Key Takeaways: Smart Contract Transactions
- Blockchain validation is the backbone: Every smart contract transaction follows predefined rules before execution.
- No middlemen are required: The blockchain itself verifies, approves, or rejects transactions automatically.
- Multiple checks ensure correctness: Transactions are checked for wallet validity, balance, transaction format, and smart contract logic.
- Consensus ensures trust: Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) ensures that the majority of nodes agree on transaction validity, preventing fraud or manipulation.
- Failed validations protect users: Invalid transactions are stopped before any funds or data are changed.
- Transactions become immutable: Once validated and added to a block, transactions cannot be altered or deleted.
- Transparency and trust: Anyone can verify smart contract transactions on the blockchain.
- Real-world use cases rely on validation: DeFi lending, NFTs, and token transfers operate securely and fairly thanks to validation.
- Reliability and predictability: Blockchain validation makes smart contracts dependable for financial and real-world applications.
Smart contracts are digital agreements that work on blockchain technology. They run automatically and do not need banks lawyers or middlemen. But for smart contracts to work safely every transaction must be checked properly. This checking process is called blockchain validation.
Blockchain validation makes sure that smart contract transactions follow all the rules written in the code. Before any action happens such as sending money transferring tokens or approving a deal the blockchain checks everything. If something is wrong the transaction is stopped.
This process keeps smart contracts safe, fair and trustworthy. It helps avoid fraud, mistakes and unfair actions. In this content you will learn how blockchain validates smart contract transactions step by step in simple and easy language.
Why Validation Matters in Smart Contract Transactions
Validation is important because smart contracts operate without middlemen. There is no bank, lawyer, or central authority to review or approve transactions. Instead, the blockchain itself checks and verifies every action. This automatic verification ensures that smart contracts run safely and fairly for everyone involved.
Blockchain validation makes sure that only genuine and rule-following transactions are processed. Every transaction is checked against predefined conditions written inside the smart contract. If those conditions are not met, the transaction is rejected immediately. This protects the system from misuse and errors.
Why validation matters in smart contract transactions:
- Prevents fraud: Invalid or fake transactions are stopped before they reach the blockchain.
- Ensures accuracy: Smart contracts execute exactly as programmed, without changes.
- Builds trust: Participants can trust outcomes without knowing or relying on each other.
- Protects funds: Malicious actions are automatically blocked by the network.
- Maintains decentralization: No single authority controls decisions or approvals.
Without validation, smart contracts could be manipulated, leading to financial loss and system failure. Validation is what makes smart contracts secure, reliable, and trustworthy in a decentralized environment.
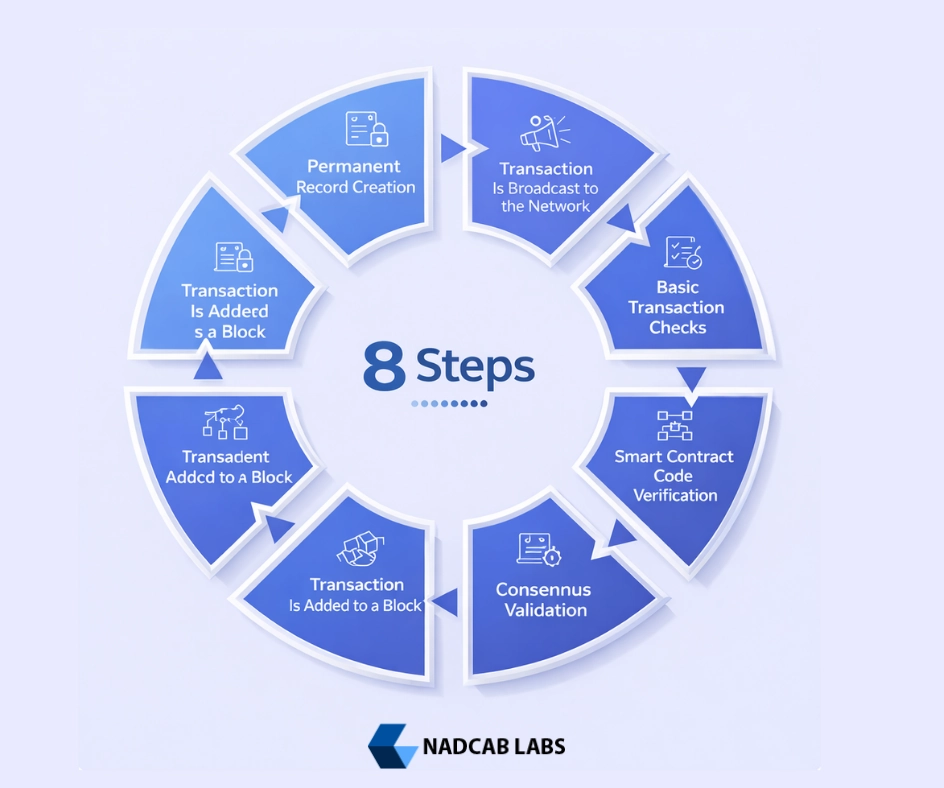
Step-by-Step: How Blockchain Validates Smart Contract Transactions
Blockchain validation is the process that checks whether a smart contract transactions is correct before it becomes part of the blockchain. Since smart contracts work without banks or middlemen, this validation process is extremely important. It ensures that every action follows the rules written inside the smart contract and that no fake or wrong transaction enters the network.
Let’s understand this complete process step by step in simple language.
Step 1: Transaction Is Created
The blockchain validation process starts when a user interacts with a smart contract. This interaction can be anything the smart contract allows, such as:
- Sending tokens to another wallet
- Minting an NFT
- Approving a token transfer
- Calling a function in the contract
When the user performs any of these actions, a smart contract transaction request is created. This request contains important details like the sender’s wallet address, the smart contract’s address, the function being called, and any input data required for execution.
At this stage, the transaction is not yet confirmed. According to Economic Times News, it is only a request waiting to be verified by the blockchain network.
Key points:
- Transaction starts when the user interacts with a smart contract
- Contains all necessary details for execution
- Not yet validated or added to the blockchain
This step is essential because it clearly defines what the smart contract should do once processed.
Step 2: Transaction Is Broadcast to the Network
After a transaction is created, it is sent out to the blockchain network. This process is called broadcasting. Broadcasting allows many computers in the network to receive and check the transaction.
The blockchain network is made up of many computers called nodes. These nodes are located all over the world and work together to maintain the blockchain. No single node controls the system, which makes it decentralized and secure.
When a transaction is broadcast:
- Multiple nodes receive the transaction simultaneously
- Each node prepares to verify it independently
- Nodes do not rely on any central authority
Key points:
- Broadcasting shares the transaction with the entire network
- Every node participates in validation
- Decentralization increases trust and security
This step ensures that the transaction is visible to the network, ready for validation, and cannot be manipulated by any single party.
Step 3: Basic Transaction Checks
Before a smart contract can run, the blockchain nodes perform basic transaction checks. These checks make sure that the smart contract transaction is valid and correctly formed. They act as the first line of defense against errors, fake transactions, or spam.
During this stage, nodes verify:
- Wallet address check: Is the sender’s wallet address real and properly formatted?
- Balance check: Does the sender have enough cryptocurrency to pay for gas fees and send tokens?
- Transaction format check: Is the transaction structured according to blockchain rules?
Key points:
- Invalid transactions are rejected immediately
- Rejected transactions do not move forward
- They never reach the blockchain
These checks are important because they prevent broken or fake transactions from using network resources. Only transactions that pass these basic checks move on to the next stage, where the smart contract logic is verified. This keeps the blockchain safe and efficient.
Step 4: Smart Contract Code Verification
After a transaction passes the basic checks, the blockchain nodes start verifying the smart contract logic. Every smart contract has rules written in its code, and nodes make sure the smart contract transaction follows all these rules.
During this verification, nodes check:
- Is the function being called available in the smart contract?
- Are the input values correct and within allowed limits?
- Are all conditions required for execution satisfied?
For example, if a smart contract requires a minimum balance or a special permission, the transaction must meet those requirements.
Key points:
- Nodes strictly follow contract rules
- Incorrect inputs or unmet conditions stop execution
- Failed transactions do not change the blockchain
- Only valid actions are executed
If any rule is not met, the transaction fails, and the smart contract does not run. This step ensures that smart contracts behave exactly as programmed and remain secure.
Step 5: Consensus Validation
After a transaction passes the smart contract rules, it moves to the consensus phase. This is the stage where the blockchain network agrees whether the transaction is valid or not. Consensus ensures that no single person or computer can cheat the system.
Different blockchains use different methods to reach consensus. The most common are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Nodes solve complex puzzles to confirm transactions.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Nodes are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold.
During this stage:
- Multiple nodes check the transaction independently
- They compare their results with each other
- Most nodes must agree for the transaction to be approved
Key points:
- Ensures network-wide agreement
- Prevents fraud and manipulation
- Maintains decentralization and trust
If the majority of nodes agree, the smart contract transaction moves forward. If not, it is rejected, keeping the blockchain secure and reliable.
Step 6: Execution of Smart Contract
After the transaction is validated and approved by the network, the smart contract executes automatically. This means the blockchain performs all the actions written in the smart contract without any human intervention.
The execution is precise and follows exactly what the code specifies. No one can change or stop it once validation is complete. This makes smart contracts trustworthy and reliable because the results are predictable and tamper-proof.
Key points:
- Smart contract runs automatically
- Actions follow the written code exactly
- No one can alter or stop the process
- Execution is final and irreversible
Some common actions during execution include transferring funds between wallets, updating stored data, minting or burning tokens, and triggering other smart contracts. Automatic execution reduces delays, removes middlemen, and ensures the smart contract works safely and efficiently for all users.
Step 7: Transaction Is Added to a Block
After a smart contract is executed and validated, the transaction does not immediately become permanent. First, it is grouped with other approved transactions. These grouped transactions form a new block that will be added to the blockchain.
Each block contains important details like smart contract transaction data, timestamps, and cryptographic links that connect it to the previous block. These links ensure that all blocks are connected in a secure and unchangeable chain.
Key points:
- Validated transactions are grouped into a block
- Each block is linked to the previous block
- Blocks are added sequentially to the blockchain
- Cryptographic links make the chain tamper-resistant
This step is crucial because it maintains the order and security of transactions. Once added, the block becomes part of the blockchain, ensuring all data is permanent, transparent, and safe from tampering.
Step 8: Permanent Record Creation
Once a transaction is added to a block, it becomes a permanent part of the blockchain. This means that the transaction cannot be changed, deleted, or reversed. Whatever happened in the transaction is recorded forever in the blockchain.
This permanent record is called immutability. Immutability makes the blockchain highly secure because no one can alter past transactions. It also ensures that smart contracts execute exactly as intended, without any manipulation.
Key points:
- The transaction cannot be changed
- The transaction cannot be deleted
- Anyone can verify it at any time
This transparency builds trust among all users. Everyone on the network can see the transaction history and confirm that smart contracts worked correctly. Because of this permanent record, blockchain becomes a reliable system for finance, supply chain, NFTs, DeFi, and many other applications.
Make Sure Your Smart Contract Transactions Are Safe and Correct
Nadcab Labs helps businesses and developers check every smart contract transaction on the blockchain, so it works automatically, safely, and exactly as it should.
What Happens If Validation Fails?
If validation fails, it means the blockchain has found a problem with the transaction or smart contract. When this happens, the transaction is rejected and does not go through.
Some common reasons validation can fail are:
- The user doesn’t have enough balance to pay fees or tokens.
- The smart contract conditions are not met.
- The inputs or data provided are incorrect.
- Security checks detect something suspicious or malicious.
- There is an error in the smart contract code.
When a transaction fails:
- The smart contract does not execute.
- No money or tokens are transferred.
- The blockchain remains unchanged, keeping the system safe.
- Sometimes, a small fee (gas fee) may still be charged for attempting the smart contract transaction.
Validation failure is important because it prevents mistakes and fraud. It protects users’ funds, ensures that rules are followed, and keeps the blockchain secure.
In short, if validation fails, the transaction stops automatically, and nothing wrong is added to the blockchain. It’s the blockchain’s way of keeping everything safe and fair.
Real-Life Example of Blockchain Validation
Example: Lending Money on a DeFi Platform
Imagine you want to take a loan using a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform. The platform uses a smart contract to manage the loan automatically.
- You request a loan: You provide some cryptocurrency as collateral.
- Smart contract checks rules: The contract looks at its conditions, like whether your collateral is enough or if your account meets the platform’s rules.
- Blockchain validation happens: Multiple nodes (computers) on the blockchain verify that all the conditions are correct. They check your balance, the contract rules, and the smart contract transaction format.
- Decision is made:
- If all rules are met, the loan is approved, and funds are sent to your account automatically.
- If any condition fails, the transaction is rejected, and no funds are transferred.
This entire process happens without a bank, lawyer, or middleman. According to Ultimaco Blog, Blockchain validation ensures that only valid, safe, and rule-following transactions succeed.
Note: Blockchain validation in smart contracts makes digital transactions secure, automatic, and trustworthy in real life, just like this loan example.
Final Words
Blockchain validation is very important for smart contracts. It checks every smart contract transaction before it becomes part of the blockchain. This makes sure that only correct and genuine transactions are completed.
When validation is done properly smart contracts work exactly as written. Funds stay safe, rules are followed and no one can change the results. Users do not need to trust each other because the blockchain itself handles everything.
In simple words blockchain validation makes smart contracts reliable and secure. It protects users, builds trust and keeps the system decentralized. That is why validation is the main reason smart contracts are used in finance, DeFi, NFTs and many real world applications.
Frequently Asked Questions - Smart Contract Transactions
A smart contract transactions is an action on the blockchain that interacts with a smart contract. It can be sending tokens, minting NFTs, approving transfers, or calling a function in the contract. Each smart contract transaction contains instructions for the smart contract, telling it what to do automatically without needing banks, lawyers, or other middlemen.
Blockchain nodes, also called validators or miners, validate smart contract transactions. These are independent computers in the network that check every smart contract transaction. They verify that the sender is genuine, the rules of the smart contract are followed, and everything is correct. No central authority like a bank or lawyer is needed.
During validation, nodes check key details of a transaction. They verify the sender’s wallet address, digital signature, available balance, transaction format, gas fees, and whether all smart contract conditions are met. Only if all these checks pass does the transaction move forward, keeping the blockchain safe and secure from fraud or mistakes.
Validation is necessary because smart contracts work automatically without middlemen. It ensures that only real and correct transactions are executed. This protects users from fraud, mistakes, or rule-breaking actions. Without validation, smart contracts could be manipulated, money could be lost, and the system would not be safe or trustworthy.
If a smart contract transaction fails validation, it is rejected immediately. The smart contract does not execute, no funds are sent, and the blockchain stays safe. Sometimes, a small gas fee may still be charged for the attempt. Validation failure stops mistakes or fraud, protecting both the system and the users’ money.
The basic idea of validation is the same on all blockchains: checking transactions before execution. However, the process can differ depending on the blockchain’s design, consensus system (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake), and virtual machine. Every blockchain may handle validation slightly differently, but the goal is always safety and accuracy.
The time for validation depends on the blockchain network, congestion, and transaction fees. Some networks confirm smart contract transactions in a few seconds, while others may take a few minutes. Faster networks or higher fees usually make validation quicker. Once validated, the transaction is executed safely and permanently on the blockchain.
Blockchain validation is crucial for DeFi and NFTs because it ensures all smart contract transactions are secure and follow smart contract rules. Loans, token swaps, or NFT ownership transfers happen automatically and safely. Validation prevents mistakes, fraud, or manipulation, building trust among users without requiring banks, lawyers, or other middlemen.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







