💡 Key Takeaways Smart Contracts in NFT Marketplaces
- ✓Smart contracts are the core foundation of NFT marketplaces, enabling decentralized ownership, automated transactions, and transparent trading without intermediaries.
- ✓NFT marketplaces rely on smart contracts for minting, ownership tracking, trading logic, and royalty distribution, making them essential for trustless operations.
- ✓Standardized smart contracts such as ERC-721, ERC-1155, and EIP-2981 ensure interoperability, security, and compatibility across multiple NFT platforms.
- ✓Smart contracts execute atomic transactions, ensuring that payments and asset transfers either complete together or fail entirely—protecting both buyers and sellers.
- ✓Security is critical, as smart contract bugs are immutable and can result in permanent asset loss or platform failure if not audited properly.
- ✓NFT marketplace architecture places smart contracts as the execution layer, supported by frontend interfaces, backend indexing services, and decentralized storage.
- ✓While smart contracts operate on decentralized networks, marketplaces must still account for legal, compliance, and intellectual property considerations through hybrid on-chain and off-chain models.
- ✓Expert smart contract development reflects technical expertise, security awareness, and long-term scalability, directly impacting marketplace credibility and user trust.
- ✓As NFT ecosystems mature, smart contracts continue to evolve toward cross-chain compatibility, dynamic NFTs, and advanced automation, while remaining the single source of truth.
NFT marketplaces have become a cornerstone of the Web3 economy, enabling users to create, buy, sell, and trade unique digital assets without relying on centralized intermediaries. From digital art and music to in-game assets, intellectual property, and enterprise tokenization, NFT marketplaces are reshaping how ownership is defined in the digital world.
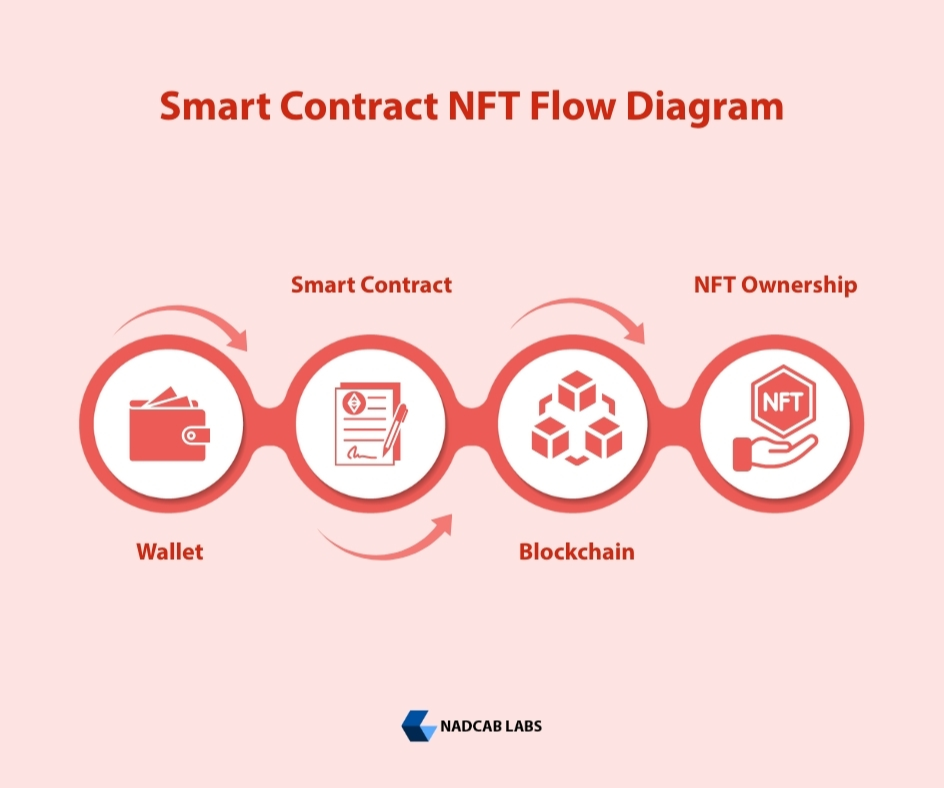
At the heart of every NFT marketplace lies a critical technological component: smart contracts. While users interact with sleek interfaces and wallets, the actual logic that governs minting, ownership transfer, royalties, and marketplace rules is executed by smart contracts deployed on the blockchain.
This bucket blog focuses exclusively on explaining smart contracts as a foundational concept in NFT marketplaces. It covers what smart contracts are, how they function, the roles they play, security considerations, and why they are essential before discussing advanced topics like scaling, monetization, or compliance.
What Are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a self-executing digital agreement written in code and deployed on a blockchain. Once deployed, it operates autonomously, executing predefined rules when specific conditions are met.
Unlike traditional contracts that require legal enforcement or intermediaries, smart contracts:
Execute automatically
Are transparent and verifiable
Cannot be modified once deployed
Remove the need for trust between parties
In NFT marketplaces, smart contracts replace centralized backend logic with decentralized, tamper-proof execution.
NFT marketplaces differ from traditional digital platforms because they handle real economic value and verifiable ownership. Centralized systems can be manipulated, censored, or altered—but blockchain-based smart contracts cannot.
Smart contracts ensure:
NFTs are truly unique and non-duplicable
Ownership history is immutable
Transactions are executed fairly and transparently
Creator royalties are enforced automatically
Without smart contracts, NFTs would lose their core properties of decentralization and trustlessness
Key Functions of Smart Contracts in NFT Marketplaces
NFT Minting Logic
Minting converts a digital file into an NFT. Smart contracts:
- Generate a unique token ID
- Assign ownership to a wallet address
- Reference metadata stored on decentralized storage
- This ensures that each NFT is verifiable and cannot be forged.
Ownership Management
Smart contracts maintain a permanent record of:
- Current owner
- Previous owners
- Transfer history
- This public ownership trail builds trust and provenance, especially for high-value NFTs.
Marketplace Trading Rules
NFT marketplace smart contracts define:
- Fixed-price sales
- Auction mechanisms
- Offer and bid logic
- All trades occur on-chain, ensuring no party can manipulate the transaction.
Royalty Enforcement
Smart contracts allow creators to earn royalties on secondary sales by automatically distributing a predefined percentage during every resale.
Permission & Access Control
Admin functions such as pausing contracts, upgrading systems, or approving collections are controlled via smart contract permissions.
Smart Contract Responsibilities at a Glance
| Function | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Minting | Create NFTs | Enables digital ownership |
| Transfers | Move assets | Facilitates trustless trading |
| Sales | Execute trades | Ensures fair transactions |
| Royalties | Reward creators | Promotes a sustainable economy |
| Access Control | Restrict actions | Enhances security |
NFT Smart Contract Standards Explained
NFT marketplaces rely on standardized smart contracts to ensure interoperability across platforms.
ERC-721
ERC-721 defines fully unique, non-fungible tokens. It is widely used for:
- Digital art
- Collectibles
- One-of-one assets
ERC-1155
ERC-1155 allows both fungible and non-fungible tokens in a single contract. It is ideal for:
- Gaming assets
- Semi-fungible items
- Batch minting
EIP-2981
This standard defines how royalties should be implemented at the contract level, improving consistency across marketplaces.
How Smart Contracts Enable Trustless NFT Transactions
Trustless systems do not require users to rely on intermediaries. Smart contracts enforce fairness by ensuring that:
- Payment is transferred only if ownership is transferred
- Royalties are paid automatically
- Failed transactions revert entirely
This atomic execution protects both buyers and sellers.
Smart Contracts vs Traditional Marketplace Logic
| Aspect | Traditional Marketplaces | NFT Marketplaces |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Centralized servers | Blockchain smart contracts |
| Trust Mechanism | Platform-dependent | Code-based |
| Transparency | Limited | Fully public |
| Ownership | Platform-controlled | User-owned |
This shift is what makes NFTs fundamentally different from Web2 platforms.
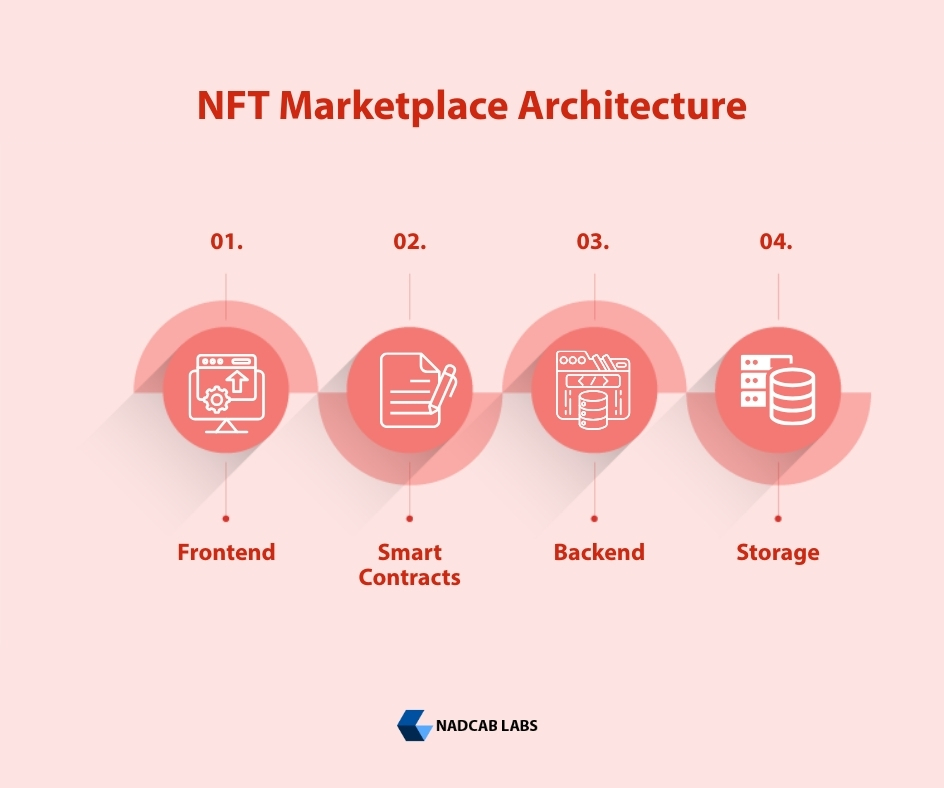
Role of Smart Contracts in NFT Marketplace Architecture
NFT marketplaces consist of multiple layers:
- Frontend (UI, wallet integration)
- Smart contracts (core logic)
- Backend services (indexing, analytics)
- Decentralized storage (IPFS, Arweave)
Smart contracts act as the execution layer, while other components support performance and usability.
Security Risks in NFT Smart Contracts
Because smart contracts are immutable, errors can have severe consequences.
Common Vulnerabilities
- Reentrancy attacks
- Improper access control
- Unchecked external calls
- Integer overflows
Security Best Practices
- Use audited libraries
- Limit contract complexity
- Conduct regular security audits
- Apply the principle of least privilege
- Security is not optional—it is foundational.
Compliance & Legal Awareness in Smart Contracts
While smart contracts operate on decentralized networks, NFT marketplaces must still consider:
- Intellectual property ownership
- Consumer protection laws
- Regulatory compliance
Many platforms combine on-chain smart contracts with off-chain compliance checks, ensuring flexibility without compromising decentralization.
EEAT Perspective: Why Expertise Matters
From an industry perspective, poorly designed smart contracts are the leading cause of NFT marketplace failures. Projects that skip audits or rely on inexperienced developers often face:
Contract exploits
User fund losses
Permanent reputational damage
Expert-built smart contracts demonstrate:
Technical competence
Security awareness
Long-term scalability planning
This is why foundational understanding matters before development begins.
Future of Smart Contracts in NFT Marketplaces
As NFT ecosystems mature, smart contracts are evolving to support:
Cross-chain NFT transfers
AI-assisted pricing logic
Upgradeable architectures
However, the core principle remains the same: smart contracts are the source of truth.
Build Secure NFT Marketplaces with Expert Smart Contract Development
Talk to our blockchain experts to build secure and scalable smart contracts
Final Thoughts
Smart contracts are the foundation of NFT marketplaces. They enable decentralized ownership, trustless transactions, automated royalties, and transparent trading. Without them, NFTs would lose their defining characteristics. Understanding smart contracts as a core concept is essential for anyone building, investing in, or using NFT marketplaces. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for exploring advanced topics like scalability, monetization, and regulatory compliance
Frequently Asked Questions
Smart contracts in NFT marketplaces are blockchain-based programs that define how NFTs are created, owned, and traded. At a basic level, they automate actions such as minting NFTs, transferring ownership, and processing payments. From a technical perspective, these contracts act as the single source of truth, ensuring that ownership data and transaction logic remain immutable and verifiable across the blockchain network.
Smart contracts are essential because they remove the need for intermediaries and establish trust through code rather than centralized authority. For beginners, this means safer and more transparent NFT transactions. For advanced users and developers, smart contracts ensure atomic execution, meaning that asset transfers and payments happen together, preventing partial or fraudulent transactions.
When an NFT is minted, the smart contract generates a unique token ID and assigns ownership to a specific wallet address. Ownership records are permanently stored on the blockchain, allowing anyone to verify authenticity and provenance. Technically, this is achieved using standardized token interfaces that track balances, ownership mappings, and transfer events in a transparent and auditable manner.
Yes, NFT marketplace smart contracts can be customized to include features such as custom royalty logic, auction mechanisms, platform fees, or restricted access controls. However, customization increases complexity and risk. From an advanced standpoint, developers must follow secure coding practices, use audited libraries, and perform rigorous testing to avoid vulnerabilities that could lead to irreversible asset loss.
Smart contracts automatically calculate and distribute royalties during every secondary sale of an NFT. For creators, this ensures recurring income without relying on marketplace operators. Technically, royalty enforcement is implemented using predefined percentage rules within the contract, often aligned with standards like EIP-2981 to improve compatibility across platforms.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







