Key Takeaways
-
Synthetic Minting in DeFi enables permissionless access to global financial markets by allowing users to create blockchain-based synthetic assets representing stocks, commodities, fiat currencies, and derivatives without centralized intermediaries.
-
Users can gain exposure to multiple asset classes without selling their crypto holdings, significantly improving capital efficiency and enabling advanced portfolio diversification strategies.
-
Overcollateralized smart contracts form the foundation of synthetic assets, ensuring system solvency through automated collateral management and liquidation mechanisms.
-
Decentralized oracle networks are critical for accurate price tracking, maintaining synthetic asset pegs and preventing manipulation or incorrect liquidations.
-
Synthetic assets function as standard ERC-20 tokens, making them composable with lending, trading, yield farming, and other DeFi protocols.
-
DeFi Synthetic Minting removes traditional financial barriers such as geographic restrictions, high capital requirements, and complex onboarding processes.
-
Liquidation risk, smart contract vulnerabilities, and oracle failures remain key challenges, requiring users to actively manage positions and protocols to implement robust security measures.
-
Synthetic minting differs fundamentally from traditional asset tokenization by using crypto collateral instead of custodial ownership of real-world assets.
-
The composability of synthetic assets unlocks advanced use cases including hedging, leveraged trading, cross-border finance, and yield optimization.
-
As DeFi matures, synthetic minting is emerging as core financial infrastructure, driving innovation, institutional interest, and the future of decentralized global markets.
The emergence of Synthetic Minting in DeFi has fundamentally transformed how individuals interact with global financial markets through decentralized protocols. This groundbreaking innovation enables users to create synthetic representations of virtually any asset class including equities, commodities, fiat currencies, and even complex financial derivatives without the need for centralized intermediaries. The technology leverages smart contracts and blockchain infrastructure to democratize access to financial instruments that were previously restricted to specific geographic regions or required substantial capital commitments.
Traditional financial systems have long imposed barriers that limit participation in global markets through regulatory restrictions, high transaction costs, and complex onboarding procedures. Synthetic Minting in DeFi addresses these challenges by creating a permissionless environment where anyone with an internet connection can gain exposure to diverse asset classes. The process maintains the integrity of price discovery through decentralized oracle networks while ensuring that all synthetic assets remain properly collateralized throughout their existence.
The significance of DeFi Synthetic Minting extends beyond simple asset representation as it introduces new paradigms for capital efficiency and market participation. Users can leverage their existing cryptocurrency holdings to mint synthetic assets without selling their original positions, effectively maintaining exposure to multiple markets simultaneously. This innovative approach has catalyzed the development of sophisticated trading strategies and financial products that were previously impossible within purely decentralized environments.
Understanding Synthetic Assets in Decentralized Finance
Synthetic assets within decentralized finance represent tokenized derivatives that track the value of underlying assets through algorithmic mechanisms and collateral backing. These digital instruments provide economic exposure to real world assets without requiring direct ownership or custody of the underlying asset itself. The concept draws inspiration from traditional synthetic derivatives but implements them through transparent, auditable smart contracts that operate on blockchain networks.
The fundamental principle behind synthetic assets involves creating a token whose value remains pegged to an external reference price through various stabilization mechanisms. DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols employ sophisticated algorithms that continuously monitor collateralization ratios and trigger liquidation events when necessary to protect the system’s solvency. This approach ensures that synthetic assets maintain their peg to the underlying asset while providing sufficient security for all participants in the ecosystem.
Users benefit from synthetic assets by gaining exposure to price movements of assets that might otherwise be inaccessible due to regulatory constraints, geographic limitations, or capital requirements. For instance, an individual in any part of the world can obtain exposure to major stock indices, precious metals, or foreign currencies through Synthetic Minting in DeFi without needing brokerage accounts or navigating complex international trading regulations. The composability of these synthetic assets with other DeFi protocols further amplifies their utility within the broader decentralized finance ecosystem.
What Is Synthetic Minting and How It Works
Synthetic Minting in DeFi represents the process through which users create synthetic assets by locking collateral within smart contract protocols and issuing tokens that track the value of target assets. This mechanism operates through a series of interconnected components including collateral vaults, price oracles, liquidation engines, and governance systems that work together to maintain the stability and security of the synthetic asset ecosystem.
The minting process begins when a user deposits accepted collateral into a protocol’s smart contract vault. The system then allows the user to mint synthetic assets up to a predetermined collateralization ratio, typically ranging from 150% to 750% depending on the protocol’s risk parameters and the volatility characteristics of both the collateral and the synthetic asset being created. This overcollateralization serves as a safety buffer to protect against price fluctuations and ensure that synthetic assets remain fully backed even during market volatility.
Once minted, synthetic assets function as standard ERC20 tokens that can be transferred, traded, or utilized within other DeFi applications. The value of these tokens remains tied to their underlying reference asset through continuous price feeds provided by decentralized oracle networks. Users who have minted synthetic assets remain responsible for maintaining adequate collateralization ratios and face liquidation if their position falls below the minimum threshold established by the protocol.
Core Components of Synthetic Minting Protocols
The infrastructure supporting DeFi Synthetic Minting comprises several critical components that work in concert to ensure the proper functioning and security of synthetic asset systems. Understanding these components provides essential insight into how these protocols maintain stability while offering users access to diverse asset classes through decentralized mechanisms.
| Component | Function | Critical Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Contract Vaults | Store collateral and manage minting operations | Ensures secure custody of user assets |
| Oracle Networks | Provide real time price data for assets | Maintains accurate asset valuations |
| Liquidation Engines | Monitor and execute undercollateralized positions | Protects protocol solvency |
| Governance Mechanisms | Enable community driven protocol updates | Ensures decentralized control |
| Stability Mechanisms | Maintain peg between synthetic and underlying assets | Preserves asset value accuracy |
Smart contract vaults form the foundation of Synthetic Minting in DeFi by providing secure storage for collateral while executing minting and burning operations according to predetermined rules. These contracts undergo extensive auditing processes to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities that could compromise user funds or protocol integrity. The vault architecture typically implements multi signature requirements and time locks for critical operations to enhance security.
Oracle networks serve as the bridge between on chain protocols and real world price data, feeding critical information that determines collateralization ratios and triggers liquidation events. The reliability and security of these oracle systems directly impact the overall stability of synthetic asset protocols. Leading DeFi Synthetic Minting platforms implement multiple oracle sources with median price calculations to prevent manipulation and ensure accurate asset valuations.
Role of Collateral in Synthetic Minting
Collateral represents the cornerstone of Synthetic Minting in DeFi systems as it provides the economic security necessary to back synthetic assets and maintain confidence in their value. The collateralization mechanism ensures that every synthetic asset has underlying value supporting its existence, protecting users from default risks and maintaining the integrity of the synthetic asset ecosystem.
The amount of collateral required to mint synthetic assets varies based on several factors including the volatility profile of both the collateral and the synthetic asset, the protocol’s risk tolerance, and market conditions. Higher collateralization ratios provide greater security buffers but reduce capital efficiency for users. DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols continuously balance these competing concerns through governance mechanisms and risk management frameworks.
When users deposit collateral to mint synthetic assets, they maintain ownership of their locked funds and can retrieve them by burning the synthetic assets they created. This mechanism creates a natural arbitrage opportunity that helps maintain the peg between synthetic assets and their underlying reference prices. If a synthetic asset trades above its reference price, arbitrageurs can mint new tokens and sell them for profit, increasing supply and pushing the price down toward the peg.
Types of Collateral Used for Minting Synthetic Assets
Different protocols supporting Synthetic Minting in DeFi accept various types of collateral assets, each with distinct risk profiles and implications for system security. The selection of acceptable collateral types significantly influences the overall risk characteristics of the protocol and determines the range of users who can participate in synthetic asset minting.
| Collateral Type | Examples | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Cryptocurrencies | ETH, BTC, BNB | High liquidity and widespread adoption | Subject to significant price volatility |
| Stablecoins | USDC, DAI, USDT | Price stability and predictable value | Centralization risks with certain stablecoins |
| Governance Tokens | UNI, AAVE, COMP | Enables protocol utility and participation | Lower liquidity than major cryptocurrencies |
| Liquid Staking Tokens | stETH, rETH | Maintains staking rewards while providing collateral | Additional smart contract risk layers |
Native cryptocurrencies like Ethereum serve as popular collateral choices for DeFi Synthetic Minting due to their deep liquidity and established market presence. These assets enable users to leverage their existing cryptocurrency holdings without converting to other tokens. However, their price volatility necessitates higher collateralization ratios to maintain system security during market downturns.
Stablecoin collateral offers advantages in terms of price stability and predictability, allowing for lower collateralization ratios and more capital efficient positions. However, the use of stablecoins introduces dependencies on centralized issuers or complex algorithmic mechanisms that carry their own risk profiles. Protocols must carefully evaluate the tradeoffs between capital efficiency and system resilience when accepting stablecoin collateral.
On Chain Price Feeds and Oracle Mechanisms
Oracle systems form the critical infrastructure that enables Synthetic Minting in DeFi to accurately track real world asset prices and maintain proper synthetic asset valuations. These decentralized networks aggregate price data from multiple sources and deliver this information to smart contracts in a secure, tamper resistant manner that prevents manipulation and ensures data integrity.
The architecture of oracle networks typically involves multiple independent node operators who fetch price data from various exchanges and data providers, then submit this information to on chain aggregation contracts. The system calculates median or weighted average prices from these submissions to filter out outliers and potential manipulation attempts. This decentralized approach significantly reduces the risk of single points of failure or coordinated attacks on price feeds.
Leading DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols implement additional security measures including time weighted average prices, circuit breakers that pause operations during extreme price movements, and multi oracle redundancy that cross references data from different networks. These safeguards protect against flash loan attacks, exchange manipulation, and oracle failures that could otherwise compromise synthetic asset valuations and trigger inappropriate liquidations.
The frequency of oracle updates represents a critical balance between accuracy and cost efficiency. More frequent updates provide better price tracking and reduce arbitrage opportunities but increase operational costs for oracle networks. Synthetic Minting in DeFi protocols optimize this balance based on the volatility characteristics of tracked assets and the requirements of their user base.
Step by Step Process of Minting Synthetic Assets
The process of creating synthetic assets through DeFi Synthetic Minting follows a structured sequence of steps that ensure proper collateralization and system security. Understanding this workflow provides clarity on how users interact with synthetic asset protocols and the mechanics underlying these innovative financial instruments.
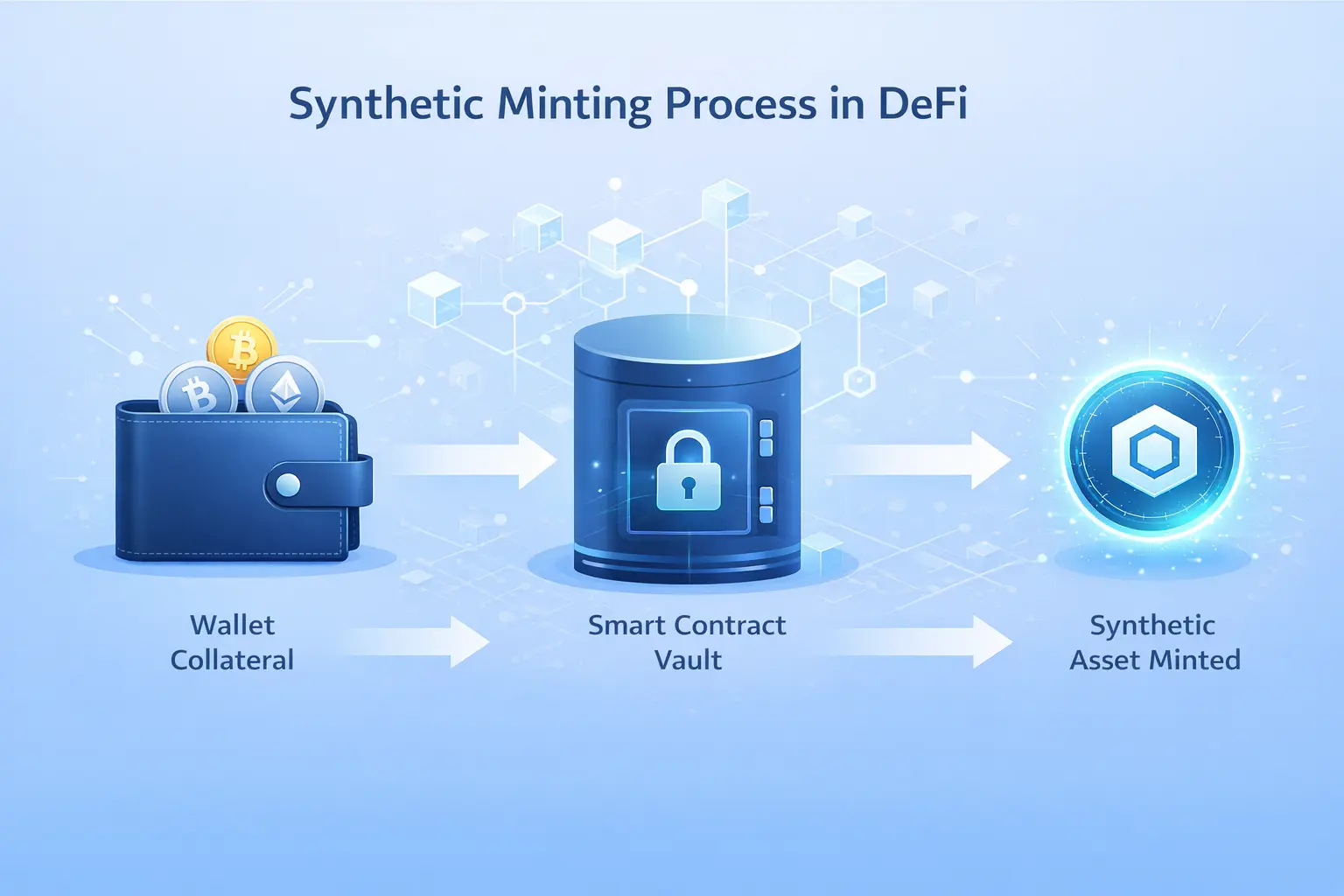
Synthetic Asset Minting Lifecycle
Step 1: Collateral Deposit
Users connect their cryptocurrency wallets to the synthetic minting protocol and approve the smart contract to access their chosen collateral assets. They then deposit the desired amount of collateral into the protocol’s vault, which locks these funds and tracks the position on chain.
Step 2: Collateralization Ratio Calculation
The protocol queries oracle networks to obtain current prices for both the deposited collateral and the desired synthetic asset. It calculates the maximum amount of synthetic assets that can be minted while maintaining the required collateralization ratio, typically displaying this information to the user.
Step 3: Synthetic Asset Minting
Users specify the quantity of synthetic assets they wish to mint within the allowable limits. The smart contract executes the minting transaction, creating new synthetic tokens and transferring them to the user’s wallet while recording the debt position associated with their collateral.
Step 4: Position Management
After minting, users can trade, transfer, or utilize their synthetic assets within the broader DeFi ecosystem. They must actively monitor their collateralization ratio and add collateral or burn synthetic assets if market movements threaten to push their position below the minimum threshold.
Step 5: Position Closure
To retrieve collateral, users must return the minted synthetic assets to the protocol by executing a burn transaction. The smart contract verifies the burn operation, releases the corresponding collateral back to the user’s wallet, and closes the debt position.
Throughout this lifecycle, Synthetic Minting in DeFi protocols continuously monitor all open positions and trigger liquidation mechanisms when collateralization ratios fall below safe thresholds. This automated enforcement ensures that synthetic assets remain properly backed even during periods of significant market volatility. Users receive notifications and warnings as their positions approach dangerous territory, providing opportunities to add collateral before liquidation occurs.
Synthetic Minting vs Traditional Asset Tokenization
Understanding the distinction between Synthetic Minting in DeFi and traditional asset tokenization clarifies the unique value proposition and mechanics of synthetic assets within decentralized finance ecosystems. While both approaches aim to represent real world assets on blockchain networks, they employ fundamentally different mechanisms and offer distinct advantages and limitations.
| Aspect | Synthetic Minting | Traditional Tokenization |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Backing | Backed by cryptocurrency collateral | Backed by actual underlying assets in custody |
| Creation Process | Algorithmic minting through smart contracts | Requires asset acquisition and legal wrapper |
| Accessibility | Permissionless and globally accessible | Often restricted by jurisdiction and regulations |
| Capital Requirements | Only requires cryptocurrency collateral | Requires purchase of underlying assets |
| Counterparty Risk | Protocol risk but no custodian dependency | Depends on custodian and issuer reliability |
| Regulatory Status | Evolving and uncertain framework | More established regulatory pathways |
Traditional asset tokenization involves creating blockchain representations of physical or financial assets held in custody by trusted entities. This approach requires legal frameworks, custodial arrangements, and often regulatory approval before tokens can be issued. While this provides a more direct claim on underlying assets, it introduces centralization risks and geographic limitations that contradict the permissionless ethos of decentralized finance.
DeFi Synthetic Minting circumvents these limitations by creating derivative instruments that track asset prices without requiring direct ownership or custody. This approach enables truly global access and removes dependencies on centralized custodians, though it introduces different risk factors related to collateralization mechanisms and oracle reliability. The synthetic approach proves particularly valuable for assets that face significant regulatory barriers to tokenization or where custody arrangements would be impractical.
Popular DeFi Protocols Supporting Synthetic Minting
Several pioneering protocols have established themselves as leaders in the Synthetic Minting in DeFi space, each implementing unique approaches to synthetic asset creation and management. These platforms have collectively processed billions of dollars in synthetic asset transactions and demonstrated the viability of decentralized synthetic asset systems.
Synthetix represents one of the earliest and most influential protocols in the synthetic asset space, enabling users to mint synthetic versions of cryptocurrencies, commodities, fiat currencies, and indices. The platform utilizes its native SNX token as collateral with a high collateralization ratio to ensure system security. Users who stake SNX to mint synthetic assets earn trading fees from the platform’s exchange, creating economic incentives for providing system collateral.
Mirror Protocol brought synthetic stocks to the blockchain, allowing users to gain exposure to traditional equities through synthetic representations. The platform employs a different collateral model that accepts multiple assets and implements unique liquidation mechanisms designed to maintain price pegs during volatile market conditions. This innovation demonstrated how DeFi Synthetic Minting could extend beyond crypto native assets to encompass traditional financial instruments.
Other notable protocols have emerged with specialized focuses including synthetic commodity markets, algorithmic stablecoin systems that utilize synthetic assets, and cross chain synthetic asset platforms that enable synthetic minting across multiple blockchain networks. This diversity of approaches reflects the ongoing innovation within the defi application development community as developers explore new mechanisms and use cases for synthetic assets.
Use Cases of Synthetic Minting in DeFi Ecosystems
The applications of Synthetic Minting in DeFi extend far beyond simple asset representation, enabling sophisticated financial strategies and use cases that were previously impossible within purely decentralized systems. These use cases demonstrate the transformative potential of synthetic assets for global finance and investment strategies.
Portfolio diversification represents a primary use case as investors leverage synthetic assets to gain exposure to multiple asset classes without leaving the cryptocurrency ecosystem. A trader holding Ethereum can mint synthetic gold, synthetic stock indices, and synthetic foreign currencies simultaneously, creating a diversified portfolio while maintaining their original ETH position. This capability dramatically expands the investment options available to cryptocurrency holders.
Hedging strategies become more accessible through DeFi Synthetic Minting as users can create offsetting positions to protect against market downturns. Cryptocurrency investors concerned about potential price declines can mint synthetic inverse tokens that gain value as the market falls, effectively hedging their exposure without selling their holdings. This mechanism provides risk management tools comparable to traditional derivatives markets.
Cross border trading and remittances benefit from synthetic fiat currencies that enable seamless currency exchange without traditional banking intermediaries. Users in countries with capital controls or limited access to foreign exchange markets can utilize synthetic assets to gain exposure to stable currencies or conduct international transactions. The permissionless nature of these systems removes barriers that prevent many individuals from participating in global commerce.
Yield generation strategies combine synthetic assets with other DeFi protocols to create complex income producing positions. Users might mint synthetic assets and provide liquidity on decentralized exchanges, stake synthetic tokens in yield farming protocols, or utilize synthetic assets as collateral for additional borrowing. The composability of DeFi Synthetic Minting with other protocols unlocks numerous possibilities for capital optimization.
Benefits of Synthetic Minting for DeFi Users
The advantages offered by Synthetic Minting in DeFi create compelling value propositions for users seeking to maximize their participation in decentralized finance while accessing diverse asset classes. These benefits address fundamental limitations of traditional financial systems and expand the possibilities available to cryptocurrency holders.
Capital efficiency stands out as a primary benefit as users can maintain their original cryptocurrency positions while gaining exposure to additional assets through synthetic minting. Unlike traditional investment approaches that require selling one asset to purchase another, synthetic minting enables simultaneous exposure to multiple markets. This efficiency allows sophisticated investors to maximize their capital utilization and construct complex portfolio strategies.
Global accessibility removes geographic barriers that restrict participation in traditional financial markets. Users anywhere in the world with internet access can mint synthetic assets representing stocks, commodities, or currencies from any market without requiring brokerage accounts, meeting minimum capital requirements, or navigating complex regulatory frameworks. This democratization of access represents a fundamental shift in how individuals can participate in global finance.
Twenty four hour trading availability through DeFi Synthetic Minting eliminates the time constraints imposed by traditional market hours. Synthetic assets can be minted, traded, and managed at any time, enabling users to respond immediately to global events regardless of when traditional markets are closed. This continuous accessibility provides significant advantages for risk management and opportunistic trading strategies.
Transparency and auditability inherent to blockchain systems provide users with complete visibility into protocol operations, collateralization levels, and transaction history. Every synthetic minting operation, liquidation event, and protocol parameter change can be verified on chain, creating unprecedented transparency compared to traditional financial systems where such information remains opaque or restricted to privileged participants.
Risks and Challenges in Synthetic Minting
Despite the numerous advantages, Synthetic Minting in DeFi involves significant risks that users must understand and evaluate before participating in these systems. Recognizing these challenges enables informed decision making and appropriate risk management strategies for synthetic asset positions.
Liquidation risk represents the most immediate danger for users who mint synthetic assets with insufficient safety margins. Market volatility can rapidly decrease collateralization ratios, triggering automated liquidation processes that close positions at unfavorable prices and impose liquidation penalties. Users must actively monitor their positions and maintain adequate collateral buffers to avoid these forced liquidations.
Smart contract vulnerabilities pose existential risks to synthetic asset protocols as exploits can drain collateral pools or manipulate minting mechanisms. While leading protocols undergo extensive auditing and maintain bug bounty programs, the complexity of DeFi Synthetic Minting systems creates surfaces for potential attacks. Historical incidents have demonstrated how smart contract exploits can result in significant user losses despite security precautions.
Oracle failures or manipulation attempts can cause synthetic assets to track incorrect prices, leading to inappropriate liquidations or arbitrage opportunities that drain protocol value. The dependency on external price feeds creates a critical vulnerability that attackers might exploit through flash loan attacks or by manipulating source exchanges during periods of low liquidity. Protocols implement various safeguards but cannot entirely eliminate oracle related risks.
Regulatory uncertainty surrounding synthetic assets creates compliance risks for both protocols and users. Authorities in various jurisdictions are developing frameworks to address DeFi Synthetic Minting but current regulations remain unclear or conflicting. Users may face unexpected legal obligations or restrictions as regulatory approaches evolve, particularly regarding synthetic assets that track securities or other regulated instruments.
Security Considerations in Synthetic Asset Protocols
Ensuring robust security measures represents a paramount concern for protocols implementing Synthetic Minting in DeFi functionality. The high value locked in these systems and their complex technical architecture necessitate comprehensive security approaches that address multiple attack vectors and failure modes.
Multi layered auditing processes form the foundation of security for synthetic asset protocols, with leading platforms engaging multiple independent security firms to review smart contract code before deployment. These audits identify potential vulnerabilities in minting logic, collateralization calculations, liquidation mechanisms, and access control systems. Continuous auditing throughout protocol upgrades ensures that new features do not introduce security regressions.
Formal verification techniques provide mathematical proofs that smart contracts behave according to their specifications under all possible conditions. This rigorous approach catches edge cases and logical errors that traditional auditing might miss. Protocols investing in formal verification demonstrate commitment to security that goes beyond standard industry practices for defi application development.
Emergency response mechanisms enable protocols to pause operations or implement protective measures when threats are detected. These systems balance security needs against decentralization principles, typically requiring multi signature approvals from protocol governance or security councils before executing emergency actions. Clear communication channels ensure users stay informed during security incidents.
Insurance mechanisms and reserve funds provide additional protection layers for DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols. Some platforms maintain treasury reserves specifically allocated for covering losses from security incidents, while others integrate with decentralized insurance protocols that offer coverage for smart contract exploits. These financial safeguards demonstrate protocol commitment to user protection beyond technical security measures.
Regulatory Implications of Synthetic Minting in DeFi
The regulatory landscape surrounding Synthetic Minting in DeFi continues evolving as authorities worldwide grapple with how to classify and oversee these novel financial instruments. Understanding regulatory considerations helps users and developers navigate compliance requirements while participating in synthetic asset ecosystems.
Securities classification represents a primary regulatory concern as synthetic assets that track stocks or other securities may themselves be considered securities under various jurisdictions. This classification would subject protocols and users to securities regulations including registration requirements, trading restrictions, and disclosure obligations. The decentralized nature of DeFi Synthetic Minting complicates enforcement of traditional securities frameworks designed for centralized intermediaries.
Anti money laundering and know your customer regulations pose challenges for permissionless synthetic asset protocols. Traditional financial regulations require customer identification and transaction monitoring to prevent illicit activities, but implementing these requirements contradicts the open access philosophy of decentralized finance. Some protocols explore decentralized identity solutions or tiered access models that balance regulatory compliance with accessibility.
Tax implications of synthetic asset transactions vary significantly across jurisdictions and remain unclear in many cases. Users may face capital gains obligations when minting or burning synthetic assets, trading them, or receiving rewards from protocol participation. The complexity of tracking tax basis and calculating gains across multiple transactions and protocols creates significant compliance burdens for synthetic asset users.
Cross border regulatory coordination becomes essential as DeFi Synthetic Minting operates globally without regard for national boundaries. Inconsistent regulations across jurisdictions create uncertainty for protocol developers and users while potentially enabling regulatory arbitrage. International cooperation on DeFi regulation could provide clarity but risks imposing restrictions that limit innovation in synthetic asset development.
Synthetic Minting and Capital Efficiency
The capital efficiency enabled by Synthetic Minting in DeFi represents one of its most transformative characteristics, allowing users to maximize the productive use of their cryptocurrency holdings. This efficiency manifests through various mechanisms that enable simultaneous participation in multiple markets and strategies without fragmenting capital across separate positions.
Leveraged exposure through synthetic minting enables users to amplify their market participation beyond what their capital would otherwise permit. By using cryptocurrency as collateral to mint synthetic assets worth a fraction of the collateral value, users effectively create leveraged positions that magnify both gains and losses. This capability must be managed carefully as excessive leverage increases liquidation risks during market volatility.
Multi market participation becomes possible as users maintain their original cryptocurrency holdings while gaining exposure to synthetic representations of other assets. A holder of Ethereum who believes both in ETH appreciation and wants exposure to gold prices can mint synthetic gold without selling their ETH position. This simultaneous participation across markets was previously impossible without dividing capital or using complex derivative strategies.
Collateral recycling represents an advanced strategy where synthetic assets themselves serve as collateral for additional minting or borrowing operations. Some DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols allow users to deposit synthetic assets as collateral to mint other synthetic assets, creating recursive leverage opportunities. While powerful, these strategies require careful risk management as they compound liquidation risks across multiple layers.
Yield optimization strategies combine synthetic asset positions with lending protocols, liquidity provision, and staking mechanisms to generate returns from multiple sources simultaneously. Users might mint synthetic stablecoins and deposit them into yield farming protocols while maintaining their original collateral exposure and earning additional rewards from the minting protocol itself. This composability creates unique opportunities for capital efficiency unmatched in traditional finance.
Future Trends in Synthetic Minting and DeFi Innovation
The evolution of Synthetic Minting in DeFi continues accelerating as developers explore new mechanisms, expand asset coverage, and integrate synthetic assets more deeply into the broader decentralized finance ecosystem. Several emerging trends point toward the future direction of synthetic asset protocols[1] and their role in global finance.
Cross chain synthetic assets represent a major development frontier as protocols work to enable synthetic minting and trading across multiple blockchain networks. This interoperability would allow users to mint synthetic assets on one chain using collateral from another, dramatically expanding the liquidity and accessibility of synthetic asset markets. Bridge protocols and layer two scaling solutions play crucial roles in enabling this cross chain functionality.
Expanded asset coverage continues as protocols add synthetic representations of increasingly diverse and exotic instruments. Beyond traditional stocks and commodities, emerging synthetic assets include carbon credits, real estate indices, insurance products, and prediction market outcomes. This expansion transforms DeFi Synthetic Minting into a universal interface for accessing virtually any quantifiable asset or market.
Improved oracle technologies promise to enhance the accuracy and security of price feeds that underpin synthetic asset valuations. Innovations including zero knowledge proofs for oracle data, decentralized validator networks, and machine learning based anomaly detection systems will reduce manipulation risks and improve the reliability of DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols. These advancements address one of the primary risk factors limiting broader adoption of synthetic assets.
Integration with traditional finance through compliant synthetic asset offerings could bridge DeFi and conventional markets. Some protocols explore regulatory compliant approaches that implement identity verification and transaction monitoring while maintaining many benefits of decentralized systems. This hybrid approach might accelerate institutional adoption of synthetic assets and increase total value locked in DeFi Synthetic Minting protocols.
Algorithmic improvements in collateral management and liquidation mechanisms will enhance capital efficiency and reduce risks for synthetic asset users. Research into dynamic collateralization ratios that adjust based on market conditions, improved liquidation algorithms that minimize impact on users, and novel collateral types including non fungible tokens and real world assets continues advancing the technical capabilities of synthetic minting systems.
The Growing Importance of Synthetic Minting in DeFi
As decentralized finance matures and attracts increasing participation from both retail users and institutional investors, Synthetic Minting in DeFi emerges as a cornerstone technology enabling the next phase of financial system evolution. The ability to create and trade synthetic representations of any asset within permissionless, transparent systems fundamentally challenges traditional financial intermediation and market access restrictions.
The total value locked in synthetic asset protocols has grown substantially as users recognize the advantages of capital efficient market participation and global accessibility. This growth reflects broader DeFi adoption trends while demonstrating specific demand for the unique capabilities that DeFi Synthetic Minting provides. As protocols mature and security track records strengthen, institutional interest in synthetic assets continues increasing.
Educational initiatives and improved user interfaces are making synthetic assets more accessible to mainstream users who lack deep technical knowledge of blockchain systems. Simplified minting flows, clear risk disclosures, and integrated portfolio management tools help users understand and effectively utilize synthetic asset capabilities. This accessibility expansion drives adoption beyond early cryptocurrency enthusiasts toward broader market participation.
The composability of synthetic assets with other DeFi protocols creates network effects that amplify their utility and importance within the ecosystem. As more protocols accept synthetic assets as collateral, trading pairs, or yield bearing instruments, the value proposition of minting these assets strengthens. This positive feedback loop contributes to the growing centrality of Synthetic Minting in DeFi infrastructure.
Take Your DeFi Knowledge to the Next Level
Learn how Synthetic Minting in DeFi works and start participating in global financial markets without intermediaries or restrictions.
With over 8 years of specialized experience in blockchain development and DeFi protocol implementation, Nadcab Labs stands as a leading authority in synthetic asset systems and defi application development. Our team has successfully delivered numerous complex DeFi projects incorporating advanced synthetic minting mechanisms, oracle integration, and sophisticated collateral management systems.
Our expertise encompasses the complete spectrum of DeFi Synthetic Minting development including smart contract architecture design, security auditing, oracle network integration, liquidation engine implementation, and governance system deployment. We understand the intricate balance between capital efficiency, system security, and user experience that defines successful synthetic asset protocols.
The team has demonstrated proficiency across multiple blockchain networks and has helped clients navigate the complex regulatory considerations surrounding synthetic assets. Our portfolio includes work with leading DeFi protocols, institutional clients exploring synthetic asset integration, and innovative startups building next generation financial infrastructure.
We provide comprehensive services covering initial protocol design, technical architecture development, smart contract coding and testing, security auditing, deployment support, and ongoing maintenance. Our methodical approach ensures that synthetic minting implementations achieve optimal security while delivering the capital efficiency and accessibility that users demand.
Whether you are launching a new synthetic asset protocol, integrating DeFi Synthetic Minting capabilities into an existing platform, or seeking to optimize current implementations, Nadcab Labs brings the technical expertise and industry experience necessary to realize your vision. Our commitment to excellence in blockchain development and deep understanding of decentralized finance positions us as the ideal partner for your synthetic asset initiatives.
FAQs: Synthetic Minting in DeFi
Synthetic assets maintain price pegs through arbitrage mechanisms and oracle price feeds. When a synthetic asset trades above its reference price, arbitrageurs can mint new tokens using collateral and sell them for profit, increasing supply and pushing prices down. When trading below the peg, users can buy discounted synthetic assets and burn them to reclaim collateral at the reference price. Decentralized oracles continuously update reference prices to reflect real world asset values, ensuring synthetic assets track their targets accurately.
Cross chain synthetic asset usage is emerging through bridge protocols and layer two solutions that enable interoperability between different blockchain networks. Some synthetic minting protocols deploy on multiple chains simultaneously, while others utilize wrapped tokens or bridge mechanisms to transfer synthetic assets between networks. However, cross chain functionality introduces additional complexity and security considerations including bridge risks and liquidity fragmentation across different networks.
Oracle failures represent significant risks for synthetic minting protocols. Leading platforms implement multiple safeguards including aggregating data from numerous oracle sources, using median price calculations to filter outliers, implementing circuit breakers that pause operations during extreme price anomalies, and maintaining insurance funds to cover losses from oracle related incidents. Some protocols also utilize time weighted average prices to smooth out temporary price spikes that might trigger inappropriate liquidations.
Synthetic minting protocols typically do not impose minimum capital requirements beyond what is necessary to cover transaction fees and minimum collateralization ratios. Users can theoretically mint very small amounts of synthetic assets as long as they provide sufficient collateral and can pay network transaction fees. However, gas costs on certain blockchains may make extremely small positions economically inefficient as transaction fees could exceed the value of minted assets.
Liquidation mechanisms automatically close undercollateralized positions before they threaten protocol solvency. When a position’s collateralization ratio falls below the minimum threshold, liquidation bots or protocol participants can trigger liquidation events that sell collateral to cover the synthetic asset debt. Users whose positions are liquidated typically pay penalty fees that compensate liquidators and discourage excessive leverage. These mechanisms ensure that synthetic assets remain fully backed even during severe market volatility.
Collateralized synthetic assets require users to lock cryptocurrency as backing for minted tokens, ensuring that synthetic assets always have underlying value supporting them. Algorithmic synthetic assets attempt to maintain pegs through supply adjustments and economic incentives without full collateral backing. Collateralized approaches provide greater security but require capital lockup, while algorithmic methods offer capital efficiency at the cost of increased risk during market stress when maintaining pegs becomes challenging.
Traditional financial institutions face regulatory and compliance challenges when participating in permissionless synthetic asset markets. Some institutions explore participation through compliant DeFi platforms that implement identity verification and transaction monitoring. Others invest in synthetic asset protocols indirectly through venture capital or establish partnerships with blockchain firms. Regulatory clarity and institutional grade custody solutions will likely drive increased traditional finance participation in synthetic minting ecosystems.
Governance systems enable token holders to vote on critical protocol parameters including acceptable collateral types, minimum collateralization ratios, liquidation penalties, and fee structures. These decentralized governance mechanisms ensure that protocols can adapt to changing market conditions and user needs without centralized control. Effective governance requires active community participation and careful balance between responsiveness to threats and maintaining stability for existing users.
Decentralized exchanges provide crucial liquidity infrastructure for trading synthetic assets and enable price discovery through automated market makers. Many synthetic minting protocols integrate directly with DEX platforms or operate their own exchange mechanisms. Deep liquidity on DEX platforms helps maintain synthetic asset pegs by facilitating arbitrage opportunities and enabling users to easily enter or exit positions without significant price impact.
Users can mitigate smart contract risks by researching protocol audit histories, starting with small positions to test functionality, diversifying across multiple protocols rather than concentrating in single platforms, utilizing protocols with established track records and substantial total value locked, monitoring community channels for security updates, and considering insurance products that cover smart contract exploits. Understanding that no DeFi protocol is entirely risk free helps users make informed decisions about position sizing and risk exposure.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







