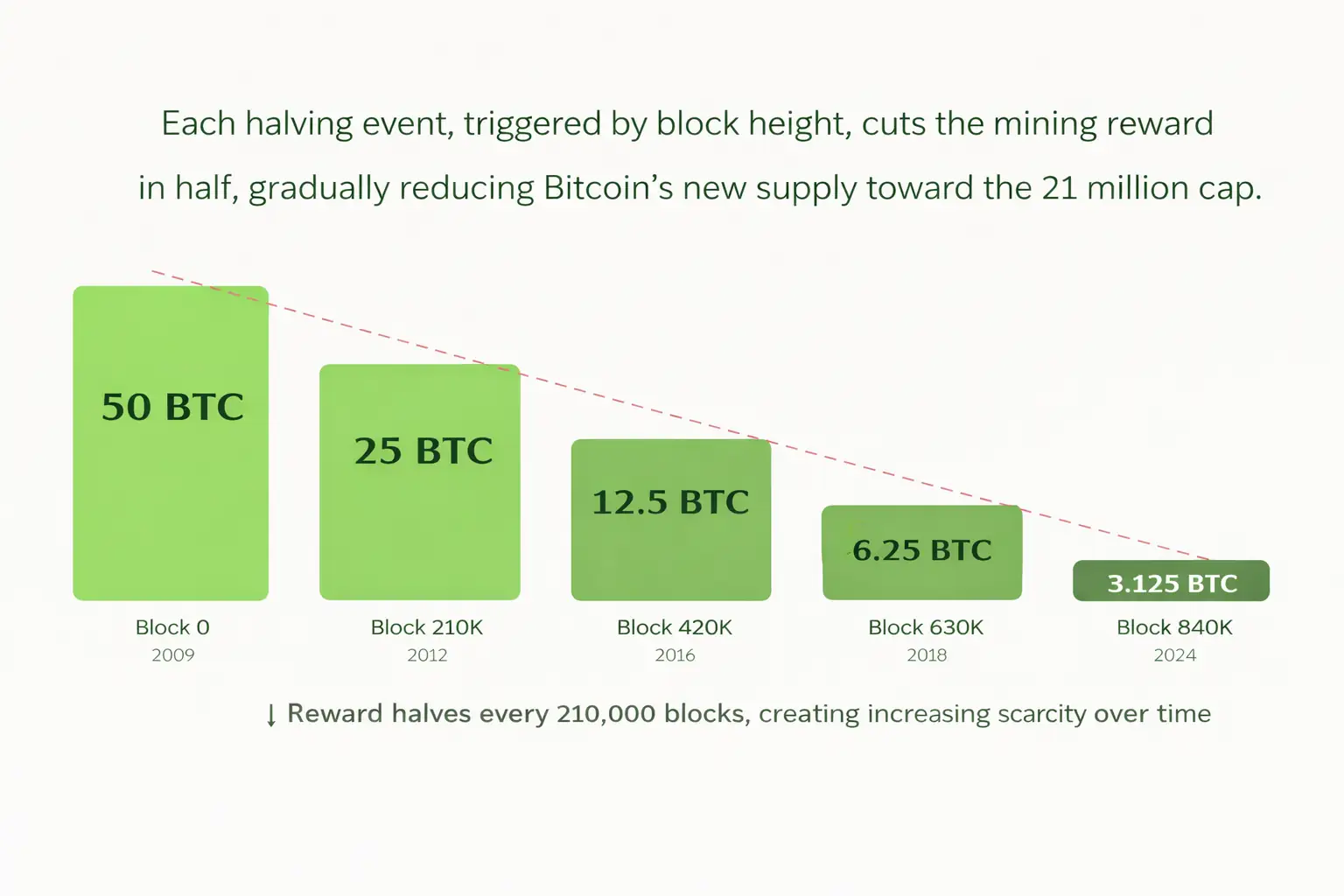
History of Bitcoin Halvings
Bitcoin has undergone four halvings since its launch, each triggered precisely at the designated block height:
Bitcoin Halving History and Block Height Milestones
| Halving Event | Block Height | Approx. Date | Reward After |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genesis (Launch) | 0 | January 2009 | 50 BTC |
| First Halving | 210,000 | November 2012 | 25 BTC |
| Second Halving | 420,000 | July 2016 | 12.5 BTC |
| Third Halving | 630,000 | May 2020 | 6.25 BTC |
| Fourth Halving | 840,000 | April 2024 | 3.125 BTC |
Notice how each halving happens at a block height that is a perfect multiple of 210,000. This is not a coincidence. It is a rule written directly into Bitcoin’s source code by its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto.
What Happened to Bitcoin’s Price After Past Halvings?
Historically, each Bitcoin halving has been followed by a significant price increase, though gains materialized over months rather than instantly. After the 2012 halving, Bitcoin rose from about $12 to over $1,000 within a year. After 2016, it climbed from roughly $650 to nearly $20,000 by late 2017. The 2020 halving preceded a rally from approximately $8,500 to over $60,000 in 2021.
It is crucial to remember that past performance does not guarantee future results. Market conditions, regulatory developments, and institutional adoption all influence price alongside the halving’s supply effect.
How Halving Affects Bitcoin Miners
When a halving occurs, miners suddenly receive half the block reward they were previously earning. This directly impacts revenue. Miners with older, less efficient hardware may find operations unprofitable and shut down. Meanwhile, miners with cheap electricity and modern rigs can continue profitably.
Halvings also drive innovation. After each event, the industry pushes toward more energy efficient mining hardware, larger scale operations, and creative solutions such as renewable energy sourcing and waste heat recovery.
Why Halving Creates Scarcity
Bitcoin has a fixed maximum supply of 21 million coins. Halving events reduce the rate at which new coins enter circulation. Over time, the flow of new Bitcoin becomes a smaller and smaller fraction of existing supply. This decreasing issuance mirrors the scarcity of precious metals like gold, which is why Bitcoin is often called “digital gold.”
By approximately the year 2140, all 21 million Bitcoin will have been mined and the block reward will reach zero. After that point, miners will rely entirely on transaction fees. Block height will be the counter that marks every step of this journey.
Common Myths About Bitcoin Halving
Myth: Halving happens on a fixed calendar date.
Reality: Halving is triggered by block height, not the calendar. Because block mining times vary slightly, the exact date is always an estimate until the target block is actually mined.
Myth: Bitcoin’s price always doubles after a halving.
Reality: While historical data shows notable price gains following halvings, the magnitude and timing vary greatly. External market forces play a significant role, and no specific outcome is guaranteed.
Myth: Halving makes Bitcoin less secure.
Reality: The difficulty adjustment mechanism ensures network security adapts to changes in mining power. Additionally, growing transaction fees are expected to increasingly compensate miners over time.
Myth: Only miners are affected by halving.
Reality: Halving impacts the entire ecosystem including traders, investors, exchanges, wallet providers, and application developers. Reduced supply issuance influences market dynamics and the economic models of blockchain businesses.
▶ How Wallets and Exchanges Rely on Block Height for Confirmations
When you send Bitcoin, the transaction is included in a block. But how does the recipient know the payment is secure? This is where block confirmations come in, and they are calculated using block height.
A transaction gains one confirmation when included in a block. It gets a second confirmation when the next block is mined on top, a third when another block follows, and so on. The formula is simple: confirmations equal the current block height minus the block height where the transaction was first included, plus one.
Most wallets and exchanges consider a transaction safe after six confirmations, which takes roughly 60 minutes. For smaller amounts, some services accept fewer confirmations. The key point is that all confirmation tracking is built entirely on block height.
Industry Insight: When building custom wallets, exchange platforms, or payment processing systems, developers need reliable confirmation tracking based on block height. Nadcab Labs provides the infrastructure expertise to ensure these systems work accurately and securely for enterprises at scale.
▶ How Miners Depend on Block Height
Miners are among the most directly affected participants when it comes to block height. Here is how they depend on it:
- Reward Calculation: The block reward a miner receives is determined by the current block height. The protocol checks which halving epoch the block falls into and assigns the appropriate reward amount.
- Difficulty Adjustment: Every 2,016 blocks (measured by block height), mining difficulty is recalculated. Miners monitor block height to anticipate when the next adjustment will occur.
- Consensus Rule Compliance: If a protocol upgrade is scheduled at a certain block height, miners must update their software before that height is reached. Failing to do so could result in mining invalid blocks.
- Coinbase Maturity: Newly mined coins cannot be spent until 100 additional blocks have been mined on top. Miners track this using block height to know when their rewards become spendable.
▶ Block Height in Soft Forks and Hard Forks
Forks are changes to the Bitcoin protocol rules, and they come in two main forms: soft forks and hard forks. Both use block height as a coordination mechanism.
A soft fork is a backward compatible change. Nodes that have not upgraded can still participate in the network, though they may not validate new features. Activation is tied to a specific block height; once reached, upgraded nodes begin enforcing the new rules.
A hard forks is not backward compatible. After the designated block height, upgraded and non upgraded nodes follow different rules, creating two separate chains. The Bitcoin Cash fork of August 2017 is a notable example.
Using block height as the activation point ensures transitions happen at a predictable, verifiable moment in the blockchain’s history. Every node can independently confirm whether the activation threshold has been passed.
▶ Real World Use Cases in Blockchain Infrastructure
Block height is not just a theoretical concept. It has practical implications for every part of the blockchain ecosystem:
Node Operators
Use block height to monitor synchronization status. If a node’s height is behind the network’s latest, the operator knows it needs attention.
Block Explorers
Platforms like Mempool.space display block height prominently, letting anyone look up transactions, blocks, and network status using this simple number.
Time Locked Transactions
Smart contract platforms use block height to trigger time locked payments. A payment channel might be programmed to expire after a certain number of blocks.
Enterprise Solutions
Organizations working with providers like Nadcab Labs use block height for audit trails, compliance reporting, and scheduling automated on chain processes.
For deeper technical understanding, the Bitcoin.org How It Works page offers an excellent primer on how blocks and the blockchain work together.
▶ Benefits of Using Block Height as a Reference Point
✓Precision: Block height offers an exact, unambiguous reference point that every participant on the network can independently verify and agree upon.
✓Decentralization Friendly: Because each node calculates block height independently, there is no need for any central authority to coordinate events or upgrades.
✓Full Transparency: Anyone in the world can verify the current block height and audit when specific events were triggered, making the system completely open.
✓Tamper Resistance: Since each block references the one before it, altering a block’s height would require rewriting the entire chain from that point onward, which is computationally infeasible.
✓Cross Timezone Reliability: Unlike calendar dates, block height is the same for everyone, everywhere, at all times. No time zone confusion, no ambiguity.
▶ Limitations and Common Misunderstandings About Block Height
While block height is incredibly useful, it is important to understand its limitations:
Block height does not equal time. Although blocks are mined roughly every 10 minutes on average, actual timing can range from seconds to over an hour. You cannot convert a block height to a precise timestamp without examining the actual block data.
Block height alone does not guarantee uniqueness during temporary forks. In rare situations, two miners may find valid blocks at nearly the same time, temporarily producing two blocks at the same height. The network resolves this by adopting the longer chain.
Block height is not a measure of blockchain size. A higher block height does not necessarily mean a larger blockchain in terms of data storage. Block sizes vary based on the number and complexity of included transactions.
Understanding these nuances is critical for developers and infrastructure teams. Organizations partnering with blockchain providers like Nadcab Labs benefit from expert guidance when handling edge cases related to block height in production environments.
The World Economic Forum’s blockchain coverage also provides valuable context on how these technical foundations support real world applications.
▶ The Future Role of Block Height in Bitcoin Evolution
As Bitcoin continues to mature, block height will remain central to its development. Future protocol upgrades focused on scalability, privacy, and smart contract capabilities will continue using block height as the activation mechanism.
The gradual transition from block rewards to a fee based economy will also be marked by block height milestones. Each halving reduces the reward further until it eventually reaches zero, and the block height at which this happens will be one of the most significant moments in Bitcoin’s entire history.
Layer 2 solutions like the Lightning Network and sidechains also reference main chain block height for security and settlement. As these technologies grow, the importance of accurate block height tracking will only increase.
For enterprises building on Bitcoin or integrating blockchain technology, understanding block height is not optional. It is foundational knowledge that informs architecture decisions, security models, and operational workflows.
▶ Conclusion
Block height is one of those foundational concepts that quietly powers everything in the Bitcoin ecosystem. From triggering halving events and coordinating protocol upgrades to enabling transaction confirmations and maintaining global network consensus, block height affects Bitcoin development at every single level.
For beginners, understanding block height is the gateway to truly grasping how Bitcoin works beneath the surface. For developers and businesses, it is an indispensable technical reference that informs design decisions, upgrade planning, and security architecture.
As the Bitcoin network continues to grow and evolve, block height will remain the steady, reliable counter that marks every step of its journey. Whether the next milestone is a halving, a major protocol upgrade, or the mining of the very last Bitcoin, block height will be the number that tells the story.
Frequently Asked Questions
Block height is the number that tells you the position of a block in the Bitcoin blockchain. The first block is height 0, the second is height 1, and so on. Think of it as a page number in a book that grows every time a new page is added, roughly once every 10 minutes.
Bitcoin’s halving is triggered entirely by block height, not by a calendar date. Every 210,000 blocks, the mining reward is cut in half. This means the halving is a built in, automatic event that is hardcoded into Bitcoin’s protocol and cannot be manually changed.
Block height is a sequential position number (like a shelf number in a library), while a block hash is a unique cryptographic fingerprint of the block’s data (like an ISBN for a specific book). Height tells you where the block is; the hash tells you exactly what it contains.
Yes, but only temporarily. In rare cases when two miners solve a block at nearly the same time, two blocks can briefly share the same height. The network resolves this quickly by adopting the longer chain and discarding the orphan block.
Developers set a specific block height as the activation point for protocol upgrades. When every node on the network reaches that block height, it automatically switches to the new consensus rules. This ensures a synchronized, global transition without manual coordination.
Exchanges count how many blocks have been mined after the block containing your transaction. Each additional block (measured by height) adds one confirmation. Most exchanges require six confirmations (about 60 minutes) before considering a Bitcoin transaction as final and secure.
Bitcoin’s block height increases continuously. As of early 2025, it has surpassed 880,000. You can check the real time block height on any block explorer such as Mempool.space or Blockchain.com at any time.
No. Block height only tells you the position of the block, not the exact time it was created. While blocks are mined approximately every 10 minutes on average, actual times can vary. To find the exact time, you need to look at the block’s timestamp data.
Nadcab Labs uses block height data when building and deploying blockchain nodes, managing protocol upgrades, implementing transaction confirmation systems, and creating enterprise grade smart contract solutions. Block height is a core reference point in all of these processes.
Absolutely. Even after all Bitcoin is mined (expected around the year 2140), block height will continue to increase with every new block. It will remain essential for tracking confirmations, coordinating upgrades, maintaining consensus, and serving as the universal timeline of the Bitcoin network.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







