Key Takeaways: DeFi Governance
- Decentralized governance lets users make collective decisions without a central authority
- DAOs organize DeFi governance by automating proposals, voting, and execution through smart contracts
- Governance tokens determine voting power but large holders can have more influence, which protocols try to balance
- Smart contracts enforce decisions automatically ensuring transparency and reducing human error
- Participation is essential and incentives like token rewards or delegation encourage engagement
- Conflicts are resolved through voting, forums, or emergency mechanisms to maintain protocol stability
- Poor decisions can have financial consequences so safety measures like time delays or multisig approvals are important
- Delegated and representative voting help governance scale as communities grow
- Incentives and safeguards prevent manipulation and ensure decisions align with long-term protocol goals
- Decentralized governance increases transparency and trust allowing users to participate in shaping the protocol’s future
The decentralized finance landscape has revolutionized how we think about financial systems, removing intermediaries and giving power back to users. At the heart of this transformation lies decentralized governance, a mechanism that ensures protocols remain transparent, fair, and responsive to community needs. Unlike traditional financial institutions where decisions are made behind closed doors by a select few, DeFi governance invites every token holder to participate in shaping the future of protocols they use and invest in.
Trust has always been the cornerstone of any financial system. In decentralized finance, this trust is not placed in institutions or individuals but in transparent, auditable, and community-driven governance structures. This fundamental shift represents more than just a technological innovation; it embodies a philosophical change in how we approach collective decision making and resource management in the digital age.
A Complete Guide to Decentralized Governance in DeFi
Understanding decentralized governance requires examining both its theoretical foundations and practical implementations. At its core, governance in DeFi operates through smart contracts that automatically execute community decisions once voting thresholds are met. This automation eliminates the need for trusted intermediaries to implement approved changes, ensuring that community will translates directly into protocol action.
| Governance Component | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Governance Tokens | Digital assets that grant voting rights to holders | Enable proportional voting power based on stake |
| Proposal System | Mechanism for submitting protocol changes | Allow community members to suggest improvements |
| Voting Mechanism | System for casting and counting votes on proposals | Facilitate democratic decision making process |
| Timelock Contracts | Delay between approval and execution of changes | Provide security buffer for community review |
| Treasury Management | Community controlled funds for development | Finance protocol growth and maintenance |
The governance lifecycle typically begins when a community member identifies an opportunity for protocol improvement. They draft a proposal detailing the change, its expected impact, and implementation steps. This proposal enters a discussion phase where the community debates its merits, suggests modifications, and evaluates potential risks. If the proposal gains sufficient support, it moves to formal voting where token holders cast their votes over a predetermined period.
Understanding Decentralized Governance and Its Role in DeFi Ecosystems
Decentralized governance serves as the nervous system of DeFi ecosystems, coordinating responses to challenges and opportunities while maintaining the core principle of distributed control. In traditional systems, governance happens through hierarchical structures where authority flows from top to bottom. DeFi inverts this model, creating horizontal governance where power emanates from the community itself.
This role extends beyond simple protocol parameter adjustments. Governance systems make decisions about security upgrades, partnership agreements, treasury allocations, and strategic direction. Each decision reflects the collective intelligence of thousands of stakeholders who bring diverse expertise and perspectives to the table. The result is a more resilient, adaptive system that can weather market volatility and regulatory uncertainty better than centrally controlled alternatives.
How Decentralized Governance Is Shaping the DeFi Protocols
Decentralized governance is fundamentally reshaping how DeFi protocols evolve and adapt to market conditions. Through governance tokens, users gain voting rights proportional to their stake in the protocol, creating a democratic system where collective wisdom guides development decisions. This model ensures that those most invested in a protocol’s success have the loudest voice in determining its future direction.
The beauty of this system lies in its ability to aggregate diverse perspectives from across the global community. A developer in Singapore, a trader in New York, and an investor in London can all contribute equally to protocol decisions, breaking down geographical and institutional barriers that have traditionally limited participation in financial governance.
Key Benefits of Decentralized Protocol Governance
Transparency in decision making processes ensures all stakeholders can track proposals from submission to implementation. Every vote is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable audit trail that holds the community accountable.
Rapid adaptation to market changes becomes possible when governance is distributed across thousands of participants who can quickly respond to emerging threats or opportunities.
Reduced central points of failure protect protocols from single entity risks, whether regulatory, operational, or malicious in nature.
Real World Example: Compound Protocol
Compound, one of the pioneering lending protocols in DeFi, transitioned from centralized control to full community governance in 2020. The protocol distributed COMP tokens to users, giving them voting rights over crucial decisions like which assets to support, interest rate models, and protocol upgrades. This transition demonstrated how decentralized governance could manage a protocol holding billions in value while maintaining security and efficiency.
Through governance proposals, the community has successfully navigated market crashes, implemented security improvements, and expanded to multiple blockchain networks. Each decision reflected careful deliberation and voting by token holders who had skin in the game, creating alignment between decision makers and those affected by decisions.
How DeFi Governance Models Empower Communities and Protocol Growth
Community empowerment through governance creates a virtuous cycle where engaged users become invested stakeholders who actively contribute to protocol success. This empowerment manifests in several ways, from casual users suggesting interface improvements to sophisticated investors proposing complex tokenomics changes. Every participant, regardless of their technical expertise or financial resources, can contribute ideas and vote on proposals that shape protocol evolution.
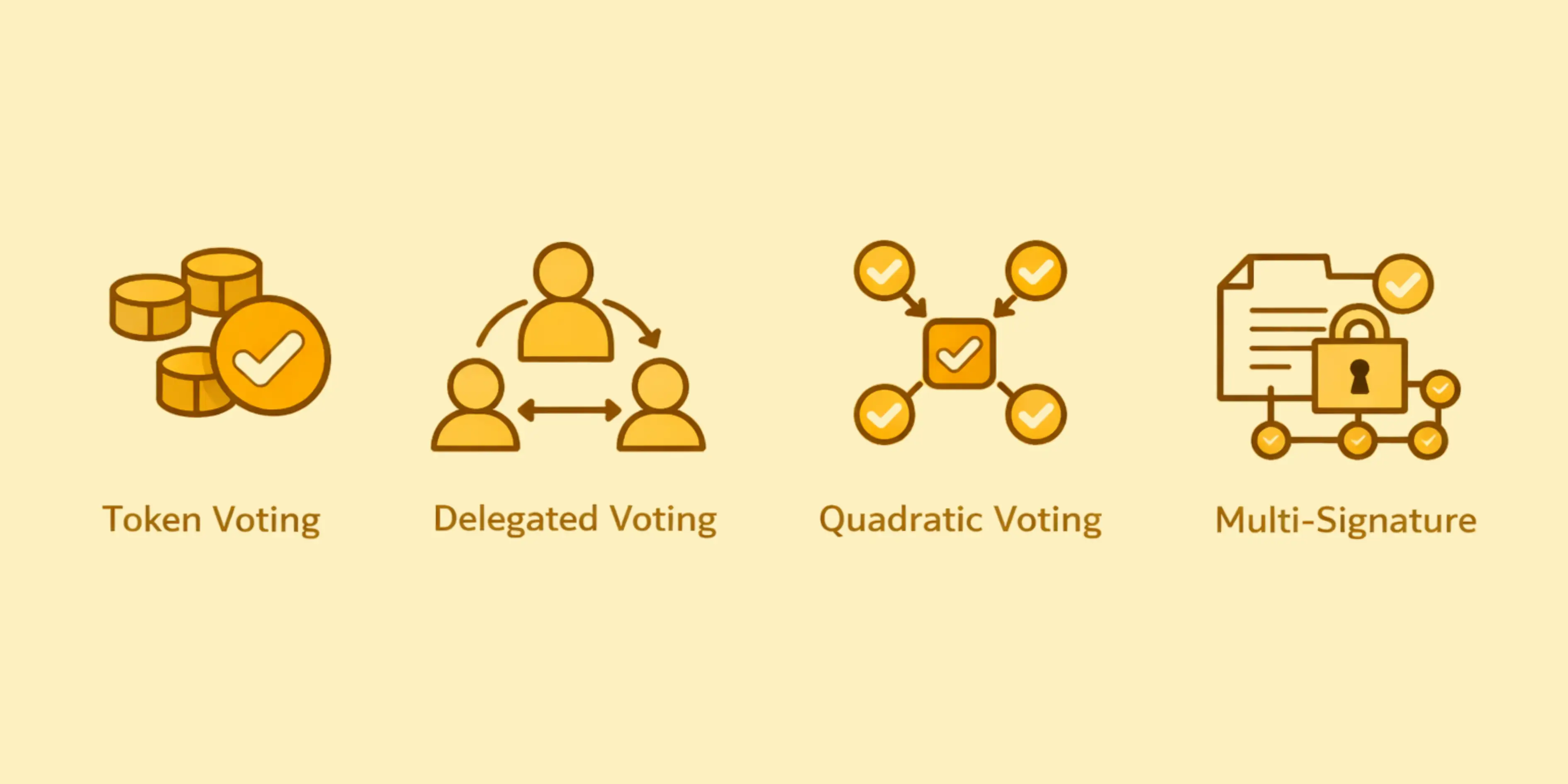
| Governance Model | Characteristics | Advantages | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Token Based Voting | One token equals one vote with direct democracy | Simple, transparent, incentive aligned | Mature protocols with distributed ownership |
| Delegated Voting | Token holders delegate votes to representatives | Increases participation, leverages expertise | Complex protocols requiring specialized knowledge |
| Quadratic Voting | Cost of votes increases quadratically | Reduces whale influence, promotes fairness | Community focused projects prioritizing equality |
| Multi Signature | Multiple parties must approve changes | Enhanced security, prevents single point failure | Early stage protocols prioritizing security |
Protocol growth accelerates when communities feel ownership over outcomes. Governance participants become ambassadors who promote the protocol, contribute to documentation, help onboard new users, and defend against criticism. This organic growth driven by genuine enthusiasm proves more sustainable than marketing campaigns or token incentives alone. The community becomes the protocol’s greatest asset, providing resilience during bear markets and momentum during bull runs.
Exploring Governance Mechanisms That Drive Decentralized Finance
Various governance mechanisms have emerged to address different challenges in decentralized decision making. Each mechanism represents an experiment in collective coordination, attempting to balance efficiency with inclusivity, security with flexibility, and short term needs with long term sustainability.
Snapshot Voting
Off chain voting system that records token holder preferences without gas fees. Provides signal for community sentiment before on chain execution. Ideal for temperature checks and preliminary voting rounds.
On Chain Governance
Voting occurs directly on blockchain with automatic execution through smart contracts. Provides immutable record and guaranteed implementation. Essential for critical protocol changes requiring trustless execution.
Conviction Voting
Voting power increases the longer tokens remain staked on a proposal. Rewards long term thinking and commitment. Prevents last minute vote manipulation and encourages thoughtful consideration.
The choice of governance mechanism significantly impacts how protocols evolve. Fast moving markets might favor simpler voting systems that enable rapid response, while protocols managing substantial value might prefer multi layered governance with extensive security checks. The most sophisticated protocols often combine multiple mechanisms, using each where it provides the most value.
Decentralized Governance Explained: How DeFi Protocols Are Managed
Managing a DeFi protocol through decentralized governance requires careful orchestration of technical infrastructure, community engagement, and economic incentives. The process begins with establishing clear governance parameters: who can vote, how proposals are submitted, what thresholds must be met for approval, and how changes are implemented once approved.
Governance Lifecycle
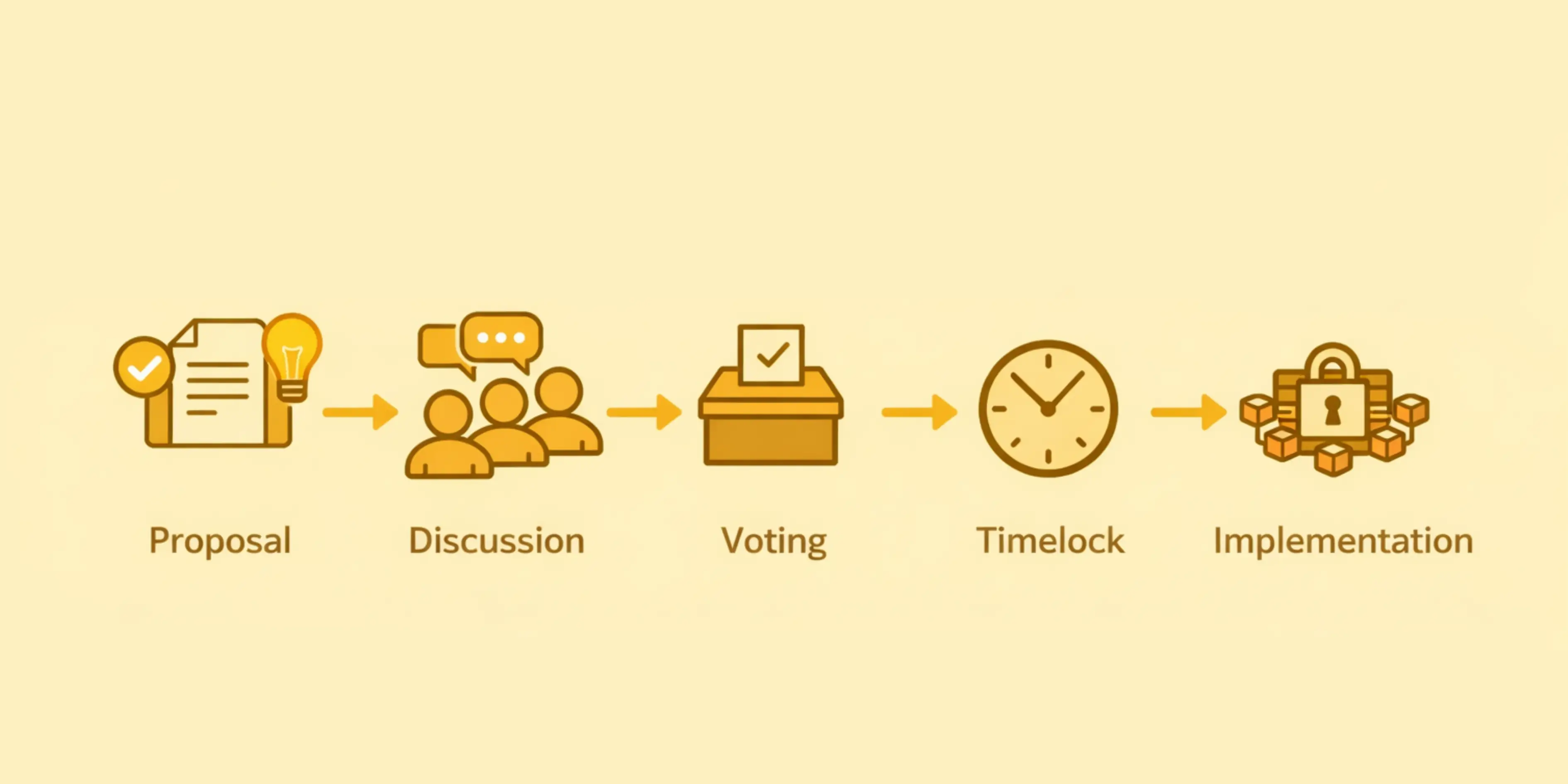
Ideation Phase:
Community members discuss potential improvements in forums and social channels, gathering feedback and refining concepts.
Proposal Submission:
Formal proposal is drafted with technical specifications, expected outcomes, and implementation timeline.
Discussion Period:
Community reviews proposal, asks questions, suggests modifications, and debates merits over designated timeframe.
Voting Phase:
Token holders cast votes over predetermined period, with real time tracking of voting progress and quorum status.
Timelock Period:
Approved proposals enter a mandatory waiting period, allowing community to review and prepare for upcoming changes.
Implementation:
Smart contracts automatically execute approved changes, with community monitoring outcomes and impacts.
This structured approach ensures that changes to critical protocol infrastructure receive appropriate scrutiny while maintaining the ability to respond quickly when necessary. Emergency procedures often exist alongside normal governance processes, allowing rapid response to security threats while preserving community oversight.
Governance tokens play a central role in decentralized governance systems by giving holders voting rights and influence over protocol changes, such as parameter adjustments, treasury management, and upgrades. These tokens empower community members to participate in decision-making through proposal creation, discussion, and voting processes, often with mechanisms like token‑weighted, quadratic, or delegated voting to balance influence among stakeholders. For a deeper look at how governance tokens work and common parameters across DeFi protocols, see Secured Finance’s guide to governance tokens[1]
The Evolution of Governance Systems in Decentralized Finance Platforms
The journey of DeFi governance has been marked by continuous experimentation and learning. Early protocols often launched with centralized control, planning to decentralize governance gradually. This approach allowed teams to refine protocols before distributing control, but it also created trust challenges as communities wondered when and how decentralization would occur.
More recent protocols have embraced progressive decentralization from launch, establishing governance frameworks even while retaining some centralized capabilities during early development. This hybrid approach acknowledges that full decentralization requires mature infrastructure while demonstrating commitment to community control from the outset.
| Evolution Stage | Control Structure | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Genesis Phase | Fully Centralized | Core team controls all decisions, rapid iteration, building foundation |
| Early Adoption | Hybrid Control | Advisory votes introduced, community feedback considered, gradual power sharing |
| Transition Phase | Shared Governance | Binding votes on specific issues, emergency controls retained, active delegation |
| Maturity Phase | Full Decentralization | Complete community control, on chain execution, transparent treasury management |
The evolution continues as protocols learn from each other’s successes and failures. Cross protocol governance experiments, where multiple protocols coordinate on shared infrastructure, represent the frontier of governance innovation. These experiments test whether decentralized systems can cooperate at scale, creating governance networks that span entire ecosystems.
Why Decentralized Governance Is Essential for Sustainable DeFi Projects
Sustainability in DeFi extends beyond financial metrics to encompass community resilience, adaptive capacity, and long term value creation. Decentralized governance proves essential for sustainability because it distributes the burden of protocol stewardship across the entire community rather than concentrating it in a small team that might lose interest, face personal challenges, or pursue conflicting priorities.
Projects with strong governance frameworks weather market downturns better because their communities remain engaged and committed even when token prices decline. This engagement manifests in continued development contributions, marketing efforts, and strategic planning that keeps protocols relevant and competitive. Centralized projects often struggle during difficult periods as core teams face pressure to abandon unprofitable ventures or pivot to more lucrative opportunities.
Critical Sustainability Factors
Economic Sustainability
Governance ensures protocol revenues support ongoing development and community incentives without depleting treasuries.
Technical Sustainability
Community oversight maintains code quality, security standards, and infrastructure reliability over time.
Social Sustainability
Active governance fosters strong community bonds that persist through market cycles and external challenges.
A Deep Dive into Community Driven Governance in DeFi
Community driven governance represents the purest expression of DeFi’s decentralization ethos. It transforms users from passive consumers into active participants who shape the services they use. This transformation requires more than just distributing governance tokens; it demands creating cultures where participation is valued, diverse perspectives are welcomed, and constructive disagreement leads to better outcomes.
Successful community governance depends on several pillars. First, accessible information ensures all participants can make informed decisions regardless of their technical background. Second, inclusive processes welcome contributions from diverse community members, not just wealthy token holders or technical experts. Third, transparent execution builds trust by showing that community decisions translate into concrete actions. Fourth, continuous learning allows communities to refine their governance processes based on experience.
Design Governance That Empowers DeFi Communities
Strong decentralized governance is essential for sustainable DeFi growth. Nadcab Labs brings deep expertise in DAO design, governance token models, and smart-contract execution to help you build systems your community can trust.
Best Practices for Community Engagement
Regular Communication: Establish consistent channels for updates, discussions, and feedback that accommodate different time zones and communication preferences.
Education Programs: Provide resources that help community members understand governance processes, economic mechanisms, and technical concepts.
Incentive Alignment: Design reward structures that encourage long term participation and thoughtful contribution rather than short term speculation.
Conflict Resolution: Develop clear processes for addressing disputes and ensuring that disagreements strengthen rather than fracture communities.
The most vibrant DeFi communities treat governance as an ongoing conversation rather than a series of discrete votes. They create spaces for casual discussion, formal debate, and collaborative problem solving. These communities recognize that good governance emerges from sustained engagement rather than sporadic participation during crisis moments.
Expert Insights from Nadcab Labs
With over 8 years of experience in blockchain development and DeFi protocol design, Nadcab Labs has witnessed the evolution of governance systems from simple voting mechanisms to sophisticated coordination tools. Our team has contributed to numerous governance implementations across various blockchain ecosystems, gaining deep insights into what makes governance frameworks succeed or fail.
Through our extensive work with DeFi protocols, we have observed that successful governance requires balancing competing priorities: speed versus deliberation, simplicity versus sophistication, inclusivity versus efficiency. The protocols that thrive are those that recognize governance as a living system requiring constant refinement rather than a static structure implemented once and left unchanged.
Our experience shows that technical excellence in smart contract implementation matters less than creating governance cultures where participants feel heard, respected, and empowered. The most secure multisig setup or the most elegant voting algorithm cannot compensate for a community that feels excluded or manipulated. Building trust through transparent, fair, and responsive governance processes remains the foundation of sustainable DeFi projects.
At Nadcab Labs, we help projects design governance frameworks that align with their values, engage their communities, and adapt to changing circumstances. Our approach combines technical rigor with deep understanding of community dynamics, ensuring that governance systems support rather than hinder protocol growth and user trust.
FAQs on Decentralized Governance in DeFi
Not exactly. In DeFi, a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is a structure that implements decentralized governance, usually via token-based voting. Decentralized governance is the concept of distributing decision-making across community members, and DAOs are one of the primary tools used to achieve it in DeFi protocols. Not all DeFi projects are DAOs, but most rely on similar governance mechanisms to let users influence protocol parameters, upgrades, or treasury management.
Technically yes, but blockchain is central to DeFi governance. DeFi protocols rely on smart contracts to enforce rules and ensure transparency. Without blockchain, decentralized governance in DeFi would require trust in a central database or authority, which defeats the purpose of decentralization. Blockchain ensures that votes, proposals, and protocol changes are tamper-proof and automated.
Many DeFi protocols use governance tokens, which give voting power based on holdings. This can favor large token holders, creating a risk of governance centralization, or “whale control.” To mitigate this, some protocols use quadratic voting, delegated voting, or time-weighted voting to make governance more equitable. True democratic participation is challenging in DeFi because financial incentives naturally create influence disparities.
Conflicts usually arise when the community disagrees on protocol upgrades or fund allocation. DeFi projects often resolve disputes through governance proposals, discussions on forums, and community voting. Some also include arbitration mechanisms, where a group of trusted members or a multisig wallet executes a resolution if consensus fails. Conflict resolution is critical to avoid forks or loss of community trust.
Decisions are enforced automatically through smart contracts. Once a proposal passes voting, smart contracts implement changes such as adjusting interest rates, reallocating funds, or upgrading the protocol. This automation ensures transparency and reduces human error, but it also means mistakes or malicious proposals can have irreversible consequences.
Participants need to understand the protocol, tokenomics, and potential risks. Knowledge of smart contracts, DeFi mechanics (like liquidity pools, lending, and yield farming), and governance proposals is critical. Being informed helps voters make decisions that protect the protocol, maximize community benefits, and avoid financial losses.
Many DeFi protocols incentivize participation with governance token rewards or other benefits like fee discounts. Some allow delegated voting, where users assign voting power to trusted participants, ensuring decisions are made even with low individual participation. Transparency and education also help—participants are more likely to vote when they understand that their choices directly affect protocol performance and their assets.
In DeFi, bad decisions can have immediate financial consequences. For example, approving a risky parameter change could drain liquidity pools or destabilize a lending protocol. Some protocols implement time locks or multisig approvals to allow a review period before execution. Others may have emergency pause mechanisms to stop harmful actions. However, irreversible smart contract changes mean the stakes are high.
Many DeFi protocols include emergency pause functions in their smart contracts, often controlled by a multisig wallet or emergency committee. This allows critical actions, like freezing withdrawals or stopping a protocol exploit, while maintaining accountability. After the immediate threat, the broader community can vote on permanent fixes or protocol updates.
Rules are usually created by the protocol team or early developers and then handed over to the community through governance. Updates to the protocol are proposed as governance proposals, discussed publicly, and voted on by token holders. Once approved, smart contracts automatically implement the change, maintaining a decentralized and transparent process.
Reviewed & Edited By

Aman Vaths
Founder of Nadcab Labs
Aman Vaths is the Founder & CTO of Nadcab Labs, a global digital engineering company delivering enterprise-grade solutions across AI, Web3, Blockchain, Big Data, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and Modern Application Development. With deep technical leadership and product innovation experience, Aman has positioned Nadcab Labs as one of the most advanced engineering companies driving the next era of intelligent, secure, and scalable software systems. Under his leadership, Nadcab Labs has built 2,000+ global projects across sectors including fintech, banking, healthcare, real estate, logistics, gaming, manufacturing, and next-generation DePIN networks. Aman’s strength lies in architecting high-performance systems, end-to-end platform engineering, and designing enterprise solutions that operate at global scale.







