Key Takeaways
- ERC721 in smart contract establishes the foundational standard for non-fungible tokens, enabling unique digital asset representation with verifiable ownership.
- Understanding ERC721 in smart contract architecture is essential for building secure NFT platforms across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets.
- The ERC721 in smart contract standard defines nine core functions for ownership management, transfers, and approval delegation mechanisms.
- Proper implementation of ERC721 in smart contract requires careful attention to reentrancy protection, access controls, and safe transfer validation.
- Metadata storage decisions in ERC721 in smart contract impact gas costs, permanence, and user experience across NFT marketplace integrations.
- Enterprises leverage ERC721 in smart contract for real estate tokenization, digital collectibles, supply chain tracking, and identity verification systems.
- Gas optimization techniques for ERC721 in smart contract include batch minting, lazy minting, and efficient storage patterns reducing transaction costs.
- ERC721 in smart contract compliance ensures interoperability across OpenSea, Rarible, and other major NFT marketplaces globally.
Introduction to ERC721 and Its Role in Secure NFT Architecture
ERC721 in smart contract represents the foundational standard that revolutionized digital ownership through non-fungible tokens. With over eight years of experience building blockchain solutions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets, our agency has implemented countless ERC721 contracts for enterprises ranging from digital art platforms to real estate tokenization projects. This standard introduced the concept of provably unique digital assets, enabling applications previously impossible in traditional systems. Understanding how ERC721 in smart contract architecture works is essential for any organization entering the NFT space with production-ready, secure, and scalable implementations.
Understanding the ERC721 Standard: Core Principles and Specifications
The ERC721 in smart contract standard was finalized in January 2018, establishing a universal interface for non-fungible tokens on Ethereum and EVM-compatible chains. The specification defines mandatory functions including balanceOf, ownerOf, safeTransferFrom, transferFrom, approve, setApprovalForAll, getApproved, and isApprovedForAll. These functions enable standardized interactions for ownership queries, secure transfers, and delegation management. The standard also introduces the ERC721Metadata extension for tokenURI functionality and ERC721Enumerable for token indexing, providing comprehensive NFT capabilities.[1]
How ERC721 Smart Contract Design Differs from Fungible Token Standards
| Characteristic | ERC721 (NFT) | ERC20 (Fungible) |
|---|---|---|
| Token Identity | Unique token IDs | Identical units |
| Divisibility | Indivisible | Divisible to decimals |
| Ownership Tracking | Per-token mapping | Balance mapping |
| Metadata | Per-token URI | Contract-level only |
| Use Cases | Collectibles, real estate, identity | Currency, governance, utility |
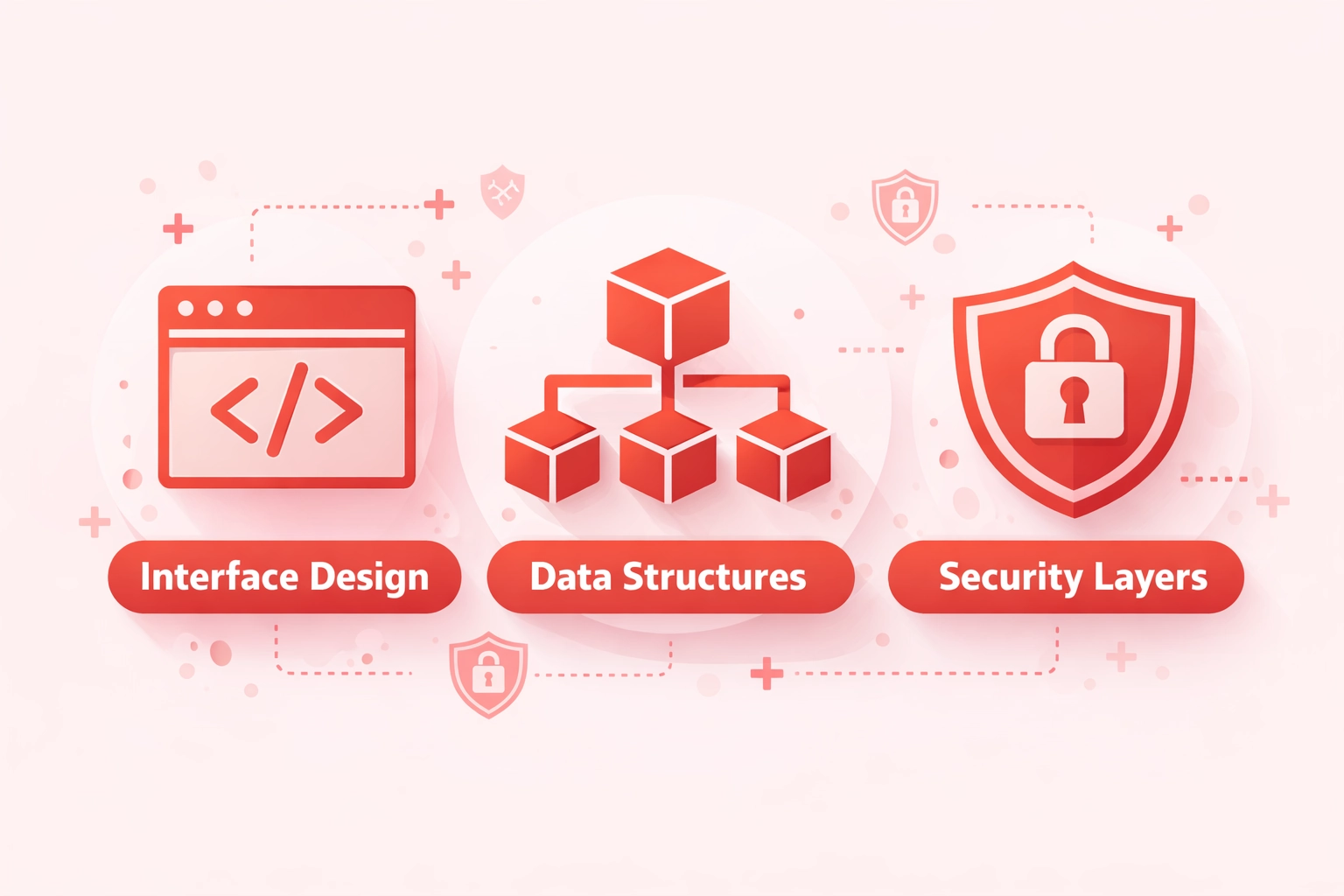
Designing Secure NFT Data Models Using ERC721 Interfaces
Interface Design
- IERC721 core interface
- IERC721Metadata extension
- IERC721Enumerable option
- Custom extensions
Data Structures
- Ownership mappings
- Approval registries
- Token enumeration
- Metadata references
Security Layers
- Access control checks
- Reentrancy guards
- Safe transfer hooks
- Input validation
Token Ownership and Transfer Logic in ERC721 Smart Contracts
ERC721 in smart contract implements sophisticated ownership and transfer mechanisms ensuring secure asset movement. The transferFrom function enables direct transfers when the caller is the owner, approved address, or authorized operator. The safeTransferFrom variant adds recipient verification, checking if the target is a contract and calling onERC721Received to confirm acceptance. This prevents tokens from being permanently locked in contracts unable to handle NFTs, a critical protection for enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada managing valuable digital assets.
Security Note: Always use safeTransferFrom when transferring to unknown addresses to prevent permanent token loss in incompatible contracts.
Metadata Storage Models: On-Chain vs Off-Chain in ERC721 NFTs
| Storage Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| On-Chain | Permanent, trustless, immutable | High gas costs, size limits |
| IPFS | Decentralized, content-addressed | Requires pinning services |
| Arweave | Permanent storage, one-time fee | Higher upfront cost |
| Centralized Server | Low cost, easy updates | Single point of failure |
Implementing Access Control and Authorization in ERC721 Contracts
Access control in ERC721 in smart contract governs who can mint, burn, and manage tokens. OpenZeppelin’s AccessControl and Ownable patterns provide battle-tested implementations. Role-based access control enables granular permissions for minters, administrators, and operators. The approval mechanism allows token owners to delegate transfer rights to specific addresses or operators for marketplace integration.
Single Admin
Multi-Role
Delegation
Preventing Common Security Risks in ERC721 Smart Contract Design
Security vulnerabilities in ERC721 in smart contract implementations can result in token theft or permanent loss. Reentrancy attacks exploit callbacks in safeTransferFrom to manipulate state before completion. Integer overflow in token ID generation can cause collisions. Missing access control on mint functions enables unauthorized token creation. Front-running attacks on marketplace listings require careful consideration. Our agency has audited numerous ERC721 contracts across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada, consistently finding these patterns requiring attention.[2]
ERC721 NFT Implementation Lifecycle
Requirements Definition
Define NFT collection requirements, metadata structure, and business logic for ERC721 implementation.
Contract Architecture
Design contract structure including inheritance, extensions, and custom functionality.
Implementation
Write Solidity code using OpenZeppelin ERC721 base contracts with custom extensions.
Metadata Setup
Configure metadata storage on IPFS, Arweave, or on-chain with proper URI structure.
Testing Suite
Create comprehensive unit and integration tests covering all ERC721 functions.
Security Audit
Engage professional auditors to review contract for vulnerabilities before deployment.
Testnet Deployment
Deploy to testnet for real-world testing with marketplace integrations.
Mainnet Launch
Deploy verified contract to mainnet with monitoring and incident response procedures.
Event Emission and State Tracking for Transparent NFT Architecture
ERC721 in smart contract requires specific event emissions for Transfer, Approval, and ApprovalForAll actions. These events enable off-chain indexing services to track ownership changes, build marketplace displays, and provide transaction history. Proper event emission is essential for NFT platform functionality. Additional custom events can track minting, burning, and metadata updates for comprehensive audit trails.
Extending ERC721 with Custom Data Models and Business Logic
Royalty Extensions
- ERC2981 royalty standard
- Secondary sale fees
- Creator compensation
- Marketplace support
Soulbound Tokens
- Non-transferable NFTs
- Identity verification
- Credential systems
- Reputation tokens
Dynamic NFTs
- Mutable metadata
- Oracle integration
- Evolving properties
- Real-world data
Gas Optimization Techniques for Scalable ERC721 NFT Systems
| Optimization Technique | Gas Savings | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| ERC721A Batch Minting | Up to 90% per batch | Azuki implementation |
| Lazy Minting | Deferred until sale | Signature-based minting |
| Packed Storage | 30-50% reduction | Single slot variables |
| Remove Enumerable | 20-30% on mint | Skip enumeration mapping |
ERC721 Compliance and Interoperability Across NFT Marketplaces
Proper ERC721 in smart contract compliance ensures seamless integration with OpenSea, Rarible, LooksRare, and other major marketplaces. The standard interface enables automatic listing, bidding, and trading functionality. Metadata format following OpenSea standards ensures proper display of images, attributes, and descriptions. Royalty implementation via ERC2981 guarantees creator compensation across compliant platforms.
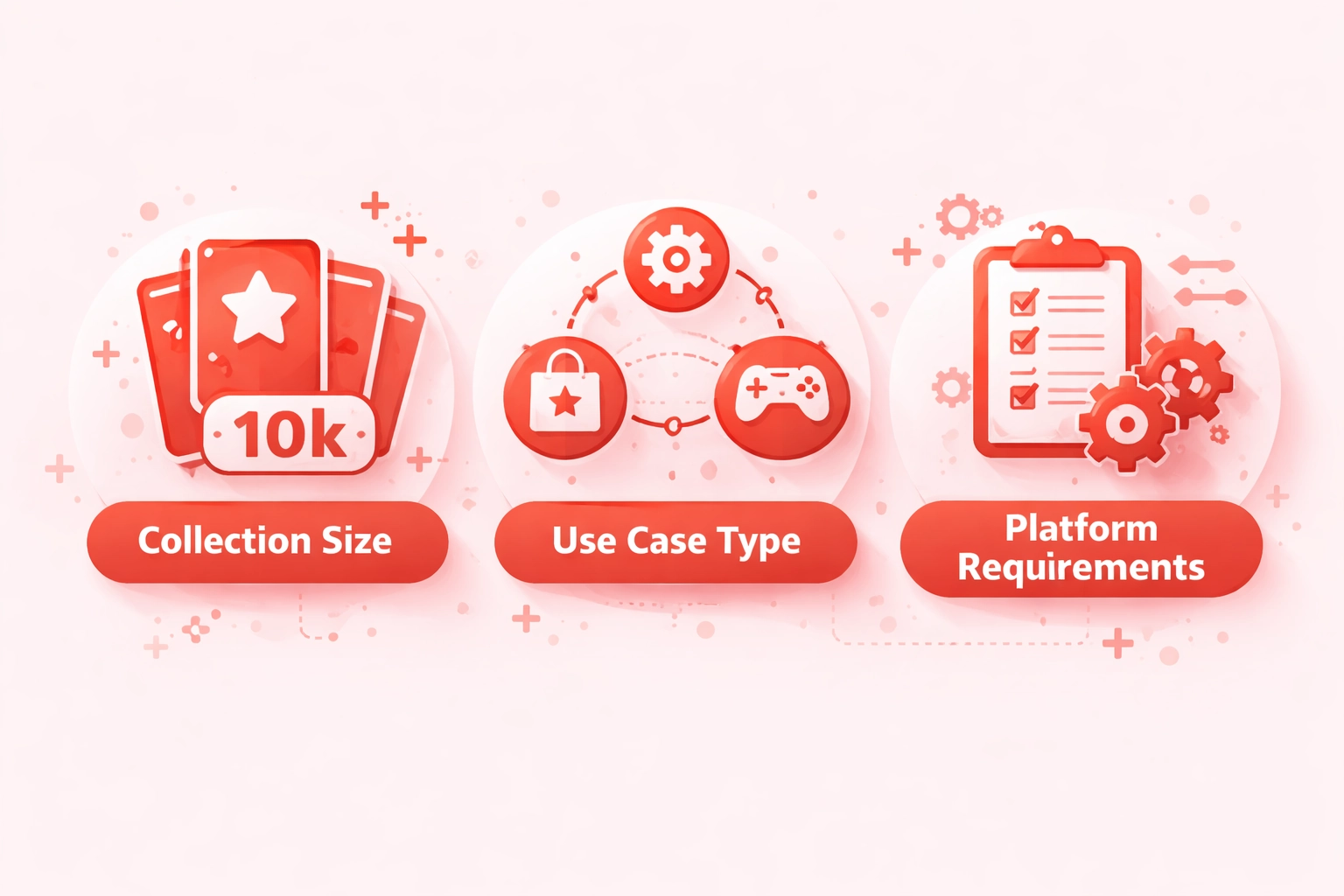
ERC721 Implementation Selection Criteria
Collection Size
- Small: Standard ERC721
- Large: ERC721A batch
- Unlimited: Lazy minting
- Dynamic: Custom logic
Use Case Type
- Art: Standard metadata
- Gaming: Dynamic NFTs
- Identity: Soulbound
- Finance: Composable
Platform Requirements
- Ethereum: Full features
- Polygon: Low cost
- Solana: Different standard
- Multi-chain: Bridges
Upgradable ERC721 Architectures and Long-Term Data Integrity
Implementing upgradable ERC721 in smart contract patterns enables bug fixes and feature additions while preserving ownership data. Proxy patterns like UUPS and Transparent Proxy separate storage from logic, allowing implementation updates. However, upgradeability introduces trust assumptions and potential centralization risks. Enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada must balance flexibility against immutability guarantees when designing long-term NFT systems.
Industry Standards for ERC721 Smart Contract Security
Standard 1: Use OpenZeppelin ERC721 base contracts as the foundation for all NFT implementations.
Standard 2: Always use safeTransferFrom for transfers to unknown addresses to prevent token loss.
Standard 3: Implement reentrancy guards on all state-modifying functions that interact with external contracts.
Standard 4: Store immutable metadata on IPFS or Arweave with content-addressed URIs for permanence.
Standard 5: Require professional security audit before any mainnet deployment managing significant value.
Standard 6: Implement ERC2981 royalty standard for creator compensation across compliant marketplaces.
Best Practices for Building Production-Ready ERC721 NFT Smart Contracts
Building production-ready ERC721 in smart contract implementations requires comprehensive testing, security audits, and careful architectural decisions. Start with battle-tested OpenZeppelin contracts, extend carefully with custom functionality, and thoroughly test all paths. Consider gas optimization for user experience, implement proper access controls, and ensure metadata availability. Document all contract functions and administrative capabilities.
With eight years of experience building ERC721 in smart contract solutions across USA, UK, UAE, and Canadian markets, our agency has delivered secure, scalable NFT platforms for enterprises worldwide. The ERC721 standard continues evolving with extensions for royalties, dynamic metadata, and cross-chain functionality, making it the foundation for the next generation of digital ownership applications.
Build Secure ERC721 NFT Solutions
Our blockchain experts design and implement production-ready ERC721 smart contracts for enterprise NFT platforms and digital asset applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
ERC721 in smart contract is the Ethereum standard for non-fungible tokens that enables unique digital asset representation. Each token has a distinct identifier and ownership record stored on the blockchain. The standard defines core functions for minting, transferring, and querying ownership of unique assets.
ERC721 in smart contract creates non-fungible tokens where each unit is unique and non-interchangeable, unlike ERC20 fungible tokens. ERC721 tracks individual token IDs with distinct metadata, while ERC20 manages identical, divisible units. This uniqueness enables digital collectibles, real estate, and identity applications.
ERC721 in smart contract requires balanceOf, ownerOf, safeTransferFrom, transferFrom, approve, setApprovalForAll, getApproved, and isApprovedForAll functions. These enable ownership queries, secure transfers, and delegation management. The tokenURI function provides metadata access for displaying NFT information.
Enterprises across USA, UK, UAE, and Canada implement ERC721 in smart contract for digital collectibles, real estate tokenization, supply chain tracking, and identity verification. The standard provides proven architecture for representing unique physical and digital assets with verifiable ownership records.
ERC721 in smart contract requires protection against reentrancy attacks, unauthorized transfers, and metadata manipulation. Implementing proper access controls, using OpenZeppelin libraries, and conducting security audits are essential. Safe transfer functions verify recipient contract compatibility to prevent token loss.
ERC721 in smart contract supports both on-chain and off-chain metadata storage. On-chain storage ensures permanence but costs more gas. Off-chain storage using IPFS or Arweave reduces costs while maintaining decentralization. Hybrid approaches balance cost efficiency with data availability guarantees.
NFT marketplaces interact with ERC721 in smart contract through standardized interfaces for listing, bidding, and transferring tokens. The approval mechanism enables marketplaces to transfer tokens on behalf of sellers. Events like Transfer and Approval provide indexing data for marketplace displays.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.