Key Takeaways
- Chain abstraction eliminates the need for users to manage multiple wallets, gas tokens, and understand blockchain technicalities, enabling true Web3 mass adoption
- Unlike traditional interoperability solutions that still require manual chain selection, chain abstraction provides a unified experience where cross-chain complexity becomes invisible
- Developers can build chain-agnostic applications once and deploy across multiple networks, reducing costs and time-to-market by up to 70%
- Chain abstraction technology combines account abstraction, cross-chain messaging, and intent-based transactions to create seamless multi-chain experiences
- Enterprise adoption of Web3 accelerates when organizations can integrate blockchain solutions without committing to single-chain dependencies
- DeFi protocols leveraging cross-chain abstraction can access unified liquidity pools, eliminating fragmentation that limits capital efficiency
- Security considerations remain paramount, requiring careful evaluation of trust assumptions in abstraction layers and smart contract implementations
- The convergence of Layer 2, Layer 3, and modular blockchain architecture makes chain abstraction essential Web3 infrastructure for scalable applications
Introduction to Chain Abstraction in Web3
The blockchain industry has undergone remarkable transformation since the introduction of Bitcoin and subsequent smart contract platforms. Today’s Web3 ecosystem comprises hundreds of distinct blockchain networks, each offering unique capabilities, consensus mechanisms, and community ecosystems. While this diversity represents tremendous innovation, it has created a fragmented landscape that challenges both users and developers seeking to harness blockchain technology’s full potential.
Chain abstraction in Web3 emerges as a transformative approach to solving this fragmentation crisis. By creating unified interaction layers that hide underlying blockchain complexity, chain abstraction promises to deliver the seamless experiences users expect from modern applications while preserving the decentralization and security benefits that make blockchain technology valuable.
The Evolution of Web3 Architecture
Understanding chain abstraction requires examining how blockchain architecture has evolved and why current approaches create friction that limits adoption.
From Single-Chain to Multi-Chain Ecosystems
Early blockchain applications operated within single-chain environments where all activity occurred on one network. Ethereum pioneered smart contract functionality, while subsequent platforms like Solana, Avalanche, and Polygon emerged to address scalability limitations and offer alternative approaches to consensus and execution. This evolution created a multi-chain architecture where applications and assets became distributed across numerous networks, each with distinct advantages for specific use cases.
The transition from single-chain to multi-chain models initially seemed beneficial, offering users choice and developers flexibility. However, this fragmentation introduced complexity that traditional internet users find overwhelming. Managing assets across multiple chains requires separate wallets, different gas tokens, and understanding of bridge mechanisms that average users struggle to navigate safely.
Growing Complexity in Blockchain Networks
As blockchain scalability solutions proliferated, the complexity facing users multiplied exponentially. Layer 2 networks introduced rollup technology that improved transaction throughput but added another layer of decision-making for users. Application-specific chains emerged to optimize for particular use cases, further fragmenting the ecosystem.
This complexity directly contradicts Web3’s vision of an accessible, user-owned internet. When interacting with decentralized applications requires understanding which chain offers optimal gas fees, how to bridge assets safely, and which wallet supports necessary networks, mainstream adoption remains elusive.
Why Web3 Needs Chain Abstraction
The case for chain abstraction technology becomes clear when examining specific challenges that current multi-chain models impose on users and the broader ecosystem.
User Experience Challenges in Web3
Consider a typical user attempting to purchase an NFT on a marketplace. They may need to bridge ETH from Ethereum mainnet to Polygon, swap for MATIC to pay gas fees, approve token spending, and finally execute the purchase. Each step introduces potential failure points, confusing interfaces, and security risks from interacting with bridge contracts. This multi-step process stands in stark contrast to the one-click purchases users expect from traditional e-commerce.
Web3 innovation cannot achieve mainstream relevance while requiring users to become blockchain experts. Chain abstraction addresses this fundamental barrier by handling all cross-chain operations behind the scenes, presenting users with simple, familiar interfaces regardless of which blockchain ultimately processes their transactions.
Fragmentation Across Blockchains
Liquidity fragmentation represents another critical challenge that chain abstraction solves. When capital spreads across dozens of chains, individual markets suffer from thin order books, high slippage, and inefficient price discovery. DeFi protocols must choose which chains to support, limiting their potential user base and forcing users to move assets to access specific applications.
Cross-chain abstraction enables protocols to aggregate liquidity across all supported networks, creating deeper markets that benefit traders and liquidity providers alike. This unified approach to liquidity management represents a fundamental shift in how decentralized finance can operate at scale.
Understanding Chain Abstraction
To fully appreciate chain abstraction’s transformative potential, we must examine its technical foundations and core mechanisms that enable seamless multi-chain experiences.
What Is Chain Abstraction in Web3
Chain abstraction Web3 solutions represent a fundamental rethinking of how users and applications interact with blockchain infrastructure. Rather than requiring explicit chain selection and management, chain abstraction creates unified interfaces that automatically handle cross-chain complexity.
Definition of Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction is a technological framework that removes the need for users and developers to interact directly with individual blockchain networks. It provides a unified layer that automatically routes transactions, manages assets, and handles cross-chain communication without requiring users to understand underlying blockchain specifics. This abstraction layer sits between applications and blockchain infrastructure, translating user intentions into optimized multi-chain operations.
Core Components of a Chain Abstraction Layer
Effective chain abstraction requires several interconnected components working together seamlessly. These include unified account systems that maintain consistent identities across chains, cross-chain messaging protocols that enable secure communication, solver networks that optimize transaction routing, and gas abstraction mechanisms that allow flexible fee payment.
| Component | Function | User Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Unified Account System | Single identity across all chains | One wallet for all networks |
| Cross-Chain Messaging | Secure inter-chain communication | Seamless asset transfers |
| Solver Network | Optimal transaction routing | Best prices and speeds |
| Gas Abstraction | Flexible fee payment | Pay gas in any token |
| Liquidity Aggregation | Cross-chain liquidity access | Deeper markets, better rates |
How Chain Abstraction Works
The mechanics of chain abstraction involve sophisticated coordination between multiple systems to deliver seamless user experiences.
Abstracting Blockchain Logic
Chain abstraction layers intercept user requests and translate them into blockchain-specific operations. When a user initiates a transaction, the abstraction layer determines which chain or chains should process the request, handles any necessary asset bridging, manages gas payments across networks, and aggregates results into a unified response. This process occurs transparently, with users seeing only their intended action and outcome.
Unified Interaction Across Chains
Achieving unified interaction requires standardized interfaces that work consistently regardless of underlying blockchain differences. Chain abstraction protocols define common transaction formats, state representations, and event structures that map to chain-specific implementations. This standardization enables applications to treat all supported chains as a single, unified execution environment.
Limitations of Traditional Multi-Chain Models

Before chain abstraction, multi-chain Web3 systems relied on approaches that, while functional, created significant friction for users and developers alike.
Complexity in Multi-Chain Web3 Systems
Traditional multi-chain architecture places the burden of chain management squarely on end users, requiring them to navigate complexities that technical users often take for granted.
Multiple Wallets and Gas Tokens
Users interacting with multiple chains typically need to maintain separate wallet balances for gas tokens on each network. This requirement means holding ETH for Ethereum, MATIC for Polygon, AVAX for Avalanche, and native tokens for every other chain they use. Managing these balances, understanding fee structures, and ensuring sufficient gas availability creates ongoing friction that discourages casual users.
Cross-Chain Transaction Friction
Moving assets between chains using traditional bridges involves multiple steps, confirmation delays, and security risks. Users must understand which bridges serve their needs, trust bridge security implementations, and often pay premium fees for expedited transfers. Failed bridge transactions can leave assets temporarily inaccessible, creating anxiety for users unfamiliar with blockchain recovery procedures.
Important: Cross-chain bridges represent some of the highest-risk infrastructure in blockchain systems. Historical bridge exploits have resulted in billions of dollars in losses, underscoring the importance of evaluating security models carefully before trusting abstraction solutions with significant assets.
Developer Challenges in Multi-Chain Environments
Developers face their own set of obstacles when building applications for multi-chain ecosystems.
Increased Costs for Building and Maintenance
Supporting multiple blockchains requires writing chain-specific code, managing separate deployments, and maintaining compatibility as each chain evolves independently. Development teams must possess expertise across different virtual machines, programming languages, and tooling ecosystems. These requirements multiply costs and extend timelines, particularly for smaller teams with limited resources.
Scalability Bottlenecks
Traditional multi-chain architecture creates scalability bottlenecks as applications must coordinate state across networks with different finality times, block sizes, and throughput characteristics. Achieving consistency across chains requires sophisticated synchronization mechanisms that add latency and complexity to application logic.
How Chain Abstraction Transforms Web3 Infrastructure
Chain abstraction fundamentally reshapes Web3 infrastructure by shifting complexity from users and applications to specialized abstraction layers optimized for cross-chain coordination.
Chain-Agnostic Application Building
The ability to build applications without chain dependencies represents a paradigm shift for Web3 builders seeking to maximize their reach and impact.
Building dApps Without Chain Dependency
Chain abstraction enables developers to write application logic once and deploy across all supported networks. Instead of implementing chain-specific integrations, developers interact with unified APIs that handle blockchain differences automatically. This approach allows teams to focus on their core product rather than infrastructure management. Organizations looking to build blockchain solutions and decentralized applications can significantly accelerate delivery timelines through chain-agnostic architectures.
Simplified Deployment Across Networks
Deployment processes simplify dramatically with chain abstraction. Rather than managing separate deployment pipelines for each chain, developers push to a single abstraction layer that handles distribution across networks. Updates and patches apply uniformly, ensuring consistent behavior regardless of which chain processes specific transactions.
Seamless Cross-Chain Execution
Chain abstraction enables execution patterns previously impossible or impractical in fragmented multi-chain environments.
Unified Transaction Flow
Complex operations spanning multiple chains execute as single transactions from the user’s perspective. Behind the scenes, chain abstraction protocols coordinate atomic execution across networks, ensuring either complete success or clean rollback. This atomicity eliminates the partial failure states that plague manual cross-chain operations.
Reduced Blockchain Fragmentation
By enabling seamless interaction across chains, abstraction reduces the practical fragmentation of blockchain ecosystems. Assets can flow freely where needed, liquidity concentrates around actual demand rather than chain boundaries, and users access the best opportunities regardless of which network hosts them.
Impact of Chain Abstraction on Web3 User Experience
User experience improvements represent chain abstraction’s most visible benefits, directly addressing adoption barriers that have limited Web3 growth.
Simplifying Web3 Interactions
Chain abstraction transforms complex blockchain operations into simple, intuitive actions familiar to mainstream users.
One-Click Cross-Chain Transactions
Operations that previously required multiple steps across different interfaces become single-click actions. Users express their intent, whether purchasing an NFT, swapping tokens, or providing liquidity, and chain abstraction handles all underlying complexity. This simplification brings Web3 user experience closer to the standards users expect from Web2 applications.
Gas and Wallet Abstraction
Combined gas and wallet abstraction allows users to pay transaction fees in any token they hold, eliminating the need to maintain native gas token balances across multiple chains. Smart wallet implementations can even sponsor gas for new users, removing this barrier entirely for onboarding flows.
Enabling Mass Adoption of Web3
Mass adoption requires removing barriers that currently limit blockchain technology to technically sophisticated early adopters.
Lower Entry Barriers for Users
Chain abstraction lowers entry barriers by eliminating the need for users to understand blockchain architecture. New users can interact with decentralized applications without learning about chains, gas, or bridges. This accessibility expansion opens Web3 to demographics previously excluded by technical complexity.
Improved Accessibility and Usability
Usability improvements extend beyond simplification to include features impossible without chain abstraction. Applications can automatically select the cheapest or fastest chain for each transaction, optimize asset placement across networks, and provide unified views of cross-chain portfolios.
Benefits of Chain Abstraction for Builders and Enterprises
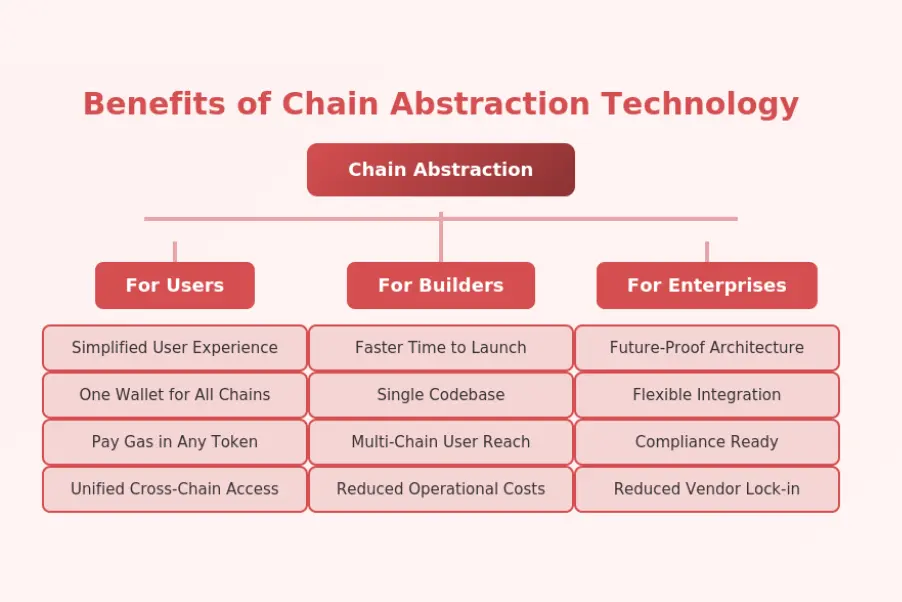
Beyond user experience, chain abstraction delivers substantial benefits for organizations building Web3 products and services.
Faster and Scalable dApp Building
Chain abstraction accelerates timelines and enables scaling patterns previously difficult to achieve.
Reduced Infrastructure Complexity
Development teams offload chain-specific infrastructure management to abstraction layers, reducing the expertise required to build multi-chain applications. This simplification allows smaller teams to compete effectively with larger organizations that can afford dedicated blockchain infrastructure teams.
Improved Time-to-Market
Projects launching with chain abstraction from the start avoid the iterative process of adding chain support sequentially. Initial releases can target all supported networks simultaneously, maximizing potential user acquisition from launch day.
| Aspect | Traditional Multi-Chain | Chain Abstraction |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Launch | 6-12 months per chain | Single deployment, all chains |
| Team Size Required | Specialists per chain | Generalist blockchain team |
| Maintenance Burden | Multiplies with each chain | Single codebase |
| User Reach | Limited to supported chains | All chains simultaneously |
| Liquidity Access | Fragmented per chain | Unified cross-chain |
Enterprise-Grade Web3 Solutions
Enterprises considering blockchain adoption particularly benefit from chain abstraction’s flexibility and future-proofing.
Easier Integration With Multiple Blockchains
Enterprise systems can integrate once with a chain abstraction layer rather than maintaining connections to individual networks. This approach simplifies compliance, reduces vendor lock-in risk, and provides flexibility to leverage different chains as business needs evolve.
Long-Term Maintainability
Chain abstraction provides insulation from underlying blockchain changes. When chains upgrade, fork, or become obsolete, abstraction layers handle transitions without requiring application-level modifications. This architectural resilience protects enterprise investments in blockchain integration.
Chain Abstraction vs Blockchain Interoperability
Understanding the distinction between chain abstraction and traditional interoperability clarifies why abstraction represents an evolutionary step beyond existing cross-chain solutions.
Understanding Interoperability Solutions
Blockchain interoperability has been pursued through various mechanisms, each with distinct trade-offs.
Cross-Chain Bridges and Messaging Protocols
Bridges enable asset transfers between chains by locking tokens on source chains and minting representations on destinations. Messaging protocols like LayerZero and Wormhole allow cross-chain communication for more complex interactions. These solutions enable interoperability but still require users to explicitly initiate and manage cross-chain operations.
Limitations of Traditional Interoperability
Traditional interoperability solutions require users to understand which bridge to use, manage wrapped asset versions, and navigate different interfaces for each cross-chain action. While technically enabling multi-chain interaction, these approaches do not deliver the seamless experience that mainstream adoption requires.
Why Chain Abstraction Goes Further
Chain abstraction builds upon interoperability infrastructure while adding crucial experience optimization layers.
Abstraction Beyond Communication
While interoperability enables cross-chain communication, abstraction encompasses the entire user journey. This includes account unification, transaction optimization, fee management, and state aggregation. Chain abstraction uses interoperability protocols as infrastructure components while hiding their complexity from end users.
Future-Proof Web3 Architecture
Chain abstraction creates architectures that adapt as the blockchain landscape evolves. New chains integrate through abstraction layers without requiring application updates. This future-proofing protects investments in Web3 applications as the ecosystem continues rapid development.
Role of Chain Abstraction in Web3 Innovation
Chain abstraction Web3 innovation extends beyond user experience to enable entirely new application patterns and business models.
Powering Next-Generation dApps
Advanced applications leverage chain abstraction capabilities to deliver experiences impossible in single-chain or manually-coordinated multi-chain environments.
Modular Blockchain Architecture
Modular blockchain designs separate execution, settlement, and data availability layers across specialized chains. Chain abstraction enables applications to leverage this modularity while presenting unified interfaces, combining best-in-class components from different networks transparently.
Intent-Based Transactions
Intent-based systems allow users to express desired outcomes rather than specific transaction steps. Solver networks competing to fulfill intents find optimal execution paths across chains, delivering better prices and user experiences than manually constructed transactions could achieve.
Supporting Advanced Web3 Models
Chain abstraction enables sophisticated Web3 patterns that require seamless multi-chain coordination.
Account Abstraction Integration
When combined with account abstraction, chain abstraction delivers powerful wallet experiences including social recovery, session keys, and programmable spending limits that work consistently across all chains. This integration represents the convergence of two transformative technologies into unified user experiences.
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Compatibility
Blockchain scalability solutions spanning multiple layers benefit significantly from chain abstraction. Users can leverage Layer 2 cost savings without understanding rollup mechanics, while Layer 3 application chains integrate seamlessly into broader ecosystem interactions. This compatibility ensures scalability improvements reach end users without adding complexity.
Selecting a Chain Abstraction Solution: Key Criteria
When evaluating chain abstraction protocols for your project, consider these essential factors:
- Security Model: Understand trust assumptions, validator requirements, and historical audit results
- Chain Coverage: Ensure support for all networks your application and users need
- Latency Performance: Evaluate transaction confirmation times for your use case requirements
- Cost Structure: Analyze fee models and compare against direct chain interaction costs
- Builder Support: Assess documentation quality, SDK maturity, and community resources
- Decentralization: Examine governance structures and centralization risks in critical components
Real-World Use Cases of Chain Abstraction
Practical applications demonstrate chain abstraction’s value across diverse blockchain use cases.
DeFi and Cross-Chain Liquidity
Decentralized finance applications particularly benefit from cross-chain abstractioChain n capabilities.
Unified DeFi Experiences
Users access lending, trading, and yield opportunities across all chains through single interfaces. Chain abstraction automatically routes transactions to protocols offering best rates, rebalances positions across networks, and presents unified portfolio views regardless of where assets reside.
Reduced Liquidity Fragmentation
DeFi protocols can aggregate liquidity from all supported chains, creating deeper markets with tighter spreads. Liquidity providers earn fees from cross-chain volume while traders access better execution than any single-chain market could offer. This aggregation transforms the economics of decentralized exchange and lending.
NFTs, Gaming, and Metaverse
Digital asset and entertainment use cases showcase chain abstraction’s potential for consumer applications.
Multi-Chain NFT Marketplaces
NFT platforms supporting chain abstraction enable seamless purchases regardless of which chain hosts the NFT or which tokens the buyer holds. Collections can span multiple chains while appearing unified to collectors, maximizing exposure and liquidity for creators.
Seamless Web3 Gaming Economies
Gaming economies leveraging chain abstraction allow players to trade items, transfer characters, and participate in events across games on different chains. This interoperability creates richer gaming experiences and more liquid in-game asset markets.
Teams building crypto exchanges and trading platforms find chain abstraction particularly valuable for aggregating liquidity and simplifying user onboarding across multiple networks.
Enterprise and Institutional Adoption
Business applications require the reliability and flexibility that chain abstraction provides.
Blockchain-Agnostic Enterprise Apps
Enterprises can deploy blockchain applications without committing to single-chain dependencies that may become liabilities as the ecosystem evolves. Supply chain tracking, asset tokenization, and credential verification systems all benefit from chain-agnostic architectures that abstraction enables.
Compliance-Friendly Web3 Solutions
Regulatory requirements often demand flexibility in blockchain infrastructure selection. Chain abstraction allows organizations to route transactions through compliant chains while maintaining unified application experiences, adapting to evolving regulatory landscapes without architectural changes.
Challenges and Risks in Chain Abstraction
Despite its benefits, chain abstraction introduces challenges that require careful consideration and ongoing attention.
Security Considerations
Adding abstraction layers introduces new security surfaces that must be protected.
Trust Assumptions in Abstraction Layers
Chain abstraction protocols require trust in their operators, validators, or cryptographic assumptions. Users must understand these trust models and evaluate whether they align with security requirements. Different abstraction approaches involve varying trust trade-offs that impact risk profiles.
Smart Contract Risks
Abstraction layers rely on smart contracts that may contain vulnerabilities. The complexity of cross-chain coordination logic creates significant audit challenges, and exploits could affect users across all supported chains simultaneously. Robust security practices and insurance mechanisms help mitigate these risks.
Performance and Standardization Issues
Technical challenges remain in delivering consistent, high-performance chain abstraction.
Latency and Execution Overhead
Coordinating across multiple chains inevitably adds latency compared to single-chain operations. Abstraction layers must optimize routing and execution to minimize delays while maintaining security guarantees. For latency-sensitive applications, these trade-offs require careful evaluation.
Lack of Unified Standards
The chain abstraction ecosystem lacks unified standards, leading to fragmentation among competing approaches. This diversity promotes innovation but complicates integration decisions and may result in incompatible systems that limit interoperability between abstraction providers.
| Phase | Stage | Activities | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intent Capture | User expresses desired action through unified interface | Standardized intent object created |
| 2 | Route Optimization | Solver network evaluates execution paths across chains | Optimal route selected |
| 3 | Transaction Construction | Chain-specific transactions generated from intent | Executable transaction bundle |
| 4 | Cross-Chain Execution | Coordinated submission to relevant chains | Atomic multi-chain settlement |
| 5 | Result Aggregation | Outcomes collected and verified across chains | Unified result presented to user |
The Future of Chain Abstraction in Web3
Chain abstraction positions itself as essential Web3 infrastructure as the ecosystem matures and mainstream adoption accelerates.
Chain Abstraction as Core Web3 Infrastructure
The trajectory of blockchain technology points toward abstraction becoming foundational rather than optional.
Driving Web3 Scalability
Blockchain scalability solutions increasingly rely on multi-chain and multi-layer architectures. As more activity migrates to Layer 2, Layer 3, and application-specific chains, abstraction layers become essential for maintaining coherent user experiences. Chain abstraction transforms scalability improvements from technical achievements into accessible user benefits.
Improving Long-Term Usability
Long-term Web3 usability depends on hiding blockchain complexity from mainstream users. Just as internet users need not understand TCP/IP to browse websites, Web3 users should not need blockchain expertise to use decentralized applications. Chain abstraction provides this crucial usability layer that enables mainstream adoption.
Adoption Trends and Industry Outlook
Market trends indicate growing recognition of chain abstraction’s importance.
Growing Demand for Chain-Agnostic Solutions
Enterprise and institutional interest in blockchain consistently emphasizes flexibility and future-proofing. Chain abstraction addresses these requirements directly, positioning solutions that implement it favorably for enterprise adoption. As more organizations evaluate Web3 integration, demand for chain-agnostic architectures will accelerate.
Chain Abstraction and Web3 Mass Adoption
The path to Web3 mass adoption runs through user experience improvements that chain abstraction uniquely enables. By eliminating the technical barriers that have limited blockchain to early adopters, abstraction opens decentralized applications to billions of potential users. This expansion represents the ultimate validation of chain abstraction’s transformative potential.
Step into the future of Web3
Learn how chain abstraction removes complexity and accelerates innovation.
Unlock Web3 Innovation
Conclusion
Chain abstraction represents a pivotal evolution in blockchain technology that addresses fundamental barriers limiting Web3 adoption and innovation.
Why Chain Abstraction Is the Future of Web3 Innovation
The evidence clearly demonstrates chain abstraction’s essential role in Web3’s future development and mainstream adoption.
Summary of Key Benefits
Chain abstraction delivers transformative benefits across the Web3 ecosystem. Users gain intuitive experiences freed from blockchain complexity. Application builders access simplified processes and broader reach. Enterprises obtain flexible, future-proof architectures. The entire ecosystem benefits from unified liquidity and reduced fragmentation. These advantages compound as adoption grows, creating network effects that reinforce chain abstraction’s value proposition.
Final Thoughts on the Next Phase of Web3
Web3 innovation stands at an inflection point where user experience improvements determine whether blockchain technology achieves mainstream relevance. Chain abstraction provides the crucial bridge between powerful decentralized infrastructure and accessible user experiences. As the ecosystem continues rapid evolution across multiple chains and layers, abstraction will transition from competitive advantage to baseline requirement.
Organizations building for the future of Web3 should prioritize chain abstraction in their architectural decisions. Whether through native implementation, integration with existing protocols, or strategic partnerships with abstraction providers, embracing this technology positions projects for success in an increasingly multi-chain world. The future of Web3 is chain-agnostic, and chain abstraction is the technology that makes this future possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Chain abstraction is a technology layer that hides the complexity of interacting with multiple blockchain networks from end users and developers. It enables applications to work seamlessly across different chains without requiring users to understand which blockchain they are using. This approach simplifies cross-chain interactions by providing a unified interface that handles all underlying blockchain operations automatically.
Chain abstraction addresses one of the biggest barriers to mainstream Web3 adoption by eliminating the need for users to understand blockchain technicalities. New users often struggle with managing multiple wallets, acquiring different gas tokens, and navigating between chains, which chain abstraction solves. By providing a familiar, Web2-like experience while maintaining decentralization benefits, chain abstraction can attract millions of users who would otherwise avoid blockchain technology.
A chain abstraction layer typically includes unified account systems that work across chains, cross-chain messaging infrastructure, liquidity aggregation protocols, and solver networks that optimize transaction routing. It also incorporates gas abstraction mechanisms that allow users to pay fees in any token and smart routing algorithms that determine the most efficient execution path. These components work together to create a seamless experience regardless of which blockchain processes the transaction.
Developers using chain abstraction can build applications once and deploy them across multiple blockchains without writing chain-specific code for each network. This significantly reduces development time, maintenance costs, and the technical complexity of supporting multiple chains. Chain abstraction also allows developers to access liquidity and users across all supported chains, maximizing their application’s reach and potential user base.
Chain abstraction security depends heavily on the underlying infrastructure, including the trust assumptions of bridges, validators, and solver networks used. Reputable chain abstraction protocols implement multiple security layers including cryptographic proofs, multi-signature validation, and economic incentives aligned with honest behavior. However, users should evaluate the security model of any chain abstraction solution and understand that additional complexity can introduce new attack vectors.
While blockchain interoperability focuses on enabling communication between different chains through bridges and messaging protocols, chain abstraction goes further by completely hiding the multi-chain complexity from users. Interoperability solutions still require users to manually select networks and manage multiple wallets, whereas chain abstraction creates a single, unified experience. Chain abstraction builds on interoperability infrastructure but adds a layer of user experience optimization that makes cross-chain operations invisible.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






