Key Takeaways
- ▸Smart contracts automate identity verification reducing processing times from days to seconds while cutting operational costs by 70-85% through elimination of manual review processes across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
- ▸Decentralized identity architecture powered by smart contracts eliminates centralized honeypot databases containing billions of records vulnerable to breaches, improving security by distributing credentials across user-controlled wallets with cryptographic protection.
- ▸Verifiable credentials executed through smart contracts enable instant verification without contacting issuing authorities, operating 24/7 with 99.9% uptime compared to business-hours limitations of traditional centralized verification systems globally.
- ▸Privacy-preserving identity verification using zero-knowledge proofs allows users to prove attributes without revealing underlying data, complying with GDPR, CCPA, and privacy regulations while maintaining complete verification accuracy across jurisdictions.
- ▸Automated lifecycle management through smart contracts handles credential issuance, renewal, updates, and revocation without manual intervention, reducing administrative overhead by 60-75% while ensuring consistent policy enforcement and real-time compliance monitoring.
- ▸Cross-platform identity verification interoperability through standardized smart contract protocols enables credentials issued on one blockchain to be verified on others, reducing integration costs by 50-70% and eliminating vendor lock-in concerns.
- ▸Security audits for identity verification smart contracts cost $30,000-$150,000 but protect against vulnerabilities including replay attacks, unauthorized access, and credential theft, essential for production deployments handling sensitive personal information.
Introduction to Smart Contract-Based Identity Verification
Identity verification represents a critical infrastructure challenge affecting billions of transactions daily across financial services, healthcare, government, and digital commerce. With over eight years of experience implementing blockchain identity solutions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada, our agency has witnessed smart contracts revolutionize verification processes through automated enforcement, cryptographic security, and decentralized architecture. Traditional centralized systems suffer from data breaches affecting hundreds of millions of users annually, processing delays spanning days or weeks, and operational costs consuming 30-40% of verification budgets.
Smart contracts address these fundamental limitations by encoding verification rules into self-executing programs on blockchain networks, eliminating manual review bottlenecks while ensuring consistent, transparent, and auditable identity verification. These programmable contracts verify credentials cryptographically against predefined rules, execute instantly without business hour constraints, and provide immutable records of verification events. Leading implementations report 70-85% cost reductions, 95% faster processing times, and superior security compared to legacy systems serving global markets.
Evolution of Identity Verification Before Blockchain
Traditional identity verification evolved from paper-based documentation to centralized digital databases, yet fundamental architectural weaknesses persisted. Organizations maintain massive databases containing billions of personally identifiable information records, creating attractive targets for cybercriminals. The 2017 Equifax breach exposed 147 million records, 2019 Capital One breach affected 106 million customers, and 2021 T-Mobile breach compromised 54 million individuals. These centralized honeypots represent single points of failure where one successful attack yields massive credential theft affecting millions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian populations.
Secure Your Identity Verification with Smart Contracts
Get expert consulting on privacy-preserving identity verification, regulatory compliance, and automated lifecycle management. Professional audits and implementation support available.
Processing inefficiencies compounded security vulnerabilities as manual review workflows created delays spanning days or weeks. Identity verification for financial account opening requires 3-7 business days on average, background checks take 5-10 days, and credential verification across jurisdictions extends to 2-4 weeks. Organizations employ thousands of verification specialists reviewing documents manually, introducing human error rates of 5-15% and consuming substantial operational budgets. The combination of security risks, processing delays, and high costs necessitated fundamental architectural reimagining that smart contracts now provide.
Why Traditional Identity Systems Fail at Scale
Traditional identity verification systems encounter fundamental scalability limitations as transaction volumes increase and regulatory requirements expand. Centralized databases require expensive infrastructure maintaining availability, redundancy, and disaster recovery across global operations. Processing capacity constraints create bottlenecks during peak demand, while compliance with divergent regional regulations including GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and PIPEDA in Canada multiplies complexity. Interoperability challenges prevent seamless verification across platforms, jurisdictions, and service providers, forcing users to repeatedly submit identical credentials.
| Challenge Category | Traditional Systems | Smart Contract Solution | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | 3-7 days manual review | Seconds automated verification | 95% faster |
| Operational Cost | $15-$50 per verification | $2-$8 automated processing | 70-85% reduction |
| Security Vulnerability | Centralized database honeypots | Distributed user-controlled wallets | Eliminated single point |
| Error Rate | 5-15% human error | 0.1% cryptographic verification | 99% accuracy gain |
| Availability | Business hours 9-5 | 24/7 blockchain operation | 99.9% uptime |
Smart Contracts as Trustless Identity Enforcers
Smart contracts establish trustless identity verification through cryptographic enforcement of verification rules without requiring trust in centralized authorities. These self-executing programs verify digital signatures, validate credential expiration dates, check revocation status, and enforce access control policies automatically based on predefined logic. When a user presents a verifiable credential, the smart contract validates the issuer’s signature using public key cryptography, confirms the credential hasn’t been revoked by checking on-chain revocation registries, and verifies attribute values meet specified requirements without external intervention across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Decentralized Identity Architecture Powered by Smart Contracts
Decentralized identity verification architecture distributes credential storage and verification across blockchain networks rather than centralizing data in vulnerable databases. Users control credentials in personal wallets, issuers sign credentials with private keys, and smart contracts verify signatures using public keys without accessing underlying personal data. This architecture implements the W3C Decentralized Identifier (DID) specification and Verifiable Credentials standard, enabling interoperability across platforms and jurisdictions. The separation of credential storage from verification logic eliminates centralized honeypots while providing users complete control over personal information sharing.
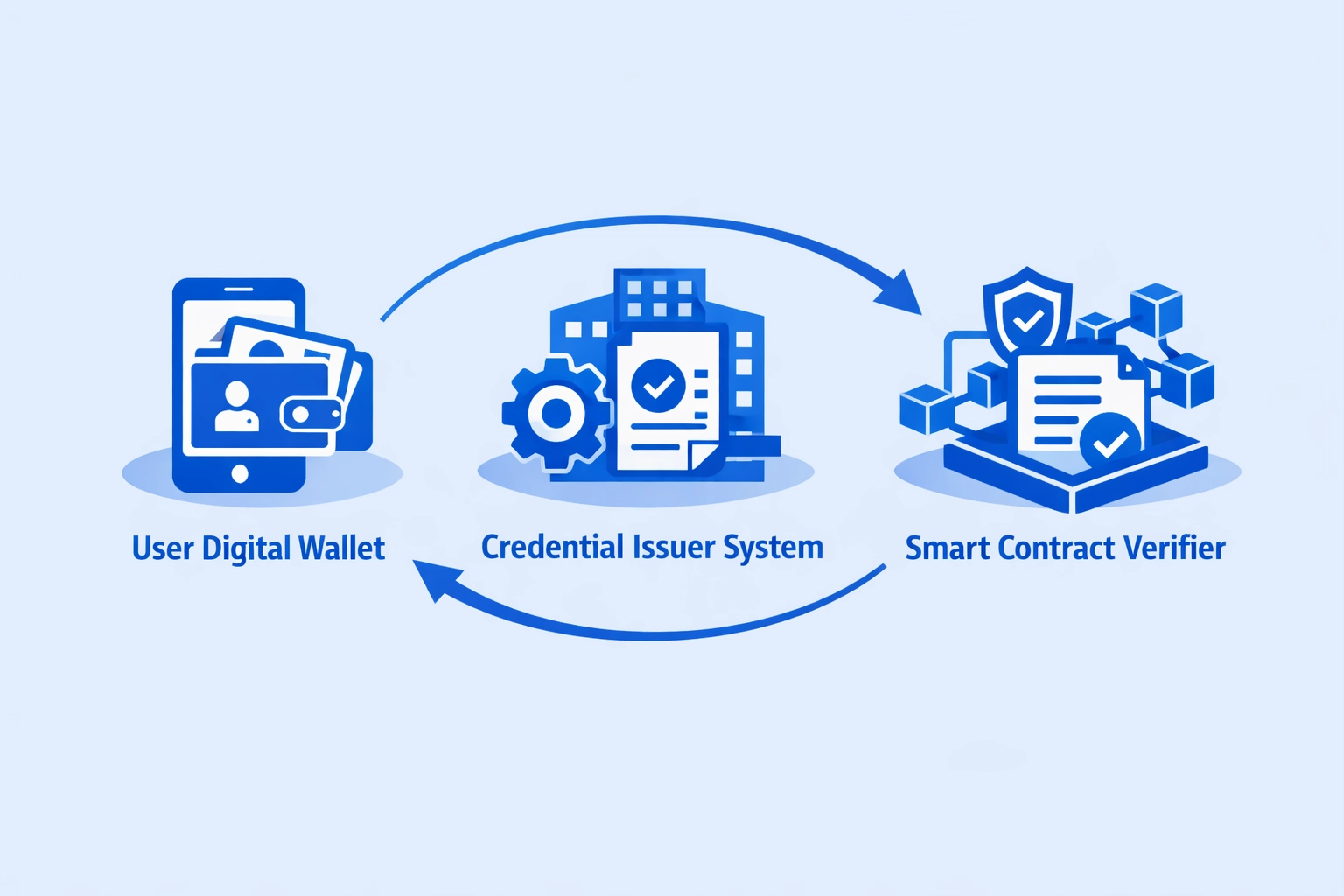
Decentralized Identity Verification Components
User Digital Wallet
- Stores verifiable credentials locally
- Controls selective disclosure permissions
- Manages private keys securely
- Presents credentials to verifiers
- Maintains complete data sovereignty
Credential Issuer System
- Signs credentials with private keys
- Publishes public keys on blockchain
- Maintains revocation registries
- Updates credential schemas
- Manages issuer DID resolution
Smart Contract Verifier
- Validates cryptographic signatures
- Checks credential expiration dates
- Verifies revocation status on-chain
- Enforces attribute requirements
- Logs verification events immutably
How Identity Verification Rules Are Encoded into Smart Contracts
Encoding identity verification rules into smart contracts involves translating business policies and regulatory requirements into executable code implementing verification logic. A financial institution requiring age verification above 18, accredited investor status, and non-sanctioned status encodes these requirements as smart contract functions checking credential attributes, validating signatures, and comparing values against thresholds. The contracts implement conditional logic, execute cryptographic operations, access on-chain data sources, and trigger appropriate actions based on verification outcomes without manual intervention across global implementations.
Smart Contract-Driven Identity Lifecycle Management
Automated lifecycle management through smart contracts handles complete identity verification journeys from initial credential issuance through renewal, updates, and eventual revocation. Smart contracts monitor expiration dates triggering renewal notifications, execute automatic updates when user attributes change, immediately revoke compromised credentials when fraud is detected, and maintain comprehensive audit trails of all lifecycle events. This automation eliminates manual tracking reducing administrative costs by 60-75% while ensuring consistent policy enforcement and real-time compliance across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations serving millions of users.[1]
Identity Verification Credential Lifecycle
Credential Issuance and Activation
Issuer verifies user identity, creates signed credential with attributes and expiration, publishes to user wallet, registers on blockchain for verification.
Active Verification and Monitoring
Smart contracts validate credentials on demand, check revocation status, monitor expiration dates, log verification events immutably.
Renewal, Update, or Revocation
Automated renewal before expiration, attribute updates when information changes, immediate revocation upon fraud detection or policy violation.
Verifiable Credentials Execution Through Smart Contracts
Verifiable credentials executed through smart contracts enable instant identity verification without contacting issuing authorities, providing 24/7 operation with superior privacy protection. When a university issues a degree credential, they sign it with their private key creating a cryptographic proof of authenticity. Users store credentials in digital wallets presenting them to employers or educational institutions. Smart contracts verify the university’s signature using publicly available keys on blockchain, confirm credential validity and expiration, and grant access or privileges automatically without ever contacting the university, operating continuously across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Privacy-Preserving Identity Verification Using Smart Logic
Privacy-preserving identity verification through smart contracts leverages zero-knowledge proofs enabling users to prove attributes without revealing underlying data. A user can demonstrate they are over 18 without disclosing their exact birthdate, prove accredited investor status without exposing net worth details, or confirm non-sanctioned status without revealing nationality. Smart contracts verify cryptographic proofs confirming claim validity while maintaining complete data privacy, complying with GDPR, CCPA, and regulatory requirements across jurisdictions. This approach minimizes data exposure reducing breach impact while maintaining verification accuracy.
Consent Management and User Control via Smart Contracts
Consent management through smart contracts provides users granular control over identity verification data sharing and usage. Users define consent policies specifying which attributes can be shared with particular verifiers, for what purposes, and for how long. Smart contracts enforce these policies automatically, logging all data access events immutably, triggering alerts when consent boundaries are approached, and automatically revoking access when consent expires. This architecture implements privacy-by-design principles providing users complete sovereignty over personal information across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Cross-Platform Identity Verification Interoperability on Blockchain
Cross-platform identity verification interoperability through standardized smart contract protocols enables credentials issued on one blockchain to be verified on others without centralized bridges. Implementations leverage W3C Verifiable Credentials standards, DID specifications, and cross-chain communication protocols creating seamless interoperability. A credential issued on Ethereum can be verified on Polygon, Solana, or private enterprise blockchains through compatible smart contract verification logic. This interoperability eliminates vendor lock-in, expands credential utility across ecosystems, and reduces integration costs by 50-70% for organizations operating across multiple platforms.
| Interoperability Feature | Centralized Systems | Smart Contract Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Platform Verification | Requires custom API integrations per platform | Standardized W3C protocol verification |
| Integration Timeline | 3-6 months per new platform | Days with standardized contracts |
| Vendor Lock-In | High proprietary format dependency | Eliminated through open standards |
| Maintenance Cost | $50K-$200K annually per integration | $10K-$40K shared infrastructure |
Automating Identity Revocation and Updates with Smart Contracts
Automated revocation and updates through smart contracts enable real-time identity verification status management without manual intervention. When fraud is detected, compromised credentials are immediately revoked by updating on-chain revocation registries that smart contracts check during verification. Attribute updates trigger automatic credential refreshes maintaining accuracy without user re-verification. Batch revocations occur instantly affecting thousands of credentials simultaneously, critical for security incidents. This automation provides superior security compared to manual revocation processes requiring days or weeks in traditional centralized systems across global implementations.
Security Considerations in Identity-Focused Smart Contracts
Security considerations for identity verification smart contracts include protection against replay attacks through nonce validation, defense against unauthorized access via proper permission controls, and prevention of credential theft through encryption and secure key management. Smart contracts must implement reentrancy guards preventing recursive calls, validate all inputs avoiding injection attacks, and use audited cryptographic libraries ensuring signature verification integrity. Professional security audits costing $30,000-$150,000 identify vulnerabilities before deployment, while bug bounty programs offering rewards up to $500,000 incentivize ongoing security research across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Emerging Identity Models Enabled by Smart Contract Innovation
The evolution of identity verification through smart contracts continues accelerating with emerging models including soulbound tokens representing non-transferable credentials permanently linked to individuals, reputation scoring systems aggregating verification history across platforms, and AI-driven fraud detection integrated with blockchain verification. Biometric authentication through zero-knowledge proofs enables passwordless verification while maintaining privacy, and quantum-resistant cryptography prepares identity systems for future computational threats. These innovations expand identity verification capabilities beyond simple attribute checks to sophisticated trust frameworks.
Our eight years of blockchain identity implementation experience across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada demonstrates that smart contracts deliver transformative improvements in cost, speed, security, and user control compared to traditional centralized systems. As technology matures, regulatory frameworks evolve, and standardization progresses, blockchain-based identity verification will transition from innovative pilot to mainstream infrastructure powering digital commerce, government services, healthcare, and financial systems globally. The convergence of cryptographic security, automated enforcement, and decentralized architecture creates unprecedented opportunities for reimagining identity verification serving billions of users with enhanced privacy, efficiency, and security fundamentally transforming how digital trust operates worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Smart contracts enhance identity verification through automated rule enforcement, eliminating manual review bottlenecks reducing processing time from days to seconds. These self-executing programs verify credentials cryptographically against predefined rules, ensuring consistency and preventing human error. Smart contracts provide immutable audit trails of verification events, enable instant revocation when credentials expire, and eliminate centralized honeypot databases vulnerable to breaches. Across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada, organizations report 70-85% cost reductions and 95% faster verification while maintaining superior security compared to legacy centralized identity systems requiring extensive infrastructure and personnel.
Verifiable credentials are cryptographically signed digital attestations that smart contracts validate without contacting issuing authorities, enabling privacy-preserving identity verification. Issuers like governments or universities sign credentials with private keys, users store them in digital wallets, and smart contracts verify signatures using public keys on blockchain. This architecture eliminates continuous third-party verification requests, protects user privacy through selective disclosure, and operates 24/7 without relying on external systems. Smart contracts execute verification logic instantly, checking credential validity, expiration, and revocation status automatically across global networks serving USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian implementations.
Smart contracts enable privacy-preserving identity verification through zero-knowledge proofs allowing users to prove attributes without revealing underlying data. A user can demonstrate they are over 18 without disclosing their exact birthdate, or prove accredited investor status without exposing financial details. Smart contracts verify cryptographic proofs confirming claim validity while maintaining complete data privacy. This approach complies with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy regulations across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada by minimizing data exposure. Advanced implementations use zk-SNARKs or zk-STARKs enabling complex verification logic while preserving user anonymity throughout the verification process.
Smart contracts automate complete identity verification lifecycles through programmable state transitions managing credential issuance, renewal, updates, and revocation. Upon verification, smart contracts issue credentials recording issuance timestamps and expiration dates on blockchain. Automated monitoring triggers renewal prompts before expiration, executes updates when user attributes change, and immediately revokes credentials upon detecting fraud or policy violations. This automation eliminates manual tracking, ensures consistent enforcement, and provides real-time status visibility. Organizations report 60-75% administrative cost reductions while improving compliance through automated lifecycle management across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian identity verification implementations.
Security considerations for identity verification smart contracts include protection against replay attacks through nonce validation, defense against unauthorized access via proper permission controls, and prevention of credential theft through encryption and secure key management. Smart contracts must implement reentrancy guards preventing recursive calls, validate all inputs avoiding injection attacks, and use audited cryptographic libraries ensuring signature verification integrity. Professional security audits costing $30,000-$150,000 identify vulnerabilities before deployment. Key management remains critical, with multi-signature controls and hardware security modules protecting issuer keys. Regular penetration testing and bug bounty programs maintain ongoing security across production systems.
Smart contracts enable cross-platform identity verification through standardized protocols allowing credentials issued on one blockchain to be verified on another without centralized bridges. Implementations use W3C Verifiable Credentials standards, DID (Decentralized Identifier) specifications, and cross-chain communication protocols enabling seamless interoperability. A credential issued on Ethereum can be verified on Polygon, Solana, or private enterprise blockchains through smart contract verification logic. This interoperability eliminates vendor lock-in, expands credential utility across ecosystems, and reduces integration costs by 50-70%. Organizations across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada leverage interoperable identity verification for supply chain, healthcare, and financial services applications.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.






