Key Takeaways
- ✓ AI applications combine machine learning models, neural networks, and intelligent algorithms to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence, including pattern recognition, natural language understanding, and predictive analytics.
- ✓ The global AI application market is projected to exceed $500 billion by 2027, with healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing sectors leading adoption rates across enterprise implementations.
- ✓ Successful AI application development requires a structured lifecycle approach encompassing problem definition, data collection, model training, testing, deployment, and continuous optimization phases.
- ✓ Data quality remains the most critical factor in AI application success, with organizations investing 60 to 80 percent of development time in data preparation, cleaning, and feature engineering activities.
- ✓ Cloud-based AI platforms from providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure have democratized AI development, reducing infrastructure costs by up to 70 percent for small and medium businesses.
- ✓ Security and ethical considerations, including data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency, have become mandatory compliance requirements for AI applications across regulated industries.
- ✓ Edge AI and on-device processing are emerging trends enabling real-time AI functionality without constant cloud connectivity, particularly valuable for IoT and mobile applications.
- ✓ Hiring experienced AI developers requires evaluating technical expertise in frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch alongside domain knowledge and proven project delivery capabilities.
- ✓ ROI from AI applications typically materializes within 12 to 24 months, with successful implementations showing 25 to 40 percent improvement in operational efficiency metrics.
- ✓ Future AI applications will increasingly leverage multimodal capabilities, combining text, image, audio, and video processing within unified intelligent systems for comprehensive user experiences.
Introduction to AI Applications
The landscape of software development has undergone a revolutionary transformation with the emergence of AI applications as the driving force behind digital innovation. Unlike traditional software that operates on predefined rules and static logic, AI applications possess the remarkable ability to learn from data, adapt to changing conditions, and improve their performance over time without explicit reprogramming. This fundamental shift represents one of the most significant technological advancements of the 21st century, enabling machines to perform cognitive tasks that were once exclusive to human intelligence.
In the context of modern business operations, AI applications serve as intelligent assistants that augment human capabilities rather than replace them entirely. From customer service chatbots that handle thousands of inquiries simultaneously to sophisticated fraud detection systems that analyze millions of transactions in real time, these applications have become indispensable tools for organizations seeking operational excellence. The integration of AI into business processes has created unprecedented opportunities for efficiency gains, cost reductions, and enhanced customer experiences across virtually every industry vertical.
The democratization of AI technologies through accessible development platforms and pre-trained models has lowered entry barriers significantly. Today, businesses of all sizes can leverage AI capabilities without building complex infrastructure from scratch. This accessibility has sparked an innovation wave where startups and established enterprises alike experiment with AI powered solutions to solve unique business challenges. The convergence of cloud computing, big data analytics, and advanced algorithms has created a perfect ecosystem for AI applications to flourish and deliver tangible business value.[1]
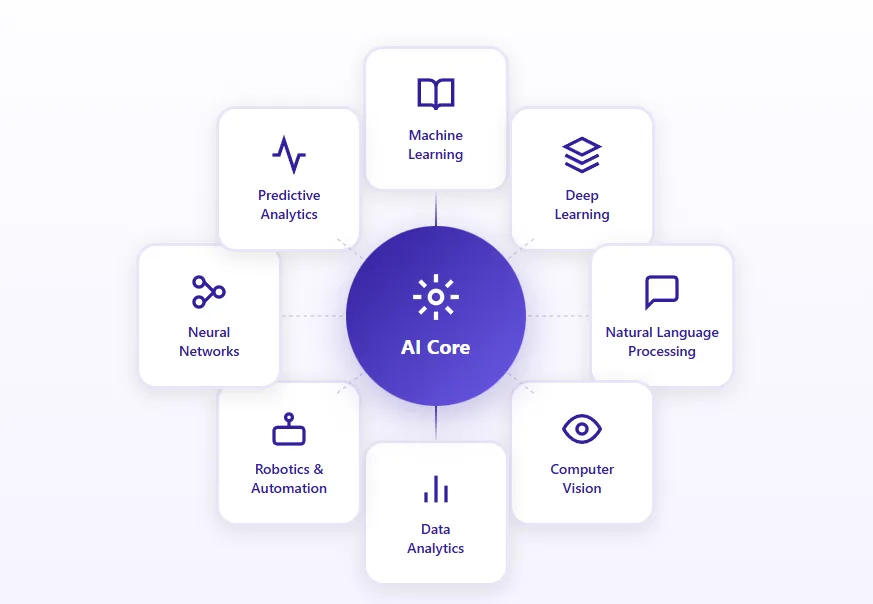
What Is an AI Application? Definition and Core Components
An AI application is a software system that incorporates artificial intelligence technologies to perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, including reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. These applications differ fundamentally from conventional software in their ability to process unstructured data, recognize complex patterns, and generate insights without explicit programming for every possible scenario. At their core, AI applications transform raw data into actionable intelligence through sophisticated computational processes that mimic cognitive functions.
The architecture of modern AI applications comprises several interconnected components working harmoniously to deliver intelligent functionality. The data layer serves as the foundation, collecting, storing, and managing the vast amounts of information required for training and inference. Above this sits the processing layer, where machine learning algorithms analyze data patterns and extract meaningful features. The model layer contains trained neural networks or statistical models that encode learned knowledge and decision-making logic. Finally, the application layer provides user interfaces and integration points that make AI capabilities accessible to end users and other systems.
| Core Component | Function | Technologies Used |
|---|---|---|
| Data Layer | Collection, storage, and management of training and operational data | Data Lakes, SQL/NoSQL Databases, Data Warehouses |
| Processing Layer | Data preprocessing, feature extraction, and transformation | Apache Spark, Pandas, NumPy, ETL Tools |
| Model Layer | Machine learning models and neural networks for predictions | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit learn, Keras |
| Application Layer | User interfaces, APIs, and system integrations | REST APIs, GraphQL, Web Frameworks, Mobile SDKs |
| Infrastructure Layer | Computing resources for training and deployment | GPU Clusters, Cloud Platforms, Kubernetes, Docker |
How AI Applications Work: Models, Data, and Algorithms
Understanding how AI applications function requires examining the interplay between three fundamental elements: data, algorithms, and models. Data serves as the raw material from which AI systems derive knowledge and patterns. Algorithms provide the mathematical frameworks and computational procedures that process this data systematically. Models represent the learned representations that capture patterns and relationships discovered during training, enabling the application to make predictions or decisions on new, unseen data.
The learning process in AI applications follows a structured approach where algorithms iteratively adjust model parameters to minimize prediction errors. During supervised learning, the system receives labeled examples and learns to map inputs to desired outputs by comparing predictions against known correct answers. Unsupervised learning discovers hidden patterns in unlabeled data through clustering and dimensionality reduction techniques. Reinforcement learning enables applications to learn optimal behaviors through trial-and-error interactions with environments, receiving rewards for successful actions.
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has revolutionized AI applications through neural networks with multiple layers capable of learning hierarchical representations. These deep neural networks excel at processing complex data types, including images, audio, and natural language. Convolutional neural networks have become the standard for computer vision tasks, while transformer architectures power modern natural language processing applications. The ability to automatically learn relevant features from raw data eliminates much of the manual feature engineering required by traditional machine learning approaches.
Evolution of AI Applications in Modern Software
The evolution of AI applications traces a fascinating journey from early expert systems of the 1970s and 1980s to today’s sophisticated deep learning powered solutions. Early AI applications relied on hand-coded rules and knowledge bases curated by domain experts, limiting their flexibility and scalability. These rule-based systems excelled in narrow domains but struggled with the complexity and ambiguity inherent in real-world problems. The knowledge acquisition bottleneck became a significant barrier to widespread AI adoption during this era.
The machine learning revolution of the 1990s and 2000s shifted the paradigm from explicit programming to learning from data. Statistical methods and algorithms like support vector machines, decision trees, and ensemble methods enabled AI applications to discover patterns automatically. However, these approaches still required careful feature engineering by human experts. The breakthrough came with deep learning’s resurgence around 2012, when convolutional neural networks demonstrated superhuman performance on image recognition benchmarks, sparking renewed interest and investment in AI technologies.
The current generation of AI applications benefits from unprecedented computational power, massive datasets, and advanced architectures. Large language models have transformed natural language processing, enabling applications that understand and generate human-like text with remarkable fluency. Multimodal AI systems can process and integrate information from multiple sources, including text, images, audio, and video. The emergence of generative AI has opened new frontiers in content creation, code generation, and creative applications that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
Types of AI Applications
AI applications span a diverse spectrum of capabilities and use cases, each leveraging specific AI technologies to address particular problem domains. Understanding these categories helps organizations identify the most appropriate AI solutions for their needs and align technology choices with business objectives. The following classification provides a comprehensive overview of major AI application types prevalent in today’s technology landscape.
| AI Application Type | Description | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing Apps | Applications that understand, interpret, and generate human language | Chatbots, Translation Services, Sentiment Analysis, Content Generation |
| Computer Vision Apps | Applications that analyze and interpret visual information from images and videos | Facial Recognition, Object Detection, Medical Imaging, Quality Inspection |
| Predictive Analytics Apps | Applications that forecast future outcomes based on historical data patterns | Demand Forecasting, Risk Assessment, Maintenance Prediction, Sales Forecasting |
| Recommendation Systems | Applications that suggest relevant items based on user preferences and behavior | Product Recommendations, Content Suggestions, Music Playlists, News Feeds |
| Speech Recognition Apps | Applications that convert spoken language into text or commands | Voice Assistants, Transcription Services, Voice Commands, Dictation Software |
| Autonomous Systems | Applications that operate independently with minimal human intervention | Self-Driving Vehicles, Drones, Robotics, Automated Trading Systems |
| Generative AI Apps | Applications that create new content, including text, images, audio, and code | AI Art Generators, Code Assistants, Writing Tools, Music Composition |
Common AI Application Use Cases Across Industries
AI applications have penetrated virtually every industry sector, transforming traditional business processes and creating entirely new value propositions. The versatility of AI technologies enables organizations to address diverse challenges ranging from operational efficiency improvements to revolutionary customer experiences. Examining use cases across different industries reveals the breadth and depth of AI’s transformative potential in the modern business landscape.
Healthcare and Life Sciences: AI applications in healthcare have revolutionized patient care through intelligent diagnostics, personalized treatment recommendations, and drug discovery acceleration. Medical imaging AI can detect cancers, tumors, and abnormalities with accuracy rivaling experienced radiologists. Natural language processing extracts valuable insights from clinical notes and research literature. Predictive models identify patients at risk of deterioration, enabling proactive interventions that save lives and reduce costs.
Financial Services: The finance industry leverages AI applications for fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading, and customer service automation. Machine learning models analyze transaction patterns to identify suspicious activities in real time, preventing financial losses. Robo advisors provide personalized investment recommendations based on individual risk profiles and goals. Chatbots handle routine banking inquiries, freeing human agents for complex customer needs.
Retail and E-Commerce: Retail AI applications enhance customer experiences through personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing, and inventory optimization. Computer vision enables cashier-less stores and virtual try-on experiences. Demand forecasting models optimize stock levels across distribution networks. Sentiment analysis monitors brand perception across social media and review platforms, informing marketing strategies.
Manufacturing and Industry: Smart manufacturing powered by AI applications drives operational excellence through predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. Computer vision systems inspect products for defects at speeds impossible for human inspectors. Digital twins simulate production processes, enabling optimization without disrupting actual operations. Robotic process automation handles repetitive tasks with precision and consistency.
Benefits of AI Applications for Businesses and Users
The adoption of AI applications delivers multifaceted benefits that extend beyond simple automation to fundamentally transform how organizations operate and compete. These advantages manifest across operational, financial, and strategic dimensions, creating compelling business cases for AI investment. Understanding these benefits helps stakeholders articulate value propositions and prioritize AI initiatives within their organizations.
| Benefit Category | Specific Benefits | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Process automation, reduced manual effort, faster task completion | 25 to 40% productivity improvement, reduced operational costs |
| Decision Making | Data-driven insights, predictive capabilities, and reduced bias | Better strategic decisions, reduced risks, improved outcomes |
| Customer Experience | Personalization, 24/7 availability, faster response times | Higher satisfaction scores, increased loyalty, improved retention |
| Cost Reduction | Labor cost savings, error reduction, resource optimization | 20 to 35% reduction in operational expenses |
| Scalability | Handle increased workloads without proportional resource increase | Support business growth, maintain quality at scale |
| Innovation | New product possibilities, service enhancements, competitive advantages | Market differentiation, new revenue streams |
For end users, AI applications deliver convenience, personalization, and enhanced capabilities that improve daily experiences. Intelligent assistants simplify complex tasks and provide instant access to information. Recommendation systems help users discover relevant content and products without extensive searching. Accessibility features powered by AI break down barriers for users with disabilities, enabling participation in digital experiences previously unavailable to them.
Key Technologies Powering AI Applications
The technological foundation of AI applications comprises a sophisticated stack of tools, frameworks, and infrastructure components working together to enable intelligent functionality. Understanding these technologies helps organizations make informed decisions about technical architecture and resource allocation for AI initiatives. The rapid evolution of this technology landscape continues to expand possibilities while reducing barriers to AI adoption.
Machine Learning Frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit learn form the backbone of AI model development. TensorFlow offers production-ready deployment options and extensive tooling support. PyTorch provides flexibility and intuitive debugging favored by researchers. Scikit learn delivers accessible implementations of traditional machine learning algorithms suitable for structured data analysis.
Cloud AI Platforms: Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure provide comprehensive AI services ranging from pre-built models to custom training infrastructure. These platforms offer managed services for computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, and more. Auto ML capabilities enable model development without deep expertise in machine learning techniques.
Data Processing Technologies: Apache Spark enables the distributed processing of massive datasets required for training AI models. Data pipeline tools like Apache Airflow orchestrate complex data workflows. Feature stores maintain curated datasets optimized for model training and inference. Vector databases support similarity search operations fundamental to modern AI applications.
Hardware Acceleration: Graphics Processing Units and Tensor Processing Units dramatically accelerate AI workloads through parallel computation. Edge AI chips enable on device inference for mobile and IoT applications. Specialized AI accelerators continue to push performance boundaries while improving energy efficiency.
AI Application Development Lifecycle
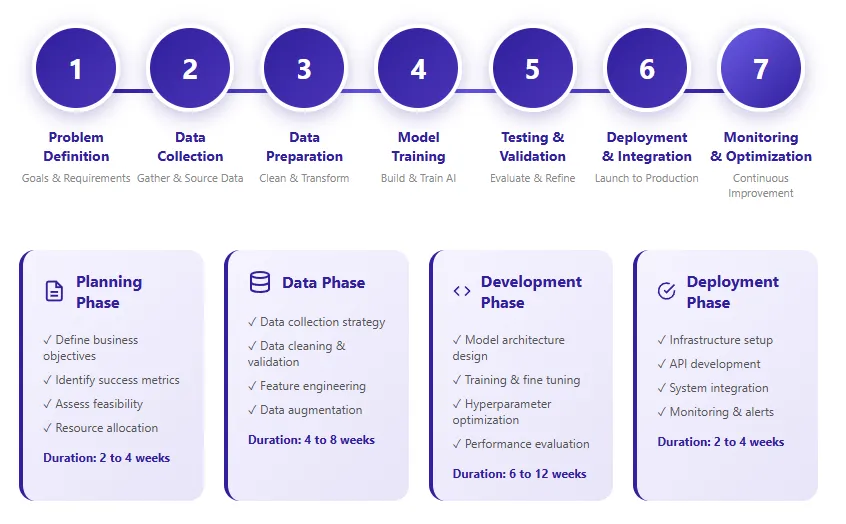
Developing AI applications requires a structured approach that differs significantly from traditional software development methodologies. The AI application lifecycle encompasses iterative phases of problem definition, data preparation, model development, testing, deployment, and continuous improvement. Understanding this lifecycle enables organizations to plan projects effectively, allocate resources appropriately, and set realistic expectations for timelines and outcomes.
AI Application Development Lifecycle Stages
1
Problem Definition
2
Data Collection
3
Data Preparation
4
Model Training
5
Testing & Validation
6
Deployment
7
Monitoring & Optimization
The iterative nature of AI development means that teams frequently revisit earlier phases based on insights gained during later stages. Poor model performance may indicate data quality issues requiring additional preparation work. Deployment challenges might necessitate model simplification or architecture changes. This iterative approach, while sometimes frustrating, ultimately leads to more robust and reliable AI applications that deliver sustained business value.
Data Collection and Preparation for AI Applications
Data collection and preparation represent the most time-intensive and critical phases of AI application development. Industry research consistently shows that organizations spend 60 to 80 percent of their AI project time on data-related activities. The quality, quantity, and relevance of training data directly determine the performance ceiling of resulting AI models. Investing adequately in data preparation pays dividends through better model performance and reduced downstream issues.
Data collection strategies vary based on application requirements and available resources. Internal data from business operations often provides the most relevant training examples but may require extensive cleaning and normalization. Public datasets offer convenient starting points but may not represent target use cases accurately. Synthetic data generation creates artificial examples to augment limited real-world data. Data labeling, whether performed by human annotators or automated systems, adds the ground truth information essential for supervised learning approaches.
Data preprocessing transforms raw data into formats suitable for model training. Missing value handling addresses gaps in datasets through imputation or removal strategies. Feature engineering creates informative variables from raw attributes, often requiring domain expertise to identify meaningful transformations. Normalization and scaling ensure consistent ranges across features, preventing certain variables from dominating model learning. Data augmentation techniques artificially expand training sets through transformations like rotation, cropping, and noise injection for image data.
Model Training, Testing, and Optimisation
Model training involves feeding prepared data through chosen algorithms to learn patterns and relationships that enable predictions on new data. The training process adjusts model parameters iteratively to minimize errors between predictions and actual outcomes. Hyperparameter tuning optimizes settings that control learning behavior, such as learning rates, batch sizes, and regularization strengths. Training requires significant computational resources, with complex deep learning models often needing days or weeks on specialized hardware.
Testing and validation ensure models generalize beyond training data to perform reliably on unseen examples. Cross-validation techniques assess model stability across different data subsets. Holdout test sets provide unbiased performance estimates on data never seen during training. Performance metrics appropriate to the problem type, whether accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, or custom measures, quantify model effectiveness against business requirements.
| Optimization Technique | Purpose | When to Apply |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperparameter Tuning | Find optimal learning parameters | After the baseline model is established |
| Regularization | Prevent overfitting to training data | When validation performance lags training |
| Ensemble Methods | Combine multiple models for better accuracy | When the single model performance plateaus |
| Model Pruning | Reduce model size for faster inference | Before deployment to resource-constrained environments |
| Quantization | Reduce numerical precision for efficiency | For edge deployment and mobile applications |
Deployment and Integration of AI Applications
Deploying AI applications transitions models from research environments to production systems where they deliver actual business value. Deployment strategies must address performance requirements, scalability needs, and integration with existing infrastructure. The choice between cloud deployment, on-premises installation, or edge deployment depends on latency requirements, data privacy considerations, and operational preferences.
Containerization technologies like Docker package AI models with their dependencies for consistent deployment across environments. Kubernetes orchestrates containerized applications, managing scaling and fault tolerance automatically. Model serving frameworks such as TensorFlow Serving, TorchServe, and MLflow provide optimized inference endpoints. API gateways handle authentication, rate limiting, and request routing for production AI services.
Integration patterns connect AI applications with existing business systems and workflows. REST APIs expose model predictions to applications across the enterprise. Event-driven architectures enable real-time AI processing within streaming data pipelines. Batch processing integrations support scheduled predictions on large datasets. Webhook callbacks notify downstream systems of AI-generated insights requiring action.
MLOps practices, combining machine learning with DevOps principles, establish robust processes for continuous integration, deployment, and monitoring of AI applications. Version control for data, code, and models ensures reproducibility. Automated pipelines validate model quality before deployment. A/B testing frameworks enable the gradual rollout of model updates with performance monitoring.
Security, Privacy, and Ethical Considerations in AI Applications

AI applications raise significant security, privacy, and ethical considerations that responsible organizations must address proactively. The sensitive nature of training data, potential for model manipulation, and societal impacts of AI decisions demand careful attention throughout the development lifecycle. Regulatory frameworks, including GDPR, CCPA, and emerging AI-specific legislation, establish compliance requirements for AI applications handling personal data.
Data privacy protections ensure personal information used in AI applications remains secure and compliant with applicable regulations. Anonymization and pseudonymization techniques protect individual identities within training datasets. Differential privacy adds mathematical guarantees against inference attacks. Federated learning enables model training across distributed data sources without centralizing sensitive information.
Algorithmic bias presents ethical challenges when AI applications produce unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Bias can enter through unrepresentative training data, feature selection choices, or optimization objectives that inadvertently favor certain groups. Fairness metrics quantify disparities in model performance across demographic segments. Bias mitigation techniques adjust training processes or post process predictions to improve equity.
Transparency and explainability enable stakeholders to understand how AI applications reach decisions. Interpretable models provide inherent explanations through transparent decision logic. Post hoc explanation methods generate insights into complex model behavior. Documentation of model limitations, intended uses, and failure modes supports responsible deployment. Human oversight mechanisms ensure appropriate human involvement in high stakes AI decisions.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Applications
Despite remarkable capabilities, AI applications face inherent challenges and limitations that organizations must acknowledge and address. Understanding these constraints enables realistic expectations and appropriate risk management strategies. Technical limitations, organizational barriers, and external factors all contribute to the challenges of successful AI implementation.
Data Dependencies: AI applications require substantial high quality data to achieve acceptable performance levels. Organizations lacking sufficient data or facing data quality issues struggle to develop effective AI solutions. Domain shifts, where production data differs from training data, degrade model performance over time, requiring continuous monitoring and retraining.
Talent Scarcity: The shortage of skilled AI practitioners constrains organizational capacity to develop and maintain AI applications. Competition for experienced machine learning engineers, data scientists, and MLOps specialists drives compensation costs upward. Building internal AI capabilities requires significant investment in training and retention programs.
Interpretability Challenges: Complex AI models, particularly deep neural networks, often function as black boxes whose decision logic resists human understanding. This opacity complicates debugging, creates challenges for regulated industries requiring explainability, and may undermine user trust in AI recommendations.
Integration Complexity: Incorporating AI applications into existing enterprise systems and workflows presents technical and organizational challenges. Legacy systems may lack APIs suitable for AI integration. Business processes may require restructuring to leverage AI capabilities effectively. Change management across affected teams demands careful planning and communication.
Cost and Scalability of AI Applications
Understanding the cost structure and scalability characteristics of AI applications enables informed investment decisions and appropriate resource planning. AI projects involve both upfront development costs and ongoing operational expenses that must be factored into business cases. Scalability considerations determine how AI applications handle growing workloads and expanding use cases over time.
| Cost Category | Typical Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Simple AI Features (Chatbots, Basic Automation) | $10,000 to $50,000 | Pre-built models, limited customization, standard integrations |
| Medium Complexity (Custom Models, Multiple Features) | $50,000 to $200,000 | Custom training, moderate data requirements, enterprise integrations |
| Enterprise Solutions (Advanced AI Systems) | $200,000 to $1,000,000+ | Complex architectures, massive datasets, and high availability requirements |
| Ongoing Operations (Annual) | 20 to 30% of the initial investment | Cloud compute, model retraining, monitoring, and maintenance |
Scalability strategies ensure AI applications handle increased demand without proportional cost increases. Horizontal scaling distributes workloads across multiple servers or instances. Model optimization techniques reduce computational requirements without sacrificing accuracy. Caching strategies avoid redundant predictions for repeated queries. Auto scaling dynamically adjusts resources based on demand patterns, optimizing cost efficiency during low usage periods.
Future Trends in AI Applications
The AI applications landscape continues evolving rapidly, with emerging technologies and shifting market dynamics shaping future possibilities. Organizations that anticipate these trends position themselves to leverage new capabilities as they mature. Understanding the trajectory of AI technology helps inform strategic planning and investment decisions.
Multimodal AI: Future AI applications will seamlessly integrate understanding across text, images, audio, video, and other data modalities. These unified models process complex real-world inputs more naturally, enabling sophisticated applications in content understanding, creative generation, and human-computer interaction.
Edge AI Expansion: Processing AI workloads at the edge, on devices rather than in cloud data centers, enables real-time applications with enhanced privacy. Advances in specialized hardware and model compression techniques continue expanding edge AI possibilities across IoT, mobile, and embedded systems.
Autonomous AI Agents: AI applications are evolving from passive tools to autonomous agents capable of complex multi-step reasoning and action. These agents plan sequences of operations, interact with external systems, and accomplish goals with minimal human supervision, transforming workflows across knowledge work domains.
AI Governance and Regulation: Increasing regulatory attention to AI applications will shape development practices and deployment decisions. Organizations must prepare for compliance requirements around transparency, accountability, and fairness while maintaining innovation velocity.
Ready to Build Your AI Application?
Partner with experienced AI developers to transform your business with intelligent solutions tailored to your unique requirements.
Conclusion: The Growing Impact of AI Applications
AI applications have transitioned from experimental technologies to essential business tools that drive competitive advantage across every industry. The comprehensive ecosystem of frameworks, platforms, and best practices established over recent years has made AI development more accessible while simultaneously expanding the boundaries of what intelligent software can achieve. Organizations that embrace AI applications thoughtfully, addressing technical requirements alongside ethical considerations, position themselves for success in an increasingly AI-powered economy.
The journey from AI concept to deployed application requires expertise across multiple disciplines, including data engineering, machine learning, software development, and domain knowledge. Success depends not only on technical execution but also on clear problem definition, quality data preparation, and thoughtful integration with business processes. Organizations must balance innovation ambitions with practical considerations of cost, scalability, and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Looking ahead, AI applications will continue evolving with advances in multimodal understanding, edge deployment, and autonomous agent capabilities. Regulatory frameworks will mature, establishing clearer guidelines for responsible AI development. The organizations that invest in AI capabilities today while building foundations for continuous learning and adaptation will lead their industries into an AI-augmented future.
Why Choose Nadcab Labs for AI Application Development?
Nadcab Labs brings over 8 years of proven expertise in AI application development, blockchain integration, and enterprise software solutions. Our team of seasoned AI engineers, data scientists, and solution architects has successfully delivered hundreds of AI-powered applications across healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, and emerging technology sectors, including DAOs in DeFi Space implementations.
Our comprehensive approach encompasses the entire AI application lifecycle from strategic planning and data architecture through model development, deployment, and ongoing optimization. We leverage cutting-edge technologies, including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud native AI services, while maintaining rigorous attention to security, privacy, and ethical AI practices. Our deep understanding of industry-specific challenges enables us to deliver AI solutions that address real business needs rather than technology for its own sake.
With a track record of successful AI implementations and a commitment to client success that extends beyond project delivery, Nadcab Labs stands as your trusted partner for transforming business operations through intelligent automation. Our expertise in integrating AI with blockchain technologies, including decentralized applications and DAOs in DeFi Space, positions us uniquely to deliver next-generation solutions that leverage the best of both paradigms. Contact our team today to discuss how AI applications can drive measurable value for your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Building a custom AI application typically costs between $50,000 to $500,000, depending on complexity, features, and data requirements. Simple chatbots may cost $10,000 to $30,000, while enterprise-level solutions with advanced machine learning capabilities can exceed $1 million. Factors affecting cost include data preparation, model training time, integration complexity, and ongoing maintenance needs.
AI application development timeline ranges from 3 to 18 months based on project scope. Basic AI features take 3 to 6 months, medium complexity applications need 6 to 12 months, and enterprise-grade solutions require 12 to 18 months. Timeline depends on data availability, model complexity, testing requirements, and integration with existing systems.
Python dominates AI development due to its extensive libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit learn. R excels in statistical analysis and data visualization. Java offers scalability for enterprise applications. JavaScript enables browser-based AI with TensorFlow.js. Julia provides high-performance computing capabilities. Most developers combine multiple languages based on specific project requirements.
Yes, small businesses can leverage AI through affordable options like AI as a Service platforms, pre-built solutions, and cloud-based tools. Monthly subscriptions start from $20 to $500 for basic AI features. Companies like Google Cloud AI, AWS, and Microsoft Azure offer pay-as-you-go models, making AI accessible without massive upfront investments.
Traditional software follows fixed rules and produces predictable outputs based on programmed logic. AI applications learn from data, adapt over time, and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming for every scenario. AI handles unstructured data, recognizes patterns, and improves performance through continuous learning, unlike static traditional software.
Evaluate companies based on their portfolio of similar projects, technical expertise in relevant AI technologies, client testimonials, and industry experience. Check their data handling practices, post-deployment support, and communication transparency. Request detailed proposals, verify team credentials, and assess their understanding of your business domain before finalizing.
Data requirements depend on your AI application type. Generally, you need large volumes of relevant, clean, and labeled data. For image recognition, thousands of categorized images are needed. Natural language processing requires text datasets. Structured business data helps predictive analytics. Quality matters more than quantity, and data should represent real-world scenarios accurately.
Yes, edge AI and on device AI applications function offline by processing data locally. Smartphones use offline AI for voice assistants, camera features, and predictive text. However, offline AI has limitations in model size and capabilities compared to cloud based solutions. Hybrid approaches combine offline functionality with cloud synchronization when connectivity returns.
Measure AI ROI through quantifiable metrics like cost reduction, revenue increase, time savings, and efficiency improvements. Track specific KPIs such as customer satisfaction scores, error reduction rates, processing speed improvements, and employee productivity gains. Compare pre and post implementation performance data. Most businesses see positive ROI within 12 to 24 months.
AI applications include fallback mechanisms, human oversight options, and continuous monitoring systems to handle errors. Wrong predictions trigger alerts for human review. Regular model retraining with updated data improves accuracy. Businesses implement confidence thresholds where low confidence predictions require manual verification. Proper testing and validation minimize error rates before deployment.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.





